DOI: 10.18508/79
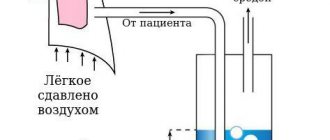
The adrenal glands are small in size and for better perception of the MSCT image of the adrenal gland, this image is used:
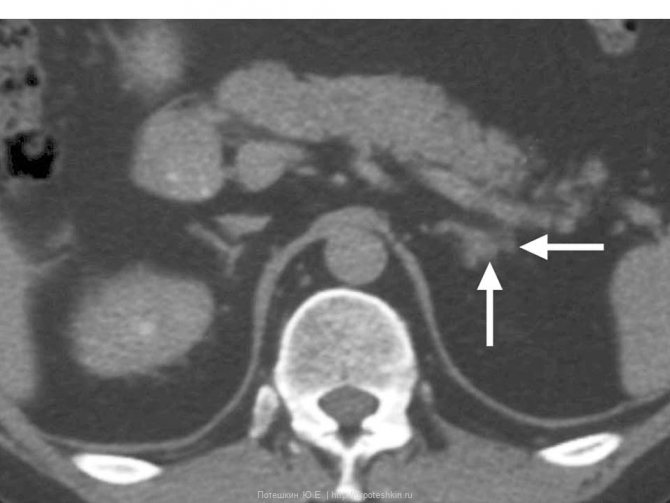
On MSCT, arrows indicate the adrenal gland:
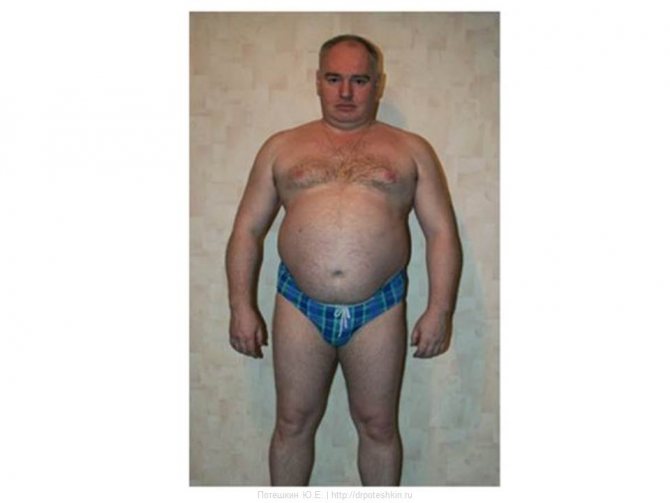
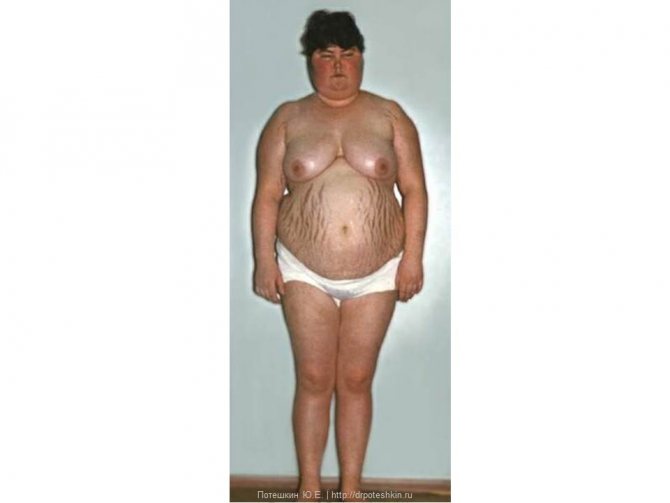
Hypercortisolism syndrome
Clinical picture
- Abdominal fat distribution
- Blush on the cheeks
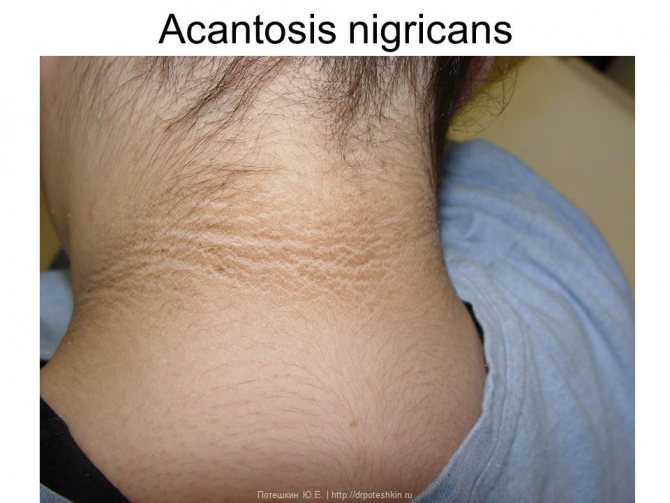
Acantosis nigricans
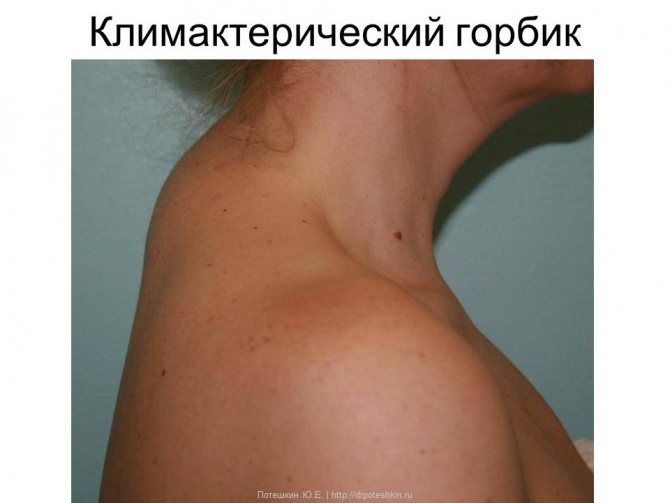
Menopausal hump
Other signs
- Striae
- Mycosis
- Hirsutism
- Hypertension
- Psychosis
Large dexamethasone test
- Day 1
- 8:00 - blood draw for Cortisol
- 23:00-0:00
- 8 mg Dexamethasone
- Day 2
- 8:00 - blood draw for Cortisol
Interpretation
- Cortisol (Day 2) vs. Cortisol (Day 1)
- Choked more than 50% Itsenko-Cushing's disease
- Itsenko-Cushing syndrome

| Drugs that accelerate the metabolism of dexamethasone due to induction of the CYP3A4 enzyme | Phenobarbital, phenytoin, carbamazepine, rifapin, rifampicin, ethosuccimide, pioglitazone |
| Drugs that slow down the metabolism of dexamethasone by reducing CYP3A4 activity | Itraconazole, ritonavir, fluoxetine, diltiazem, cimetidine |
| Drugs that increase cortisol binding globulin levels | Estrogens, mitotane |
| Drugs, the use of which leads to false positive results in determining St. cortisol in daily urine | Carbamazepine, fenofibrate, synthetic corticosteroids, 11betaHSD2 inhibitory drugs (licorice, licorice, carbenoxolone) |
Pheochromocytoma
Clinical picture
- Characterized by crises with a sharp increase in blood pressure
- Sympathetic-adrenal crisis: Feelings of fear
- Anxiety
- Shiver
- Chills
- Pale skin
- Headache
- Chest pain
- Feeling of heartbeat or irregularities in the heart area
- Nausea
- Vomit
- Increased body temperature
Flow options
- Weight loss
- Stable high blood pressure
- Stably normal blood pressure
- Stable low blood pressure
- During an attack, blood pressure may decrease
So, since the CT scan has already been done, it’s worth:
Make sure that the density of the adrenal gland formation is more than 20 unitsH.
To confirm or exclude the diagnosis, it is necessary to:
Analysis of 24-hour urine for metanephrine/normetanephrine
- Take a clean volumetric flask
- Pour 5 ml of sulfuric or hydrochloric acid (diluted) into it
- The first portion of urine is in the toilet
- All subsequent urine into the flask
- The first morning urine the next morning - into a flask
- Record volume
- Mix
- Pour into a test tube
- On the label write the patient's last name, first name, patronymic and the total amount of urine collected per day. Without this data, the analysis is not carried out!
Information content of the method
- 24-hour urine analysis (sensitivity - 93%, specificity - 75%)
- Urinalysis after an attack
- Blood test after an attack (sensitivity and specificity 95-100%)
Preparation
- Exclude Rauwolfia
- Theophylline
- Nitroglycerine
- Caffeine
- Ethanol
- Chlorpromazine
- Contrast dyes
- Hydroxymethoxyphenylglycol
- Imipramine
- Phenacetin
- Propranolol
- Products containing serotonin (chocolate, cheeses and other dairy products, bananas)
- Physical activity
Interpretation
- Increase in metanephrine or normetanephrine by more than 2 times Pheochromocytoma
Historical background (tests have very low sensitivity and specificity)
- Definition of Adrenaline
- Norepinephrine
- Vanillylmandelic acid in urine
Test with clonidine
- Patient in a supine position in a separate room
- A catheter is inserted into the vein after 30 minutes, blood is drawn for metanephrine/normetanephrine
- taking blood for metanephrine/normetanephrine
Interpretation
- Pheochromocytoma Metanephrine/normetanephrine levels do not decrease compared to basal levels
Glucagon test
- Carried out on an empty stomach
- A cubital catheter must be placed
- Phentolamine in case of crisis
- Normal blood pressure 0.5 or 1 mg glucagon administered intravenously
Interpretation
- Increase in numbers by 60/40 mmHg. Art. against baseline after administration of glucagon or an increase in blood metanephrine/normetanephrine indicates the presence of pheochromocytoma
Patient preparation rules
Preparing for the study:
the day before and during urine collection, it is necessary to: • exclude physical activity (sports training) • for 3 days before the study, exclude food and drinks rich in amines (vanilla, chocolate, coffee, cocoa, tea, cola, beer, bananas, avocados, tomatoes, alcohol), and stop smoking• agree with your doctor on the possibility of discontinuing medications: tetracycline antibiotics, reserpine, tranquilizers, adrenergic blockers, MAO inhibitors, sympathomimetics. To ensure the stability of biological material during the collection period, use a preservative (hydrochloric acid solution), which is necessary get it at the department of ML "DILA".
Collection of biological material
• add the resulting amount of preservative to a clean container for collecting urine (
important
- the volume of the container must be sufficient for the expected amount of urine per day) • do the first morning urination in the toilet. • collect all subsequent daily urine, including the morning portion of the next day into a container with a preservative• throughout the entire collection period, store the biological material in a cool, dark place• after the end of urine collection, determine its volume, mix, pour 35-40 ml into the container that contained the preservative and deliver it to the department of medical treatment "DILA" within 1-1.5 hours after collecting the last portion.
Important!
The container with the preservative must be stored at room temperature out of the reach of children. Avoid contact of the preservative with the skin and mucous membranes. The expiration date of the preservative is indicated on the packaging.
You can add this study to your cart on this page
Primary hyperaldosteronism
Clinical picture
- Severe hypertension >160–179/100–109 mm Hg.
- Hypokalemia
Diagnosis confirmation - blood test
- Renin
- Aldosterone
Preparing for blood collection
- Discontinue 4 weeks before: Spironolactone, eplerenone, triamterene, amiloride
- Diuretics
- Licorice Root Products
- Verapamil
- When staying in an upright position for no more than 2 hours
Taking blood
- It's best to use a syringe
- Don't clench your fist
- Draw blood no earlier than 5 seconds after removing the tourniquet
- Keep the test tube at room temperature
- Plasma separation no later than 30 minutes after blood collection
- Rapidly freeze plasma
- Stasis - repeated sampling
- Hemolysis - repeated sampling
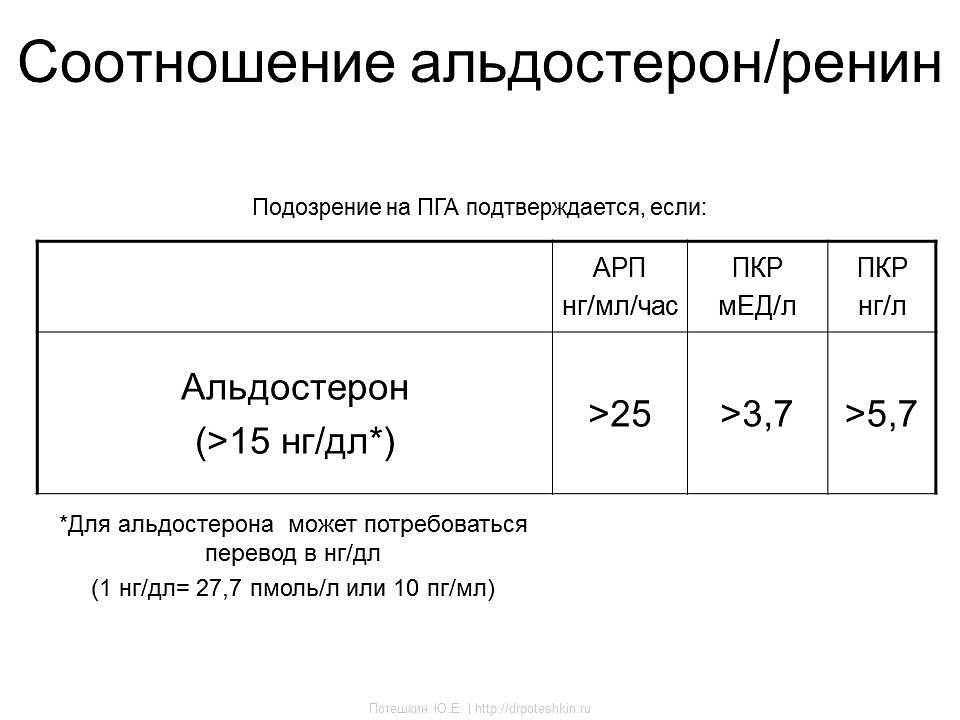
| ARP ng/ml/hour | RCC honey/l | RCC ng/l | |
| Aldosterone (>15 ng/dl*) | >25 | >3,7 | >5,7 |
*Aldosterone may require conversion to ng/dL (1 ng/dL = 27.7 pmol/L or 10 pg/ml)
Saline test
- The most informative test
- For an hour before the test, lie down
- Before the introduction of saline, control - renin, aldosterone, cortisol, potassium
- From 8:00 to 9:30, start infusion of 2 liters of 0.9% NaCl solution
- Carry out the infusion for 4 hours, at the end of the administration the control is renin, aldosterone, cortisol, potassium
Contraindications
- Severe hypertension uncontrolled by drugs
- chronic renal failure
- Decompensated heart failure
- Arrhythmia
- Severe hypokalemia
Interpretation
- PHA is unlikely if aldosterone is less than 5 ng/dL
- PGA is highly reliable if aldosterone is more than 10 ng/dL
- "Gray zone" 5-10 ng/dl
Normetanephrine free in urine (HPLC/MS)
Normetanephrines
- end products of the breakdown of one of the catecholamines - norepinephrine.
Atecholamines
are hormones produced by the adrenal glands, small organs located at the upper poles of both kidneys . Blood catecholamines have a short lifespan. The human body produces three types of catecholamines - adrenaline (epinephrine), norepinephrine and dopamine. They are released by the adrenal glands into the blood during physical overexertion or emotional stress, take part in the transmission of nerve impulses to brain tissue, stimulate the release of fatty acids and glucose - sources of energy in the body, dilate the pupils and small bronchi in the lungs. Norepinephrine constricts blood vessels, resulting in an increase in blood pressure, and adrenaline speeds up metabolism and heart contractions.
After performing their function in the body, catecholamines are converted into inactive forms: dopamine into homovanillic acid, norepinephrine into normetanephrine and vanillylmandelic acid, and adrenaline into metanephrine and vanillylmandelic acid. Both the hormones themselves and their metabolites are then excreted in the urine. At the same time, modern analyzers make it possible to distinguish between the free and bound forms of metanephrines in urine.
Metanephrines
- intermediate metabolites of catecholamines formed from adrenaline and norepinephrine.
Urine normally contains a certain amount of free normetanephrine, which increases significantly during and after stress. Some neuroendocrine tumors, in particular pheochromocytoma, produce large amounts of catecholamines, which leads to an increase in their concentration in the urine and blood. Catecholamines released by pheochromocytoma cause a persistent increase in blood pressure (and/or episodes of its sharp increase). The effects of catecholamines on the body are also manifested by other symptoms: headache, sweating, nausea, anxiety and tingling in the extremities.
Measurement of 24-hour urinary excretion of metanephrines is a sensitive screening test that is indicated when pheochromocytoma is suspected.
Indications:
- diagnosis and monitoring of catecholamine-secreting tumors - pheochromocytomas, paragangliomas, neuroblastomas;
- differential diagnosis of hypertensive conditions.
Preparation
In the morning, empty your bladder (this portion of urine is poured into the toilet). Record the time of urination, for example: “8:00”. For the next 24 hours, collect all urine excreted in a dry, clean 3-liter jar. The container with urine must be stored in a cool place (optimally in the refrigerator on the bottom shelf at a temperature of 4–8 ° C), preventing it from freezing.
After urine collection is completed, the contents of the container must be accurately measured. The container must indicate the daily volume of urine (diuresis) in milliliters. For example: “Diuresis: 2000 ml.”
Be sure to mix the urine thoroughly and immediately pour 50–60 ml into a sterile container with a lid. There is no need to bring all the urine collected during the day.
During the entire collection period and until shipment, the biomaterial should be stored in a refrigerator at 2–8°C. The material must be delivered to the medical office on the day the collection ends.
48 hours before urine collection, exclude bananas, pineapples, tomatoes, eggs, chocolate, cheese, as well as foods containing vanillin (confectionery) from the diet. It is necessary to limit as much as possible the intake of products containing caffeine and other stimulants (tea, coffee, cocoa, Coca-Cola). If possible, avoid taking medications 1–2 days before the study, except those used for health reasons.
Interpretation of results
Normetanephrine - mcg/day. Alternative units are nmol/day. Conversion factor—µg/day x 5.46 => nmol/day.
Reference values:
Age-normetanephrine-mcg/day:
- children (up to 90 days) - 47–156 mcg/day;
- children (90–180 days) – 31–111 mcg/day;
- children (180–270 days) – 42–109 mcg/day;
- children (270 days - 1 year) - 23–103 mcg/day;
- children (1–2 years) – 32–118 mcg/day;
- children (2 – 6 years old) – 50–111 mcg/day;
- children (6–10 years old) – 47–176 mcg/day;
- children (10–16 years old) - 53–290 mcg/day;
- adults
0–390 µg/day.
Increasing values:
- catecholamine-secreting tumors of neurochromaffin tissue: pheochromocytoma, paraganglioma, neuroblastoma;
- drug interference: hydrazine derivatives, MAO inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, levodopa, bushpirone, significant physical stress.