Detailed description of the study
A large number of different substances that enter the body every day with food or medicine are metabolized in the liver or kidneys. Blood passing through the kidneys is filtered, as a result of which the “needed” compounds are absorbed back, and the “unnecessary” ones are excreted in the urine. One of these “unnecessary” substances is creatinine.
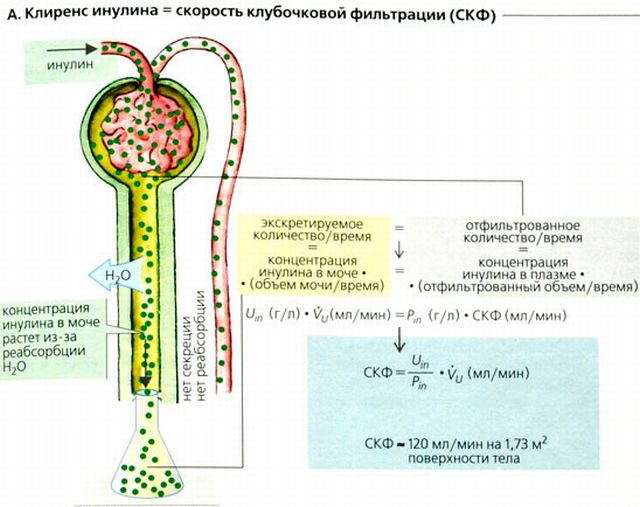
Creatinine is formed in muscles after the breakdown of creatine phosphate, a high-energy compound in muscle tissue. It is contained in the body in a more or less stable amount, which depends on the volume of a person’s muscles. Creatinine is not deposited in the kidney tubules and is normally completely excreted in the urine. Determining clearance - purification of the blood from any substance - endogenous creatinine makes it possible to assess the activity of glomerular filtration. Thus, with a reduced level of creatinine in the urine and its simultaneous increase in the blood, one can assume a decrease in its filtration in the kidneys.
Several laboratory parameters are required to assess glomerular filtration:
- The volume of blood plasma that passes through the kidney filter in one minute;
- Volume of urine excreted in one minute;
- Blood creatinine concentration;
- Urine creatinine concentration;
- Time during which urine was collected (in minutes).
During the Rehberg test, using these data, the clearance of endogenous creatinine is determined. In other words, the rate at which creatinine is released from the body by the kidneys in one minute.
To correctly assess glomerular filtration, it is necessary to determine not only the creatinine content in the urine, but also in the bloodstream. If the indicators differ greatly, they speak of a malfunction of the kidneys - the filters do not cope with their functions. At the end of the urine collection period, the patient should undergo a blood test for creatinine levels.
If the glomerular filtration level is low, the specialist will prescribe several additional tests and tests to determine the cause of the problem. Among the most common factors leading to this pathological condition are, for example, diabetes mellitus and hypertension. If they are absent, further examination of the body is required.
Periodic performance of the Rehberg test allows the doctor to observe the dynamics of kidney function and, if necessary, adjust treatment.
Research methodology
Creatinine clearance is a diagnostic test used to determine renal filtration function (GFR). During the study, the rate normally required to purify blood plasma through the nephron is calculated per unit time.
The nephron is a special anatomical and physiological unit of the kidney. It consists of a renal corpuscle (filtration glomerulus, capsule) and a tubular system that provides reabsorption (reabsorption) and excretion of various substances. International standards use glomerular filtration rate (GFR) to calculate the stage of kidney failure to provide an indication of the extent of organ damage.
Preparation
Despite the fact that the method is calculated, the key values for it must be determined in the laboratory. It is believed that test strips have a larger error, so preference is given to the classic test.
Calculation of creatinine clearance (Reberg-Tareev test) is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- 2-3 days before the analysis, exclude extractive substances (spices, excess salt), alcohol from the diet and temporarily stop taking other medications (after consultation with a doctor, since some medications are vital).
- The water regime is normal (1.5-2 l/day), protein consumption is moderate.
- The patient urinates in the morning, drinks 200 ml of clean still water and, still on an empty stomach, collects urine in designated containers for a certain time (usually two hours).
- In between the collection of urine samples, venous blood is taken from him for further research.
It is important to know! The test is carried out in a laboratory, so do not hesitate to ask the healthcare professional any questions. In the obtained materials (blood and urine), creatinine concentrations are determined biochemically, evaluating them in relation to diuresis.
Cockcroft-Gault formula
The simplest and most accurate method, which is accepted in most laboratories, is to calculate the glomerular filtration rate, taking into account the age and weight of the patient. The Cockcroft Gault formula for calculating creatinine clearance is as follows:
- For men: GFR = 1.23 * ((140 – age in years) * weight in kg))/blood creatinine (µmol/l)).
- Women: GFR = 1.05 * ((140 – age in years) * weight in kg))/blood creatinine (µmol/l)).
- Example: 1.23 *( (140-35)*65/90) = 93.3 (ml/min).
Alternatively, any other standardized formulas may be used. These include CKD-EPI or MDRD, each of which has its own characteristics and percentage of error.
References
- Post, T., Rose, B. Assessment of renal function: plasma creatinine; BUN; and G.F.R. In UpTo Date 9.1. Edited by BD Rose, 2001.
- Kasiske, B., Keane, W. Laboratory assessment of renal disease: clearance, urinalysis, and renal biopsy. In The Kidney. Sixth edition. Edited by BM Brenner. Philadelphia, WB Saunders Company, 2000. - P. 1129-1170.
- Landry, D., Bazari, H. Approach to the patient with renal disease. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Cecil Medicine. 24th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Saunders Elsevier; 2011. - Ch. 116.
- Pagana, K., Pagana, T. Mosby's Manual of Diagnostic and Laboratory Tests, 4th ed. St. Louis: MosbyElsevier, 2010.
Norm and tests for the presence of creatinine in the blood
The blood creatinine level is a constant value and is measured in micromoles/liter. In order not to lose control of the proper filtration functioning of the kidneys, it is important to monitor the creatinine level using tests and kidney samples.
Prescribing a test for the presence of creatinine in the blood in cases where:
- assessment of kidney function is necessary in cases of detected chronic renal failure
- hemodialysis is prescribed with a critical level of creatinine in the blood
- urolithiasis is suspected
- the subject decided to become a kidney donor
When preparing for the test, 2 days before donating blood, avoid increased physical activity, do not drink coffee, tea, alcohol for 24 hours, do not eat meat and protein products, do not eat half a day before the test, drink only still water.
The main source of creatinine production is human muscles. Men's muscles are very different from women's. Therefore, normal levels of creatinine in the blood of men and women have different values; in men this figure is naturally higher. Also, in addition to muscle mass, nutrition and how active your lifestyle are are also important. Athletes and gym goers may have significantly higher creatinine levels due to the increased consumption of amino acids in the body. Those on a protein diet and meat eaters may also have elevated creatinine levels. The age and pregnancy of the patient also matters.
Normal blood creatinine level:
- in an adult male 70-110 mmol/min
- in an adult woman 50-93 mmol/min
- in newborns and children under one year of age 18-35 mmol/min
- in adolescents under 15 years of age 27-75 mmol/min
High creatinine level
An excess of creatinine detected during diagnosis indicates a problem. It may be associated not only with impaired kidney function, but with other factors:
- intoxication of the body;
- thyroid dysfunction;
- dehydration;
- rapid increase in muscle mass;
- intense training or heavy physical activity on the eve of the examination;
- predominance of protein foods in the diet.
To accurately determine why creatinine increased, additional diagnostics are necessary. If the cause is a serious kidney pathology, hospital treatment will be required. When high creatinine levels are not associated with a disease, the patient needs to reconsider the work and rest regime. Physical activity should not be excessive.
A balanced diet and drinking enough fluids help improve laboratory test results. Adults with healthy kidneys should drink at least 1.5 liters of water per day. For problems with the excretory organs and cardiovascular system, the doctor will calculate the optimal amount of fluid.

Diet for people with elevated creatinine levels limits table salt
It is also important not to overload the stomach with protein foods and foods that are difficult to digest.
Forbidden
- pork meat;
- fatty poultry (duck, goose), fish;
- drinks with tannin and caffeine;
- baking from yeast dough;
- hot spices;
- fried foods.
Doctors do not recommend eating chicken eggs more than 2 times a week, and lean meat more than 3 times a week. It is worth minimizing the amount of sugar and salt in dishes.
Products that should form the basis of a diet for a person with high creatinine include the following:
- fresh, boiled, baked or stewed vegetables;
- fruits;
- porridge;
- fermented milk products with low fat content, cottage cheese;
- yeast-free and bran bread;
- vegetable oils;
- butter;
- dried fruit compotes, berry fruit drinks.
When the diet does not give the expected result, the question arises of selecting drugs that reduce creatinine levels. They regulate the production of proteins and also help cleanse the body of toxins.
How to take a urine test according to Rehberg
The test begins with the collection of urine, which is carried out according to certain rules.
Preparing to take a sample
An important point is the preparation stage. A day before the study and before its completion, the patient needs:
- give up high-protein foods (meat, fish, cottage cheese, etc.), alcoholic drinks, coffee and tea;
- exclude intensive sports and physical labor;
- keep the volume of liquid the same: this is approximately 1.5-2 liters per day;
- avoid stressful situations;
- refuse medications that can affect the test result (hormones, diuretics).
If you cannot stop taking medications due to serious health problems, you should definitely notify your doctor about this.

Urine collection rules
Before collecting urine, you need to take a three-liter jar, wash it well, rinse and dry it.
At about 6-8 o'clock in the morning you need to go to the toilet a little; this urine is not used for analysis. Then take a shower with careful hygiene of the genitals. It is not recommended to use products with fragrances or dyes for washing. Regular baby soap and water will do.
All subsequent urinations during the day should be carried out in a glass and poured into a large container, the volume of which is at least one and a half liters. There is no need to wash your face before each subsequent urination.
Urine is stored in the refrigerator. At room temperature, changes occur in it, after which the sample loses its information content.
The last urination is collected into a container with daily urine at the same time that collection begins (6-8 a.m.).
You need to submit urine for testing to the laboratory immediately after the end of its daily collection: only in this case the result will be the most accurate.
An important point: you do not need to bring the entire jar of urine collected per day to the laboratory. You need to mix the contents of the container and pour it into a standard urine collection container (about 50 ml)
It should contain a note about the date of collection of daily urine, information about the patient, the daily volume of urine received, in some cases it is important to indicate the person’s height and weight
Collection of material for the kinetic method
The patient should drink two glasses of water in the morning on an empty stomach and urinate without collecting liquid.
You also need to record the time and thirty minutes after it, blood is taken from the patient lying in bed. After another thirty minutes, all the urine is collected, the amount of which is used to calculate minute diuresis.
The collected materials are analyzed, and the final results are calculated using special formulas.
When assessing the results of the Rehberg test performed by the kinetic method, the following reference values (normal values) for creatinine clearance are used depending on age and gender, all values in ml/min/1.73 m2:
- up to 1 year, for women 65–100, for men 65–100;
- 1–30 years, women 88–146, men 81–134;
- 30–40 years, women 82–140, men 75–128;
- 40–50 years, for women 75–133, for men 69–122;
- 50–60 years, women 68–126, men 64–116;
- 60–70 years, for women 61–120, for men 58–110;
- 70 years and older, for women 55–113, for men 52–105.
Collection of daily material
When collecting daily urine, the first urination is not taken into account. The time is noted, and all subsequent portions of urine are collected entirely in a clean, dry container, which is placed in the refrigerator.
Exactly one day after the recorded time, the last portion is collected, which should occur during morning urination of the next day. Next, the volume of all collected urine is measured to the nearest 5 ml and recorded.
After which the liquid is mixed and approximately 50 ml of it is poured into a container for analysis. When donating the container, blood is also taken from a vein from the patient.
Method used for dynamic research
Determining the dynamics of GFR is usually used for scientific purposes. To do this, urine collected during the day and urine accumulated overnight are placed in separate containers.
The daytime period is taken to be from eight in the morning to eight in the evening, and the night time, respectively, from eight in the evening to eight in the morning.
For all three options, blood must be taken. And along with the volume of collected urine, the weight and height of the subject are also indicated in the direction, since these data are needed to increase the accuracy of the study.
Additionally
The collection and analysis of 24-hour urine is combined with a blood test. It allows you to determine the exact clearance of creatinine. Blood is donated in the morning on an empty stomach.