Types of diabetes
Doctors distinguish two main types of diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes
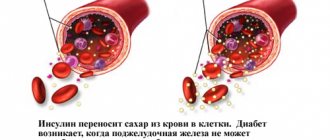
is insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM). The disease is associated with dysfunction of the pancreas. It is the pancreas that produces insulin. With significant (more than 90%) destruction of the cells responsible for its production, the amount of insulin in the blood drops and carbohydrate metabolism is disrupted. Glucose, still entering the blood, cannot be absorbed by the body. In this case, muscle tissue cells experience glucose deficiency. As a result, a person with type 1 diabetes loses weight quite quickly. Type 1 diabetes occurs more often in people under 30 years of age.
Type 2 diabetes
– non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). This type of disease is caused by tissue loss of sensitivity to insulin. In type 2 diabetes, the insulin level in the blood can be anything - normal, low or high. But the cells stop responding to it and the concentration of glucose in the blood increases. As a rule, the disease develops against the background of obesity. Type 2 diabetes most often affects people over 30 years of age.
There are other, less common types of diabetes.
What are the dangers of diabetes
Against the background of constantly high blood sugar or the so-called “swing” (alternating hyper- and hypoglycemia), the brain, which runs on pure glucose, suffers, and other organs, led by the heart and kidneys, fail. A person with diabetes can die because their blood glucose levels are too high or too low.
By affecting blood vessels and nerve endings, diabetes can lead to loss of vision, including blindness, and diabetic foot with non-healing ulcers, subsequent development of gangrene and amputation.
Complications of diabetes
Diabetes mellitus leads to decreased immunity. As a result, the patient more often suffers from various diseases, the recovery process is delayed, and the diseases often become chronic. The healing of various wounds (cuts, abrasions) is worse. Nervous tissue and blood vessels suffer. The development of atherosclerosis is stimulated, the vessels of the eyes and kidneys are affected, and the blood supply to the skin is disrupted. The combination of disorders of various systems leads to a complex of complications called diabetic foot syndrome. The foot, due to its peripheral position, turns out to be the most vulnerable - pathological changes caused by diabetes can lead here to inflammatory processes, ulcers, and tissue necrosis. In advanced cases, amputation may be required.
ketoacidosis , are dangerous
– accumulation of products of intermediate metabolism of fats (acetone) in the blood. Ketoacidosis is characteristic of type 1 diabetes.
Causes of diabetes
Among the factors contributing to the occurrence of type 1 diabetes mellitus
, usually distinguished:
- heredity. When type 1 diabetes is diagnosed in both parents, the probability of the disease is 30%;
- viral infections that cause damage to the pancreas (rubella, mumps, chicken pox, hepatitis, etc.);
- autoimmune diseases.
The main factors that increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus
, are:
- heredity. The influence of this factor in type 2 diabetes is higher than in type 1 diabetes. If one of the parents has type 2 diabetes, the probability of developing the disease is more than 40%;
- obesity, overweight;
- impaired glucose tolerance (this condition is called prediabetes
). With prediabetes, elevated blood glucose levels are recorded, while other symptoms of diabetes are absent; - age. With age, the likelihood of developing the disease increases;
- cardiovascular diseases.
Prevention
If there is a history of type 2 diabetes in your family, you are over 40 years old, you are burdened with extra pounds, you lead a sedentary lifestyle and you have high blood pressure, you should take action to prevent this disease.
Its main methods are:
- Proper nutrition. It should be based on complex carbohydrates and foods rich in fiber. About 60% of your diet should be complex carbohydrates, 20% fats (50-70% of which are vegetable oils), 20% proteins. Give preference to poultry, lean fish, vegetables, and unsweetened juices.
- Eliminate canned food, sweets and fatty foods. Steam;
- Quitting alcohol and tobacco. Both increase the risk of developing carbohydrate metabolism disorders;
- Daily physical activity: at least half an hour of sports or walking in the fresh air;
- Stress management and regular medical examinations. People at risk need to have their blood tested for sugar once every six months.
10 unexpected circumstances that increase blood sugar levels
Sometimes blood sugar can rise due to unobvious reasons. Blood glucose levels can be affected by:
- Sunburn – pain causes stress, and stress increases blood sugar levels.
- Artificial sweeteners - Some studies show that these may raise blood sugar levels.
- Coffee - even without sweetener. Some people's blood sugar levels are very sensitive to caffeine.
- Lack of sleep – Even one sleepless night can reduce the effectiveness of insulin in the body.
- Skipping breakfast – Skipping your morning meal can raise your blood sugar levels both after lunch and after dinner.
- Time of day – It is more difficult to control your blood sugar levels late in the day than during the day.
- Dawn - People experience a surge in hormones early in the morning, whether they have diabetes or not. For people with diabetes, their blood sugar levels may spike at dawn.
- Dehydration – less water in the body means higher concentrations of sugar in the blood.
- Nasal spray - Some of these contain chemicals that cause your liver to release more sugar into your blood.
- Gum disease – This complication of diabetes can cause high blood sugar levels.
People with diabetes should also avoid situations that could cause their blood sugar levels to drop sharply. For example, extreme heat can cause blood vessels to dilate, which speeds up the absorption of insulin and can lead to low blood sugar.
Symptoms of diabetes
The main symptoms of type 1 and type 2 diabetes are the same, but each type of disease has its own specifics.
The complex of main symptoms is caused by elevated levels of glucose in the blood. However, if in type 1 diabetes these symptoms are immediately noticeable, then type 2 diabetes may initially proceed for a long time without obvious symptoms.
Increased urine output
With a long-term concentration level above 6 mmol/l, glucose begins to penetrate into the urine. If the disease develops and the patient's condition worsens, the concentration of glucose in the urine increases. To lower it, the kidneys begin to secrete more water. As a result, the amount of urine excreted per day increases. This condition is called polyuria
.
Thirst
Because the body loses a large amount of water, the patient experiences constant thirst (polydipsia). The amount of fluid consumed increases. Lack of water in the body also manifests itself through dry skin and a feeling of dry mouth.
Increased appetite
For type 1 diabetes, a typical symptom is polyphagia - increased appetite or even a constant feeling of hunger.
Weight loss
Despite an increased appetite, a person with type 1 diabetes loses weight quickly.
Increased fatigue
Patients with diabetes are characterized by weakness (increased fatigue).
Deterioration of vision
The development of diabetes mellitus leads to visual impairment.
More about the symptom
Itching of the genitals
Diabetes mellitus can cause itching of the genitals.
Furunculosis
Diabetes mellitus leads to the development of inflammatory skin lesions and furunculosis (the appearance of boils).
Methods for diagnosing diabetes mellitus
If you suspect diabetes, you should definitely consult an endocrinologist. JSC “Family Doctor” offers to use the laboratory profile “Assessing the risk of developing diabetes mellitus,” which includes all the necessary tests. Based on the data obtained, the doctor will be able to assess the condition of your body and give the necessary recommendations.
Diabetes is diagnosed based on laboratory tests, primarily assessing blood glucose levels.
Measuring blood sugar levels
Nowadays, it is easy to purchase a glucometer for home use. Having such a device, patients with diabetes can quickly monitor their blood sugar levels. To do this, measurements should be taken in the morning on an empty stomach, and also 2 hours after eating. The second analysis will assess how well the body copes with the absorption of food.
Analysis for glycated hemoglobin
Glycohemoglobin (glycated hemoglobin) is a biochemical indicator that allows you to assess the degree of binding of hemoglobin with sugar molecules. This analysis is used both to diagnose diabetes and to monitor the progress of treatment (the patient’s condition). Those who have been diagnosed with diabetes should undergo this diagnosis once every three months. For those who are at risk of developing the disease - once every six months.
Blood chemistry
A biochemical blood test allows you to assess the level of glucose in the blood. Other indicators that make it possible to draw conclusions about the state of metabolic processes in the body are also important.
More information about the diagnostic method
Blood test for C-peptide
A blood test for C-peptide is a hormone test. This test allows you to estimate how much insulin is produced inside the body.
General blood analysis
A general blood test makes it possible to assess the general condition of the body. In particular, an increased hemoglobin value may indicate dehydration, while a decreased value may indicate internal bleeding. the likelihood of which increases with diabetes.
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
OAM
To obtain a more accurate assessment of a diabetic's health status, blood and urine tests must be taken at the same time. The OAM is taken once every 6 months, and how the OAM allows you to identify various hidden processes in the body.
This analysis allows you to assess:
- physical properties of urine, its acidity, level of transparency, presence of sediment, etc.;
- chemical properties of urine;
- specific gravity of urine, thanks to which the condition of the kidneys can be determined;
- protein, glucose and ketone levels.
Any deviations from the norm in diabetes mellitus require additional examination of the patient. And often for this purpose, an analysis is also taken to determine microalbuminaria.
Methods for treating diabetes mellitus
Today, diabetes mellitus is no longer a disease in which it is impossible to live normally, work, play sports, etc. Modern medicine has the necessary tools to make the life of a person with diabetes mellitus no different from the life of healthy people. However, for this it is necessary to identify the disease in a timely manner, constantly monitor blood sugar levels and follow all the doctor’s prescriptions.
Treatment for diabetes mellitus is aimed at achieving compensation. Compensation for diabetes mellitus is maintaining blood glucose levels within the normal range. This condition allows you to normalize hydrocarbon metabolism, as well as improve fat, protein and water-salt metabolism.
Treatment of diabetes mellitus is complex and includes a special diet, the use of medications, and physical activity in the required amount.
Specialist consultation
It is important to teach the patient to independently monitor his condition and control his behavior. For people suffering from diabetes, endocrinologists at the “Family Doctor” conduct special classes “School for Diabetes Patients”, where doctors talk about the disease, the characteristics of the diabetic diet and the regime of necessary physical activity.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Treatment
Treatment of diabetes is all about managing the disease throughout your life. Type 1 diabetes involves constant administration of the missing hormone to the patient - insulin. In addition, adherence to diet, proper distribution of physical activity and self-discipline play an important role in treatment.
Drug treatment: insulin therapy
People with type 1 diabetes need insulin injections every day to control blood sugar levels and get the energy the body needs. The doctor, together with the patient, selects the most effective type and regimen of drug administration.
Entering a fixed dose of insulin
When choosing this regimen, the patient injects himself with a fixed dose of insulin throughout the day. In this case, you need to carefully monitor the amount of carbohydrates consumed and take into account physical activity so as not to cause a state of hyper- or hypoglycemia.
Basal-bolus regimen
This scheme simulates the production of insulin by the pancreas. Following this, the patient injects himself with long-acting basal insulin to maintain blood sugar levels in the absence of food. Before meals, to eliminate sugar surges, a bolus of short-acting insulin is also administered.
Its dose depends on the blood sugar level and the amount of carbohydrates in the dishes consumed. This is a more flexible scheme in terms of power mode. The main thing is to correctly measure how much insulin you need.
Important! Your attending physician and specialists from the School of Diabetes will teach you how to dose insulin depending on the calorie content of food and physical activity. Check her address at your local clinic. Muscovites can find him out at this link. It is advisable to take classes at such a school annually. You will have to carefully analyze everything you eat, calculate how many units of insulin you need to inject for this, and monitor how the body reacts to the injection.
How to administer insulin
There is no need to be afraid of insulin therapy. For convenient administration of insulin, easy-to-use devices have long been developed: an insulin pump and a “penfill” - a syringe pen with insulin.
Insulin pump
The insulin pump (Fig. 2) independently administers the required amount of insulin throughout the day, imitating the work of the pancreas. In this case, short-acting insulin is used; the insulin bolus program before meals can be adjusted depending on dietary habits.
Figure 2. Insulin pump. Source: Alan Levine/Flickr.
Pump insulin therapy has a number of contraindications, including the presence of a mental illness that can lead to improper use of the device, decreased vision (if this interferes with interaction with the interface), acute somatic (non-mental) diseases or exacerbations of chronic diseases, psycho-emotional stress.
In addition, the use of a pump is not recommended for newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus, but this is a temporary limitation due to the fact that the patient must first learn to count insulin, and only then proceed to pump therapy.
Penfill
Penfill (Fig. 3) is a syringe pen for administering insulin. The pen allows you to change the insulin dose using a selector.
Figure 3. Penfill. Source: CC0 Public Domain
Important! The dose of insulin administered should correspond as closely as possible to the amount of carbohydrates consumed. When using a pen, never inject excess insulin “just in case”! A drop in blood glucose levels (hypoglycemia) occurs very quickly and you may lose consciousness.
Sugar control
Since the dose of insulin depends on the level of sugar in the blood, it must be constantly measured using a glucometer (Fig. 4).
Figure 4. Glucometer for measuring blood sugar. Source: Amanda Mills/USCDCP/Pixnio
Ask your doctor what your goal sugar level should be and how often you should check it. Staying as close to your target as possible will help you prevent or delay diabetes-related complications.
Diabetes while traveling
Before traveling, visit your doctor for advice about your itinerary, planned physical activity, and possible changes in insulin dosage and regimen.
Bring with you the necessary amount of insulin or prescriptions to purchase it. Check to see if your drug is available where you are going. Stock up on test strips for your glucose meter: changing your diet can lead to fluctuations in glycemia. It is better to take with you 2 times more medications than you usually need.
Get a medical bracelet that indicates you have diabetes. Get travel insurance in case you miss your flight or need medical attention. Order a special meal on board or take food on the go.
Your continuous glucose meter and insulin pump may turn off during airport X-ray screening. Ask customs officials for a manual inspection.
Diet
Dietary restrictions for patients with type 1 diabetes are relevant if the dose of insulin administered is fixed. This primarily concerns carbohydrates. Their excess or deficiency can provoke surges in blood glucose.
If the dose of insulin is calculated every time before meals, you will not have to limit yourself in food. You just need to take into account how a particular product affects blood sugar levels by calculating its glycemic index (GI), and how much “short” insulin is needed to control carbohydrate metabolism after a particular food.
“A patient with type 1 diabetes can eat anything, provided that the dose of insulin is calculated correctly,” says Professor L. Yu. Morgunov.
However, the diet for type 1 diabetes should be balanced and based on the principles of healthy eating. Pay special attention to the ratio of carbohydrates, fats and proteins: the amount of insulin you need directly depends on this.
For diabetes, doctors advise reducing consumption:
- salted, smoked, pickled dishes,
- foods high in starch and fat,
- confectionery products, sauces and semi-finished products.
Drink less fruit juices, sugary drinks and fast food - these are also harmful for a healthy person.
Physiotherapy
If you regularly engage in sports or fitness, alternating strength training with cardio exercise, remember the existence of a “carbohydrate window”. Due to inexperience, you can end up in a situation of life-threatening hypoglycemia. Therefore, be sure to inform your trainer about your diagnosis and do not practice alone at first. Avoid injecting insulin before exercise to avoid causing your blood sugar to drop. Calculate with your doctor how much you need to reduce your usual insulin dose on training days.
Important! Patients with diabetes, like healthy people, benefit from feasible physical activity - walking, jogging, children - outdoor games. In the early stages of using insulin, avoid prolonged active swimming, mountain climbing, fast or strenuous cycling: an acute drop in blood sugar (due to the administration of too much insulin for such an intense activity) with weakness to the point of fainting can lead to injury and pose a threat to life.