Decoding the results
In addition, at this time it is possible to evaluate the proportions and size of the child, which are also an indicator of its normal development. First of all, during the diagnosis, the size of the arms, legs, head, chest, and abdomen is assessed. Many expectant parents wonder what the ultrasound standards are at 32 weeks of pregnancy. A healthy baby should have the following parameters:
- shoulder length from 52 to 62 mm;
- forearm length from 45 to 55 mm;
- thigh length from 55 to 65 mm;
- tibia length from 50 to 60 mm;
- biparietal head size from 75 to 90 mm;
- fronto-occipital head size from 95 to 110 mm;
- head circumference from 280 to 330 mm;
- abdominal girth from 255 to 315 mm.
The listed indicators are relative, since the most important role in the size of the fetus is given to genetic characteristics, which are already clearly manifested at this stage. However, if during the procedure the child’s parameters were discovered to be very different from the norm, then there is a risk of developing hypertrophy, which is an indicator of impaired placental maturity.
The baby's heart rate at 32 weeks should be between 140–160 beats per minute. An altered number of heartbeats indicates fetal pathology and the possibility of premature birth.
Table of fetal sizes depending on gestational age
Baby's weight
At week 32, the baby is no longer at the embryonic stage; it has quite an impressive weight. The weight of the fetus at this stage reaches 2000 g. However, if a woman is thin, then the normal weight can be from 1600 to 1700 g. In large women, the baby can reach up to 2100 g. During this period, hereditary predisposition already plays a large role. In addition, for mothers who suffered from infectious diseases during pregnancy, the baby’s body weight may be less than average.
This is not a pathological phenomenon. There are cases of low fetal weight in women with hormonal imbalances. If a woman is carrying twins or triplets, the body weight parameters of the children will differ significantly. This directly depends on how many children the pregnant woman is carrying. There are times when babies' weight varies greatly. This is due to the fact that one fruit develops more intensively than the other. Normally, the weight of twins usually ranges from 1650 to 1700 g at 32 weeks.
How many times is ultrasound performed during pregnancy?
Normally, if a woman is registered at the antenatal clinic from the moment pregnancy was established, she is prescribed 3 planned tests.
- The first is at 10-14 weeks. The goal is to identify gross malformations of the fetus, size, and also to identify genetic pathology.
- The second ultrasound is performed at 20-24 weeks. There is a spectrum of vices that can be defined more broadly. The development of internal organs, limbs, etc. is assessed. This will allow us to identify diseases that threaten not only the fetus, but also the mother, as early as possible. This is due to the fact that sometimes an artificial termination of pregnancy is necessary, which should be performed as early as possible, because it is safer and will entail much fewer consequences. It is for this reason that, in the case of a pathological decrease in hCG, an ultrasound is immediately performed, and then a therapeutic tactic is developed.
- Ultrasound at 32 weeks and above, up to 36 weeks, is the last. The condition of the placenta, blood circulation, as well as other indicators that were assessed at previous stages are assessed. The peculiarity of this ultrasound is that it most often determines intrauterine developmental delays, which are often associated with circulatory failure. But in no way should the last ultrasound be singled out more than the previous ones, because problems with blood circulation, including heart defects, can be detected at an earlier date.
Study of a woman
In addition to diagnosing the fetus, an ultrasound scan at 32 weeks of pregnancy allows you to assess the condition of the woman’s reproductive organs. Normal placental thickness should range from 25 to 42 mm. Moreover, the placenta should not be adjacent to the os of the uterus, but should extend 7 cm from it. This indicates stage 1 of placental development. On ultrasound examination, this degree of maturity is determined by shallow depressions and the appearance of a few echogenic foci.
If ultrasound determines grade 2, then this is a sign of premature aging of the placenta. This condition entails:
Interpretation of CTG during pregnancy at 32 weeks
- late toxicosis;
- infections;
- diabetes.
In this case, immediate treatment for pregnant women should be started, which can improve the situation and prevent the development of serious fetal pathologies. The thickness of the placenta should be no more than 45 mm. If during ultrasound diagnostics large parameters are determined, then this is a sign of intrauterine infection; sizes smaller than average indicate premature aging of the placenta.
During the procedure, great importance is given to calculating the volume of amniotic fluid. During calculations, the doctor conventionally divides the woman’s stomach into 4 parts vertically and horizontally. Next, all four indicators are summed. The norm is the amount of amniotic fluid from 20 to 80 mm. Exceeding these boundaries is oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios, respectively, and requires medical intervention.
During the assessment of the umbilical cord, the number of vessels, the presence of loops, knots, and entanglement around the fetal neck are determined. The doctor examines the uterus to determine whether there is increased tone, which often leads to premature birth. If a woman is diagnosed with fibroids, the blood flow is analyzed. At this stage, the cervix must be completely closed, otherwise there is a risk of premature birth.
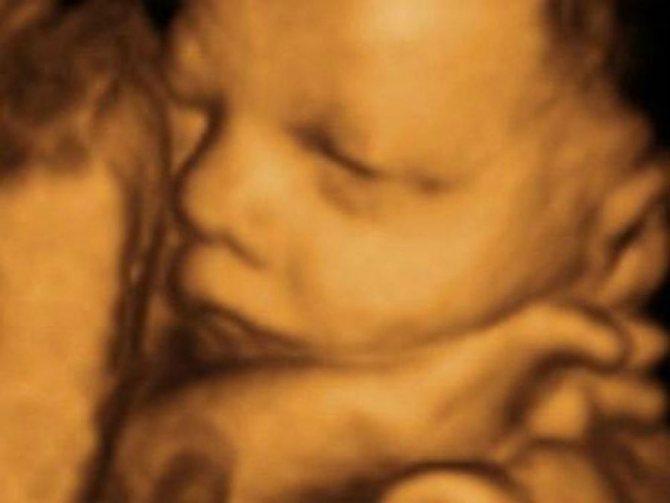
Three-dimensional scanning allows you to see the actions of the fetus at the time of diagnosis
A little about ultrasound as a diagnostic method
Ultrasound has been used in medicine for more than half a century. It’s hard to say whether it’s a lot or a little, because the speed of scientific and technological progress is very high. During this time, ultrasound research methods have developed and improved, making them one of the most widespread throughout the world.
- The reasons why this method does not stand still are very significant. Ultrasound is one of the safest diagnostic methods. Ultrasound radiation does not cause any harm to the body of the fetus or mother. This radiation itself is a very high-frequency sound that is inaudible to the human ear.
- Also, one more, almost the most important point is the quality and accuracy of the results. Ultrasound diagnostic methods fully satisfy all the requirements of doctors. And more developed techniques, for example 3D ultrasound, allow you to create a full-fledged three-dimensional model. The 3D ultrasound video obtained as a result of the study at 32 weeks is transmitted to parents for their personal viewing. Many families celebrate this as a pleasant and unforgettable moment.
In addition to ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be cited as an example of safe diagnostic methods, but this method is much less accessible and some structures of the fetal body may not be visible.
As for the question: “Is ultrasound wrong at 32 weeks?”, then everything is very ambiguous. If the diagnosis is carried out by a qualified specialist using good equipment, then the likelihood of an error is extremely low. The issue of error is closely related to the choice of institution where the diagnosis will be performed. Also, in case of suspected defect, the study is not carried out once.
Ultrasound with Doppler
There are cases when, at 32 weeks, a Doppler study is performed simultaneously with an ultrasound. It allows you to assess the condition of the arteries, the functioning of the baby’s cardiac activity, the vessels of the uterus, and the umbilical cord. Indications for Doppler examination are:
- woman's condition. This category includes the presence of arterial hypertension, kidney diseases, diabetes mellitus, late toxicosis, and Rh conflict in a pregnant woman;
- state of the woman-child system. This situation includes oligohydramnios, premature aging of the placenta, impaired blood flow through the umbilical cord arteries;
- the fetal condition includes an abnormal heart rhythm, a diagnosed heart defect, and hypoxia.
In addition, Doppler ultrasound is performed in multiple pregnancies, since multiple fetuses can lead to uneven distribution of blood flow. Also, women who have previously had miscarriages or frozen pregnancies are subject to this diagnosis. Diagnosis with Doppler can be carried out more than once. This is especially important for monitoring the quality of prescribed treatment.
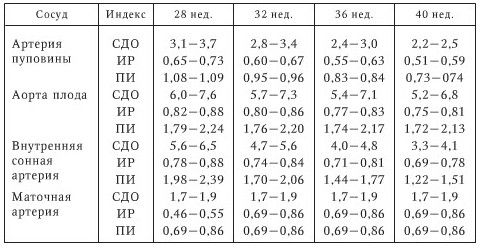
The norm of Doppler examination depending on the stage of pregnancy
Diagnosed pathologies
The third screening can diagnose the presence of the following pathologies:
- fetoplacental insufficiency, which occurs when placental maturity does not correspond to the term;
- umbilical cord entanglement. This condition does not pose a threat to the fetus if it does not cause disruption of blood flow;
- discrepancy in the size of the baby, breech presentation;
- predisposition to premature birth, which manifests itself in a shortened cervix;
- altered volume of amniotic fluid, which can manifest itself as both polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios;
- if there is a scar, identify its failure;
- oxygen starvation of the fetus.
An ultrasound performed at 32 weeks allows us to assess the condition of the baby and the woman. This diagnosis is important because it makes it possible to improve the baby’s condition.
How an ultrasound is performed at 32 weeks of pregnancy and preparation for it
- No preparation is necessary for this fetal examination. There are also no contraindications to the procedure. The only reason why an ultrasound at 31-33 weeks may not be performed is the human factor and the prejudices of parents. Ultrasound examination is performed only using the transabdominal method. At this stage, there is enough amniotic fluid, which is a good conductor for ultrasonic waves.
- The pregnant woman arrives at the appointed time and lies down on the couch. The doctor then applies a special gel to the area to be examined. It is necessary to improve the conductivity of ultrasound; more precisely, it removes excess air between the sensor and the skin, which prevents the conduction of ultrasound waves, as it leads to distortion and a significant decrease in the reliability of the results.
The ultrasound will take 10-30 minutes, after which there will be a short wait and the woman will receive the results of the study, with which she should go to her obstetrician-gynecologist.