CTE of the fetus by week of pregnancy: table
When a woman registers for pregnancy, the doctor prescribes a series of examinations and tests to determine the gestational age and identify possible disorders in the development of the child.
One of the most famous, accessible and effective diagnostic methods today is ultrasound examination.
It allows you to obtain very accurate information about many vital indicators of the baby’s development.
Among such parameters, a special place is occupied by KTR - the coccygeal-parietal size of the fetus.
Fetal CTE: what is it?
The abbreviation KTP in the ultrasound examination results sheet often confuses the expectant mother, because most women do not know what this parameter means.

The coccygeal-parietal size of the fetus is the length from the child’s tailbone to his crown, measured in millimeters.
This indicator is relevant only from the 7th to 14th weeks of pregnancy.
Until the end of the 6th week, the fetus is still too small, so the CTE does not yet provide reliable information about the pace of its development.
Starting from the 15th week, the doctor will use other parameters of the baby’s body size, who has already grown noticeably at this point (the girth of his head, chest, etc.).
Photo of ultrasound during pregnancy, photo of the fetus during ultrasound during pregnancy
4-5 weeks
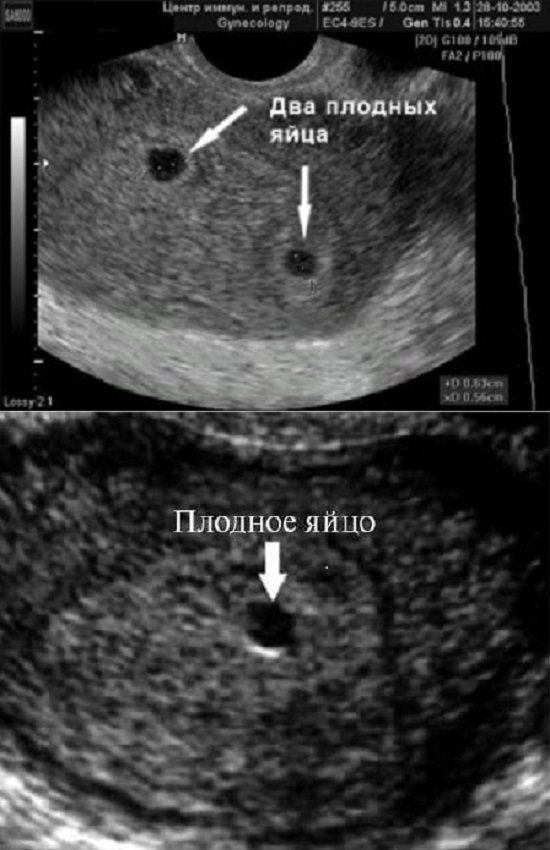
The blood hCG level must be at least 1000 mU/ml. At this time, neither the embryo nor the yolk sac is visible. When two gestational sacs are visualized, it can be argued that this is a dichorionic multiple pregnancy. When visualizing one ovum, it can be stated that this is a monochorionic pregnancy. But at this stage we still cannot say how many embryos are in each fertilized egg. In addition, during a single ultrasound we cannot yet say whether this pregnancy is progressing, since the embryo does not yet have a heartbeat. The average internal diameter (ID) of the fetal egg at this stage is 2-10 mm. The conclusion will indicate: Short term intrauterine pregnancy.
Read more about ultrasound in early pregnancy
5-6 weeks
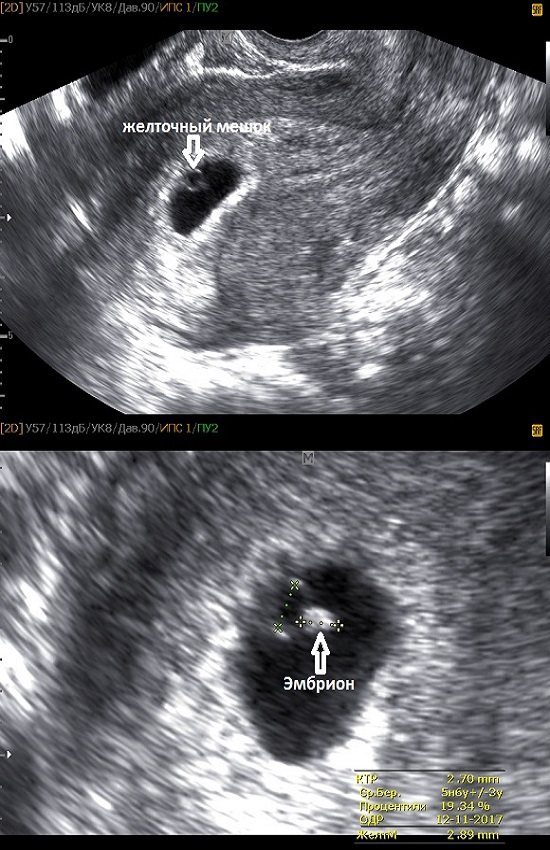
At this stage, a white ring appears inside the fetal egg - this is the yolk sac.
Foci of erythropoiesis form in the wall of the yolk sac, which form a capillary network, supplying erythroblasts (nuclear red blood cells) to the primary circulatory system of the fetus. The yolk sac is the source of primary germ cells that migrate from its wall to the gonads of the embryo. Until the 6th week after fertilization, the yolk sac, playing the role of the “primary liver,” produces many proteins important for the embryo - alpha-fetoprotein, transferrins, alpha2-microglobulin. By the end of the first trimester of pregnancy, this provisional organ ceases to function and is reduced.
The normal size of the yolk sac is 2-6 mm. If two yolk sacs are visualized in the fertilized egg, this means a monochorionic multiple pregnancy. But if one yolk sac is visible inside the fertilized egg, and the embryo is not yet clearly visualized, then it may still be monochorionic monoamniotic twins.
The embryo at the beginning of the 5th week is practically indistinguishable on the wall of the yolk sac, but by the end of the week the coccygeal-parietal size (CPR) of the embryo reaches 3 mm.
SVD of the ovum is 11-16 mm.
Fetal CTE table by week
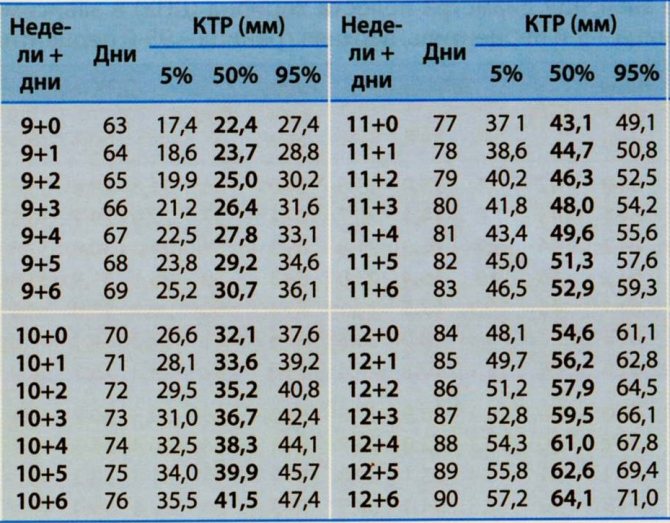
Using the table, you can see how quickly the baby is growing at this time: from 8 mm in the seventh week to 76 mm in the fourteenth. The dimensions are, of course, tiny, but if you calculate the relative increase in length, you can get an impressive result.
In just eight weeks, the growth of the future little man increases almost 10 times! The baby’s weight gain during this period will be just as rapid.
Thus, using CTE, the doctor is able to determine the gestational age, and very accurately. This is a convenient way to calculate the preliminary due date. It is especially important if a woman has menstrual irregularities, and counting from the first day of her period does not make sense.
On the other hand, if the gestational age is reliably determined by other parameters, it is possible to assess the rate of fetal development and identify possible disorders.
Deviations in fetal CTE values by week of pregnancy
If the doctor knows exactly the baby’s age in weeks, but the CTE indicators are ahead of him, this may indicate that the fetal growth rate is too high. In this case, the expectant mother needs to be prepared for the birth of a real hero with a large body weight.
Monitoring the course of pregnancy should be more careful, because the risk of complications increases.
In the case when the fetal CTE indicators are less than the lower limit of normal, the doctor should look for reasons for the child’s growth retardation. The following options are possible:
1 Insufficient supply of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus due to a disruption in its connection with the maternal body. This happens when there are defects in the uterine wall, especially after a previous abortion.
2 Hormonal levels are disrupted in a pregnant woman's body, the production of pregnancy hormones is reduced, which is a serious obstacle to the normal development of the fetus.
3

CTE may not correspond to the norm if the fetus is frozen.
The doctor should pay attention to the baby's movement and contractions of his heart - if they are not there, the baby is really dead.
4 Infectious diseases can adversely affect the condition of the fetus and its growth rate.
To confirm or refute this reason, you need to undergo tests, including for sexually transmitted infections.
5 Growth retardation is possible due to genetic abnormalities. The most common diseases of this kind are Edwards, Patau, and Down syndromes. To clarify the diagnosis, there are special tests.
6 If a pregnant woman has chronic diseases (especially thyroid dysfunction), it is worth looking for the reason for the deviation of CTE in them, because they also affect the course of pregnancy.
But most often, the reason for the non-compliance of the CTE with the norm is precisely the erroneous determination of the gestational age, therefore, if there are deviations in the indicators, you should not panic; it is necessary to perform additional tests, studies and calculations.
If for some reason a woman is prescribed more than one ultrasound examination for the period from the 7th to the 14th week, you can observe the dynamics of the increase in fetal CTE over the weeks.
CTE and gestational age, how is CTE calculated?
Let's start with the fact that CTE depends almost entirely on the duration of pregnancy and is practically not affected by factors such as the sex of the fetus, race or other individual characteristics. But with the help of CTE indicators, women who suffered from irregularities in the menstrual cycle before pregnancy have the opportunity to almost accurately determine the duration of pregnancy. It is no secret that the obstetric period for problems with the cycle can often be erroneous.
Calculation of CTE is carried out starting from the 11th week of pregnancy. In this case, a normal error of 3-4 days is allowed in both one and the other direction, since the embryo grows quite quickly. It should be noted that after 16 weeks, CTE is usually not measured; after this period, other indicators are important.
The measurement of the coccygeal-parietal size is carried out by sagittal scanning of the fetus. Note that the sagittal plane divides the body into two symmetrical halves, from front to back. If the baby moves during the measurement, the specialist will record the CTE at the moment of maximum extension.
Following the table of CTE values, the doctor determines the gestational age. In principle, you can compare or study the results yourself, since we will also present a table of values in today’s publication.
CTE of the fetus by week of pregnancy
With pregnancy, women have to learn a lot of new things, including various medical terms and indicators. Unfortunately, not all doctors explain the meaning of certain concepts. So, fetal CTE - what is it? Decoding the abbreviation - coccygeal-parietal size - is one of the main indicators that allows you to monitor the correct course of pregnancy up to 12-14 weeks.
After this, completely different indicators make sense. Mainly, using the CTE, the ultrasound specialist determines the gestational age, the weight of the child and other indicators in order to compare them with the norm and identify possible deviations.
The coccygeal-parietal size of the fetus is normal
Below is a table of normal fetal development indicators by week and day.
| Gestation period (week+day) | KTE, mm |
| 6+3 | 7 |
| 6+4 | 8 |
| 6+6 | 9 |
| 7 | 10 |
| 7+2 | 11 |
| 7+3 | 12 |
| 7+4 | 13 |
| 7+5 | 14 |
| 7+6 | 15 |
| Gestation period (week+day) | KTE, mm |
| 8 | 16 |
| 8+1 | 17 |
| 8+2 | 18 |
| 8+3 | 19 |
| 8+4 | 20 |
| 8+5 | 21 |
| 8+6 | 22 |
| 9 | 23 |
| 9+1 | 24 |
| 9+2 | 25 |
| 9+3 | 26-27 |
| 9+4 | 28 |
| 9+5 | 29 |
| 9+6 | 30 |
| 10 | 31-32 |
| 10+1 | 33 |
| 10+2 | 34-35 |
| 10+3 | 36 |
| 10+4 | 37 |
| 10+5 | 38 |
| 10+6 | 39 |
| 11 | 40-41 |
| 11+1 | 42 |
| 11+2 | 43-44 |
| Gestation period (week+day) | KTE, mm |
| 11+3 | 45-46 |
| 11+4 | 47 |
| 11+5 | 48-49 |
| 11+6 | 50-51 |
| 12 | 52 |
| 12+1 | 53 |
| 12+2 | 54-57 |
| 12+3 | 58 |
| 12+4 | 60-61 |
| 12+5 | 62-63 |
| 12+6 | 64-65 |
| 13 | 66 |
| 13+1 | 68-69 |
| 13+2 | 70-71 |
| 13+3 | 72-73 |
| 13+4 | 75 |
| 13+5 | 76-77 |
| 13+6 | 79-80 |
So what is CTE obtained in fetal ultrasound images, and what does it mean? In fact, this is the maximum length of the body between the coccyx and the crown of the head for different views of the fetus.
It should be noted that only by the end of the 12th, 13th week does the fetus complete the formation of primary sexual characteristics. And after 15 weeks, the doctor can determine the gender. And this depends on many factors, among which important are the professionalism of the doctor and the location of the child inside the uterus. Therefore, it makes no sense to ask the doctor to name the sex of the child at the first screening, since determining the fetal calcific factor and comparing it with the table data for weeks of pregnancy have nothing to do with gender.
How to find out fetal growth
Often during an ultrasound examination, parents ask how tall our baby is?
The fact is that in the second and third trimester of pregnancy, fetal growth becomes large and cannot be measured in length during ultrasound examination. Fetal growth is measured only up to 12-14 weeks of pregnancy, and is reflected in the conclusion under the term CTR (coccygeal-parietal size) - the length of the fetus from the coccyx to the crown, excluding the length of the legs. In a longer period, the legs and torso of the fetus are in a bent or other arbitrary position. Therefore, measuring fetal length is technically difficult (ultrasound probes are of limited length) and time-consuming, without being clinically useful. Instead, fetometry is performed (measuring the size of individual parts of the fetus: limbs, head circumference, abdomen, etc., and comparing the results obtained with the norm for a given period).
How can you easily find out your baby's height?
To do this, you just need to know the length of the fetal shoulder in millimeters (mm). Ask your ultrasound doctor for this parameter, then subtract 14 from the resulting figure, and you will get your child’s height! For example, with a shoulder length of 64 mm, you need to subtract 14 from 64, total 64-14 = 50 cm. It’s simple!
Rice. 1 Pregnancy 20-21 weeks. The legs of the fetus are extended above its head.
To diagnose fetal growth V.N. Demidov et al. The following formula is proposed:
P = 10.O x P - 14.0
or
P = 3.75 x N - 0.88,
where P is the height of the fetus (in cm), P is the length of the humerus (in cm), H is the length of the leg (the sum of the length of the femur and tibia, in cm).
Table 1. Fetal growth by week.
| weeks | Fetal height (from heels to crown), cm | Fetal height (from buttocks to crown), cm |
| 14 weeks | 8-10 | 6-7 |
| 15 weeks | 10-11 | 7-8 |
| 16 weeks | 14-17 | 11 |
| 17 weeks | 21,5 | 13,5-14,5 |
| 18 weeks | 22,5 | 14-15 |
| 19 weeks | 22-23,5 | 13-15,5 |
| 20 weeks | 23-25,4 | 14-16,5 |
| 21 weeks | 24-26 | 18 |
| 22 weeks | 25-26,5 | 19 |
| 23 weeks | 26-27 | 20,5 |
| 24 weeks | 27-27,5 | 22 |
| 25 weeks | 28 | 23 |
| 26 weeks | 30 | 24-25 |
| 27 weeks | 32-36 | 27-27,5 |
| 28 weeks | 36-38 | 27-28 |
| 29 weeks | 38-40 | 28 |
| 30 weeks | 40-42 | 28 |
| 31 weeks | 40-43 | 29 |
| 32 weeks | 43-44 | 29 |
| 33 weeks | 44-45 | 29 |
| 34 weeks | 45-46 | 30 |
| 35 weeks | 45-47 | 30-31 |
| 36 weeks | 48-50 | 31-31,5 |
| 37 weeks | 50-53 | 32 |
| 38 weeks | 53-54 | 32,5 |
| 39 weeks | 53-56 | 33 |
| 40 weeks | 53-56 | 32-34 |
Table 2 Length at birth in percentiles for male (Germany, 1992, singleton pregnancy).
Table 3. Length at birth in percentiles for female (Germany, 1992, singleton pregnancy).
Deviations from the norm
What to do if the ultrasound results reveal a discrepancy with the standards? Deviation is possible in both larger and smaller directions.
The ultrasound specialist takes an accurate measurement
In the first case, the decrease may be caused by a number of reasons:
- pregnancy fading;
- late fertilization;
- lack of production of progesterone or other hormones;
- presence of infection;
- genetic disease.
A frozen pregnancy at the initial stage, as a rule, is a consequence of an empty ovum or a serious genetic abnormality in the development of the fetus.
In the case of fertilization of the egg during late ovulation, a time shift also occurs. In this case, it is simply necessary to track the CTE of the fetus over time in order to make sure that development is taking place, but there is a shift in the moment of conception, hence the difference from the data table by week.
Improper functioning of a woman's hormonal system, in particular a lack of progesterone production, can also lead to a shift. In this case, it is necessary to consult a doctor in order to eliminate the problem in a timely manner, if necessary, prescribing progesterone in the form of Utrozhestan or Duphaston.
The presence of infectious diseases is one of the causes of developmental delays. It is urgent to get tested, and then promptly begin treatment as soon as possible in order to maintain the pregnancy.
Various types of genetic failures can lead to the development of pathologies in the fetus, such as Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, etc. Such cases require immediate further research, including biochemical blood tests, genetic research, etc.
Increased fetal CTE by week is also a violation. Possible reasons include the presence of:
- tumor neoplasms;
- diabetes mellitus (in women);
- Rhesus conflict;
- increased fetal growth (due to increased metabolism).
Each item on the list requires an individual approach. In the latter case, it is necessary to stop taking vitamin complexes and other things that increase metabolism. Because this threatens a very large fetus and a complicated birth due to this.

After attending an ultrasound examination of your baby
Fetal CTE by week is determined during screening in the first trimester, among other indicators. It is carried out in almost all medical institutions. As an example, the table shows the names of clinics where ultrasounds are performed for pregnant women, as well as their addresses and the cost of the study.
| Name of the medical center | Address | Cost of consultation |
| INVITRO | Moscow People's Militia st., 42k1 | 1300 rub. |
| MARCH | St. Petersburg Maly pr. V.O., 54, building 3 | 1350 rub. |
| idealMED infinity | Minsk, st. F. Skaryny, 12, room 303 | 569 rub. |
| Healthy family | Kiev st. Kruglouniversitetskaya, 3-5 | 721 rub. |
Considering the fact that the fetal CTE is determined exclusively by ultrasound, the reason for contacting a doctor will be the recommendation of an uzist. If the indicator differs from normal, it is necessary to contact the supervising doctor as soon as possible in order to identify and eliminate the causes in time.
When to see a doctor?
Based on the deviations from the norm described above, failure to consult a doctor in a timely manner can lead to consequences including a threat to the life of the mother and child.
If, after an ultrasound, a diagnosis of “frozen pregnancy” is made, it is very important to seek qualified medical help in a timely manner, since intoxication of the body, bleeding, etc. are possible.
Dear photo
Lack of hormone production, especially the pregnancy hormone progesterone, will slow down the development of the fetus, posing a threat to its life. In this case, the CTE value obtained from the results of a fetal ultrasound will be significantly less than the norm, according to the table for weeks of pregnancy.
If before conception or while expecting a child a woman becomes infected with any infection, the days count. Any penetration of infections is dangerous for the child’s life. And the peculiarity of the situation does not allow the use of most medications that are simply incompatible with bearing a child. Therefore, only timely consultation, necessary tests and treatment are the only way to preserve the health and life of mother and child.
Various genetic abnormalities, as noted above, require additional tests. Today, by the 12th week, every woman, in addition to determining the CTE during fetal ultrasound, is required to undergo a genetic study of possible disorders determined by a blood test. It is important not to neglect this, but to follow the doctor’s instructions.
It is known that it is better to prevent possible disorders, when possible, than to treat them later.
By following these simple recommendations, as well as visiting the doctor monitoring your pregnancy on time, you can have a great time waiting for your baby without unnecessary complications.
About the author : Borovikova Olga
Ultrasound is an ideal method for visualizing the fetus during pregnancy and identifying various pathologies. Pregnant women are usually prescribed three ultrasounds at different times.
The first scan is carried out in the first trimester. Its main goals are to detect a developing fetus in the uterus, exclude or confirm the presence of several embryos, determine the gestational age, and identify chromosomal diseases.
During an ultrasound, several important measurements are taken. Experts determine the thickness of the collar space and the coccygeal-parietal size. The second indicator is very important. What do specialists learn when measuring CTE? For what reasons do deviations from normal values occur?
Coccygeal-parietal size: general information
What is CTE is a question that many pregnant women ask when receiving the results of an early ultrasound scan. The coccygeal-parietal size is an indicator determined by ultrasound. By the abbreviation “KTR”, experts mean the maximum distance measured from the head end of the fetus to the tailbone.
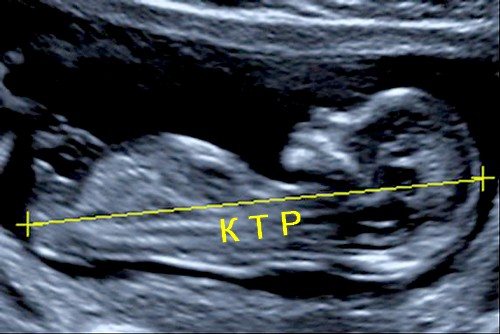
Determination of CTE by ultrasound
KTE is an informative indicator. It is used to determine the gestational age. This value is clinically important for several reasons:
- the results of some studies used in prenatal medicine depend on the exact gestational age;
- correct determination of the period allows you to avoid the use of medications that provoke the onset of labor;
- By the gestational age, precisely determined at the beginning of pregnancy, one can judge the presence or absence of intrauterine growth retardation.
The coccyx-parietal size allows us to identify chromosomal diseases. Based on the information obtained during ultrasound, specialists draw conclusions about whether the fetus has certain disorders:
- A marked slowdown in embryonic growth may indicate trisomy 18. This chromosomal disease is also called Edwards syndrome and is characterized by the presence of multiple malformations.
- With moderate growth retardation, doctors assume that the fetus has trisomy 13. In medicine, this chromosomal pathology is usually called Patau syndrome. Severe congenital defects are characteristic of this disease.
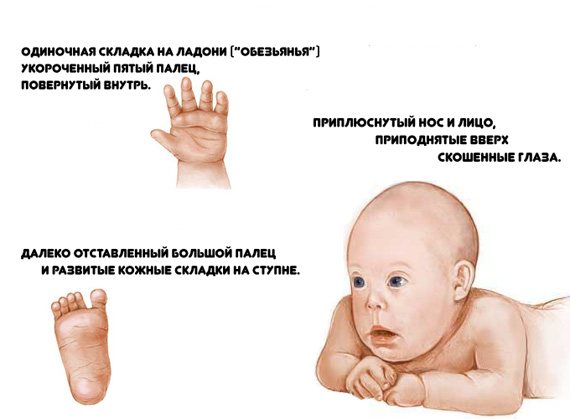
Edwards syndrome
How is CTE measured and what does its value depend on?
The coccygeal-parietal size is determined during the first screening ultrasound examination performed at 8-12 weeks. Experts distinguish several main scanning planes: sagittal, coronal and axial (transverse). Measurement of CTE is carried out only with sagittal scanning in the position of maximum extension of the fetal head.
The values of the coccygeal-parietal size directly depend on how much time has passed since fertilization. The longer the period, the higher the CTE of the fetus. That is why, when conducting several ultrasounds in the early stages, specialists evaluate the dynamics of changes in the coccygeal-parietal size.
Patau syndrome
Fetal CTE: table of values
The coccyx-parietal size in embryos is measured in millimeters. During a normal pregnancy, the fetus increases daily. Accordingly, the values of the coccyx-parietal size also become larger.
Fetal CTE by week: normal in early pregnancy
| Term | KTE, mm | Term | KTE, mm |
| At 7 weeks | about 8.2 | At 11 weeks | approximately 42.2 |
| At 7 weeks + 3 days | 11,4 | At 11 weeks + 3 days | 45,1 |
| At 8 weeks | 14,7 | At 12 weeks | 51,2 |
| At 8 weeks + 3 days | approximately 17.5 | At 12 weeks + 3 days | 57,3 |
| At 9 weeks | 22,3 | At 13 weeks | about 63.3 |
| At 9 weeks + 3 days | 25,4 | At 13 weeks + 3 days | 68,1 |
| At 10 weeks | about 31.1 | At 14 weeks | 76,8 |
| At 10 weeks + 3 days | 35,2 | At 14 weeks + 1 day | 78,0 |
Experts evaluate the coccygeal-parietal size, usually before 16 weeks. In the second trimester, this indicator is no longer important. Other parameters of the fetus come to the fore. These are the ones that experts are beginning to pay attention to.
Deviations from normal values
CTE is considered the main criterion for normal fetal growth in the early stages. Deviations of a couple of weeks in a smaller or larger direction indicate a violation of the intrauterine development of the embryo.
Why deviations occur
There are quite a few reasons why the actual CTE at 8-12 weeks and the norm differ significantly. Most often, fetal development is delayed due to fetoplacental insufficiency syndrome. This complication is diagnosed in many pregnant women. It disrupts the blood supply to the placenta. The exchange between the organisms of the fetus and mother is not maintained at the proper level.
The discrepancy between the coccygeal-parietal size and normal values may be due to a frozen pregnancy. In this condition, fetal development stops. This happens due to any disturbances in the normal course of pregnancy.
frozen pregnancy 2 weeks
The presence of infections is another reason why the actual CTE and the norm differ significantly. Pathogenic microorganisms negatively affect fetal development. To identify infections, pregnant women are prescribed the necessary tests and examinations. If the presumptive diagnosis is confirmed, appropriate treatment is carried out.
The lack of dynamics in changes in the coccygeal-parietal size may be due to hormonal insufficiency. Due to a lack of progesterone, fetal development stops. There is a possibility of miscarriage. To prevent this, hormonal levels are examined and, if necessary, special medications are prescribed.
Sometimes at 8-12 weeks the cause of slow intrauterine development of the fetus is chromosomal pathologies (Edwards and Patau syndromes). In such cases, future parents will have additional consultations with geneticists and donation of DNA markers.
The lifestyle of a pregnant woman plays an important role. If the expectant mother constantly smokes and drinks alcoholic beverages, this means that the fetus is growing in conditions of intoxication. Naturally, there can be no talk of any normal development.

Deviation of CTE from the norm can be caused by a completely harmless reason. For some people it is associated with short stature. In such cases, a small coccygeal-parietal size is a completely natural phenomenon. Expectant parents do not require examinations or treatment.
What actions to take
In order not to encounter intrauterine developmental retardation, women planning pregnancy are advised to pay special attention to their lifestyle. Fetal growth depends on nutrition, physical activity, and the absence of bad habits.

Physical activity during pregnancy shapes the child’s love of sports
If a deviation of the coccygeal-parietal size from the norm is detected during pregnancy, then it is very important to find out the specific reason . It must be eliminated, because the further course of the gestation period depends on it. When the actual CTE at 8-12 weeks and the norm are very different, the likelihood of miscarriage increases. That is why during pregnancy you need to follow all the recommendations of specialists.
When prescribing any tests or examinations, they must be completed . For example, if a frozen pregnancy is suspected, specialists perform an ultrasound to detect heartbeats in the fetus. If they are not detected, then the woman is provided with emergency medical care.
If chromosomal pathologies are confirmed, experts suggest that patients undergo an abortion at an early stage. Women themselves decide whether to follow doctors’ recommendations or continue the pregnancy.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that fetal CTE by week is a very important indicator. It is this that allows doctors to determine the exact gestational age and find out whether the pregnancy is proceeding normally. Deviations of CTE from the norm alarm specialists. If the values are too low or high, women are prescribed additional examinations.
What is KTR. How and when it is measured
The CTE of the fetus is the length of the distance in mm from the highest point of the unborn child’s head to the lowest point of its back. The indicator can be determined by ultrasound. Using this parameter, it is possible to accurately determine the duration of pregnancy at its early stage. CTG is such a universal characteristic that it absolutely does not depend on the individual characteristics of the development of the embryo and the gender of the unborn child.
The measurement is carried out using ultrasound: this is the safest method of examination during pregnancy, for both mother and child. CTE is determined, as a rule, at a period of 7-14 weeks (before the formation of the placenta), but it is most advisable to do the procedure at a period of 12-13 weeks.
It is at this time that the characteristic will be most informative, since with the onset of the 2nd trimester, fetal development is assessed by other indicators.
CTE directly depends on the duration of pregnancy, and the more weeks have passed since conception, the greater the value of this indicator. Gender and individual characteristics do not affect the coccygeal-parietal size in any way.
Here's what you need to know about CTE measurements:
- To obtain correct results, it is necessary to take measurements in such a projection that the child’s body can be divided into two identical parts.
- The indicator is recorded in the absence of fetal motor activity.
- If the child is too active at the time of the procedure, the doctor should take measurements at the moment of full straightening.
- The obtained figures are compared with data from the table, which shows the average statistical indicators of compliance standards by week of pregnancy.
What is KTR?
A woman undergoes her first ultrasound at 10-14 weeks of pregnancy. The doctor assesses the initial condition of the fetus. Thanks to the parameters of the coccygeal-parietal size, the doctor is able to identify early developmental anomalies in the fetus. In subsequent ultrasounds, this indicator is not so important, since it does not carry the necessary information - the fetus acquires individual characteristics, and therefore its size is also strictly individual.
Fetal measurement during the first ultrasound occurs according to the following algorithm:
- The baby's body is divided into two halves, which are symmetrical relative to each other.
- The line along which the indicator is measured runs along the body.
- The distance from the crown to the tailbone is measured in millimeters.
- If the fetus moves too much, the measurement is taken at the greatest extension of the body.
The calculation is carried out according to the obstetric gestational age. Obstetric period is the period from the day the last menstruation begins until the ultrasound is performed. The embryonic period is usually two weeks less than the obstetric period, since this is the moment of conception itself. Ultrasound indicators CTE is the obstetric period.
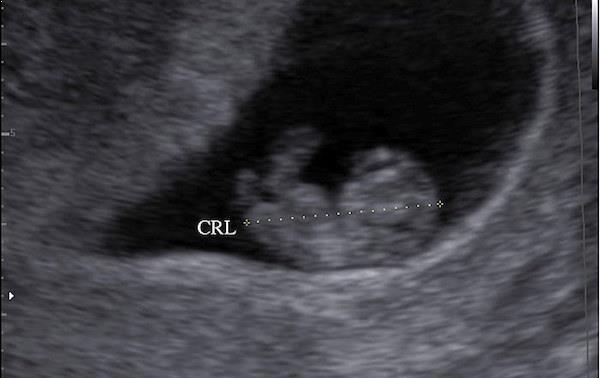
KTR by week
For each week there is a certain CTE value. The embryo changes and grows literally every day, and along with it the CTE indicator increases. The procedure for measuring CTE is usually carried out starting from the 11th week (before the onset of the 2nd trimester).
In this case, a deviation from the norm of up to 3 days in either direction is allowed, which is due to the rapid growth of the embryo or the inaccuracy of the measurement due to its high motor activity during the procedure.
There is a special table of average values that can be used to find out whether the development of the fetus corresponds to the gestational age. When comparing the obtained figures with the norms, you need to remember that every day the embryo gains 1-2 mm in height.
Reasons for deviations
At any time, both at 10 and 13 weeks of gestation, significant deviations in CTE from normal values can be detected in the fetus. If, for example, at 12 weeks the distance from the crown to the tailbone of the fetus is 62 mm, this indicates that it is simply large in size. If at 14 weeks this value is 55 mm, the cause of this phenomenon may be natural and pathological factors.
CTE deviations often occur due to an error of 2-3 days in determining the obstetric gestational age, and therefore do not require concern. In some cases, if this indicator differs greatly from the data in the CTE table, we may be talking about some kind of pathology.
Frozen pregnancy
If this parameter lags significantly behind normal values, for example, with a norm of 20 mm at the 9th week of gestation, the child’s CTE is only 12 or 14 mm, we may be talking about fetal fading. To exclude this pathology, the fetal heart rate and motor activity are checked. However, such parameters are determined only in an embryo whose CTE is more than 6 mm.
If the distance from the coccyx to the crown of the child exceeds this value, and there are no heartbeats, a repeat examination is carried out after 5-7 days or emergency measures are taken to scrape the uterine cavity and extract the fetus. The slightest delay in this case can lead to dangerous and sometimes tragic consequences.
Disturbances in a woman's hormonal background
If at the 8th week of gestation the CTE is 7-8 mm, while at this period its value should be 17 mm, the doctor may assume that the patient’s hormonal background has been disrupted. We are talking about progesterone deficiency, a decrease in the level of which is inevitable during pregnancy. In this situation, in the absence of competent prescription of replacement therapy, there is a high risk of spontaneous abortion at 2-3 weeks of gestation and later. To exclude imbalance of hormones, laboratory diagnostic methods are used.
Infectious diseases
If there is any infectious process in the female body, the CTE in the fetus may be reduced. For example, at 9 weeks of gestation this parameter is 16-17 mm or at 11-12 weeks of pregnancy it is 60 mm, which is significantly lower than normal. Most often, this is caused by genital infections (chlamydia, mycoplasmosis). To cure them, they resort to antibacterial drugs.

Uterine pathologies and genetic diseases
If, during an ultrasound examination performed at 10-11 weeks, it was revealed that the distance from the crown to the coccyx in the embryo is 13-16 mm, the cause of such a deviation may be diseases of the uterus. These include fibroids, disorders resulting from a history of artificial or spontaneous abortion.
In addition, genetic pathologies can lead to a decrease in this indicator. In this case, they resort to a biochemical examination, amniocentesis or cordocentesis.
Table of fetal CTE values in the first trimester (7-14 weeks)
| 6.5 weeks | 7 mm | 10.5 weeks | 36 mm |
| 7 weeks | 10 mm | 11 weeks | 40-41 mm |
| 7.5 weeks | 12 mm | 11.5 weeks | 45-46 mm |
| 8 weeks | 16 mm | 12 weeks | 52 mm |
| 8.5 weeks | 19 mm | 12.5 weeks | 58 mm |
| 9 weeks | 23 mm | 13 weeks | 66 mm |
| 9.5 weeks | 26-27 mm | 13.5 weeks | 73-74 mm |
| 10 weeks | 31-32 mm | 14 weeks | 78-80 mm |
Normal indicators
Decoding the data is the responsibility of the doctor. It is impossible to draw any conclusions without medical education and certain knowledge. Normal indicators, depending on the period, are presented in the table.
| A week | Minimum permissible value (mm) | Average (mm) | Maximum indicator (mm) |
| 7 | 5 | 8 | 11 |
| 8 | 10 | 14 | 18 |
| 9 | 16 | 22 | 27 |
| 10 | 24 | 31 | 38 |
| 11 | 34 | 42 | 50 |
| 12 | 42 | 51 | 59 |
| 13 | 51 | 63 | 75 |
| 14 | 63 | 76 | 89 |
After diagnosis, the doctor compares the resulting figure with the data presented in the table. Such an examination allows you to clarify the characteristics of the course of pregnancy and select the most appropriate tactics for future delivery. If the fetus is very large, a caesarean section may be recommended.

After the ultrasound, the doctor must evaluate the results and make a conclusion
If necessary, a woman may be recommended additional diagnostic methods. It is highly undesirable to ignore doctor's orders.
How to decipher KTE indicators. What does KTR say?
The results of the CTE data will help in establishing the gestational age (an error of 2-3 days is allowed). If the difference with the table values is more than 1 week (the measurement result is greater than the standard), this indicates a high probability of a large fetus.
In this case, the doctor may recommend that the woman adjust her diet and follow a diet. Also, a result that differs more from the norm may occur for other reasons:
- diabetes mellitus in a woman;
- Rhesus conflict;
- the appearance of neoplasms.
When the CTE value is less than that given in the table, this may indicate that:
- there was late ovulation (conception therefore occurred later);
- there is a possibility of a frozen pregnancy (the fetus has stopped developing, there is no heartbeat);
- some diseases of a pregnant woman (problems with the heart, thyroid gland);
- possible hormonal disorders (usually a lack of progesterone);
- there are infectious diseases in the woman’s body;
- there is a risk of genetic pathology.
We hope you will be interested in learning even more useful information about fetal development in early pregnancy. We present to your attention video material about the 11th week: the norms of development of the unborn child and the necessary examinations at this period.
What do deviations indicate?
All pregnancies proceed differently, some suffer from toxicosis, while others, on the contrary, feel a surge of strength. For some, the restructuring of the body causes pain, while others, until the middle of the 2nd trimester, do not feel that there is a child at all.
Discomfort is not always associated with deviations in the baby’s life, although it is worth listening to the body carefully.
After the first screening, expectant mothers receive the first indicator on the basis of which the development of the embryo can be judged. For example, CTE at 9 weeks of pregnancy is already more than 2 centimeters.
In most cases, it is within normal limits, but deviations from the fetal CTE by week of pregnancy from the table do occur.
Excess
A high measurement may be due to an incorrectly determined day of conception. For example, if a girl has recently suffered from an infectious disease, then ovulation occurs earlier than the average time, which shifts the day of actual conception.
However, it happens that the baby simply begins to grow quickly from the very beginning. In the early stages, a diagnosis of a large or giant baby is not made, but the doctor can give certain recommendations.
- Monitor the amount of food you eat.
- Do not use large amounts of vitamin-mineral complexes.
- Do special exercises for pregnant women.
Women with diabetes often give birth to large children.
Reduced
A reduced rate occurs quite often and is usually caused by an initially incorrectly determined day of conception. This is permissible under the following circumstances:
- the girl gave the wrong dates of her last menstruation - not everyone keeps count;
- ovulation occurred later than two weeks after menstruation;
- implantation of the embryo occurred with a delay.

If the discrepancy in information is more than 7 days, then a repeat study is prescribed. It is important to track the dynamics of the baby’s life. If the growth is normal, then the maximum growth rate is calculated based on the results of the study.
Accelerated growth
An accelerated increase in coccygeal-parietal size is not very common. In most cases, children develop within the limits of acceptable values. If the increase is too rapid, then doctors will pay attention to the following possible reasons:
- metabolic disorders in the mother;
- genetic pathologies;
- Rhesus conflict.
A woman will also experience rapid growth rates in the early stages, and her thyroid function will be impaired. Additionally, you will need to be observed by an endocrinologist.
Slow growth
A slow increase in size, on the one hand, indicates that the child is developing, and on the other hand, signals the presence of some problems. They are often caused by a lack of progesterone, a hormone that the baby needs in the early stages. If its measurements in the blood of the expectant mother are low, she is prescribed special therapy.
Low growth rates may also be associated with chronic maternal diseases of infectious origin. The decision here is made individually. In some cases, drug intervention is permissible, and sometimes artificial termination of pregnancy is recommended.
Fetal CTE is one of the key measurements in the early stages of expecting a baby. While the embryo is still very small, the presence of pathologies and the dynamics of development can only be determined by its growth.
The material was prepared specifically for the website kakrodit.ru, edited by diagnostician O.S. Vasilyeva.