What happens in the mother's body. 3 weeks after IVF
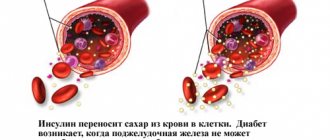
In the third week, the embryo is already firmly implanted into the wall of the uterus, which triggers the mechanisms of hormonal changes in the mother’s body. In the ovary, at the site where the egg is released, the corpus luteum is formed - the main source of progesterone for pregnant women in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. Under the influence of progesterone, changes begin in all systems of a woman’s body:
- Immunity decreases. This is necessary so that the body does not reject a tiny organism that is perceived as foreign;
- The contractility of the uterus decreases, which allows the embryo to remain on its wall;
- The maturation of eggs stops for the entire period of pregnancy;
- Changes begin in the mammary glands, accompanied by the proliferation of glandular tissue and its preparation for lactation.
Estrogen is also produced in large quantities, which helps improve the elasticity of muscle fibers, changes in blood supply and growth of the uterus.
During in vitro fertilization, 3 weeks after embryo transfer, the woman most often continues to take hormonal drugs that increase the amount of estrogen and progesterone and reduce the likelihood of miscarriage.
How does the embryo transfer into the uterine cavity occur?
At the clinic, you are taken to a special room - the embryo transfer room, which borders the embryology laboratory, where you sit on a gynecological chair. Using an ultrasound, the doctor measures the length of the cervical canal, examines the ovaries, fluid in the retrouterine space if the transfer occurs in a “fresh” cycle, and tells the embryologist the length of the cervical canal so that the embryologist places a mark on the catheter (in which the embryo will be placed). The doctor then uses a speculum to expose (expose) the cervix. Use a soft tampon to treat the mucous membrane of the cervix and vagina. How is the mucous membrane treated? Most often this is a neutral medium, for example, saline solution), treatment with nutrient media is allowed. After the mucous membrane of the cervix and vagina has been treated, the doctor tells the embryologist that he is ready for the transfer. The embryologist, under a binocular magnifying glass, draws the embryo into the catheter along with the nutrient medium. There is a sequence for recruiting the embryo into the catheter: medium-bubble-embryo-bubble-medium. Catheters that are used for embryo transfer are different: with a guide, with a soft tip, more rigid, curved and straight. In our clinic we use only imported catheters. Each doctor chooses the most suitable catheter for himself.
In America, some doctors prefer metal catheters, we prefer disposable plastic ones. All catheters are certified and tested for biological safety. The speed of embryo transfer is very important; the embryo does not like light and air.
The embryologist then hands the catheter to the doctor and says the name of the patient whose embryo he is transferring. This is important for patient identification.
The doctor inserts a catheter into the cervical canal and passes beyond the internal os, about 2 cm, and presses the plunger of the syringe to which the catheter is attached. Then the catheter is removed from the uterine cavity, while the syringe plunger is not released so that the embryo does not “suck” back into the catheter.
The catheter is passed into the hands of an embryologist, who checks under a magnifying glass whether the embryo remains in the catheter? If the transfer has occurred and there is no embryo left in the catheter, the doctor removes the gynecological speculum and uses ultrasound to check where the embryo is located in the uterine cavity. What does the doctor see?
On ultrasound in the uterine cavity we see bubbles that have a hyperechoic structure. We cannot see the embryo with our eyes because it is very small.
Feelings of a woman. 3 weeks after IVF
3 weeks after in vitro fertilization, the expectant mother may encounter the main signs of pregnancy accompanying changes in the body. Most often women note:
- Morning sickness. Early toxicosis is the most characteristic symptom of pregnancy, especially for women taking maintenance medications;
- Mood changes. Changing hormonal levels lead to emotional lability in most pregnant women. Exacerbation of nervous reactions is a natural process, but it is especially important for women after IVF to avoid negative emotions;
- Breast tenderness. Increased sensitivity of the mammary glands and an increase in their volume is one of the first signs of any pregnancy. Changes in the structure of the mammary glands begin from the first day of conception, and it is the proliferation of glandular tissue that leads to increased sensitivity and some pain when touched.
In addition to the main three signs that accompany most pregnancies, there are others that are individual in nature, for example: drowsiness, increased fatigue, heaviness in the lower abdomen, increased sense of smell, etc.
What is the examination before IVF?
IVF is strictly regulated by the legislation of the Russian Federation and includes a preliminary comprehensive diagnosis of both spouses. A detailed examination allows you to: identify pathological processes that may become contraindications to the procedure.
A woman is examined especially carefully before IVF. The more information specialists have about the patient’s health, the more accurately the procedure will be selected.
List of studies that a woman should undergo
During preparation for IVF, a woman should visit a gynecologist, therapist, endocrinologist, or geneticist. In addition, the patient is prescribed a comprehensive examination, consisting of laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods.
Tests for syphilis.
Syphilis is an infectious disease that is predominantly transmitted sexually. The causative agent of the disease is bacteria of the species Treponema pallidum. These infectious agents have a complex structure, which makes diagnosing the disease difficult.
During the period of preparation for IVF, to exclude errors, a woman takes two tests for syphilis:
- RPR is a nonspecific test used for initial screening of infection. Designed to detect immunoglobulins of the IgG and IgM classes against phospholipids (substances made of alcohols and acids), which are released from cells affected by syphilis;
- RPGA is a test aimed at detecting specific antibodies to Treponema pallidum. Performed to confirm the result of a nonspecific test for infection.
HIV research.
HIV is a low-grade infection that attacks the immune system. The main test for HIV is an enzyme immunoassay designed to detect antibodies to the virus in the blood.
HBsAg study.
This test is designed to detect viral hepatitis B. HBsAg is a protein shell that surrounds the hepatitis B virus. Thanks to this shell, pathogenic microorganisms are able to selectively adhere to liver cells and penetrate them.
There are several markers of infection. The HBsAg antigen is the earliest of them. It is detected in a person's blood 3-5 weeks after hepatitis B infection.
If the HBsAg test result is positive, IVF can be performed, but this requires a conclusion from an infectious disease specialist about the absence of contraindications to the procedure.
Study to determine total antibodies to the hepatitis C virus
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease that is primarily transmitted through blood and affects liver cells. The a-HCV test is used to detect antibodies to the virus. Antibodies are determined in blood serum using an enzyme immunoassay method.
As in the previous case, if the test result is positive, an infectious disease specialist’s conclusion is required that there are no contraindications to IVF.
Tests for herpes viruses
Before IVF, a woman undergoes tests for:
- herpes virus type 1 (labial or labial);
- herpes virus type 2 (genital);
- herpes virus type 5 (cytomegalovirus).
Determination of these viruses in the blood is carried out using the enzyme immunoassay method or the PCR method.
Clinical blood test with leukocyte formula microscopy
An extensive laboratory study, during which the total number of red blood cells, leukocytes, platelets, red blood cell indices, hemoglobin, and the percentage of various types of leukocytes are determined.
Blood chemistry
The analysis allows us to identify even the slightest deviations in the functioning of vital organs. During the study, the following indicators are mandatory:
- total protein;
- bilirubin (total, direct);
- ALT—alanine aminotransferase;
- AST—aspartate aminotransferase;
- cholesterol;
- glucose;
- urea;
- creatinine;
- calcium level.
Chemical coagulogram.
A comprehensive hematological study aimed at assessing the state of the homeostasis system. The main indicators are thrombin time, prothrombin index, blood clotting time.
Enzyme immunoassay for IgM, IgG antibodies to the rubella virus.
Rubella is an infectious disease that negatively affects the course of pregnancy and leads to severe fetal malformations. Children born to infected mothers are often diagnosed with congenital rubella. The pathology is accompanied by damage to the organs of vision and hearing, the cardiovascular and nervous systems of the child.
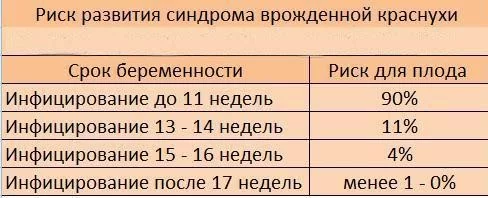
An enzyme immunoassay for rubella antibodies allows you to find out:
- whether the woman is currently infected with the virus;
- Does she need rubella vaccination?
General urine analysis with sediment microscopy
OAM with sediment microscopy is a set of laboratory tests that determine:
- general properties of urine - color, transparency, pH value, etc.;
- level of protein, glucose, ketones and other substances;
- presence of salts, cylinders.
The study is necessary to assess the general condition of the body, diagnose diseases of the urinary system, digestive tract, and metabolic disorders.
Cytological examination of a smear for microflora
A smear is taken from the walls of the vagina, cervical canal and cervix. The study allows you to obtain information about the functional state of the genital area, the presence or absence of inflammatory diseases.
Cytological examination of a smear for oncocytology of the cervix
The test is carried out to diagnose malignant processes and precancerous conditions. The biomaterial is taken from the vaginal area of the cervix and cervical canal (inner part).
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs
An instrumental research method allows you to assess the condition of a woman’s reproductive system, detect polyps, cysts, tumors, and inflammatory processes.
Ultrasound of the mammary glands
During an ultrasound, all areas of the mammary gland adjacent to the chest are examined. The study can detect mastopathy (benign lesions of the mammary gland), cysts, malignant formations, pathologies of the lymph nodes
Electrocardiography
Serves to determine heart rate, diagnose acute and chronic pathologies of the heart muscle, and cardiac conduction disorders.
List of studies that a man must undergo
The list of studies that a man must undergo before IVF is shorter. It includes:
- HIV research.
- Tests for syphilis.
- HBsAg study.
- Test for determining total antibodies to the hepatitis C virus.
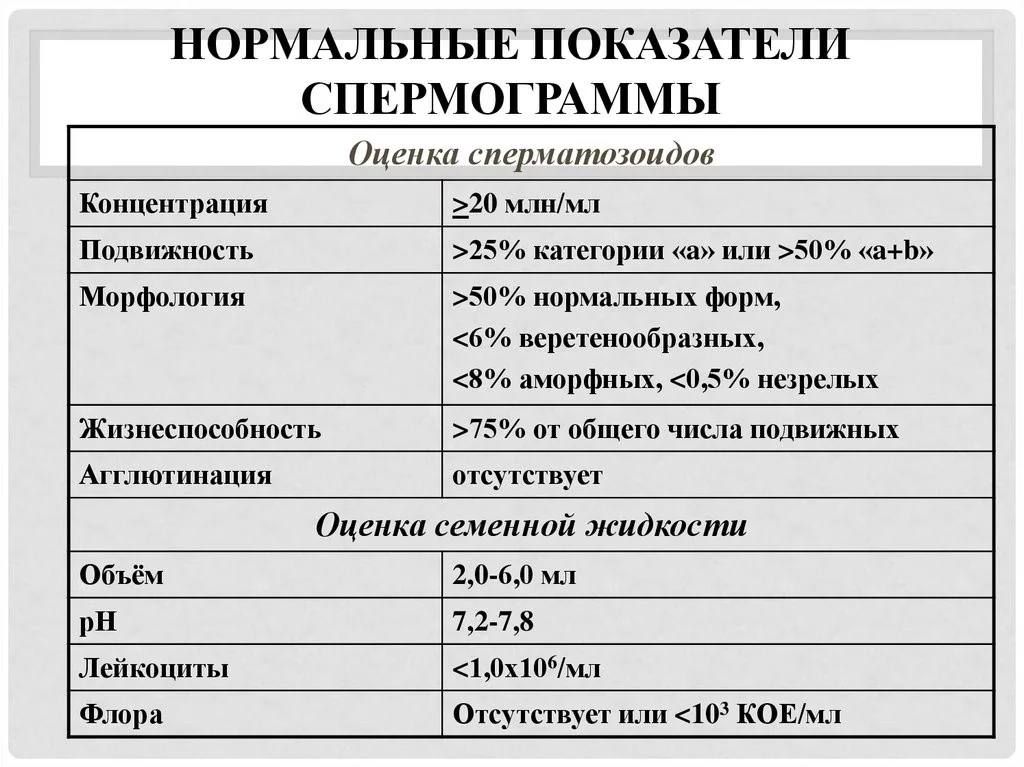
- Spermogram + morphology + MAR test. Studies can detect possible problems with fertility, inflammatory and hormonal pathologies. The MAR test determines whether the male body produces antibodies to its own germ cells:
- Molecular diagnostics using PCR method of scraping from the urethra. Allows you to identify pathogens of infectious diseases and determine their quantity.
Three weeks after IVF. Embryo development
In the third week of pregnancy after IVF, the embryo develops a neural tube. The gastrulation phase is completed and the embryo now has a neurula shape. At the site of the future spinal column, a gradually deepening bend is formed. When they meet, the edges of the depression form the neural tube, the precursor of the child’s brain and spinal cord. The formation of the heart rudiment also occurs.
During this same period, the growth of the placenta, a unique organ that provides protection and nutrition to the fetus, begins. The amnion and chorion are formed from the trophoblast and ectoderm. The amniotic cavity is filled with amniotic fluid, and the chorion begins to actively produce hCG. The size of the embryo reaches 4 mm and can already be seen on ultrasound.
Diagnosis of frozen pregnancy by ultrasound
Ultrasound helps to timely detect intrauterine embryo death. The diagnostician gives a conclusion about a failed abortion if one of the following signs is present:
- The CTP (coccygeal-parietal size of the fetus) has reached 7 mm, and no heartbeat can be heard.
- After the initial detection of the fertilized egg, 2 weeks have passed, and no heartbeat is detected.
- The ovum is less than 24 mm, and there is no heartbeat.
- The embryo is not visualized when the size of the fertilized egg is more than 25 mm.
Experienced reproductive specialists recommend not agreeing to curettage after the first ultrasound and insist on monitoring the development of the fetus over time. In their practice, there are often cases when a woman is given a terrible diagnosis during a consultation and is sent for surgery. The woman does not agree, writes a refusal and does an ultrasound the next day. A repeat ultrasound shows normal fetal development. You should not lose hope ahead of time and, if there is no general deterioration in your health, you can wait for a repeat ultrasound.
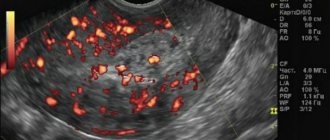
Ultrasound examination of a woman 3 weeks after IVF
After testing for the level of human chorionic gonadotropin in the blood, a woman can already know that she is carrying a new life within herself. After 3 weeks of pregnancy, what is happening to the fetus can be seen using ultrasound.
At this stage, the embryo is a tiny ball with a barely visible head and tail, surrounded by a fertilized egg. Ultrasound diagnostics in early pregnancy is carried out in two ways:
- Transvaginal, in which a small sensor emitting ultrasound waves is inserted directly into the vagina. It is this procedure that allows you to examine in more detail the condition of the uterus and the fertilized egg in it. To prepare for the scan, no special preparations are required, except for eliminating foods that cause increased gas formation from the diet a few days before the ultrasound, as well as emptying the intestines and bladder immediately before the procedure;
- It is recommended to use the transabdominal method for longer periods. Such an examination does not require any preparation, but is also less detailed due to the greater number of structures in the ultrasound path.
It is ultrasound in the third week after the introduction of embryos that is a method that allows one to reliably determine the presence of pregnancy, since IVF, unfortunately, cannot always guarantee a successful result.
In addition, using ultrasound scanning you can see:
- Number of viable embryos in the uterus;
- Location of the fertilized egg;
- Changes in the ovaries.
The first ultrasound is extremely important to exclude serious pathologies such as ectopic pregnancy, fetal development arrest, determination of multiple pregnancy and the need for further or correction of maintenance therapy.
Recommendations before starting IVF treatment
- To the patient
- Featured articles

It is important to remember that each patient has her own individual response to the medications received during treatment, and that each subsequent treatment cycle is different from the previous one. This means that in reality your response will be different from the response of other patients to the same drugs, but your body may also respond differently to each subsequent cycle of IVF treatment, i.e., not the same as in the previous cycle ECO. In this regard, your examination, treatment and, accordingly, its results may differ from those of other patients. The results of your examination and treatment, as well as planned future treatment, cannot be compared with the results of examination and treatment obtained in other patients. Although there are many similarities, it must be remembered that IVF and ICSI treatment is a personal matter and that most patients feel uncomfortable and embarrassed when discussing their personal problems in public.
If you are planning IVF treatment, it is recommended that you consult a doctor approximately 1-2 months before the start of the cycle you have chosen for IVF to resolve all your questions. At the appointment, the results of the preliminary examination are re-evaluated, including: examination on a chair, ultrasound, hormonal studies, identification of pathogens of sexually transmitted infections, i.e. standard examination for patients before IVF treatment. According to indications, additional examination methods are carried out.
For review and subsequent registration, the patient is given an agreement for IVF treatment (including ICSI methods, assisted hatching, fragmentation removal). All forms of agreement between the parties for each procedure must be signed before the start of the treatment cycle.
One of the main requirements for starting IVF treatment is protection from pregnancy in the cycle in which treatment begins using not hormonal, but barrier methods of contraception (condom).
Activities that help increase the chances of success in this treatment cycle
For women:
- Avoid, if possible, taking any medications other than regular aspirin. If you are prescribed any medications by another doctor, you must inform your doctor before starting treatment.
- Avoid smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Limit your intake of coffee and caffeinated drinks as much as possible (no more than 2 cups per day).
- Avoid dietary changes and weight loss diets during your IVF cycle.
- Refrain from sexual intercourse for 3-4 days before follicle puncture, and subsequently after embryo transfer until the day of the pregnancy test (detailed recommendations will be given to you in the statement on the day of embryo transfer). Ordinary physical activity, as well as physical exercise, are not contraindicated until the enlarged ovaries as a result of treatment do not create some discomfort.
- Avoid hot baths, baths and saunas.
- Try to avoid contact with patients with acute respiratory viral infections (ARVI), avoid hypothermia. If your body temperature rises or cold symptoms appear, tell your doctor.
For men:
- An increase in body temperature above 38°C 1-2 months before the IVF / ICSI procedure can negatively affect sperm quality; If you are sick, please measure your body temperature and report any increase (any illness or illness accompanied by an increase in body temperature).
- Visiting baths and saunas is not recommended, as elevated temperatures can adversely affect sperm quality; please refrain from visiting them for at least 3 months before you are due to start treatment.
- Taking medications, drinking alcohol and smoking cigarettes should be avoided before starting IVF/ICSI treatment.
- Do not start any new sports or strenuous activities for 3 months prior to starting IVF/ICSI. If you run, please try to switch to walking without overload.
- Refrain from wearing tight underwear.
- Avoid sexual intercourse for at least 3 days, but no more than 7 days before sperm collection (on the day of follicular puncture).
For both spouses:
If you have a genital herpes infection, you must report the appearance of symptoms preceding the disease (general malaise, general weakness, unmotivated fatigue), acute manifestations of the disease or healing rashes. Regardless of whether a man or a woman suffers from genital herpes, any of the indicated stages of herpes infection will require immediate cessation of IVF/ICSI treatment.
Start of the IVF program (entry into the program)
On the eve of the start of the IVF program, 7-10 days before menstruation, you need to make an appointment with your attending physician to conduct an ultrasound of the pelvic organs and assess the condition of the ovaries and the thickness of the endometrium (uterine mucosa). After the doctor verifies the normal condition of the ovaries (absence of ovarian cysts) and endometrium, in the presence of the necessary official documents (a contract for the provision of medical services, an agreement for this method of treatment, signed by both partners) and the results of the necessary examinations, the doctor enters the patient into the program (IVF treatment cycle).
The patient is given an individual prescription sheet, the rules for administering medications and the “lifestyle” during the IVF treatment cycle are explained in detail. The patient should come to each subsequent appointment with an appointment sheet. The prescription sheet indicates the patient’s name, her age, outpatient card number and describes in detail the entire treatment regimen: the name of the drugs, daily doses, frequency, route and sequence of their administration and the date of each subsequent appearance at the doctor’s appointment. During the treatment cycle, both spouses must strictly follow all prescriptions and recommendations of the attending physician and appear for examination at the appointed time.
The patient is given directions (vouchers) to pay for each stage of IVF treatment. Before each stage of treatment begins, it must be paid in advance. The ongoing treatment can be stopped at any stage if, in the opinion of the doctor, the chances of successful completion and obtaining good results are extremely low. In this case, the patient must be given a refund for the uncompleted stages of treatment.
The first stage is stimulation of superovulation
Its goal is to increase the chances of pregnancy. To do this, a woman is prescribed hormonal drugs that cause the simultaneous maturation of several follicles in her ovaries. In each of the follicles, one egg matures, which is collected during puncture. After their fertilization, several embryos are obtained. The more embryos were obtained, the greater the chances of successful development of pregnancy after their transfer to the patient’s uterus.
Drugs to stimulate superovulation:
GnRH agonists (a-GnRH) – “Diferelin” or “Decapeptyl”;
GnRH antagonists (anti-GnRH) – “Orgalutran”, “Cetrotide”;
Preparations of human menopausal gonadotropins (HMG) - “Menopur”;
FSH preparations – “Puregon”, “Gonal-F”;
Preparations of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) – “Pregnil”.
All these drugs are prescribed according to developed treatment regimens or “protocols for stimulating superovulation.” Currently, several such “stimulation protocols” have been developed and successfully used all over the world, providing for the joint or sequential use of drugs from these groups to achieve the main goal of ovarian stimulation in IVF cycles - the growth of several follicles. Before stimulation begins, your doctor will discuss with you the stimulation protocol that is most suitable for you.
As a rule, a GnRH agonist, Diferelin or Decapeptyl, is first prescribed for 10-14 days from the middle of the second phase of the previous cycle (21 days of the menstrual cycle) to suppress spontaneous ovarian activity. This is not the stimulation itself, but only the preparation of the ovaries for its implementation with HMG or FSH drugs. It is very important because... increases the effectiveness of subsequent stimulation and allows you to reduce the dose of prescribed HMG (FSH) drugs and, accordingly, the cost of treatment. This is an important argument, since all stimulation protocols used in IVF are carried out exclusively with expensive hormonal drugs.
The start of administration of a - GRG usually occurs on the 21st day in a 28-day cycle or the 23rd in a 30-day cycle and lasts, on average, 10-14 days, but possibly longer if the need arises. This scheme for stimulating superovulation is the most traditional and most widespread of all those proposed today. It is called the “long” stimulation protocol.
There are other stimulation schemes (“short” and “ultra-short” protocols), but they are used less frequently.
During the 10-14 days of ovarian preparation, the patient needs to come to see the doctor only twice: before the start of the administration of a-GRG (1st appointment, that is, directly entering the IVF program) and after this period (2nd appointment). Of course, unless there are any unforeseen reasons for an additional visit to the doctor.
After the required degree of ovarian suppression is achieved under the influence of a-GnH (as judged by the doctor at the 2nd appointment by the decrease in the concentration of estradiol in the blood and the characteristic ultrasound picture), the doctor makes additional prescriptions for the patient. The dose of a-GnRH is halved and a new drug is prescribed directly to stimulate the “suppressed” ovaries - gonadotropic hormone preparations - Menopur or Puregon (Gonal-F) in addition to a-GrH for 12 - 14 days.
The scheme described above - the α-GRG + HMG (FSH) complex - can significantly increase the number of follicles in the ovaries. This, in turn, increases the number of embryos obtained.
This stimulation continues until a single appointment in the middle of the cycle of the hCG drug, which causes the maturation of the eggs in the follicles, which allows them to be prepared for puncture at the second stage of treatment (the stage of puncture of the resulting follicles).
To stimulate ovulation, as a rule, three types of gonadotropins are used: HMG - Menopur and FSH - Puregon or Gonal-F.
The first day of administration of gonadotropins is considered the first day of the cycle, and further counting is carried out from this day. The drugs act on the ovaries and stimulate the maturation of follicles. The dose of the administered drug to stimulate follicular growth is selected individually, taking into account the woman’s age, her weight and the initial state of the ovaries (their functional reserve) and depends on the response of the ovaries to the IVF treatment. This reaction is assessed periodically by the level of sex hormones in the blood serum (estradiol) and the ultrasound picture (the number and size of follicles in each of the ovaries, as well as the thickness of the endometrium).
Carrying out an ultrasound and determining the concentration of estradiol during treatment with hormonal drugs is called “Ultrasound and hormonal monitoring”.
Ultrasound and hormonal monitoring
Organizational aspects
Ultrasound monitoring is carried out by the attending physician at the appointment, and a blood test for estradiol is taken upon the doctor’s direction in a diagnostic laboratory. As a rule, monitoring is not paid separately, since its cost is included in the cost of this stage of treatment. The frequency of monitoring is set by the doctor depending on the results obtained (ultrasonic picture and estradiol concentration). The date and time of each subsequent visit to the doctor for monitoring is entered on the appointment sheet held by the patient. As a rule, the number of visits does not exceed 4 or 5. The time must be chosen taking into account the wishes of the patient, because most of them continue to work.
Typically, ultrasound is performed using a vaginal probe (abdominal ultrasound), which is significantly more informative than conventional ultrasound through the abdominal wall. Before performing a abdominal ultrasound, you will need to empty your bladder to improve the quality of the resulting image.
The nurse invites you to the monitoring room. You will be asked to undress as if for a gynecological examination, after which you lie down on a prepared gynecological chair and your attending physician is invited. The sensor is inserted by the doctor into the patient’s vagina; a sterile condom is first put on it, which is discarded after use.
The ultrasound procedure is completely painless and safe. Some patients may experience a feeling of discomfort or embarrassment, and there may be slight vaginal discharge after the end of the ultrasound procedure, mainly due to the use of a special gel to improve the quality of the resulting image.
What is assessed during monitoring?
The first ultrasound monitoring is usually carried out on the 5th or 6th day of stimulation with gonadotropins to assess the response of the ovaries (dynamics of follicle growth) and endometrial thickness in order to select the most optimal dose of the drug and determine the date of the next visit. Before the active growth of follicles begins (until they reach sizes of 10 mm and above), an ultrasound scan is performed once every 4-5 days, then the ovaries are examined more often - once every 2-3 days. Blood tests for estradiol are taken either with the same frequency or somewhat less frequently (depending on the specific situation).
Depending on the dynamics of follicle growth and hormonal levels, the attending physician determines the frequency of attendance for monitoring individually for each patient and selects the exact dose of drugs.
At each monitoring, the doctor determines the number of follicles in each ovary, measures the diameter of each follicle, and evaluates the thickness of the uterine mucosa.
Finally, when your doctor decides that you are ready for follicle puncture (more precisely, the follicles are mature enough for puncture to collect oocytes), you will be given an injection of hCG. As a rule, this drug is prescribed 35 - 36 hours before the puncture itself for the final maturation of the eggs. If the puncture is not performed, ovulation occurs 42 - 48 hours after the time of injection.
The main and mandatory conditions for prescribing hCG are a certain degree of follicular development according to ultrasound (at least 3 mature follicles). A potentially mature follicle against the background of stimulation is a follicle measuring 18-20 millimeters.
The second stage is follicle puncture
The purpose of this stage is to obtain eggs from the follicles of the stimulated ovaries by puncturing them with a hollow needle (puncture). This intervention is performed under ultrasound guidance, in sterile conditions (operating room) and under intravenous anesthesia.
The time for the puncture is scheduled by the doctor in advance and according to the standard schedule: 35-36 hours after the administration of hCG. The date and time of the proposed puncture are recorded on the patient’s appointment sheet.
The contents of the follicle (follicular fluid with eggs) are transported to the embryology laboratory in special sterile disposable plastic containers made of non-toxic polymer. The entire follicle puncture procedure lasts, on average, 15-20 minutes.
Memo for patients before follicular puncture
In order to avoid vomiting during and after anesthesia, you must:
In the evening, on the eve of the puncture, refrain from eating after 18-00 and from taking any liquids after 24-00.
On the day of the procedure, refrain from eating or drinking any liquids until the procedure begins.
We strongly ask that you come to the puncture without makeup, contact lenses, manicure or jewelry. You don't have to take off your wedding ring. By the time the puncture is completed, the spouse or donor must donate sperm for subsequent analysis, special processing and fertilization of the resulting eggs. Then the patient is invited to a special room for changing clothes: her body temperature and blood pressure are measured, her general well-being is determined, and she is asked to completely empty her bladder. She is escorted to the operating room, where she is prepared for the puncture: they are helped to lie down in a gynecological chair, and the external genitalia are treated.
An anesthesiologist and an attending physician are invited to the operating room. After the administration of drugs for anesthesia (that is, when you fall asleep), the procedure itself is carried out.
After the puncture, you are under the supervision of hospital medical personnel for 1.5-2 hours. Once the anesthesiologist is satisfied that your condition is satisfactory and you are feeling well, you will be allowed to stand up. The IVF laboratory nurse will accompany you and your husband to the attending physician.
Memo for patients after follicular puncture
The doctor informs you about the results of the puncture, makes new appointments, and sets the date and time for embryo transfer. After the puncture, you can eat and drink as you see fit, depending on how you feel. In order to prevent the occurrence of an infectious process after puncture, you will be recommended to take antibiotics (a single loading dose of a broad-spectrum antibiotic - for example, 1 capsule of doxycycline).
After the procedure, you may experience some soreness in the pelvic area, a feeling of fatigue, or even drowsiness (the latter is associated with the use of anesthesia). Slight bleeding from the genital tract after puncture is also possible, associated with a puncture of the vaginal wall during puncture. As a rule, they are scanty and vary in color from red to dark brown.
Please tell your doctor if you experience the following symptoms after the puncture:
- High temperature (over 37 degrees C).
- Severe bleeding from the vagina.
- Unusual or severe pain in the pelvic area.
- Difficulty urinating or bowel movements.
- Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
- Sharp or shooting pain.
- Pain or sting when urinating.
- Unusual back pain.
- Increase in abdominal circumference.
Support corpus luteum function
In place of the punctured follicles, yellow bodies are formed. Normally, at the site of a mature follicle that “burst” during ovulation in a woman of reproductive age, a corpus luteum is also formed, the main function of which is the production of the hormone progesterone, which “prepares” the uterine mucosa for the attachment of the embryo. However, in IVF cycles, α-GnRH drugs are used to stimulate ovulation, which reduce the function of the corpus luteum. Moreover, levels of the hormone estradiol in stimulated cycles are disproportionately increased compared to progesterone. Therefore, drug support for the function of the corpus luteum and normalization of the ratio of estrogen and progesterone are necessary, starting from the day of follicle puncture. This improves the condition of the uterine mucosa - the endometrium and thereby increases the chances of successful implantation (attachment) of embryos.
In most cases, the natural hormone progesterone is prescribed in the form of the pharmaceutical drug Utrozhestan or synthetic progesterone Duphaston.
"Utrozhestan" is available in the form of capsules for oral administration (oral) or vaginal administration. The vaginal method of administering the drug is preferable, since in this case it immediately goes to the uterus, bypassing the systemic (general) blood flow. Duphaston is available in tablet form and is taken orally only.
In some cases, after puncture of the follicles, until the day of the pregnancy test, medications such as, for example, Proginova or Estrofem are prescribed. Both drugs contain another female hormone, estradiol, which also takes part in preparing the uterine lining for implantation. The drugs are available in tablet form, but Proginova is taken orally, and Estrofem is inserted into the vagina.
The type and dosage of the drug is selected individually. All prescriptions are recorded by your attending physician on the prescription sheet immediately after the puncture, and then after the embryo transfer the dosage of the drugs is adjusted.
The third stage is fertilization of eggs and cultivation of embryos
After the follicular fluid arrives at the laboratory, the embryologist conducts a “search” for eggs, which are then placed in an incubator. Fertilization is carried out with concentrated sperm 4-6 hours after receiving the eggs. For normal fertilization, approximately 50 thousand sperm are used for each egg. If sperm parameters do not meet the requirements of standard IVF or previous IVF attempts have been unsuccessful, further treatment tactics are discussed (possibly ICSI or IVF using donor sperm). The ICSI technique is used to fertilize mature eggs in case of insufficient sperm count in the spouse.
If it is difficult to obtain sperm on the day of puncture or there are no sperm in the ejaculate, a special procedure is provided - testicular biopsy.
The day of puncture is considered day zero of embryo culture; The first day of cultivation is the day following the puncture. It is on this day that most eggs show the first signs of fertilization. They are already noticeable 16 - 18 hours after the union of eggs with sperm (insemination). Fertilization is re-evaluated 24-26 hours after insemination. Fertilization control is carried out by an embryologist when viewing dishes with cultured cells under a microscope.
One of the reasons for IVF failure is the lack of fertilization of eggs. Often the reason for this is not possible to establish, despite the extensive knowledge of scientists in this area. No one is immune from this, and such an outcome is often difficult to predict, but it must be remembered. If your couple did not have eggs fertilized using the standard IVF method, you and your husband need to visit a doctor to decide on further management tactics for your couple. Possible options: repeat donation of sperm and performing the ICSI procedure or performing ICSI with sperm already obtained on the day of puncture (if it is of good quality). It is advisable from the very beginning, even before the puncture, to discuss the possibility of switching to ICSI if the standard IVF procedure fails.
Stages of embryo development
A fertilized egg is called a zygote - it is a one-cell embryo that already contains a double set of chromosomes, that is, from the paternal and maternal organism. However, the presence of zygotes is not yet sufficient to resolve the issue of the possibility of embryo transfer into the uterine cavity. First you need to make sure that the embryos are splitting and developing normally. This can only be judged based on the quantity and quality of the dividing cells of the embryo and not earlier than one day after fertilization, when the first signs of fragmentation appear. They appear most clearly only on the second day of cultivation. Every day, an embryologist evaluates embryos, recording all parameters: the number and quality of embryonic cells (blastomeres), the rate of fragmentation, the presence of abnormalities, etc.
Only good quality embryos can be transferred. Embryo transfer is carried out on the 2nd - 5th day of cultivation, depending on the pace of their development and the quality of the embryos.
Until recently, embryos were cultured for three days and then transferred into the uterus and/or frozen. Nowadays, so-called extended culturing of embryos for five or six days until they reach the blastocyst stage is common. Blastocysts have a higher implantation success rate, allowing fewer embryos to be transferred and reducing the risk of multiple pregnancies while increasing pregnancy rates.
Stage four - embryo transfer
As mentioned above, embryo transfer is carried out on the 2nd - 5th day of cultivation, depending on the stage of their development.
On the day of embryo transfer, you must arrive 30 minutes before the appointed time. The presence of the husband is possible, but not required. On the day of the transfer, we allow patients a light breakfast, but liquid intake should be limited. This will reduce the discomfort associated with a full bladder.
Immediately before embryo transfer, the doctor, embryologist and couple decide on the number of embryos to be transferred. The embryologist demonstrates in photographs the embryos selected for transfer and answers questions of interest to the couple.
After receiving information about the doctor’s readiness to carry out the embryo transfer procedure, the embryologist collects the embryos into a transfer catheter, which is a thin plastic tube with an attached syringe, and hands it over to the doctor performing the transfer.
The embryo transfer procedure is technically simple. The patient lies down on the gynecological chair. The doctor exposes the cervix in the speculum, and then inserts a catheter through the cervical canal into the uterine cavity. The catheter contains embryos that enter the uterine cavity. The doctor then passes the catheter to an embryologist, who examines its contents under a microscope for any embryos remaining in the catheter.
Embryo transfer usually does not take long (5-10 minutes). The procedure is painless, although sometimes the patient may experience slight discomfort.
If, after embryo transfer, a couple has “extra” embryos of good quality, the couple is offered to freeze them for further storage and subsequent transfer after thawing in the event of no pregnancy after this IVF attempt (“Embryo Cryopreservation”).
After embryo transfer, you are in a horizontal position for 40 - 45 minutes, after which you get dressed and are invited to see your doctor to discuss further features of treatment and lifestyle.
How to behave after embryo transfer?
Your attending physician will provide a detailed statement in 2 copies (to you and your attending physician at your place of residence) about the IVF treatment performed. The extract indicates: lifestyle recommendations, timing of pregnancy tests and ultrasound examinations, dosages and duration of medication use. In addition, if necessary (working patients), a certificate of incapacity for work (sick leave) is issued. Nonresident patients are issued an open sick leave certificate, which they can extend at their place of residence.
After embryo transfer, the dose of progesterone drugs (Utrozhestan or Duphaston) is usually doubled, and their use can continue until 12-14 weeks of pregnancy, when the placenta (baby place) is formed and releases “its” progesterone in sufficient concentration.
After the transfer, some patients report slight spotting or the release of air bubbles from the genital tract. Please don't worry about this. This does not mean that at this time your embryos are expelled from the uterine cavity.
Immediately after embryo transfer, it is very useful to come home, lie down and try to relax. From the moment of transfer until the pregnancy test, you can safely return to most of your daily activities and responsibilities with the exception of excessive physical activity.
It is considered absolutely normal that if the pregnancy test results are negative, you will blame yourself for doing something or, conversely, not doing something during this period of time - the waiting time.
In this regard, try not to do anything that you will reproach yourself for if pregnancy does not occur, and adhere to the recommendations below:
- Do not take a bath or swim for the first 24 hours after the transfer.
- Do not shower or splash yourself with water.
- Don't use tampons.
- Do not be sexually active until you receive your first pregnancy test.
- Do not engage in running, aerobics, tennis, skiing, mountaineering or other similar sports.
- Do not start other sports or physical activities.
- Don't lift heavy things.
You can return to "work" after 24 hours in bed and one or two days of moderate physical activity. Try to do something and thus distract yourself from waiting for the results of the pregnancy test, which will help you survive these 12 - 14 days.
You may have some spotting or spotting from your vagina before taking a pregnancy test. Approximately 50% of our pregnant patients after IVF had similar discharge before the test and even after receiving a positive result! Don't lose optimism! You should definitely get your blood tested, even if you think that this discharge is menstruation and pregnancy has not occurred. A quantitative pregnancy test must be done - determination of hCG in the blood.
Diagnosis of pregnancy
Quantitative hCG pregnancy test must be done 14 days after embryo transfer. If this time falls on a “Sunday” day off, the test can be done on Monday.
Patients from other cities are advised to do an hCG test at their place of residence and inform us by phone about its results.
A blood test for hCG determines the hormone (human chorionic gonadotropin) released by the embryo when it implants in the uterine cavity. As a rule, the concentration of this hormone is comparable to the result of IVF treatment: the presence of pregnancy, the number of embryos in the uterine cavity, etc.
Most pregnancy tests give either positive or negative results. However, sometimes there are “weakly positive” results - a low concentration of hCG in the blood.
If you were given exactly this result, it may indicate the following:
- Delayed but normal embryo implantation.
- Interrupted pregnancy.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Laboratory error.
Further monitoring of hCG is extremely important in each of the above situations. 2-3 days after the weakly positive result, you need to repeat this study. A repeat blood test for hCG will give us the opportunity to determine whether your pregnancy is progressing and whether it is developing normally.
The first ultrasound is recommended to be performed one week after the day of the pregnancy test (or 3 weeks after the embryo transfer). This ultrasound at such an early stage is extremely important in terms of the possibility of termination of pregnancy (miscarriage), ectopic pregnancy and multiple pregnancies. Ectopic tubal pregnancy can occur in 2-3% of IVF pregnancies.
Timely, early diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy and laparoscopic surgery allows one to avoid serious complications that threaten the woman’s life.
The second ultrasound examination is carried out 10 days after the first to confirm the normal development of pregnancy - to determine the fetal heartbeat. As soon as the doctor detects a fetal heartbeat, he recommends that you contact your obstetrician-gynecologist for early pregnancy registration. The approximate pregnancy period at the moment will be 6-7 weeks.
If the pregnancy test is negative, you stop taking progesterone medications. It will take 3 or 5 days before your period arrives, if it has not arrived earlier. Your menstrual flow may be different from your usual periods (heavier, lighter, shorter or longer). If menstruation does not come within the next week, inform your doctor and repeat the hCG blood test.
As you know, IVF is a rather complex and expensive procedure that takes a lot of time and money, but, alas, does not guarantee a positive result.
The reasons for failure can be different, both physiological and psychological. And if your doctor will help you sort out the first ones, then psychological problems, as a rule, remain unattended in the process of preparing for IVF. However, their influence on the result is very great!