Lactating women, due to a weakened immune system, often encounter infectious diseases of viral and bacterial origin. One of the most common pathologies among nursing mothers is pharyngitis. This is a disease in which the pharynx becomes inflamed. The disease manifests itself as a sore throat, dry mucous membranes, and discomfort during swallowing.
Treatment of pharyngitis during lactation should be carried out under the supervision of a physician. This is explained by the fact that many drugs are prohibited for nursing mothers, as they negatively affect the newborn.
Types and causes of pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is an infectious disease with a migratory nature. It is quite simple to identify the inflammatory process on the mucous membrane. Pharyngitis can occur in acute and chronic forms.
The disease in its acute form develops quickly. Inflammation is provoked by pathogens that penetrate the mucous membrane of the pharynx, smoking, alcohol, hypothermia, etc. Depending on the pathogen, pharyngitis can be viral, bacterial, allergic and fungal. But the first 2 forms of the disease are most common.
In the chronic form of the disease, acute inflammation becomes permanent. Chronic pharyngitis is divided into the following types:
- Hypertrophic - all layers of the pharyngeal mucosa are affected, as a result of which it thickens.
- Atrophic - the inner membrane becomes thinner.
- Catarrhal - manifested by diffuse redness of the mucous membrane.
In most cases, pharyngitis in a nursing mother occurs for the following reasons:
- irritation of the inner shell by chemical compounds;
- penetration of viruses, bacteria or fungi into the throat;
- hypothermia of the throat mucosa (when breathing through the mouth in the cold).

The likelihood of pharyngitis increases if a woman smokes, drinks alcohol, hot or cold food, or lives in a region with poor environmental conditions. Additional provoking factors: diseases of the digestive tract, teeth, hormonal imbalance. In the absence of proper treatment of acute pharyngitis, it becomes chronic.
Diagnostics
The doctor makes a final diagnosis based on the results of a patient interview and pharyngoscopy. Auxiliary methods for diagnosing pharyngitis used during pregnancy are bacterial culture and blood tests.

During the interview, the doctor tries to find out what caused the pharyngitis. And also a number of additional questions allows us to establish the form of the disease.
Next, the mucous membrane of the pharynx is examined. At the same time, its color, the amount of mucous secretions, the presence of swelling, and vascular pattern are assessed.
The presence of purulent growths indicates the bacterial origin of the disease. In the presence of pinpoint bruises, the causative agent of pharyngitis is group A hemolytic streptococcus.
In some cases, to clarify the data obtained, an analysis is performed for bacterial culture of the nasopharynx. The analysis result will be ready within 7 days, so this method is classified as an additional group. In order to exclude the presence of infectious mononucleosis, doctors prescribe a blood smear to detect atypical monocytes.
Clinical picture
Acute pharyngitis is manifested by pain during swallowing, dry mucous membranes, and soreness. In addition, there is a possibility of fever and general weakness. Some patients complain that the discomfort spreads to the ears.
Pharyngitis can easily be confused with severe infectious diseases (measles, rubella, scarlet fever). Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor in time, who will accurately diagnose.
With chronic pharyngitis, there is a lump in the throat, the mucous membrane is constantly irritated, which causes a desire to cough. In addition, there is constant malaise and fever. The cough in the chronic form of the disease is dry and hacking. All these symptoms reduce the quality of life, and as a result, the nursing mother becomes irritable.
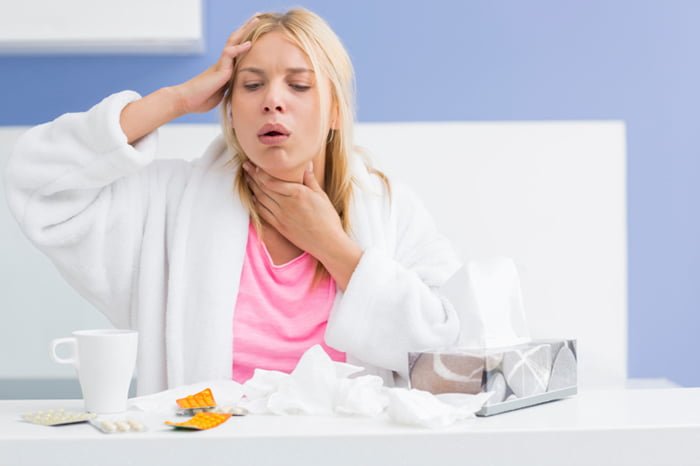

Symptoms
There are two main forms of the disease: acute and chronic. Acute pharyngitis during pregnancy occurs as a result of the action of harmful factors on the laryngeal mucosa: smoking, cold weather, dirty or dry air. Sources of infection, as a rule, are viruses, fungi and bacteria.
Acute pharyngitis during pregnancy is manifested by the following symptoms:
- discomfort and feeling of dryness in the throat;
- elevated body temperature: 37.5–38 °C;
- enlarged and painful lymph nodes;
- swelling and redness of the back of the throat;
- hoarse voice.
With prolonged exposure to negative factors and lack of treatment, the disease becomes chronic. Chronic pharyngitis during pregnancy can be accompanied by regular exacerbations, and its symptoms vary depending on the stage of the disease:
- Catarrhal. At the first stage, the patient complains of dryness and swelling of the throat. Symptoms are aggravated by talking for a long time and by inhaling cold air.
- Granular. Added to the soreness is the feeling of a lump in the throat. The back wall of the throat is covered with small red tubercles. The mucous membrane has a glossy sheen.
- Atrophic. The swallowing process becomes difficult. Foreign odors appear in the mouth. The back wall of the throat is covered with a dry crust. The mucous membrane becomes thinner.
All stages are characterized by a constant dry cough. Regular outbreaks of exacerbation are observed in the autumn-spring period.
Danger of disease
When the pharynx becomes inflamed, a lactating woman often transfers her newborn to artificial feeding, fearing that the baby may become infected. However, such measures are necessary in rare cases.
Particles of pathogenic microorganisms enter the baby’s body along with milk, which are not capable of infecting it. In addition, along with milk, the child consumes antibodies that protect him from infection.
The real danger to the newborn are microbes that come from the mother's mouth. For this reason, a woman should wear a mask during treatment for pharyngitis.
In addition, medications that the mother takes during therapy are dangerous for the baby. Most of them are contraindicated, as they negatively affect the child. The decision on choosing an effective and safe drug will be made by the doctor after making a diagnosis.

Treatment of pharyngitis in the early stages is a prerequisite for a quick recovery. If a woman delays therapy or carries out independent treatment, the likelihood of the following complications increases:
- Chronic pharyngitis.
- Purulent inflammation of the lymph nodes and retropharyngeal space.
- Inflammation of the trachea.
- Acute polyarthritis.
- Quinsy.
- Chronic inflammation of the bronchi.
- Poststreptococcal glomerular nephritis.
- Eustachitis, internal otitis.
- Inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes.
- Inflammation of the salivary gland.
To avoid such complications, start treatment after the first symptoms of pharyngitis appear.
What happens if you ignore a sore throat?
If you think that a nursing mother’s sore throat will go away on its own and do not resort to treatment, then you can “earn” complications: a runny nose, sinusitis, otitis media and bronchitis will follow.
Inflammation of the posterior wall of the larynx spreads to the tonsils, then to a sore throat. Sore throat, in turn, leads to diseases of the joints, kidneys and heart. So, a sore throat should not be ignored.
A nursing mother definitely needs to take care of her hygiene.
Usually the child does not become infected because he immediately begins to receive immunoglobulins along with breast milk.
However, precautions will not be superfluous.
- If you start to feel discomfort in your throat, it is better to wear a mask or bandage over your mouth.
- Don't kiss the baby.
- Wash your hands often and with soap, because mucus settles on them and is infested with bacteria and viruses.
- Instead of a handkerchief, purchase disposable paper napkins.
For more information on how to raise a healthy child, see the online course Healthy Child: Workshop for Mom>>>
Breastfeeding mothers should drink more fluids when they have a cold because it prevents dehydration. Drinking also effectively rids the body of toxins that make you feel worse.
It is recommended that nursing mothers get more rest. If possible, ask your family to sit with the child while you sleep, or just lie down. If you don't have one, you can sleep with your baby while he suckles and falls asleep on his own. Read a useful article: How can a mother be less tired>>>
It is better, of course, to see a doctor so that he can choose the right treatment for you.
Many young breastfeeding mothers are at a loss when they get sick. They doubt whether lactation can be continued. When you have a cold, nothing happens to the milk; it does not turn sour or burn out.
So keep breastfeeding, take care of yourself and get well!
Treatment methods
Nursing mothers who are faced with pharyngitis are trying to find options on how to treat the disease so as not to harm the baby. Most of them believe that during therapy it is impossible to do without antibacterial drugs, but this is not necessary. Local antibiotics may only be needed during an exacerbation of chronic pharyngitis. In general, treatment should be comprehensive: medications (local), folk recipes and non-drug measures.
To speed up your recovery, follow these rules:
- Try to talk less so as not to strain your vocal cords.
- Avoid spicy, hot or cold foods and drinks.
- If a woman is not predisposed to edema, then she needs to drink at least 2 liters of warm liquid per day.
- It is recommended to get a good night's sleep and be sure to rest during the day.
- Install an air humidifier in the room to improve the microclimate and prevent drying out of the mucous membranes. How to choose it, read the article at the link.
- Ventilate the bedroom frequently.

Treatment of pharyngitis is allowed only after its causative agent has been identified. If a woman does not tolerate fever well, she can take paracetamol-based antipyretics (Paracetamol, Ibuprofen). Antipyretics (antipyretics) are allowed to be used only at temperatures above 38° and no more than 2 times. Aspirin is contraindicated during lactation, however, if there are no other drugs at hand, then a single dose is acceptable.
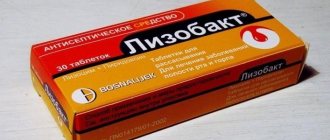
For hepatitis B, local homeopathic remedies based on interferon are allowed.
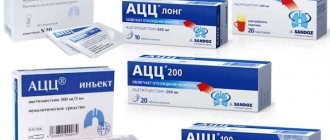
Antibacterial drugs are used in rare cases and only after the approval of a doctor. It is important to follow the treatment regimen prescribed by the doctor so that the drug has time to be eliminated from the mother’s body before the next feeding. Otherwise, the baby can be switched to artificial nutrition or periodically fed in this way.
To treat pharyngitis in lactating women, folk recipes are used:
- Dilute 5 g of soda in 220 ml of warm boiled water, stir, strain and gargle 6 to 8 times a day.
- Crush 1 clove of garlic, mix it with 5 g of honey. Dissolve this mixture 3 times a day.
- Take 50 g of dry larch, add 1 liter of water, boil for 10 minutes over low heat. Strain the cooled broth and use it for inhalation, which should be done three times in 24 hours.
- Grind the beets and squeeze the juice out of them. Mix 220 ml of juice with 30 ml of apple cider vinegar. Use the resulting solution to gargle 4 times a day.
- To get rid of cough, use the following solution. To prepare it, mix 220 ml of warm milk, 10 g of butter, 3 g of soda and 5 g of honey.

Before using traditional recipes, consult your doctor, as they can cause allergies, especially bee products.
Folk remedies
Many people do not believe in the effectiveness of various home treatments, but they really help. If a young mother has a sore throat, then she can always turn to simple methods that will not take much time and money.
The first thing you need for a common cold is tea with lemon and honey. But it is worth remembering that a hot drink will only promote the proliferation of microbes. Therefore, it should be consumed only warm, in small sips, so that it is easier for the honey to coat the throat. There is no need to try to drink as many cups of tea as possible, as it will wash out potassium, an important cardiac nutrient. You should also reduce your intake of sugar, which creates excellent conditions for the spread of infection throughout a woman’s body.
A young mother should drink as much warm boiled water as possible. You can add lemon juice to it, which will speed up the healing process. Don’t forget about other citrus fruits, the benefits of which should never be reduced. Orange, lime, grapefruit, tangerine are also good for sore throat. They kill germs and “disinfect” the surface of the throat.
If there is nothing in the house except salt and soda, then they too can cope with a sore throat. For one glass of warm boiled water, add a tablespoon of salt and soda. Then stir thoroughly and gargle with this solution. The procedure should be repeated several times a day. These products cleanse the throat of harmful bacteria well and quickly.
Taboos in the treatment of pharyngitis
In order not to worsen her condition and not harm the baby, a lactating woman should know about the prohibitions during treatment of pharyngitis:
- Self-medication.
- Hot, cold, spicy food.
- Uncontrolled use of local throat medications.
- The use of vasoconstrictor nasal drops.
- Self-administration of vitamin complexes.
- Excessive consumption of bee products.
In addition, it is forbidden to steam your feet or visit a bathhouse or sauna. If your condition does not improve after 2 days of home treatment, visit your doctor.

Preventive measures
Cure pharyngitis is more difficult than preventing the disease. To avoid infection, follow these rules:
- Treat ENT diseases before pregnancy.
- Treat dental diseases.
- Strengthen your immune system.
- Avoid crowded places during the cold season.
- Ventilate your living space, but avoid drafts.
- Wash your hands and rinse your nasal cavity with saline solution after visiting crowded places.
- Use preventive medications prescribed by your doctor.
- Take a walk in the fresh air.
- Don't get too cold.
Thus, treatment of pharyngitis during breastfeeding should be supervised by a doctor. Otherwise, the woman may worsen her condition and endanger the health of the baby. With adequate treatment, the symptoms of pharyngitis with hepatitis B will disappear after 5 days.
Subscribe to our VKontakte group
Subscribe to our group
March 5, 2015, 09:00
Hello girls.
Well, Tryndets and I got sick, and I got it. I have acute pharyngitis, my throat hurts, it’s terrible, the pain radiates to my ears, my head is cracking and I have snot. I’ve been sick for the 3rd day, the doctor really prescribed a rinse with soda, salt, iodine, manganese and Larinpront tablet under the tongue, I was treated with this for 2 days and it only got worse, It turns out I damaged the mucous membrane, I read on the internet that you can’t use a saline solution, the scribe doctor doesn’t understand that it’s impossible, I’m suffering damn it right now. I burned the mucous membrane a little. Yesterday I brewed some chamomile, I drink a sip and gargle, I drink milk, I added a little honey, I know that the allergen is Honey, but everything seems to be fine with my daughter, I wash my nose with Aqualor and drop gripferon, drink plenty of warm teas, fruit drinks. I wear a mask at home, I’m very afraid of infecting my daughter, but I hope everything will be fine with breastfeeding and my daughter won’t get sick, no I would like this, we are like the 3rd day after DTP vaccination.
Girls who were sick with breastfeeding, how were they treated, what did they gargle with? Only without antibiotics.
Pharyngitis is one of the most common acute respiratory diseases. A woman's body weakens during pregnancy and her chances of infection increase. She needs effective preventive measures and care.
Pharyngitis during pregnancy and breastfeeding negatively affects the process of bearing and developing a child. In addition, the use of certain medications is contraindicated for pregnant women, which significantly delays the recovery period. And if pharyngitis starts, it can become chronic.