Every mother strives to maintain natural feeding for as long as possible. And during this period, everything that happens in the life of a young mother, illnesses during lactation are no exception. Sometimes women have to undergo a medical examination and the therapist may order x-rays to establish an accurate diagnosis. But is it possible to do an x-ray while breastfeeding and how does this procedure affect milk? These are questions to which you need to know the answers before going to the clinic.
X-rays during breastfeeding are not contraindicated and can be performed on a nursing mother if absolutely necessary.
Are lactation and x-ray examination compatible?
In recent years, a lot of scientific research has been carried out to determine how radiation affects mother's milk. It has been established that the quality of milk produced does not change after the procedure, so X-rays and breastfeeding are quite compatible and there are no prerequisites for refusing feeding. The mother can continue breastfeeding even after the test. For example, X-rays of the stomach using barium are considered safe. This substance does not settle in the female body, is not absorbed and does not have a negative effect on the quality and production of milk.
It is only necessary to wait a certain period of time after an x-ray if an examination of internal organs is being carried out. Since for this procedure other contrast agents are used, which help to see the picture of what is happening more clearly.
However, breastfeeding is not a contraindication for x-rays. This is rather a precautionary measure, which is reported by the manufacturers of X-ray machines, in order to in no case allow negative consequences of the procedure for both mother and baby.
In what cases is the procedure necessary?
Radiography is a study that modern medicine practices quite often. In some cases, you may not need to take an x-ray. But if a nursing woman feels unwell for quite a long time, then it is better to carry out the procedure in order to identify the exact cause of the malaise.
X-rays are justified in cases where:
- trauma and possible fracture or crack;
- signs of tuberculosis - a strong, suffocating cough with a possible increase in temperature for quite a long period of time;
- symptoms of sinusitis;
- signs of bronchitis;
- sharp, cutting pain in the stomach;
- toothache and dental complications.
Dental examination during breastfeeding
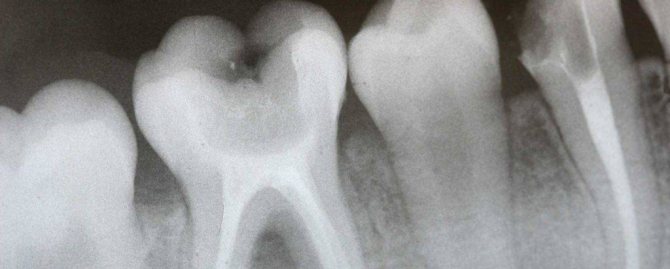
Most often, dental x-rays during breastfeeding are prescribed for:
- identifying the source of pain or the cause of curvature;
- viewing the location of the seal;
- detection of a focus of inflammation or cyst, as well as in diseases of soft tissues;
- clarifying the possibility of saving the tooth;
- diagnosis of caries.
Dentists assure that the procedure while breastfeeding is safe and does not affect breast milk in any way. But if there is an opportunity to conduct the study in a good clinic with modern equipment and a minimum dose of radiation, it is better to take advantage of it and not put yourself and the baby at risk.
Is an MRI procedure acceptable during lactation?
Such a study is prescribed to identify the following pathologies:
- malfunction of nerve cells;
- congenital brain diseases;
- possible abnormalities in brain activity;
- breast cancer;
- neoplasms on organs: liver, kidneys, pancreas;
- diseases of the inner ear or nasopharynx;
- damage to bone tissue, joints, spine or soft tissue in case of infection.
In general, MRI is considered a permitted procedure during lactation, but the same cannot be said about gadopentetic acid. This is a substance that is used during research for clearer results. Therefore, after an X-ray using it, feeding the baby should be postponed for several days. But again, this is not a recommendation for action, but a warning, so if this is not possible, you can continue feeding. A small dose of the contrast agent will enter the child’s body and will not cause irreparable harm.
X-ray contrast
This is not to say that such studies are prohibited during lactation. But it is better to carry them out only in emergency situations. After all, contrast agents are passed on to the baby through mother's milk. Their excess can lead to intoxication of the child’s body, gastrointestinal upset or a general change in health status. Therefore, if contrast was performed on a nursing mother, then it will take at least 24 hours for these substances to be removed from the woman’s body. In this case, it is better to postpone feeding. Such diagnostics help to identify:
- cancers in the breast and lungs;
- development of pneumonia;
- tuberculosis.
Is it possible to breastfeed after an x-ray?
In fact, no lactation consultant can tell you the exact answer. The decision should be made only by the mother, who is guided by her own well-being, research methods and the condition of the child. After all, the doctor can only tell the woman whether an x-ray should be performed, or tell her what potential danger awaits the mother and what substances she will have to deal with during the study. Only the mother can decide whether to put her child at risk or not. It has been established that the likelihood of harmful substances entering the infant during such studies is extremely low, but there is still a risk. That's why
It is better to refrain from feeding the baby, but if this is not possible, then feeding can not be stopped.
https://youtu.be/kQ3GeFSIB1s
MRI during feeding
This procedure is prescribed to identify:
- dysfunction of the nervous system;
- pathologies of congenital cerebral vessels;
- degenerative brain diseases;
- breast cancer;
- tumors in the liver, kidneys, tumors in the brain, pancreas;
- diseases of the inner ear, pituitary pathologies, sinuses;
- infectious lesions of soft tissues, bone apparatus, joints, spine.
The procedure itself does not have a negative effect on the milk produced, but this effect is characterized by the contrast agent - gadopentetic acid, which clarifies the result of the study.
Therefore, doctors advise, if possible, to stop breastfeeding for a day or two after the x-ray.
If this is not possible, then you can feed the baby without much fear for his health. If we calculate that only 1% of the contrast agent is released into mother's milk, and the baby's body absorbs 1% of this amount, then when a woman receives a dose of 0.2 mmol/kg, the baby will be exposed to a substance in the amount of 0.00008 mmol/kg . This is a very small dose that is not capable of harming the baby , and his body will cope with this effect.
How to prepare for research
If the procedure is so necessary, then it is better to prepare your body in advance and protect your health using the following actions:
- X-rays should be performed only when necessary, if there are no other ways to identify the cause of the disease or if the risk to the mother’s health is much higher than limiting the baby to breastfeeding for a couple of days. You can feed the baby immediately before the procedure, and then use the expressed reserves. After this time, the mother will be able to continue breastfeeding, and in order to maintain lactation, she needs to express milk after the x-ray and pour it out.
- It is important to make sure that the equipment used for the study is in good working order and whether its service life corresponds to that stated in the documentation.
- When carrying out the procedure, do not neglect a special apron to protect the organs.
- If iodine-containing substances are used, the next feeding of the newborn should be no earlier than 24 hours later.
How often can an x-ray be taken?
In this case, we are talking about preventive examinations. When we mean treatment, the permissible dose will be higher. How to understand what these dosages are? What can these 1000 μSv be compared to? This indicator is equal to the radiation of 500 images on a computer radiovisiograph or 100 images on high-quality X-ray equipment. One thousand microsieverts is 80 digital photographs. Which of us exposes our body to so much radiation per year?
Any radiation is harmful to the body. But the development of diseases occurs only with a high dose of radiation. A dental X-ray affects a person in such small doses that it cannot provoke pathological processes. If the patient has doubts, it is necessary to consult a doctor. However, you should understand how important such a diagnosis is, and what health problems may arise if you refuse it.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kQ3GeFSIB1s
From all of the above, we can conclude: do not be afraid to take an x-ray if the dentist sends you for an x-ray.
How to Minimize Exposure to Harmful Rays
Medical practice involves taking x-rays at different stages of life, including during guarding. To reduce the negative impact of radiation, the most effective method is to wean the baby from the breast during the procedure and for several days after it. If this is not possible, then doctors advise drinking a glass of wine (red) immediately after the procedure, and for the week following that day include the following foods in your diet:
- cottage cheese, sour cream;
- seafood delicacies;
- Walnut;
- raw carrots;
- pork, but not too fatty.
For a nursing woman, the consumption of wine will have to be excluded, but the remaining ingredients can be included in the menu without fear.
X-ray examination of infants
When an X-ray examination is performed on a baby, it is worth remembering that this can be harmful to the health of the baby.
Although the chance of harm is low, it is still present, so doctors very rarely prescribe this procedure.
Typically, an x-ray is necessary to confirm or refute suspicions of the presence of pathology. It is generally recommended to do this procedure if the child receives an injury during childbirth. For example, damage to the nasal bones during childbirth requires x-ray diagnosis, although doctors believe that it is extremely undesirable to irradiate a child’s head.
During the procedure, all areas of the baby’s body, with the exception of the area requiring diagnosis, are covered from radiation with aprons.
Infants should not have x-rays if:
- for examination of the thyroid gland;
- for diagnosing pathologies of the pelvic organs in girls;
- for examination of the testicles in boys.

X-rays for infants are contraindicated:
- in the presence of increased sensitivity to ionized radiation;
- with close proximity of organs;
- with uneven development of organs;
- with other individual characteristics.
Alternative Research Methods
In some cases, minimal radiation doses can lead to negative consequences. Therefore, if it is possible to make a diagnosis using alternative research methods, then it is better to resort to ultrasound. And if the results obtained are not enough, then a more expensive research method is used - MRI.
Women at risk and those whose babies are susceptible to allergies should approach such diagnostic methods with caution. But you shouldn’t neglect your health, so if the procedure is recommended and justified, then it is better to take an x-ray and, if possible, protect the baby as much as possible. After all, if the mother is healthy, then the baby will grow strong and healthy.
Fluorography and radiography
Fluorography and radiography are methods of radiographic examination. Fluorography is often used for mass, routine screening of tuberculosis.
Nowadays digital fluorography is mainly used . Film fluorography is an outdated research method. Digital fluorography has a lower radiation exposure to a person, but at the same time its resolution (that is, the ability to transmit a real image) is lower in comparison with x-rays of the lungs in direct projection.
X-rays contain more information and pathological changes are more clearly visible.
The radiation exposure is low for both methods (digital devices have lower radiation exposure).
Recommendations for the recovery period
In order to avoid complications after surgery, you need to follow all the doctor's advice. After the procedure, the doctor applies a cotton swab to stop the bleeding. It should be held for no more than 10 minutes, otherwise the blood clot will dry out and come off along with the cotton wool. With high blood pressure, bleeding continues for a longer time, so the tampon can be kept in place for 15 - 20 minutes.
In the first days you cannot:
- overheat the body, apply warming compresses;
- engage in heavy physical labor and sports;
- lick a blood clot;
- eat hot, spicy, rough food;
- drink through a straw;
- smoke;
- touch the socket with a toothbrush and other objects.
You are allowed to eat after 3-4 hours. The issue of feeding a child should be discussed with a doctor. Local anesthetics practically do not enter the blood, and components penetrate into mother's milk in minimal quantities. If the doctor has not prescribed other medications, then you can feed the baby within a few hours.
After the anesthetic wears off, pain appears. Possible increase in body temperature. To relieve acute symptoms, you can take Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Naproxen. You can reduce pain and swelling by using cold compresses.
Rinsing your mouth and brushing your teeth is allowed on the second day. For rinsing, pharmaceutical preparations are used: Romazulan, Chlorhexidine, Miramestin. They will prevent the development of infection and inflammation. You can rinse your mouth with an aqueous solution of baking soda and salt. To improve the healing of damaged tissue, decoctions of oak bark, chamomile, and calendula are used.