In the modern world, health information is perhaps one of the first places among the information that interests people more than anything else. And information about pregnancy management is the most in demand, since today women understand perfectly well that not only the health, but also the life of the future person often depends on how these nine months go. Therefore, the joy of the upcoming meeting with the child is always accompanied by worry about the state of his health. But if earlier these experiences could last all nine months, today there is a second screening during pregnancy, which helps to understand with a certain degree of certainty how the baby grows in the womb and how its development occurs.
Let's try to thoroughly understand: who should undergo 2nd screening during pregnancy, what procedures the doctor can prescribe in the second trimester, what exactly the test results will show and which path to choose when receiving negative test results.
At what stage is 2nd screening performed during pregnancy?
The possibility of screening to detect possible developmental problems in an unborn child appeared not so long ago - it began to be performed on expectant mothers only in 2000. Typically, the first screening is done at 10-13 weeks of pregnancy: this study helps to identify the risks associated with the presence of chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus. The second examination is usually carried out at 16-20 weeks of pregnancy, but doctors tend to schedule such screening before the 19th week, since diagnosis at this period will show more reliable results than at a later time. Screening may be complete or incomplete, including, for example, only ultrasound examination (ultrasound): in this case, it may be prescribed later, at 19-22 weeks of pregnancy.
Why is 2nd screening performed during pregnancy? The main task of the study is to either refute the results of the first screening (usually negative) or confirm them. The obtained indicators are subjected to a thorough analysis, after which they are compared with the values accepted as the norm. When compared, it becomes obvious how the fetus develops and grows.
How reliable are the research results?
Pregnant women should refrain from interpreting screening results on their own. Each of the obtained indicators is assessed by doctors not individually, but only in conjunction with other parameters.
Important! Risk calculations are based on the results of a blood test for biochemical markers and data from the first ultrasound performed at 11-13 weeks.
Initially, research data is interpreted by an obstetrician-gynecologist who is managing the pregnancy. If discrepancies are detected, the woman is referred to a geneticist, who, together with an obstetrician-gynecologist, determines further examination tactics.

When is screening necessary in the second trimester of pregnancy?
- if both parents have reached the age of 35+;
- when there are hereditary genetic diseases in the family;
- if a pregnant woman has had a viral infection in the early stages: some seemingly “harmless” diseases can negatively affect the health of the unborn child;
- if the woman’s history has already included cases related to frozen pregnancy, miscarriage, or stillbirth;
- when the pregnant woman used drugs that have a teratogenic effect;
- if the expectant mother or father has an alcohol or drug addiction;
- if chromosomal abnormalities were detected in children born from previous pregnancies;
- if the expectant mother has chronic or autoimmune diseases that can affect the development of the unborn child and its growth;
- in cases of detection of malignant neoplasms in a woman who is already in the third month or later of pregnancy;
- when one of the parents of the unborn child, shortly before the time of conception or during this period, worked in an industry where there is radiation exposure or has a “harmful” status.
The second screening during pregnancy allows you to see those problems and pathologies that could not be detected in the early stages. In addition, screening helps to determine the expected risks of dangerous conditions that may develop in the near future, as well as to see deviations in the functioning of the main systems of the fetal body. And although doctors consider the studies conducted during the first screening to be more informative, the importance of the second screening cannot be underestimated. After all, many pregnant women are looking forward to confirmation or refutation of information received earlier.
Standards for 2nd screening
To determine possible pathologies, the condition of the placenta and the formation of the fetus, the threat of pregnancy, the results obtained at the 2nd screening are compared with standard values according to the tables. Weight is calculated using certain formulas. However, the values are not always accurate; it depends on the device, the position of the baby in the womb and the qualifications of the doctor.
Usually, by the 20th week, the internal organs have already managed to fully form, and the baby weighs about 300 g. For comparison, at the 16th week. – 100 g. After 7 days, 40 g are added, then at the same interval, twice 50 g and 60 g. Body length at the 16th week. approximately equal to 11.6 cm. During each 7-day period it increases by approximately a centimeter, and by the end of the 20th week. becomes 16.4.
Table of tummy and head circumferences
| Duration in weeks | Circumference – minimum/maximum (in mm) | |
| Belly | Heads | |
| 16-17 | 88-131 | 112-149 |
| 18-19 | 104-154 | 131-174 |
| 20 | from 124 to 164 | from 154 to 186 |
Table of BPR (biparietal) and LZR (frontal and occipital) head sizes
| Duration (in weeks) | Indicators – minimum/maximum (in mm) | |
| BPR | LZR | |
| 16 | from 31 to 37 | from 41 to 49 |
| 17 | from 34 to 42 | from 46 to 54 |
| 18 | from 37 to 47 | from 49 to 59 |
| 19 | from 41 to 49 | from 53 to 63 |
| 20 | from 43 to 53 | from 56 to 68 |
Length of bones - thighs, shins, shoulders and forearms
| Duration in weeks | Length – minimum/maximum (in mm) | |||
| Hips | Shin | Brachial | Forearms | |
| 16 | from 17 to 23 | 15-21 | from 15 to 21 | 12-18 |
| 17 | from 20 to 28 | 17-25 | from 17 to 25 | 15-21 |
| 18 | from 23 to 31 | 20-28 | from 20 to 28 | 17-23 |
| 19 | from 26 to 34 | 23-31 | from 23 to 31 | 20-26 |
| 20 | from 29 to 37 | 26-34 | from 26 to 34 | 22-29 |
AI (otherwise amniotic fluid index) is a very important indicator obtained by measuring the distance (at 3 points) from the uterine walls to the developing fetus. The values can fluctuate within the normal range of 70-300 mm, and any deviations from these numbers threaten the child and require urgent medical intervention. Amniotic fluid index (week – minimum and maximum value):
- 16 – from 73 to 201;
- 17 – from 77 to 211;
- 18 – from 80 to 220;
- 19 – from 83 to 225;
- 20 – from 86 to 230.
The standards for ultrasound examination at the first and second screening are the same, and three new important indicators appear in blood biochemistry. If the blood is also tested for inhibin A, then the test is called a quadruple test. The hCG level initially increases greatly, but after 7-8 weeks it also begins to actively decrease. Estriol (E3) is a hormone responsible for the development of the placenta.
Normally, immediately at the beginning of its formation, active growth of the substance is observed. A critical decrease in hormone levels is from 40 percent of the accepted values. AFP (alpha-fetoprotein) is a protein that is produced in the fetus in the gastrointestinal tract and liver from 5-1 weeks of existence. The level of the substance begins to actively increase from the 10th week. The norms for different periods are shown in the table.
| Duration in weeks | hCG | Duration in weeks | EZ in nmol/l | AFP in IU/IU | |
| 1-2 | 150 | 16 | from 4.9 to 22.75 | 34,4 | |
| 6-7 | 50000-20000 | 17 | from 5.25 to 23.1 | 39 | |
| 11-12 | 20000-90000 | 18 | from 5.6 to 29.75 | 44,2 | |
| 13-14 | 15000-60000 | 19 | from 6.65 to 38.5 | 50,2 | |
| 15-25 | 10000-35000 | 20 | from 7.35 to 45.5 | 57 |
Deciphering the 2nd screening without the specified parameters is impossible. The results of the first ultrasound are also taken into account. This helps to identify gene diseases, the risk level of which is calculated using the MoM coefficient. It takes into account the age, weight, and pathologies that the pregnant woman has suffered from. All this ultimately leads to the digital value of the limits:
- low – 0.5;
- optimal – 1;
- top – 2.5.
Based on these values, the possibility of abnormalities occurring in the fetus is calculated. If it is 1:380, then the indicator is normal. However, if the second figure begins to decrease, then the chances of having a healthy child also decrease.
When a high risk of 1:250 (360) is detected, the woman is referred to a geneticist for consultation. If the value reaches the limit level of 1:100, then additional diagnostic methods are required to confirm or refute possible anomalies.
If the umbilical cord is attached to the middle of the placenta and the anterior wall of the peritoneum, then this is normal. Abnormal - shell-like, marginal or split, leading to fetal hypoxia, problematic childbirth, and death of the baby.
The placenta is often attached to the back of the uterus, which is the best location due to the full blood supply. It is also good at the uterine fundus. When the placenta is attached to the anterior wall of the uterus, this does not refer to a violation, but creates certain risks - severe stretching, detachment due to active movement of the fetus, presentation.
The edge of the canal connecting mother and child should be located at least 6 cm above the pharynx. The location of the placenta is considered abnormal when it is located at the bottom of the uterus or in the pharynx, blocking the exit. The thickness of the connecting canal is measured after the 20th week of gestation; before that, only the homogeneity of the structure is checked (ideally, it is solid, without inclusions).
A normal umbilical cord has two arteries and a vein. Violation is the absence of at least one vessel. However, pregnancy is considered normal if the missing artery is replaced by a functioning one 100 percent. At the same time, all indicators are normal and no defects are observed.
The normal length of the uterine cervix is at least 3 cm. When shortening or lengthening, sutures are applied or a pessary is installed. This allows you to complete the pregnancy and keep a healthy baby.
What will an ultrasound scan show in the second trimester?
The baby in the womb develops so quickly that by the time of the second trimester screening, you will notice how the baby’s appearance and physical parameters have obviously changed. An ultrasound examination will allow you to see all this: thanks to it, the doctor will assess whether the fetus’s physical data meets the standards and will look to see if there are any signs of pathological conditions. Also, during the ultrasound, the doctor will assess the condition of the placenta and uterus, and if there is a need to clarify data on the state of the circulatory system, an ultrasound examination with Doppler will be performed.
During an ultrasound scan during the second screening during pregnancy:
- the doctor will evaluate the structure of the head and facial contours of the fetus: special attention will be paid to the size and structure of the nasal bones, the absence (or presence) of a cleft between the nasal and oral cavities, and the process of formation of the eyeballs;
- the doctor will thoroughly determine the size of the fetus, consider whether the number of fingers and toes is normal;
- the specialist will also determine how mature the fetal lungs are and whether their development corresponds to the obstetric stage of pregnancy;
- problems with the condition and formation of the heart and the development of the spinal cord and brain will be noticeable;
- many internal organs should already be formed by the time of the second screening, so their location, structure and condition are clearly visible on an ultrasound examination;
- the doctor will also note in what volume of water the fetus has to develop, what tone the uterus has at the moment, in what condition the woman’s appendages are;
- the thickness of the walls and the level of maturity of the placenta are important;
- the doctor will pay attention to the organization of blood flow in the vessels of the uterus, as well as the functioning of the umbilical arteries and the middle vessel of the child’s brain;
To determine how functional the uterine vessels are, the doctor will conduct separate examinations of the left and right arteries, since when examining only one side, the results are usually false. How can we explain this? The fact is that when a state of gestosis (late toxicosis) occurs, blood flow is disrupted only in one artery of the uterus. This condition is considered one of the dangerous pathologies, quite often leading to premature birth or even the death of the newborn.
If the fetus is successfully located in the uterus, then at the second screening during pregnancy you will already find out the sex of the unborn child, because during this period the primary sexual characteristics will already be obvious.
The second ultrasound does not require special preparations or procedures. However, the day before the procedure, try not to eat foods containing potential allergens - chocolate, cocoa, seafood, citrus fruits, fried and fatty foods.
It should also be remembered that the condition for performing an ultrasound is an unfilled bladder. To obtain high-quality results of this examination, an abundant amount of amniotic fluid in the uterus is quite sufficient.
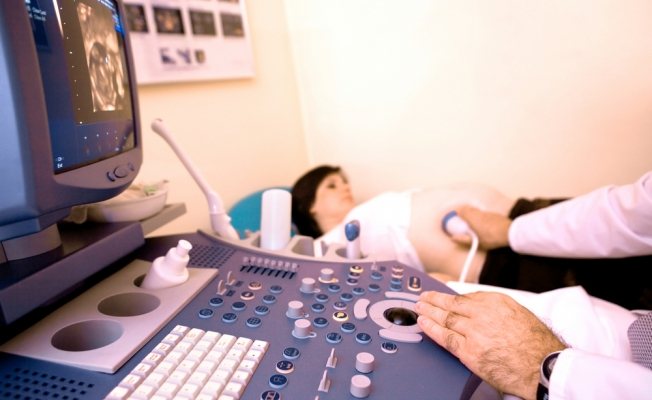
When and why is ultrasound performed in the 2nd trimester?
Many mothers wonder: when to do a second scheduled ultrasound? They say that for some the doctor prescribes a test at 19 weeks, and for others at 20. Indeed, the timing may vary in each individual case. At what week a woman will be sent for an ultrasound examination depends on the mother’s health condition and fetal development parameters identified during the first ultrasound screening.
The Russian Ministry of Health has established a rather vague framework regarding at what stage of pregnancy the second ultrasound is performed. According to the department's order, it is done between 18 and 21 weeks.
Indicators of normal ultrasound
Ultrasound at the second screening during pregnancy is performed transabdominally, that is, in a superficial way. This technique allows you to see not only the condition of the fetus, but also to evaluate the internal organs of the pregnant woman - the possible presence of tumors (provided that they are not small in size), and to assess the general picture of the condition of the pelvic organs. The technique does not require special preparation, is absolutely harmless to the body of the mother and the unborn child, and is also painless. The doctor will apply a special gel to the abdomen, which will allow the ultrasound signal to produce a clearer image. To obtain it and examine the necessary organ of the fetus or mother, the doctor moves a sensor over the skin.
All necessary assessments and measurements are made based on the data in the monitor picture. Also, looking at the general “video”, the doctor visually assesses the condition and appearance of the child. To assess the uterine vessels, the ultrasound doctor will use a special resistance index: at the time of the second screening, 0.38-0.7 units will be considered normal. However, to conduct such a study, a condition is necessary: the child must be at rest and not make rapid movements. At the same time, the baby’s pulse is also measured, which should be in the range of 119-161 beats per minute.
To exclude any pathological aspects on the ultrasound, the doctor first of all pays attention to the condition of the middle artery of the brain - there should be no hypoxia in this area. This problem can be detected by a decreased pulsation index. If a sharp increase in this indicator is diagnosed, it may indicate a cerebral hemorrhage. Normal pulsation index values during the second screening are in the range of 1.35-2.32 units.
How to prepare for the second screening?
Preparing for the second screening is usually not difficult, since women already have experience undergoing the first examination. It can only be difficult morally for mothers who received not encouraging results during first trimester screening. It is not easy to calm anxiety and bad feelings, but you need to try to do it. Before the second examination, the bladder and intestines do not need to be emptied; the fullness of the organs with urine and feces does not affect the results of the ultrasound. The day before screening, you should exclude from the menu foods that can cause allergies: citrus fruits, chocolate. On the day of donating blood for analysis, you should fast, as eating can make the laboratory test results false.
What indicators are taken into account in a blood test?
The first of these is the level of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG, it is estimated in mg/ml). HCG is one of the main tests for pregnant women; it is no coincidence that it is called a “pregnancy hormone level study.” Human chorionic gonadotropin is an active hormone, the production of which begins during the formation of the embryo and then continues throughout pregnancy.
The second important indicator is the level of estriol (estimated in mmol/l). Estriol (E3) is otherwise called estrogen. This is a low-active minor female sex hormone that is produced by the follicular apparatus of the ovaries in women.
ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme, estimated in IU/ml) is a special enzyme that is found in small doses in the epithelial tissue of the kidneys, and in large quantities in the human lungs and blood serum. The ACE level is important when the doctor determines how normal electrolyte and water metabolism are in a woman’s body.
Sometimes these three general indicators are supplemented with a fourth, establishing the level of another hormone - inhibin A. It is produced in female follicles and shows how sufficient a woman’s follicular reserve is.
What data in a blood test give rise to suspicion of pathology?
- if Down syndrome is suspected in the fetus, the level of hCG turns out to be elevated, while the levels of other hormones are decreased;
- Edwards syndrome should be suspected if all hormone levels decrease;
- liver necrosis, a defect in the formation of the neural tube or Meckel's syndrome will be indicated by an increased concentration of E3 and AFP, and hCG will maintain a normal concentration;
- if an infection occurs in the fetal area or placental insufficiency is detected, the level of free estriol will decrease; the same indicator can be seen as a result of a pregnant woman taking antibiotics.
Serious deviations from standard values in a biochemical blood test give the doctor a reason to perform an amniocentesis procedure. This is a puncture in the abdominal wall to collect a small amount of amniotic fluid, which is then sent for testing in a laboratory. Such a diagnosis is highly reliable (about 99%) and makes it possible to make a final conclusion about the presence or absence of pathology in the fetus.
It is necessary to take into account that a biochemical blood test during period 2 of screening during pregnancy is carried out on an empty stomach. It is important not to experience stress before the study and to be in a calm state of mind, as well as not to be physically overloaded and to refrain from sexual contact.
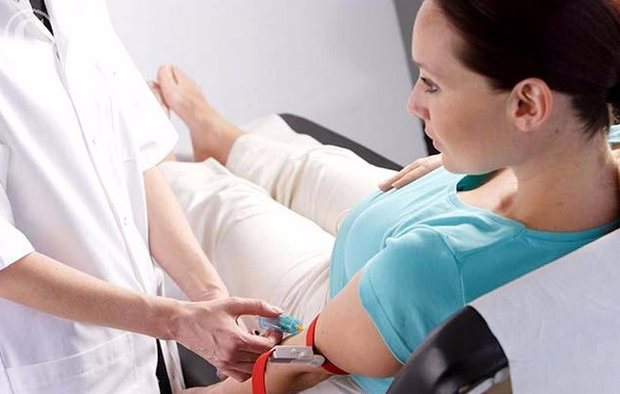
What is prenatal screening?
Prenatal (from Latin pre – “before” and natalis – “relating to birth”) – the prenatal, intrauterine, prenatal period of a child’s development, from the moment of conception to birth.
Screening (from English screening - “selection, sorting”) is a set of studies that is carried out in order to identify pathologies and diseases of the fetus.
Thus, prenatal screening is a complex of studies of the expectant mother and fetus during the prenatal period to detect pathologies of fetal development and clarify the risks of pregnancy.
A total of three screenings are carried out, one in each trimester:
- 1st screening - from the 11th to the 14th week, a double screening test is performed using a blood test to detect b-hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) and PAPP-A (pregnancy-associated plasma protein A) and an ultrasound examination to fetal measurements using several parameters.
- 2nd screening - from the 16th to the 20th week, a triple screening test is performed using a blood test for b-hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), ACE (alpha-fetoprotein) and free estriol (sometimes an additional test for inhibin A is done ) and ultrasound, which also takes measurements of the fetus.
- The 3rd screening is at the 30-34th week, and this is only an ultrasound, during which measurements of the fetus are taken and the condition of the uterus and placenta is determined. According to the indications of the 3rd screening, a caesarean section may be prescribed.
Negative results of the second screening during pregnancy
Despite the certain reliability of the second screening, these studies are still not 100% accurate. Therefore, even if the results of an ultrasound and biochemical blood test showed the risks of chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus, there is hope that the baby will be born completely healthy. However, this would be a lucky coincidence rather than an exception to the rule. Therefore, if a geneticist and gynecologist inform you about the high risks of pathologies in the fetus, be prepared for any outcome.
In some cases, a study may show false results:
- if the fruit is large enough;
- when a pregnant woman is carrying twins or triplets;
- if the conception date was set incorrectly;
- when the family used IVF methods;
- if the expectant mother has too little body weight or, on the contrary, is obese;
- when a woman suffers from diabetes.
Preparing for analysis
A referral for examination must be taken from a doctor. Preparation is practically no different from the first screening:
- the examination is carried out on an empty stomach, preferably in the first half of the day;
- all studies must be carried out on the same day and in the same clinic;
- for a day or two you should not eat sweets (especially chocolate), fatty foods, seafood, meat, fried, spicy foods;
- avoid worries and stress on the eve of the examination;
- the break between the last meal and the blood test should be at least 4 hours;
- It is better not to drink a lot of liquid before screening.
The doctor will inform you about the screening results of the pregnant woman after decoding.
Negative results: what to do?
The period of the second screening occurs in the middle of pregnancy, so doctors no longer talk about terminating it for medical reasons. Sometimes there are cases when fetal pathology can be corrected by medical methods - in this case there is hope, and doctors will offer the pregnant woman a choice of possible manipulations and interventions. If the negative results of the second screening show a high risk of developing anomalies (in a ratio of 1:360) without hope of reversing the process, then the woman is asked to decide on an artificial birth.
In any case, both parents will have to make the difficult decision to continue or terminate the pregnancy. When there is a chance to correct the pathology, the expectant mother is explained in detail: what modern methods exist to correct the situation, how risky they are, whether complications are possible during the intervention process, and what are the overall chances of having a healthy baby.
Who needs a second screening and why?
2 Ultrasound screening in our country is prescribed to every pregnant woman, regardless of the presence of complaints. But pregnant women at risk should be especially careful about the study. These include:
- primigravidas over 35 years of age;
- persons in closely related marriages;
- pregnant women with a burdened obstetric and gynecological history;
- parents suffering from alcoholism and drug addiction.
But all other expectant mothers should treat the second ultrasound screening responsibly, so as not to miss the occurrence of a pregnancy-threatening pathology at an early stage. The correspondence of the screening result and the ultrasound norm will allow the woman to feel calm, knowing that everything is fine with her and the child.
Dates
The optimal time for the second screening is from the 20th week of pregnancy. At this time, the doctor has the opportunity to determine the presence of defects or disorders that could not be identified during the first examination.
Many experts recommend undergoing a second screening examination at week 17 in order to be able to undergo additional examination or make an appointment with a geneticist if a high probability of developing any diseases in the fetus is detected.
How is the examination carried out?
First, the pregnant woman undergoes ultrasound diagnostics. The procedure is completely painless and harmless to the fetus. Ultrasound at the 2nd screening is done to correlate the established norms of indicators for measuring body parts and organs of the fetus with individual examination results in pregnant women.
The woman is laid on the couch. A disposable diaper is laid down first. Afterwards, the pregnant woman exposes her belly. The doctor applies a special ultrasound gel, which enhances the penetration of ultrasound waves. At the end of the 2nd trimester screening, the woman wipes her stomach with napkins or a disposable diaper.
After an examination with a transabdominal ultrasound probe, the pregnant woman goes to the laboratory to donate blood. When the research is completed, all that remains is to wait for the results to be deciphered. Usually the woman is asked to return for a medical report in a week.
To watch a video review of a specialist: