Indications for ultrasound screening in the 3rd trimester
Three timed ultrasound scans are recommended by WHO for all pregnant women without exception. However, there is a risk group whose patients should be screened without fail. This group includes the following categories of expectant mothers:
- Living in environmentally unfavorable regions
- Those in the age category over 35 years old
- Having a history of miscarriage
- Those who have children in the family with genetically determined diseases (syndromes, triploidy, etc.)
- Having had infectious diseases in the first trimester
- Having been treated with antibacterial drugs during pregnancy
- Those who underwent high-dose radiation training several months before conception
- Having a close relative as the father of the child
Benefits of an individual approach
Regardless of the opinion of scientists about the best moment to perform ET, embryologists and reproductive specialists prefer to resolve this issue individually. Indeed, it is very difficult to make a specific generalization in this case, so each case must be considered separately.
The main aspects that determine the transfer day include:
- quantity;
- quality;
- history of IVF cycles and their results;
- the use of additional techniques - preimplantation diagnostics, egg donation, ERA test;
- capabilities of a particular laboratory.
If preimplantation diagnosis is required, a biopsy is performed on day 3. Advanced culture is also used in IVF with donor eggs, as a large number of good quality embryos are usually available. Finally, when an ERA test is required, the PE will be scheduled at the most appropriate time, depending on the test results.
Read more about the ERA test for determining the implantation window in this material - note. altravita-ivf.ru.
What will your doctor see during your third trimester screening?
Diagnosis in the last trimester of pregnancy is important in preparing for childbirth. In the process of scanning with an abdominal sensor, the obstetrician-gynecologist receives a lot of valuable information about the placenta, amniotic fluid and the patient’s readiness for childbirth in general. Ultrasound of the 3rd trimester provides data on:
- The amount of amniotic fluid (oligohydramnios, normal, polyhydramnios)
- Maturity of the placenta and the condition of the blood vessels in it
- The condition of the internal organs of the fetus (heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, etc.)
- Fetal parameters: chest diameter, abdominal diameter and circumference, spine parameters, limb length (femur and humerus)
In addition to ultrasound, the doctor may prescribe standard studies for pregnant women such as Dopplerography and cardiotocography. These diagnostic procedures are designed to identify the speed and nature of blood flow in the placenta and assess the state of the fetal cardiovascular system.
Ultrasound screening of the third trimester
Carry out from the 30th to 34th weeks of pregnancy (the optimal time is from the 32nd to 33rd weeks)
During an ultrasound, the condition and location of the placenta is studied, the amount of amniotic fluid and the location of the fetus in the uterus are determined. momsoriginally
According to indications, the doctor may prescribe additional studies - Doppler ultrasound and cardiotocography.
Doppler testing - this study is done starting from the 24th week of pregnancy, but most often doctors prescribe it after the 30th week.
Procedure and preparation for screening
On the eve of the procedure, you should not limit yourself in eating habits.
A long gestational age allows for an informative study without any preliminary measures. Screening takes about 40 minutes and takes place in a specially equipped ultrasound diagnostic room. There is such an ultrasound room in every branch of the Medok clinic network.
The patient takes off her clothes and lies down on the couch in a comfortable position. To check fetal activity, the doctor may recommend that the pregnant woman touch her stomach or lightly tap it with her fingers.
Preparing for screening
Each individual research procedure requires individual preparation. The exceptions are ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound.
Blood is taken for analysis in the morning on an empty stomach. A couple of days before collecting biomaterial, you should stop eating fatty, spicy, fried foods, marinades and fast food. Possible allergens should also be excluded from the diet.
Cardiotocography is carried out 1.5-2 hours after eating during the period of maximum activity of the baby. According to statistics, this time is from 9.00 to 14.00 and from 19.00 to 24.00. Before the study, you should not smoke or subject your body to serious physical activity.
Only a doctor can interpret the results of the third screening. Women are strongly advised not to attempt this on their own. Identifying any deviations from the norm is not a diagnosis. The gynecologist discusses all cases with the expectant mother and, if necessary, prescribes additional studies and consultations with specialized specialists.
Interpretation of third trimester screening results
Ultrasound examination indicators correlate with the patient’s period by week.
So, the values for the 32nd week of pregnancy will differ from the same indicators at the 34th week. Normal parameters for screening at 32 weeks are:
- placenta: thickness from 25.3 to 41.6 mm
- amniotic fluid: from 81 to 278 mm
- maturity of the placenta in degrees: first/second
- cervical dimensions (length): from 30 mm
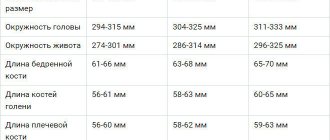
Fetal skeletal parameters at screening 32-34 weeks of pregnancy:
- biparietal size: from 85 to 89 cm
- weight: from 1790 to 2390 grams - length (height): from 43 to 47 cm
- head circumference: from 309 to 323 mm
- fronto-occipital head size: from 102 to 107 mm
- forearm (length): 46 to 55 mm
- shoulder (length): 55 to 59 mm
- Shin (length): from 52 to 57 mm
- thigh (length): 62 to 66 mm
- abdominal circumference: from 266 to 285 mm
What is included in 3rd trimester pregnancy screening?
3 screening during pregnancy includes a set of methods and means by which the doctor assesses the state of health of the fetus, the characteristics of its development (if any), and the preparedness of the woman’s pelvic organs for the upcoming birth.
One of the most important tasks that screening in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy solves is predicting labor and identifying indications for natural childbirth or cesarean section. In addition, if a number of pathologies of the mother or fetus are detected, it subsequently becomes possible to carry out special preparation for childbirth - doctors of the perinatal or maternity ward, having the relevant information, ensure that the delivery room is equipped with all the equipment and means with which appropriate medical care is provided to the mother or newborn.
A set of diagnostic procedures allows you to obtain the following information:
- Ultrasound of the third screening during pregnancy allows you to identify late pathologies of fetal development and its position in the uterus, as well as assess the maturity of the placenta and the amount of amniotic fluid.
- Dopplerography assesses the level of oxygen available to the fetus and allows you to detect hypoxia, and also assesses the state of the child’s cardiovascular system.
- A biochemical screening test in the third trimester is a reliable research method that allows you to identify genetic diseases in the fetus.
- Cardiotocography is capable of identifying deviations in the fetal heartbeat with a high degree of accuracy, as well as assessing the dependence of the child’s heart contractions on the contractions of the uterus, his own movements and external stimuli.
An ultrasound is a mandatory item, and other studies are carried out if necessary. The optimal period is 31–32 weeks.
In general, screening in the 3rd trimester takes several hours. Some procedures, such as transvaginal ultrasound or biochemical analysis, need to be prepared. You can find out about the price of the diagnostic complex, preparation for tests, possible discounts and promotions by contacting the specialists of the First Family Clinic in St. Petersburg by phone or in person.
When is 3 screening needed?
This study is not mandatory, unlike those prescribed in the second trimester of pregnancy. It is recommended to undergo the procedure, but the final decision rests with the expectant mother. However, there are a number of situations when screening is mandatory:
- The presence of deviations or shortcomings during previously performed screenings.
- Pregnancy at the age of 38 years.
- If pregnancy occurs against the background of health problems in the woman and in the presence of infections.
- If a woman smoked during pregnancy, drank alcohol, etc.
- Taking medications that could negatively affect the baby's health.
- Work in difficult physical conditions.
- Cases of genetic diseases in the family.
The decision on how many weeks to conduct such a study is made by the doctor. This can be either 28 or 30–34 weeks.
What does the third screening include?
As a rule, screening is a set of activities including:
- Ultrasound;
- cardiotocography;
- biochemical blood test (if there are appropriate indications).
All procedures can be done either on the same day or on different ones, depending on the wishes or well-being of the pregnant woman. Blood must be donated on an empty stomach, and before cardiotocography it is usually advised to eat a chocolate bar or something sweet to increase the child’s activity. An ultrasound is performed through the abdominal wall.
Indications for procedures
In the second half of pregnancy, expectant mothers have the opportunity to more accurately determine whether the fetus has developmental pathologies or various chromosomal diseases. Screening in the 3rd trimester is a comprehensive study that makes it possible to identify existing disorders with a high degree of probability. However, there is a certain percentage of error that may arise. That is why, for high accuracy, it is necessary to carry out not only biochemical studies, but also a number of examinations aimed at analyzing the physical condition of the fetus.
The absolute indications for screening in the 3rd trimester are the following:
- Diabetes mellitus in the mother. Moreover, the complexity of the course of the disease does not matter here;
- Arterial hypertension;
- The presence of an unfavorable prognosis in previous examinations;
- Rh conflict, for example, the mother has a positive Rh factor, but the fetus has a negative Rh factor. If during the first pregnancy this situation rarely causes a high probability of developing fetal pathology, then during subsequent pregnancies this possibility increases sharply.
How is it done?
In fact, screening of the 3rd trimester is a collection of venous blood, which will subsequently be examined by specialists. You should not eat before taking tests. Blood should be donated only on an empty stomach. In addition, on the day preceding this, you need to avoid eating fatty, spicy foods, smoked foods and excessively salty and peppery foods.
The analysis is carried out at 32-34 weeks of pregnancy. Our UNIONCLINIC medical center in St. Petersburg, thanks to the experience of specialists and high-precision equipment, allows us to carry out all the necessary examinations literally in one day. True, the results of biochemical blood tests will be ready after a short period of time.
Our highly qualified doctors have encountered many difficult cases of pregnancy, and therefore are able to prevent many situations in most cases, which guarantees peace of mind for the health of the expectant mother and baby.
First screening
The first ultrasound allows you to determine the presence of a fetus in the uterus and the number of fetuses. The doctor must make sure that the fetus has all four limbs and a head, and then count the fingers and the number of phalanges on each finger. During the first screening, the thickness of the collar space, which normally should not exceed three millimeters, and the size of the nasal bone, which should be more than three millimeters, are measured.
In addition, during the first study, the level of placental proteins in the fetal blood is determined: alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). With chromosomal abnormalities, the level of these proteins changes, for example, with Down syndrome, hCG decreases, but AFP increases.
Based on the questionnaire data and research results, the doctor calculates the risks. If the values are high, he may recommend a chorionic villus biopsy, an operation in which chorionic tissue is removed through a puncture in the anterior abdominal wall, which is then examined in the laboratory.