Cardiotocography (CTG) is a modern technique for assessing the condition of the fetus by the nature of its heartbeat. CTG is performed only in the third trimester of pregnancy, or more precisely after the 32nd week, since only after this period does a relationship appear between the contractions of the fetal heart and its functional state.
Carditocography is prescribed for the purpose of timely diagnosis of fetal disorders, which allows the obstetrician-gynecologist to prescribe the correct treatment, evaluate its effectiveness, and, if necessary, hospitalize the pregnant woman in the maternity hospital, where the optimal time and method of delivery are determined based on the results of CTG, ultrasound and Doppler measurements.
What is CTG
CTG during pregnancy is an effective way to assess the condition of the fetus. In the process of CTG monitoring, the frequency of his heartbeat is recorded and analyzed at rest, in motion, and during uterine contractions. Motor activity is assessed, as well as the degree of change in heart rate under the influence of various external factors (cardiac reactivity).
Like ultrasound, CTG during pregnancy is performed using medical gel. According to the results of cardiotocography, disorders such as oligohydramnios/polyhydramnios, fetoplacental insufficiency, intrauterine infections, etc. are revealed.
CTG of the fetus during pregnancy is based on the principle of reflection of ultrasound waves from moving objects (Doppler effect). Special recording sensors are placed on the anterior abdominal wall. They generate high-frequency sounds and read signals received from the uterus and fetus. A special program analyzes the data and displays it on the monitor in the format of graphics, light, and sound signals. CTG of a child during pregnancy helps the gynecologist find out about the presence of pathologies associated with the formation of the heart and blood vessels.
Assessment of fetal condition - points
To assess the condition of the fetus, doctors use scoring methods. Women often raise reasonable questions about what 4 or 5-6 points on CTG mean, which can be indicated by 10, 11 or 12 points. The interpretation depends on the calculation method used by the program or how the doctor calculated the result if the assessment was done “manually”.
The most commonly used system is the Fisher grading system.
By Fischer
Fisher scoring table (Krebs modification):
| Indicator determined on CTG | 1 point is awarded if: | 2 points are awarded if: | 3 points are awarded if: |
| Base heart rate | Less than 100 beats/min or more than 100 beats/min | 100-120 beats/min or 160-180 beats/min | 121-159 beats/min |
| Expressiveness of slow oscillations | Less than 3 beats/min | From 3 to 5 beats/min | From 6 to 25 beats/min |
| Number of slow oscillations | Less than 3 during the study period | From 3 to 6 during the study period | More than 6 during the study period |
| Number of accelerations | Not fixed | From 1 to 4 in half an hour | More than 5 in half an hour |
| Decelerations | Late or variable | Variable or late | Early or not fixed |
| Movements | Not fixed at all | 1-2 in half an hour | More than 3 in half an hour |
The interpretation of the results looks like this:
9,10, 11, 12 points – the child is healthy and feels quite comfortable, his condition does not cause concern;
- 6, - the baby’s life is not in danger, but his condition is cause for concern, since such an indicator may be a sign of initial pathological changes and adverse external influences. A woman should do CTG more often to monitor the baby’s dynamics;
- 5 points or less – the child’s condition is threatening, there is a high risk of intrauterine death, stillbirth, neonatal death in the early postpartum period. The woman is sent to the hospital, where an urgent diagnosis is carried out and in most cases it ends in an emergency caesarean section to save the baby’s life.
By FIGO
This assessment table was adopted by specialists from the International Association of Gynecologists and Obstetricians. It is used less frequently in Russia than the Fisher assessment, but is more understandable for expectant mothers.
FIGO interpretation table:
| Parameter determined during the study | Meaning – “norm” | Meaning – “doubtful” or “suspicious” | Meaning: “pathology” |
| Basal heart rate | 110-150 beats/min | 100-109 beats/min or 151-170 beats/min | Less than 100 or more than 170 beats/min |
| Variability | 2-25 beats/min | 5-10 beats/min for 40 minutes | Less than 5 bpm over 40 minutes or sinusoidal rhythm |
| Accelerations | 2 or more in 40 minutes | During the 40-minute examination there are no | Absent at all |
| Decelerations | Not registered at all or there are rare variable | Variable | Variable or late |
PSP
This is the key value that is derived from all measured and analyzed parameters.
It is very difficult to clearly imagine by what algorithms and mathematical formulas this calculation is carried out if you do not have a mathematician’s diploma on your shelf at home. This is not required. It is enough for the expectant mother to know which PSP indicators are considered normal and what they mean:
- PSP less than 1.0. This result means that the baby is healthy, he is comfortable, his well-being and condition are not impaired. This is a good result, in which the doctor sends the pregnant woman home with a clear conscience after CTG, because nothing bad should happen to the baby.
- PSP from 1.1 to 2.0. This result indicates likely initial changes that differ from normal well-being. Violations with such PSP are not fatal, but they cannot be ignored. Therefore, the woman is asked to come for CTG more often, on average once a week.
- PSP from 2.1 to 3.0. Such indicators of the fetus' condition are considered very alarming. They may indicate severe discomfort that the child experiences in the womb. The cause of the baby's unwellness may be a Rh conflict, a state of oxygen deficiency, entanglement in the umbilical cord, or intrauterine infection. The pregnant woman is sent to the hospital. She is indicated for a more thorough examination and, possibly, early delivery by cesarean section.
- PSP is above 3.0. Such results may indicate that the child’s condition is critical and he is at risk of intrauterine death, which can occur at any time. The woman is urgently hospitalized and an emergency caesarean section is indicated to save the baby.
Why is this procedure needed?
CTG during pregnancy determines what happens to the child at different periods of time. Helps to see signs of oxygen deficiency (hypoxia), assess the condition of the fetus and the expectant mother, and determine tactics for further actions during childbirth.
From which week of pregnancy CTG is performed directly depends on the woman’s condition and the presence/absence of any pathologies. An increase or decrease in fetal CV when listening with an obstetric stethoscope during an examination is a reason to prescribe cardiotocography. A referral for a CTG procedure during pregnancy is issued at the antenatal clinic during a scheduled appointment or at the maternity hospital during unscheduled examinations.
Dates
The minimum possible period when the first CTG is done during pregnancy begins at the 28th week. An earlier procedure is acceptable if there are suspicions of critical abnormalities in the fetal condition. At earlier stages, the device only records the heartbeat, without the ability to analyze changes in heart rate depending on movements. Until 28 weeks, there is still no full interaction between the autonomic nervous system and the heart, so performing cardiotocography at this time is not advisable. The CTG procedure during pregnancy begins to be done when the obstetric period approaches 30 weeks.
At what stage of pregnancy is routine fetal CTG performed?
The third trimester (about 32 weeks from the date of conception) is optimal for assessing physiological characteristics. By this time, a relationship is established between movements and cardiac activity, and the “activity-rest” cycle is formed.
The period from 30 to 32 weeks is the best time for CTG during pregnancy. The procedure is carried out both in a residential complex and in a hospital. How many weeks the first CTG is done during pregnancy directly depends on individual indications. In accordance with the order of the Ministry of Health, during normal pregnancy, cardiotocography is done once every 10 days from the beginning of 28 weeks.
If the results of previous CTG studies are unfavorable, monitoring is repeated after a week (5 days). In some cases, the parameters of the week from which fetal CTG is performed may change. For example, in case of multiple pregnancy, the study is carried out starting from the 26th week.
When asked how often a CTG can be done during pregnancy, experts answer: if there are no abnormalities on the ultrasound and there are no doubts about the woman’s condition, the test is carried out 1-2 times during the third trimester. This is an auxiliary examination to determine labor management tactics. It is assessed in conjunction with other physiological indicators.
Only an observing obstetrician-gynecologist can determine exactly how many times CTG is done during pregnancy. The number of procedures varies depending on the physical condition of the expectant mother. On average, cardiotocography is taken no more than once a week.
Additional CTG during pregnancy is prescribed in cases where the attending physician has doubts about the woman’s condition.
Key indications for frequent monitoring:
- identified malformations of the baby;
- presence of a scar on the uterus;
- umbilical cord entanglement according to ultrasound results;
- deviations in the results of previous CTG;
- decrease/increase in the amount of amniotic fluid;
- large fetus, placenta previa, narrow pelvis;
- history of premature birth or miscarriages;
- Rh factor incompatibility;
- the presence of chronic pathologies in women (thyrotoxicosis, diseases of the genitourinary system, etc.);
- gestosis (increased blood pressure, swelling, convulsions).
The number of CTG performed increases during pregnancy with twins and post-term pregnancy (more than 41 weeks). These conditions require increased attention from doctors. Therefore, how many times CTG is done during post-term pregnancy is determined by ultrasound indicators, general physical condition, and the results of clinical tests.
Studies are carried out every five days after the expected (estimated) date of birth. If intrauterine hypoxia is detected, monitoring is carried out daily until the child’s condition normalizes. Depending on the period at which CTG readings are taken during pregnancy, a treatment regimen is determined and a decision is made on the method of delivery.
Is there a threat to the baby and for how long?
The obtained data is recorded on an electronic or paper medium, reminiscent of a tape for a cardiac cardiogram, and deciphered by a specialist. Of course, the doctor performing the procedure immediately sees obvious deviations and, if urgent measures are necessary, immediately reports this.
In situations where the baby’s condition is not critical, the results can be given to the woman, and she goes with them to the obstetrician for a more thorough interpretation and, if necessary, for further recommendations. And here every caring mother, interested in the health of her unborn child, can look at the chart and become familiar with the activity of his heart. In this case, it is better to have an idea of the norms and possible deviations in the tocogram.
Heartbeat
The cardiogram records the maximum and minimum values of the fetal heart rate, but the diagnostician is interested in the average value, the norm of which is 110–160 beats per minute.
Variability
After the heart rate, the frequency and amplitude of the baby’s heart contractions are assessed. The tocogram curve shows many small teeth and a few tall ones. Small ones are deviations from the basal rhythm. Normally, at 32–39 weeks there are no more than 6 of them.

Indicators are assessed using several parameters and then added together
But counting them is not so easy, so most often doctors give an estimate of the amplitude of the deviations, expressed in changes in the height of the teeth, the norm of which is 11–25 beats per minute. A decrease in this indicator to or less than 10 beats may alert doctors.
However, it is necessary to take into account how many weeks CTG is performed - if the period is less than 28 weeks, then this is not a pathology. If the period is longer, then the procedure should be repeated - perhaps the baby was simply in a state of sleep. Exceeding the norm of this indicator may indicate entanglement in the umbilical cord or the presence of hypoxia.
Acceleration and deceleration of heart rate
To assess this indicator, high teeth on the tocogram are studied at 32–38 weeks of pregnancy. When undergoing the procedure on outdated machines, the woman is asked to press a special remote control when the fetus moves. Modern devices no longer need this action - they automatically record the baby’s activity.
When a child moves, his heart begins to beat faster and this is shown on the graph as a tall tooth. This is called acceleration and its norm is considered to be at least two in 10 minutes. Acceleration may not be displayed during the study, but do not panic - perhaps the child is just sleeping.
Slowing down - at 35-39 weeks it looks like teeth growing downwards. There is no need to worry if after acceleration there is a short and shallow deceleration, and then the graph returns to the average rhythm. High-amplitude decelerations pose a danger. In this case, it is necessary to compare the first graph with the second, which shows uterine contractions - they can slow down the rhythm.
The advantages of cardiotocography are obvious - thanks to it, you can keep the condition of the fetus under control, prepare for the upcoming birth, identify problems with the child’s development in time and find solutions. In addition, the procedure is absolutely painless and harmless for the mother and child, therefore, if mothers are concerned about the question of whether CTG is harmful or at what time it is better to undergo it, then the answer is not harmful, and the doctor will choose the period himself, guided by the well-being of the pregnant woman and the prescribed standards.
How to prepare for CTG
Special preparation for CTG during pregnancy is not needed. The optimal time for the study is from 9 to 14 and from 19-23 hours. When undergoing the procedure at other hours, deviations in heart rate variability may be observed. It affects CTG readings during pregnancy and the position that the woman takes at the time of the study. The optimal position during cardiotocography is lying on your left side. A sitting/half-sitting position is allowed. The location of the body can affect how long a CTG takes during pregnancy.
It is not recommended to lie on your back during the procedure. Due to excessive compression of the blood vessels by the uterine cavity, unreliable results may be obtained. The process of preparing for CTG during pregnancy includes visiting a gynecologist to listen to the heartbeat and determine the location of the fetus. Before the procedure, you need to get a good night's sleep, visit the toilet, and be in a positive mood.
Is it possible to eat before CTG during pregnancy?
Electronic monitoring is not done on an empty stomach or after direct (intravenous) glucose administration. This affects the child’s activity and causes errors in the tocogram. Therefore, the answer to the question whether it is possible to eat before CTG during pregnancy is positive. The optimal period of time after eating is 2-3 hours.
Features of the procedure
The main thing that CTG gives during pregnancy is the ability to determine whether the baby has enough oxygen, how he tolerates physical activity during uterine contractions, and whether he will pass through the birth canal. There are two methods for performing CTG during pregnancy: indirect and internal.
The second method is used extremely rarely and only during childbirth. The first is actively used during the period of gestation and in the first phase of labor. Cardiotocography during labor shows how well the baby copes with the load and whether additional stimulation of the birth process is required. Let's look at how CTG is done during pregnancy.
The principle of how CTG is done during pregnancy includes the main steps:
- Placement of the ultrasound sensor on the anterior abdominal wall in the area where the child’s heartbeat can be heard. The correct location of the controller affects how long the CTG will last during pregnancy.
- Application of a strain gauge to the right corner of the uterus.
- Fixing the reader with straps.
- Recording data for an hour/half an hour on paper tape in the form of graphs.
The results obtained are interpreted by an obstetrician-gynecologist. A comprehensive assessment of CTG, Doppler and ultrasound data is being carried out. If the results indicate severe hypoxia, measures are taken to eliminate it.
Types of devices
Medical facilities have various options for assessing your baby's heartbeat. Most often, the doctor simply listens to the baby’s heart rhythm using an obstetric stethoscope, but if there is any doubt (or if there is evidence), it is necessary to use a special device. What types of CTG devices are there?
CTG without automatic analysis
These outdated devices are generally quite rare in modern hospitals, but they can still be found in remote corners of our country. The main inconvenience of these devices is that the doctor must independently evaluate the fetal heartbeat graph. If the doctor has experience and masters this technique, then the effectiveness of these devices is no lower than that of new CTG devices.
CTG with computer analysis
Modern cardiotocographs not only record the graph, but also independently process the data. The doctor only needs to read the finished result and decide on the need for treatment. This version of CTG is used most often in medicine.
KTG-online
The modern mobile era offers an excellent option for monitoring the baby using a special sensor attached to the skin of the abdomen and a smartphone connected to the Internet. Information about the fetal heartbeat in real time is transmitted to the web portal, processed and provided in the form of a ready-made report to the doctor. Unfortunately, online CTG is still rarely used.
Total duration of CTG
How long does it take to do CTG during pregnancy?
The duration of this procedure varies from 30 minutes. up to one and a half hours. You can find out exactly how long a CTG will last during pregnancy from the doctor performing the procedure. In some cases, it takes no more than 20 minutes to compile a complete picture. The main factor influencing how long CTG is done during physiological pregnancy is the child’s motor activity.
The total time of the CTG procedure during pregnancy is 40-60 minutes. The estimated time also depends on the general well-being of the woman and how often CTG is done during pregnancy.
Norms and interpretations of CTG during pregnancy
What exactly does CTG show during pregnancy:
- fetal heart condition;
- the presence of intrauterine infections;
- developmental anomalies;
- fetoplacental insufficiency.
During the study, the age of the placenta and the likelihood of risk of premature birth are assessed.
To correctly assess the health of the fetus, it is important to understand how CTG is interpreted during pregnancy. When conducting the study and interpreting the results, it is taken into account that the average duration of fetal sleep is about half an hour.
The general motor activity of the child and the ability to respond to stimuli are affected by changes in the biochemical parameters of the mother’s blood. For example, changes in glucose levels. A full interpretation of fetal CTG during pregnancy is performed by an obstetrician. The obtained data corresponds to generally accepted standards. How to decipher CTG during pregnancy yourself? To do this, you can use tabular data.
Table 1. CTG indications during pregnancy interpretation
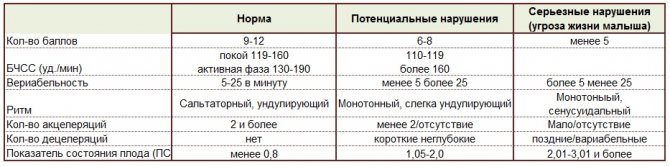
Correct interpretation of CTG data during pregnancy helps determine further treatment tactics and resolve the issue of methods and timing of delivery.
A CTG reading during pregnancy of 6 points may indicate intrauterine growth retardation and insufficient oxygen intake. A reduced heart rate as a variant of the norm is possible with a breech baby.
What does a CTG machine show during pregnancy? Explanation:
- SS frequency (basal rhythm).
- Character, amplitudes of tones (BR variability).
- Rhythm (deceleration, acceleration).
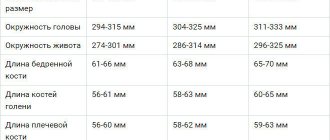
Table 2. CTG indicators during pregnancy are normal by week.
CTG analysis during pregnancy, what is it? The concept implies the assessment of tocogram indicators to identify deviations from the recommended physiological norm.
Table 3. CTG for full-term pregnancy is normal (32-38 weeks):
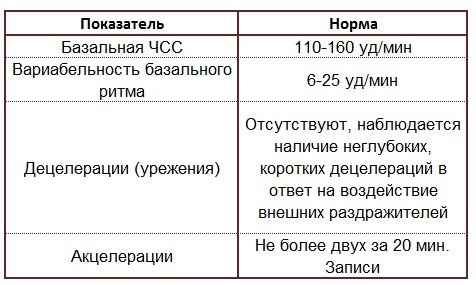
Poor CTG during pregnancy indicates deviations in the reactivity of the baby’s cardiac and vascular system. The information obtained from the study reflects changes in the mother-placenta-fetus structure. However, it is impossible to draw final conclusions about the child’s condition based on cardiotocography indicators alone. The optimal CTG indicator during pregnancy is 9 points.
Cardiotocography assessment
If fetal cardiotocography was performed, interpretation requires subjectivity and accuracy. It is for this purpose that a system for assessing this diagnostic was developed, which provides for assigning points to each of the indicators.
So, the assessment is considered correct if it is carried out according to 5 main parameters, each of which, in turn, is also assessed with specific points from 0 to 2. For example, the norm is if in total all points are about 8-10. Anything above 10 points is also considered normal. But if the score corresponds to 6-7, then this condition is diagnosed as pre-pathological and the attending physician may refer for additional studies, prescribe therapy and after it, prescribe a repeat CTG. But everything below 6 indicates that a pathological process is clearly present, namely, an intrauterine lack of fetal oxygen (or hypoxia). This condition requires both hospitalization and measures for a speedy delivery.
Harm of CTG: truth or myth
The CTG procedure during pregnancy is painless and safe. It does not harm the baby and the expectant mother, and does not stimulate the premature onset of labor. Timely conduct of cardiotocography reduces the risk of developing pathologies, allows them to be identified in the early stages, and the necessary measures to be taken to eliminate them.
How often should CTG be done during pregnancy? The optimal interval will be determined by a gynecologist based on other examinations and the woman’s general physical condition. To get a complete picture of CTG during pregnancy, you can read reviews on specialized medical or parenting forums.