What are acceptable blood sugar levels?
One of the main concerns if you are diagnosed with type 2 diabetes is your blood glucose levels. Normal blood sugar levels differ between healthy people and people with diabetes.
The latter must understand the importance of maintaining it within optimal volumes. In addition, the chosen therapy should be used comprehensively. In this case, it will be easier to prevent the complete exhaustion of the necessary reserves of the endocrine system.
Type 2 diabetes normal blood sugar before and after meals
Progressive type 2 diabetes: normal blood sugar before and after meals after 60 years, what exactly should it be? Ideally, its indicators should be as close as possible to the figures present in healthy people.
It is very important to understand for yourself what types of factors can increase the risk of developing hyperglycemia in order to successfully avoid them.
For this it will be enough:
- follow the recommended diet for insulin dependent people,
- take into account diet and proper nutrition.
We recommend that you read: Diet for type 2 diabetes mellitus is the main argument for remission of the disease
How to reduce risks
The concentration of glucose in the blood in endocrine pathology requires different levels. This is influenced by various reasons. It is easier to maintain sugar levels within normal numerical values, provided that proper nutrition is followed and the minimum necessary physical activity is performed. At the same time, the indices of its fluctuations are stabilized, and it becomes much easier to control the jumps. To reduce the risk of possible negative effects on the functioning of your organs and create obstacles to the development of concomitant diseases, diabetes should be compensated.
Reasons for the increase in carbohydrates in the body after an evening meal

A diabetic patient must constantly measure the amount of glucose in the blood plasma, and, if necessary, take adequate measures to ensure that there are no deviations from the permissible value.
New information: Which blood sugar test is more accurate: from a finger or from a vein?
Why does sugar start to rise after dinner? Most often, the reason that after some time glucose increases in a diabetic is due to the fact that a large amount of high-carbohydrate foods were consumed during meals, these can be:
- Potato.
- Pasta.
- Cereals and many other products.
Very often there is an increase in the amount of carbohydrates in the blood in the absence of the opportunity to organize adequate nutrition.
If there is an increase in indicators an hour after eating in a healthy person to a level of 6.2-6.3-6.4, then this may indicate the development of a special condition of prediabetes, which precedes the onset of diabetes.
The occurrence of jumps in carbohydrate levels in the evening is not affected by the concentration of insulin and stress hormones. In addition, this indicator is not affected by the glucose-lowering drugs taken by the patient.
This value completely depends on the nature of the patient’s diet and the amount of carbohydrates consumed by the person in food during daylight hours.
Norms for type 2 diabetes
When choosing the right approach to treating the disease, the required limits for glucose availability will most likely not be exceeded.
Sugar levels that are considered acceptable:
- In the morning before meals – 3.6-6.1 mmol/l,
- In the morning after meals – 8 mmol/l,
- Before bedtime – 6.2-7.5 mmol/l.
- Do not allow the readings to drop below 3.5 mmol/l.
In this case, developing hypoglycemia provokes coma. The body cannot cope with its functions because it is not supplied with the necessary amount of energy. Then, if you do not take the necessary methods to combat the progression of the disease, you can even expect death.
Important to know: Hypoglycemic coma, emergency care for the patient, algorithm of important actions
Type 2 diabetes mellitus suggests that the blood sugar level should also not be higher than 10 mmol/l.
Hypoglycemic coma entails irreversible changes and provokes disruptions in the stable functioning of all internal organs.
What to monitor if you have diabetes
The main important indicators that should be monitored by patients suffering from diabetes.
| Name | Meaning | Description |
| HbA1C or glycated hemoglobin | 6,5-7% | To control the level, you should undergo regular tests as recommended by your doctor. |
| Glucose in urine | 0,5% | A serious sign, if there is an increased presence of glucose in the urine, attempts should be made immediately to identify the causes of such symptoms. |
| Arterial pressure | 130/80 | Pressure surges should be brought back to normal with the help of special medications selected by the doctor. They are taken in the morning or twice a day. |
| Body mass | The values must correspond to height, weight, age. | To prevent going beyond normal limits, you should monitor your diet and engage in regular physical activity. |
| Cholesterol level | 5.2 mmol/l | In order to create obstacles and not provoke rupture of the heart muscle, it is necessary to promptly diagnose an increase in the level above normal and take the necessary measures to stabilize it. Values different from optimal values suggest possible stroke, heart attack, atherosclerosis or ischemia. |
Important to know: Causes and risk factors of insulin resistance
Why does sugar rise?
The most accurate values of the amount of sugar in the blood vessels can be tracked on a lean stomach. After the food enters your body, within an hour or two your sugar levels begin to rise.
This pattern is observed not only in those susceptible to the disease, but also in completely healthy people.
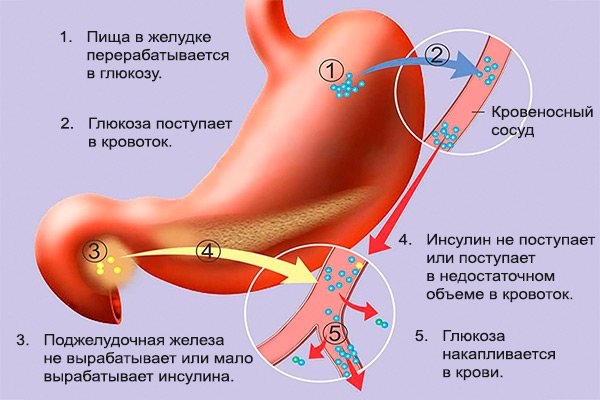
If everything is in order with the endocrine system, then after a certain time the values return to normal, without causing any harm to the body.
Due to the fact that there is no ability to perceive insulin and the production of the hormone is reduced, internal organs can no longer cope with the increased production of glucose. The result is developing diabetes mellitus, which brings with it a whole “tail” of various kinds of negative consequences for organs and systems.
Causes and symptoms of possible blood sugar abnormalities
In some cases, people susceptible to the disease themselves provoke hyperglycemia. The likelihood of critical glucose levels and decompensation of diabetes mellitus increases in cases where the recommendations of a specialist are not given due importance.
The following important points are highlighted in which the sugar spike exceeds normal levels:
- violation of recommendations for the consumption of dietary dishes;
- sweet foods, fried foods, fatty foods, canned foods, dried fruits and other items from the list of prohibited foods are allowed;
- food preparation methods do not meet the norm: food is fried, smoked, pickled, dried fruits are produced, home canning is done;
- not following the diet according to the clock;
- restriction of physical activity, neglect of physical exercises;
- excessive overeating, causing additional kilograms;
- incorrect approach to choosing a method of treating pathology of the endocrine system;
- hormonal disruption in organ activity;
- use of medications recommended by a doctor in violation of the established regimen;
- the frequency and daily value of antihyperglycemic drugs are not monitored in a timely manner;
- neglect to keep a diary of food consumed, which requires a clear calculation of the daily intake of bread;
- failure to comply with the time frame when measuring blood glucose levels.
Frequent manifestations of high sugar
Type 2 diabetes: normal blood sugar before and after meals after 60 years requires the need for daily use of a glucometer. This simple rule will help you avoid unwanted changes.
Patients need to understand what the first symptoms indicate the development of hyperglycemia:
- itchy surface of the skin and mucous membranes;
- periodically appearing “spots” before the eyes;
- increased need for fluid intake;
- increased appetite;
- negative changes affecting total body weight;
- urinating too frequently;
- dehydration of the skin and mucous membranes;
- infectious problem for the female genital organs - candidiasis;
- healing of wounds appearing on the body takes too long;
- vision problems;
- sexual function disorders in men;
- increased fatigue, decreased performance and vital activity; a constantly emerging state of apathy and excessive irritability;
- periodically occurring muscle contractions - cramps;
- predisposition to swelling of the face and legs.
How to prevent insulin therapy
In case of type 2 diabetes, following a diet and proper nutrition, you need to know at what level of sugar you start taking insulin in order to avoid unpleasant consequences.
To do this, indicators should be measured regularly.
Moreover, this is done not only from the morning until the moment of eating, but throughout the day.
When diabetes occurs in a latent form, fasting glucose levels may be within normal limits. After food enters the body, it, quite naturally, increases. Do not delay visiting the doctor if high sugar levels persist for several days.
A reading above 7.00 mmol/l indicates that it is imperative to visit an endocrinologist. A regular glucometer recommended by doctors can help you measure glucose levels at home. Currently, devices have been developed that establish indicators without the need to obtain biomaterial. When using them, no finger pricking is required, you will avoid pain and the risk of infection.
Learn more about non-invasive glucometers: Non-invasive glucometer from Apple SmartWatch: bioelectronics news
How can you achieve stabilization of indicators?
In the event that, during the measurement process, you determine that your normal glucose levels do not correspond to the norm, you need to analyze the following:
- Daily menu,
- Time to get food
- Total amount of carbohydrates consumed
- Methods of preparing ready meals.
- Most likely, you simply do not follow the recommended diet or allow yourself fried foods or sweets.
It will be easier to understand the possible causes of sudden jumps in sugar levels or constant hyperglycemia if you keep a food diary. The notes made in it about at what time, in what quantity and what specific food you consumed throughout the day will help identify what exactly you did wrong.
Consequences of an increase in blood levels

If the sugar in the patient’s body after eating begins to rise significantly above normal and does not stabilize in any way, then a state of chronic hyperglycemia develops. The patient experiences a deterioration in health, excessive thirst and a feeling of dryness in the mouth, and the process of urination increases.
In the absence of adequate therapy aimed at correcting the amount of carbohydrates in the body, the patient’s health condition noticeably worsens. In such cases, the diabetic experiences nausea, vomiting, and very often dizziness and severe weakness.
If measures are not taken to bring carbohydrates to normal, a person may lose consciousness and fall into a coma, which can lead to death.
In most cases, even a small deviation from the physiological norm provokes a large number of disturbances in the functioning of most organs and their systems in the body. In such cases, a disturbance in the functioning of the immune system and metabolism is recorded.
The presence of high levels of simple carbohydrates in the body over a long period of time without taking measures for adequate correction can provoke the following problems:
- tooth decay;
- possible development of fungal infections;
- severe toxicosis develops during pregnancy;
- cholelithiasis develops;
- the likelihood of developing eczema increases;
- inflammation of the appendix may occur.
New information: C Peptide norm for diabetes mellitus in women and men: what the analysis shows
In the case of progressive diabetes without complete correction of carbohydrate values in the body, the following pathologies may develop:
- Kidney failure.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the visual organs.
- Death of soft tissues in the lower extremities due to disturbances in the circulatory system.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the heart and vascular system.
To prevent the occurrence of these pathologies and disorders, a patient suffering from diabetes must strictly follow the instructions of the attending physician, aimed at adequate compensation for the increased level of carbohydrates.
Blood sugar levels by age
It is approximately the same for everyone without exception. The differences that exist are most often insignificant. The indicators of infants are slightly lower than those of older people.
Sugar levels depending on age
| Age category | Indicator mmol/l |
| Up to 1 month | 2,8 – 4,4 |
| Up to 14.5 years | 3,3 – 5,6 |
| Up to 60 years old | 4,1 – 5,9 |
| From 60 to 90 years | 4,6 – 6,4 |
| From 90 years old | 4,2 – 6,7 |
It turns out that type 2 diabetes assumes that the blood sugar level before and after meals will be increased after 60 years. During this period, the body can no longer cope with the function of properly using glucose, so its levels increase. This is especially true for those people who are overweight.
Glucose readings depending on time of day
As mentioned above, the process of eating affects sugar readings. It is not the same throughout the day. The change in its values is different for sick and healthy people.
Sugar standards
| Measurement time | Healthy people | Diabetics |
| Indicators mmol/l | ||
| On an empty stomach | From 5.5 to 5.7 | From 4.5 to 7.2 |
| Before meals | From 3.3 to 5.5 | From 4.5 to 7.3 |
| 2 hours after eating | Up to 7.7 | Up to 9 |
Another important coefficient that must be taken into account is glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c).
- Its value allows you to clarify the presence of glucose over the past 2.5 - 3.5 months.
- Its value is reflected as a percentage.
- In a person who is not susceptible to this dangerous disease, most often it ranges from 4.5 to 5.9%.
The International Federation, which is closely involved in the treatment of diabetes, has set a target figure for cases of no more than 6.6%. It is possible to reduce its value if strict glycemic control is established.
Currently, many experts agree that people susceptible to diabetes should strive to maintain their blood sugar levels within the normal range established for healthy people. In this case, the risk of developing complications, for example diabetic polyneuropathy, accompanying this disease becomes less.
Read more: Diabetic polyneuropathy, what is it - modern approaches to treatment
That is why the disease is type 2 diabetes: the blood sugar level before and after meals should be clearly monitored daily.
The famous doctor R. Bernstein points out the need to strive for such normal values as 4.17-4.73 mmol/l (76-87 mg/dl).
This is exactly what is stated in his famous book Diabetes Solution. In order to maintain this level of glycemia, you should adhere to a very careful diet and constant sugar measurements. This will prevent it from falling, suggesting hypoglycemia, if necessary.
A low-carbohydrate diet is very good in this case.
We recommend that you read: Nutrition for type 2 diabetes with excess weight - how to bring the body back to normal
When, after a meal, the sugar spike increases within 8.6-8.8 mmol/l, this is the first symptom of the development of diabetes mellitus. Provided that you are over 60 years old, you should definitely make an appointment with an endocrinologist. You will undergo the necessary diagnostics and confirm or refute your diagnosis. Your doctor will likely recommend the following tests:
- analysis of glycated hemoglobin,
- your body's tolerance to glucose.
- a glucose tolerance test with a final result of more than 11.2 mmol/l will indicate that you have diabetes.
Sugar standards in the elderly
60 years is considered old age, with the exception of some economically developed countries, where 65-year-olds are considered elderly.
Several years before the official retirement age, metabolic disorders begin to develop, including carbohydrate metabolism. Starting from about 60 years of age in the body:
- fasting sugar concentration increases;
- glucose tolerance decreases.
Fasting glucose (glycemia) values are determined by analyzing “lean”, i.e., “hungry” blood after a period of overnight fasting during sleep.
The glycemic norm in the fasting test - blood taken from a finger after 8 hours of fasting - differs little after 60 years from the sugar test norms in young women.
Glucose tolerance is determined after meals. You need to check your sugar level not immediately after a person has just eaten, but after a while.
Usually measured after 60 minutes or after 2 hours. This glycemia, measured after the food has been eaten, is called postprandial.
To determine to what level above normal blood sugar rises in an adult after 60 years of age after eating, it is not necessary to conduct a glucose tolerance test in a clinic. It is enough to use the glucometer yourself 2 hours after your usual breakfast or lunch.
Sugar on an empty stomach
The norm for adults under 50 years of age is 3.5 – 5.6 mmol/l. When blood is taken on an empty stomach, sugar levels in older people change little as they age.
The increase in indicators for 10 years is 0.055 mmol/l. Considering that the indicators of the glucometer when measuring the level of glucose in a capillary blood sample give values accurate to tenths, the value of 0.055 is rounded.
Table: blood sugar norms when taken from a finger on an empty stomach in women after 60 years
| Age ranges, years | norm, mmol/l |
| 60 | 3,6 – 5,7 |
| from 60 - 70 | 3,61 – 5,71 |
| 70 — 80 | 3,7 – 5,8 |
| 80 — 90 | 3,72 – 5,82 |
| 90 — 100 | 3,8 – 5,9 |
As can be seen from the indicators given in the table, the blood sugar level in women over 60 is practically no different from the norm in young people. And, given the error of the glucometer, reaching 10 - 20%, the differences can be completely neglected.
The normal fasting blood plasma sugar level when taking a sample from a vein is 6.1 for both women and men. Over 10 years, the norm increases, as in the case of capillary blood, by 0.055.
For venous plasma in the blood of women, when taken on an empty stomach from a vein, after 60 years of age, the sugar norm is:
- from 60 to 70 years – 6.21 mmol/l;
- from 70 to 80 years old – 6.3;
- from 80 to 90 years old – 6.32;
- 90 – 100 years – 6.4.
There are no gender differences in blood sugar levels from a finger and a vein. Normal blood parameters taken on an empty stomach practically do not change with aging.
Increase in sugar after eating
A feature of aging is a decrease in glucose tolerance, which is understood as an inadequate increase in sugar after eating and a slow decrease.
Up to 60 years of age, the normal blood sugar level after eating from a finger and from blood plasma from a vein is < 7.8 mmol/l. After this age, the indicators increase quite significantly.
The level of glucose in the blood 2 hours after taking the last meal increases in women after 60 years by 0.5 mmol/l every next 10 years.
Table: normal blood sugar levels after eating a regular diet in women over 60 years of age
| Age, years | Normal value, mmol/l |
| 60 | 8,3 |
| 60 — 70 | 8,8 |
| 70 – 80 l. | 9,3 |
| 80 – 90 l. | 9,8 |
| 90 — 100 | 10,3 |
Postprandial glycemia levels increase quite significantly with age. The difference observed between the normal blood sugar level after eating in women at 60 years old and at 80 years old is 1 mmol/l.
Diet for diabetics
Failure to monitor the amount of glucose your body produces on a daily basis increases your risk of hypoglycemic coma. Type 2 diabetes, normal blood sugar before and after meals after 60 years suggests that the slightest changes require immediate contact with an endocrinologist. Only he can give the necessary recommendations for stabilizing the norm and offer options for bringing it to the desired result.
Why control is necessary
A weakened pancreas and critical insulin deficiency will lead to the need to switch from pills to hormonal injections. The patient must understand when to switch to insulin and what symptoms are a consequence of the critical sugar level.
Accordingly, it is very important to constantly monitor your diet.
What to exclude from your diet
Eliminate foods with simple carbohydrates. Pay attention to sour and sweet fruits, which contain antioxidants, oils and acids that help burn excess fat. Try to activate metabolic processes by controlling how much carbohydrates your digestive system receives.
Prohibited Products

Authorized Products

Bread units and diet for diabetes
- For greater convenience, diabetic patients should have tables of bread units.
- Depending on whether you do light or heavy physical labor, what kind of lifestyle you lead (active or limited), the level of XE differs.
- Low-carb diets are an ideal option for reducing sugar levels.
But at the same time, do not allow its indicators to be critically low. In this case, you are at risk of hypoglycemic coma, which in some cases can even lead to death. When preparing food, resort to heat treatment and combine the names of different products. Replace unhealthful fatty meats with steamed meatballs. Instead of herring under a fur coat, prepare a light vegetable salad seasoned with lemon juice and natural vegetable oil. Keep in mind that it will be better if you eat the whole apple rather than juicing it, which increases your glucose levels. Fresh apricots will add 25 GI to you, but canned apricots will take away 960 GI.
Tips for proper nutrition for diabetes
A person susceptible to a serious illness must carefully monitor his daily routine and daily menu, so as not to awaken the development of more dangerous accompanying complications.
Here are the most important recommendations that everyone needs to know:
- Remove foods with increased AI and GI from the menu.
- Use strict eating hours.
- Stick to the following cooking options: steam, bake, boil.
- Avoid smoking, frying, drying and canning.
- Do not use animal fats, replace them with vegetable oils.
- Eat fruits and vegetables that are in season and fresh.
- Pay attention to seafood, but it should be low in calories and not high in GI.
- Keep count of XE.
- Tables XE, GI, AI should always be at hand.
- Make sure that the daily calorie content of the meals you receive does not exceed 2500 - 2700 kcal.
- To help your stomach digest the food you receive a little slower, eat more fiber.
- Don't forget to constantly monitor your sugar levels using a glucometer. This should be done throughout the day, before and after meals. In this case, you will be able to promptly correct hypoglycemia indicators.
- Remember that fairly high values negatively affect the work of all organs without exception.
Do not let the course of such a terrible disease as type 2 diabetes take its course; blood sugar levels before and after meals after 60 years should be constantly monitored. Please note that the functioning of your organs deteriorates with age. Changes identified in a timely manner will help you immediately react appropriately and take the necessary measures. Your personal health in many cases depends entirely on you.
We also recommend that you read:
What is insulin resistance? How to increase sensitivity to the hormone
How to take metformin correctly for type 2 diabetes: answering patient questions
Is it possible to drink coffee if you have type 2 diabetes - frequently asked questions by diabetics
The normal level of creatinine in the blood of women: how is nephropathy diagnosed in patients with diabetes mellitus