In each specific case, the speed of the study changes. It is influenced by the workload of the laboratory, their ability to conduct examinations on site (some negotiate with other laboratories and transport patients’ blood there), and the immediate urgency of issuing a conclusion.
The average speed of performing tests for the main hormones of the gonads, thyroid and adrenal glands, and pituitary gland is presented in the table.
| Hormone name | Analysis speed |
| Prolactin | The process takes several hours, the result is ready the next day |
| Follicle-stimulating hormone (FLH) | if necessary, the result can be found out in 3 hours; usually the results are issued the next day |
| Luteotropin | 1 day after blood donation |
| Estradiol | 1 day after blood donation |
| Anti-Mullerian hormone | 6 days after blood donation |
| Thyroxine and TSH | 1 day after blood donation |
| Cortisol | 1-3 days, in case of emergency you can find out the result in 4 hours |
| Adrenocorticotropic hormone of the pituitary gland | 2 days after donating blood |
| Aldosterone | 1 day after blood donation |
| Catecholamines (adrenaline, dopamine, norepinephrine) | 1 day after blood donation |
| Renin | usually 1-2 days from blood donation, but if you want to test angiotensin 1 at the same time, then the period will be 7-9 days |
| Somatotropin | from 3 hours to 2 working days |
| Vasopressin | at least 14 days |
If problems with the adrenal glands are suspected, a urine test for free cortisol (2-3 days), catecholamines (up to 5 days) and their end products of metabolism (up to 10-12 days) is no less informative.
Additionally, for men the following tests may be required:
- 17-ketosteroids in urine – research requires 1 to 2 weeks;
- dihydrotestosterone - the blood test takes 9 days if the enzyme immunoassay method is chosen;
- free testosterone in serum – ready in 5 days;
- testosterone binding globulin (blood from a vein) – one day is enough.
Read more in our article about how much hormone testing is done.
Why are hormone tests done?
The content of the article
Almost all processes that occur in the human body are controlled to one degree or another by hormones - elements constantly produced by the secretory glands. All changes directly depend on the concentration of these substances in the body - maturation, growth, pregnancy, and so on. Even minor disruptions in the functioning of the secretory glands lead to a lack or excess of their formation, which results in pathological processes. Constancy of hormonal levels is impossible, since various hormonal elements and structures in the body are constantly being formed and destroyed.
It is to identify and eliminate such disorders that studies are carried out - on hormones. Despite the fairly high price of the tests,
It is necessary to carry out all studies recommended by the doctor.
find out what hormone tests
are needed in order to keep the intensity of substance formation under control in this article.
Indications for hormone tests
As a rule, a patient is prescribed a hormone test due to the presence of the following characteristic symptoms:
- increased blood pressure;
- cardiopalmus;
- weight gain;
- menstrual irregularities;
- mood swings;
- difficulties with conceiving and so on.
Most often, these tests are prescribed to patients when various endocrine pathologies are suspected; they are needed to clarify or confirm a preliminary diagnosis.
Hormonal levels before pregnancy
Human vital activity is supported by more than 70 hormones that normalize various processes, activate the absorption of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, and destroy pathogenic substances. The lack of one or another hormone does not always immediately affect your well-being. Often a young woman does not notice health problems - her body is still full of strength, mild symptoms are ignored and attributed to PMS or fatigue. And only problems with conception or pregnancy reveal a serious hormonal imbalance.
Hormonal imbalance can cause miscarriage. Therefore, gynecologists advise undergoing an examination at the pregnancy planning stage and doing a hormone test before conception occurs. And not waste time for months looking at tests with one strip.
What tests are done for hormones?
To make or confirm a patient’s diagnosis, a doctor may need to perform the following hormonal tests:
- hormones
(
somatotropic,
adrenocorticotropic, TSH,
thyroid-stimulating,
follicle-stimulating, luteinizing hormone, prolactin); - thyroid hormones (calcitonin, T3, T4, antibodies);
- pancreatic hormones (insulin);
- adrenal hormones (cortisol, norepinephrine, adrenaline, aldosterone, progesterone,
ACTH); - sex hormones (estrogens
, that is, progesterone, estradiol, hCG, and testosterone).
- tumor markers (PSA, AFP, REA);
- adrenal hormones (progesterone,
cortisol, ACTH); - prenatal diagnosis.
When you need to take hormone tests and when not, the doctor decides.
Results
Blood testing for hormones is an important part of general diagnostics, the results of which assess the general state of health and the performance of individual organs and systems. Control over hormonal levels allows for timely detection of dysfunctions of the endocrine and reproductive systems, genital organs, thyroid gland, liver, etc.
Women are examined more often than men, due to the natural characteristics of the body (unstable hormone levels depending on menstruation, pregnancy, menopause).
It is necessary to donate blood for hormone levels in case of characteristic symptoms or in the presence of chronic diseases. The main tests are hormones of the thyroid gland, pituitary gland, adrenal glands, and sex hormones. To obtain objective results of the study, the patient requires preliminary preparation.
Tests for basic hormones
The tests most often performed in St. Petersburg are listed below.
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
in women is responsible for the formation of estrogen and the growth of follicles in the ovaries.
The critical level of FSH, which is reached in the middle of the cycle, ensures ovulation. In men, this substance is responsible for the concentration of testosterone in the blood, the maturation of sperm, and provides male strength. Deciphering this analysis
plays an important role in determining the causes of infertility. - Luteinizing hormone or LH
in men increases testosterone levels in the blood, providing conditions for sperm maturation.
In women, it is responsible for the secretion of estrogen, the formation of the corpus luteum, and ovulation. The ratio of FSH and LH in the body of patients, compliance with the norm
, is an important point in the examination for infertility. - Prolactin takes part in ovulation and activates lactation after childbirth. With a decreased or increased concentration of prolactin, the development of the follicle may stop, and as a result, the woman does not ovulate. Also, anabolic processes in the body depend on this substance (activates protein synthesis), it produces an immunomodulatory effect. In men, excess prolactin can lead to impotence, decreased libido, and infertility. how to do this test correctly
. - Progesterone is a prerequisite for the normal course of pregnancy, as well as for its occurrence.
- Testosterone is secreted in a woman’s body by the adrenal glands and ovaries; excess can cause early miscarriage and improper ovulation. A reduction in the level of testosterone in a man’s blood reduces the quality of sperm and causes erection problems. Proper preparation
for this study is important - Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is tested to rule out or confirm a patient's thyroid dysfunction. Detection of antibodies to this substance makes it possible to predict malfunctions of the thyroid gland.
Interpretation of test results
can only be carried out by a doctor, since it is difficult to understand without professional knowledge. The answer to the question of how many tests are done depends on the specific analysis.
What does sex hormone analysis show?
The content of the article
Male and female sex hormones play a very important role in the normal functioning of the organs of the reproductive system; tests for sex hormones are recommended for patients in many diseases.
Testing for sex hormones can be prescribed to a person for a wide range of indications. The analysis allows the specialist to identify deviations in female and male sexual development, determine decreased libido, find out the causes of infertility, miscarriage, and menstrual cycle irregularities. The following indications for analysis can also be distinguished:
- osteoporosis;
- myoma;
- severe menopause;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- endometriosis;
- gynecomastia in men (increase in the volume of the mammary glands);
- excessive hair growth.
In addition, analysis for female and male sex hormones makes it possible to establish the causes of persistent acne and acne on the skin of the body and face, identify adrenal tumors, the cause of obesity, mastopathy after childbirth in women, and much more.
Preparing for hormone tests
Assessing a patient’s hormonal background is an important point in diagnosing many diseases. What hormone tests are needed in a particular case is determined by the doctor. The patient is only required to comply with the rules for preparing for research, which are given below.
In order to get a reliable picture as a result of hormonal tests, the patient must take into account the basic rules for preparing for them.
- For a few days, heavy physical activity is excluded, situations that cause nervous tension are prohibited.
- Two days before the study you need to give up alcoholic beverages.
- Two hours before taking biological material, you should stop smoking.
- The analysis is carried out in a state of absolute calm, therefore, you need to sit and relax 15 minutes before it is carried out.
- Distortion of the results is possible if the patient is taking medications; you should definitely discuss this situation with your doctor.
Some types of hormonal tests
It is advisable to carry out only on specific days of the cycle (if we are talking about a woman), the doctor will definitely warn you about this.
A man can take hormone tests
any day.
To obtain a correct interpretation of the results of hormone tests, strict adherence to the following rules is necessary.
- It is advisable to donate blood in the morning (8-11). The analysis must be carried out on an empty stomach, which means that at least 8 hours must pass between the collection of biological material from the patient and the last meal. At the same time, it is not prohibited to consume water in any quantity; it does not in any way affect the study on the concentration of hormones.
- On the eve of the study, it is recommended to limit yourself to a light dinner; it is advisable to avoid fatty foods in order to avoid distorting the results.
- Approximately two days before the hormone test, doctors advise you to stop drinking alcohol. Excessive physical activity is also prohibited.
- The use of medications is not recommended. In some cases, you can take medications after first discussing this with your doctor. It is advisable to conduct the study before drug treatment or two weeks after its cessation.
- About two hours before the test is due, you need to stop smoking cigarettes. You should also not drink coffee, tea, juice, or sparkling water. There should be no physical stress (climbing stairs too quickly, running), as well as emotional arousal. It is advisable to relax and rest a little 15 minutes before the analysis.
- Donating blood after an instrumental examination, various physiotherapeutic procedures, ultrasound or X-ray examination, massage and other medical procedures is not recommended; you need to wait a certain time.
- If laboratory parameters are checked over time, it is preferable to carry out repeated studies under the same conditions, that is, at the same time of day, in the same laboratory, and so on.
- In some cases, laboratory analysis of hormones
must be carried out strictly on certain days of the cycle.
The attending physician will warn the patient about this. As a rule, we are talking about tests for hormones of the reproductive system.
In order for anal analysis to be carried out on the main hormones
turned out to be as informative as possible, it is very important to prepare for them correctly.
How to interpret hormone tests correctly
The study of hormonal levels is necessary for the effective detection of many diseases: thyroid diseases, infertility, and so on. In addition, they are carried out to confirm the presumptive diagnosis. You can try to independently decipher a blood test for hormones
, however, it is worth leaving the final diagnosis to a specialist.
When conducting most studies and determining the norm and deviations from it, factors such as the age and gender of the patient should be kept in mind. When assessing the functions of sex hormones in female patients, it is necessary to take into account the specific phase of the menstrual cycle. Therefore, it is advisable to take blood for hormones from women of reproductive age only on certain days of the cycle.
Pregnancy also seriously changes hormonal levels. At different stages of expecting a baby, the levels of hormones in the body become different. For example, in the first trimester, more than a third of pregnant women have a decrease in thyroid-stimulating hormone.
In the first trimester, the level of human chorionic gonadotropin jumps, and so on.
Since hormones have a systemic effect, their regulation is an unusually complex process; indicators are often affected by concomitant diseases (chronic and acute) and the use of medications. And finally, it is important to take into account such aspects as the ecology of the patient’s specific area of residence and the general condition of his body. Therefore, the interpretation of the results should be left to the doctor.
How to decipher a hormone test yourself
Below are the principles of an approximate decoding of tests for the main hormones.
- Testosterone
is produced in the body of women and men, for the latter it serves as the main sex
hormone
. In a man's blood, the normal level of testosterone is 2-10 ng/ml. In women, this parameter is normally in the range of 0.2-1 ng/ml. In men, excess testosterone levels may indicate early puberty and testicular tumors. A reduction in this indicator negatively affects the quality of sperm and may be a sign of dangerous liver or kidney diseases. If the concentration of this substance in the female body exceeds the norm, this can lead to a miscarriage. - Estrogens belong to the female sex hormones: estradiol, progesterone. These substances are responsible for the menstrual cycle, fertilization, guarantee the preservation of the fetus and the development of the egg. Their content in the body is determined by the phase of the cycle. Postmenopause - 51-133 pM/l, luteal phase - 439-570 pM/l, follicular phase - 198-284 pM/l - these are the normal test results for estradiol.
For progesterone, the following indicators are normal: postemnopause - 1-1.8 nM/l, luteal phase - 23-30 nM/l, follicular phase - 1-2.2 nM/l. If the levels of these substances exceed the norm, this may indicate a tumor of the adrenal cortex, ovaries, pregnancy, or cirrhosis of the liver. A contraction may indicate sclerosis, underdevelopment of the ovaries, the threat of abortion, or lack of ovulation. - Follicle-stimulating hormone
is produced by the pituitary gland and activates the development of follicles in women and seminiferous tubules in men. For the female body, the norm is 4-150 units/l (the phase of the menstrual cycle plays a role), for the male body – 2-2\10 units/l. The concentration in the body of this substance increases when sperm production fails, during menopause, or when ovarian function decreases. FGS levels also fall under the influence of hormonal contraceptives, with prostate cancer, and during pregnancy.
- LH or luteinizing hormone activates the production of sex hormones in women and men. Normally, for women the figure is 0.61-94 units/l (the figure depends on the phase of the cycle), for men – 2-9 units/l. Taking estrogen in large doses can reduce the indicators, while malfunction of the gonads can increase it.
- Prolactin in a woman’s body controls the development of the mammary glands, and after the birth of a child, the formation of breast milk. Its normal value during pregnancy is 500-10,000 mIU/l. Depending on the stage, the indicator gradually increases. This hormone is also present in men - 58-475 mIU/l is considered normal.
- of thyroid-stimulating hormone
in the body is assessed to determine the condition of the thyroid gland. An increase in indicators is a signal of insufficient thyroid function. Their reduction indicates an oversupply. A value in the range of 0.2-3.2 MIU/l is considered normal.
How long to wait for the results of hormone tests at the clinic
When diagnosing diseases of the endocrine system, one analysis is extremely rarely used. Usually you need to undergo several tests to determine which organ is affected. This is explained by multi-level control of hormone synthesis.
Thyroid gland (thyroxine and TSH)
To assess organ function and the cause of the disorders, it is necessary to determine free thyroxine and pituitary thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). Such a study is necessary if an enlarged thyroid gland, nodes in it, or symptoms of high or low hormonal activity (thyrotoxicosis or hypothyroidism) are detected.
Thyroxine and TSH are determined in venous blood serum. The analysis is based on the reaction between the hormone, antibodies and substrate. The latter has the ability to cause the solution to glow upon contact with antibody enzymes. The study requires 1 day.
Adrenal glands
The functioning of the glands can be disrupted both due to their primary damage and changes in regulation by the pituitary gland. Therefore, for the examination it is necessary to determine:
- cortisol – analysis takes 1-3 days, in emergency cases you can find out the result in 4 hours;
- adrenocorticotropic hormone of the pituitary gland – 2 days are required;
- aldosterone – result the next day;
- catecholamines (adrenaline, dopamine, norepinephrine) – 1 day is enough;
- renin - usually 1-2 days from blood donation, but if you want to study angiotensin 1 at the same time, then the period will be 7-9 days.
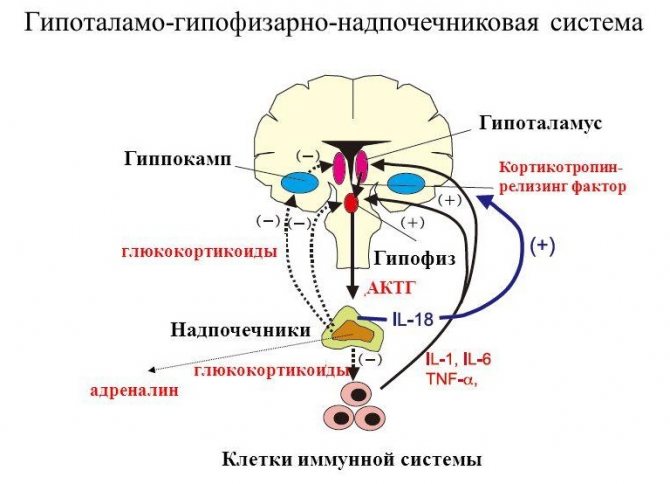
No less informative is a urine test for free cortisol (2-3 days), catecholamines (up to 5 days) and their final metabolic products (up to 10-12 days).
Pituitary gland
The anterior lobe hormones include TSH, follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone and prolactin. It is also possible to study somatotropin with accelerated or slow body growth. To determine it in the blood, different methods can be used, so the time frame will range from 3 hours to 2 working days.
The posterior lobe hormone vasopressin is produced by the hypothalamus, but enters the bloodstream from the pituitary gland. Assessment of blood levels is necessary if diabetes insipidus is suspected (thirst, excessive urination). The determination method is radioimmune and takes at least 14 days.
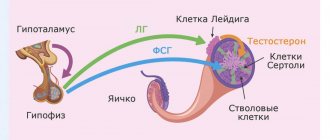
Sex glands in men
For impotence, low libido, infertility, or signs of excess hormones, an andrologist or endocrinologist may recommend the following diagnostic tests:
- 17-ketosteroids in urine – research requires 1 to 2 weeks;
- dihydrotestosterone - the blood test takes 9 days if the enzyme immunoassay method is chosen;
- free testosterone in serum – ready in 5 days;
- testosterone binding globulin (blood from a vein) – one day is enough.
We recommend reading the article about the hormone calcitonin. From it you will learn about the role and functions of the hormone calcitonin, indications for the study, how to take the test, as well as the norms for women and men.
And here is more information about thyroid hormones and which ones need to be tested.
The preparation time for tests in gynecology is one day for prolactin, follitropin and lutropin, estradiol. If an anti-Mullerian hormone test is prescribed, it will take 6 days. A hormonal examination of the thyroid gland can be completed in a day, adrenal glands - from 1 to 12 days, pituitary gland - in 1-2 days. When determining vasopressin, the results will be ready in 2 weeks. The function of the male gonads will be fully established in 15 days.
Where are hormone tests done?
Diana Medical Center offers its patients a full range of hormone tests. The drug and hardware base of our laboratory allows us to quickly and reliably determine the concentration of hormones in blood, urine and other biological fluids. In addition, the results are deciphered by our specialists, who, if necessary, will develop an optimal scheme for correcting hormonal levels.
Get tested for hormones
You can skip the line for adults, children, and pregnant women at a convenient time by making an appointment on any day - we work seven days a week. You can find out the cost of the listed studies on our website in the price list of services.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
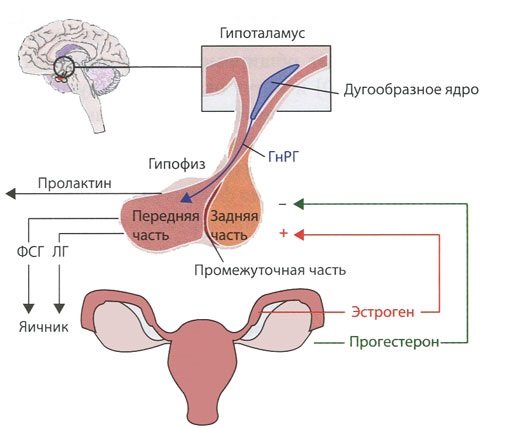
Groups of female hormones important for conception and pregnancy
Depending on their chemical structure, all hormones are divided into three groups:
- Protein-peptide group (oxytocin, vasopressin, luteal hormones, follicle-stimulating and thyroid-stimulating hormones).
- Amino acid derivatives (insulin, adrenaline, thyroxine, dopamine, serotonin, melatonin).
- Steroids (cortisol, estradiol, testosterone, progesterone, estrogen.
Hormones of the first and second groups are responsible for metabolic processes, and the third is involved in reproduction. It is the correct ratio of steroid hormones that determines the maturation of the dominant follicle, the ability of a fertilized egg to attach to the endometrium, and then develop into an embryo throughout pregnancy. A woman’s hormonal levels directly depend on the phase of the menstrual cycle. However, there are limits of acceptable values by which you can understand how conception, gestation and development of the fetus will go during pregnancy. The amount of hormones in the blood is determined in a laboratory, i.e. you need to donate blood for hormones and get a transcript from a gynecologist-endocrinologist.
| Hormone | Norm | What is he responsible for? |
| Progesterone | 0.98-85.9 nmol/l | Participates in the secretion of the corpus luteum, helps maintain pregnancy |
| Estradiol | 0.7-1.8 nmol/l | Affects the maturation of the follicle, prepares the uterus for implantation of the fertilized egg |
| Testosterone | 0.31-3.78 nmol/l | Responsible for the condition of the uterus, endometrial growth, uterine contractility |
| Prolactin | 4-23 ng/ml | Controls ovulation, prepares breasts for future feeding |
| LH (luteinizing hormone) | 0.7-7.4 mIU/ml | Responsible for the production of progesterone, follicle development, stimulates ovulation |
| FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) | 0.6-56.5 mIU/ml | Stimulates the egg to mature |
| Thyroxine T4 | 62-141 nmol/l | Supports gestation, affects fetal brain development |
| Triiodothyronine T3 | 1.17-2.18 nmol/l | Supports metabolic processes, delivers oxygen to the fetus |
| Somatotropin | 0-18 µg/l | Resists the expulsion of the fertilized egg, strengthens the muscles of the uterus |
Tests showing a complete picture of a woman’s hormonal background should be taken before pregnancy. It will take at least six months to eliminate problems if they are identified. Good hormonal levels indicate that the body is ready to accept a new life, so it is advisable to consult a gynecologist before conceiving to identify your hormonal levels. A deficiency or excess of any hormone leads to the development of various diseases; a woman becomes unable to conceive or bear a child. Each hormone is a necessary part of a huge mechanism, without which the full functioning of the entire organism is impossible.
| Hormone | a lack of | Excess |
| Progesterone | Miscarriage, miscarriage | Ovarian tumor, corpus luteum cyst, severe bleeding during menstruation develops |
| Estradiol (estrogen) | Ovulation disappears, menstruation stops, the skin ages and becomes wrinkled. | Uterine bleeding, anemia, development of a malignant tumor on the ovaries, menstruation disorders, inability of the egg to develop, infertility, hyperthyroidism |
| Testosterone | Frigidity develops, depression sets in, the amount of estrogen decreases, infertility occurs | Polycystic ovary syndrome develops, weight increases |
| Prolactin | Failure of the menstrual cycle, spontaneous miscarriages in the early stages, absence or shortage of milk after childbirth | The duration of the menstrual cycle is reduced, the corpus luteum does not develop, the egg does not mature, infertility occurs, hypothyroidism develops |
| Luteinizing hormone | The endometrium is not ready for embryo implantation, early miscarriage | Irregular menstruation, prolonged or too short periods, infertility |
| Follicle stimulating hormone | Polycystic ovary syndrome, infertility, ovarian tumor | Premature ovarian failure, onset of early menopause, development of tumors in the ovaries, congenital underdevelopment of the ovaries, endometriosis |
| Thyroxine | Development of hypothyroidism, threat of birth of a fetus with various defects | Menstrual irregularities, inability to conceive |
| Triiodothyronine | Cessation of menstruation, infertility, fetal growth restriction in a pregnant woman | Tumor in the breast, sudden weight gain, infertility |
| Somatotropin | Decreased sexual desire | Threat of having a child with congenital bone defects |
The most important hormones, without which conception is impossible, are estrogen and progesterone.
Women with a low body mass index often experience infertility. This is due precisely to a lack or excess of estrogen. Little of the hormone is produced due to the insufficiency of the fat layer in which testosterone is broken down under the influence of the aromatase enzyme. If there is too little fat, testosterone remains unbroken, its level rises, and there is not enough estrogen for the normal functioning of the reproductive system. At the same time, an increase in estrogen above normal leads to an increase in body fat, impaired ovulation and the onset of infertility.
Progesterone is responsible for maintaining pregnancy, and its lack, caused by diseases of the thyroid gland or kidneys, leads to early miscarriages. Often, due to an imbalance of these two hormones, a therapeutically healthy, young woman with no health complaints cannot become pregnant. This causes enormous psychological trauma and undermines self-confidence, although it would have been enough to find out the state of the hormonal levels at the pregnancy planning stage and restore it to normal. Ideally, a woman should check her hormonal levels once every 2 years until the age of 30, and then get tested at least once a year. This will allow you to promptly detect problems in the reproductive system and identify hormone-dependent diseases (ovarian cysts, uterine fibroids, endometriosis) at the earliest stages, when symptoms do not cause discomfort. Hormonal examination is also carried out when:
- the woman has an irregular menstrual cycle;
- The patient is diagnosed with obesity, excessive oiliness of the skin and hair, and acne;
- conception does not occur within a year or more of regular sexual activity;
- previous pregnancies ended in spontaneous miscarriage or fetal death;
- the woman has reached 35 years of age.
In addition to a blood test for hormones, the patient’s blood is taken for a biochemical analysis and urine for a general analysis to see the general condition of the body and make sure that the woman can bear and give birth to a child.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter