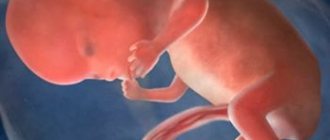
The volume of amniotic fluid becomes larger, and the placenta begins to actively develop. By week 40 she will weigh approximately 800 grams. The “growth” of the fetus is about 9 millimeters, and the weight reaches 1.3 grams. Because the baby is so small, the mother cannot yet feel him, but meanwhile he is moving very actively.
Obstetric 6th week of pregnancy is actually 4th week from conception. The baby’s body shape at this age resembles the letter “C” or looks like a curved oval. The amniotic sac is formed around it, the main function of which is protective. Until birth, it will protect the child from mechanical influences. The baby reacts to them because the development of muscle tissue has already begun.
An important stage of intrauterine development is the formation of two chambers of the heart - this is happening right now. Germinal red blood cells are produced, and the first blood vessels, ventricle and atrium grow rapidly. After a while, a septum will appear that will divide the heart into 4 chambers.
Starting from the 6th week, the fetal heartbeat can be heard on ultrasound. Its contraction frequency is 110-130 beats per minute.
Every day the fetus becomes more and more human-like. The rudiments of legs and arms have formed, and in a week tiny fingers will begin to form. Ears appear in the form of bulges on the sides of the head. The eye sockets and mouth are already visible.
What happens in the sixth week of pregnancy
Along with the rapid development of the embryo, changes in the mother’s body continue to occur. The level of hormones continues to rise, the concentration of hCG and progesterone increases. All hormones closely interact with each other, complementing each other's actions.
Such a hormonal explosion causes a change in both the physical and psycho-emotional state of a pregnant woman. She feels weak and constantly wants to sleep. Unmotivated aggression, tearfulness, bad mood - hormones are to blame for all this.
Important changes occur in the uterus. Its shape, size, consistency, reactivity changes, and blood flow increases.
The formation of the placenta is actively underway, which will be completely completed by the twelfth week of pregnancy. At the sixth week, the placenta already begins to produce hormones, and very soon it will be responsible for protecting and nourishing the baby.
Why is the embryo not visible on ultrasound?
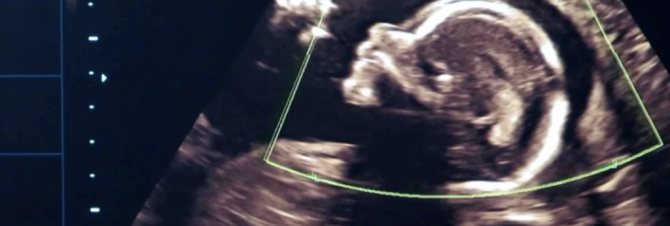
It is impossible to examine even a normally developing fetus immediately after conception - it is too small for an ultrasound scanner to distinguish it from the background of surrounding tissues and organs. Therefore, the first ultrasound to confirm pregnancy is usually done 6-7 weeks after conception. Until this point, the fact that a woman will be a mother can only be judged by the level of human chorionic gonadotropin, which begins to be secreted by the chorion (fetal membrane of the embryo) 6-7 days after conception. Normally, with the successful development of pregnancy, the concentration of hCG in the body increases along with the development of the fetus.
To understand the mechanism of anembryony, it is necessary to understand the structure of the embryo itself and its early development. It happens in several stages:
- A zygote is essentially a fertilized egg formed at the moment of conception;
- Morula is the next stage, characterized by the division of the zygote into several cells of the same type;
- Blastula is an embryo in which the cells are already divided into an inner cell mass (embryoblast) and an outer layer (trophoblast);
It is at the blastula stage that the future body of the embryo and the protective membranes surrounding it are formed. When the embryo leaves the fallopian tube and descends into the uterine cavity, enzymes secreted by the outer cells partially dissolve the endometrium, and its implantation occurs. Next, the embryo and amniotic membranes develop in parallel, gradually forming a mature fetus and placenta.
With anembryonia, this process is disrupted - the outer membrane (fertilized egg) continues to grow, releasing hCG, while the embryo either does not form at all or its development stops at an early stage. Because of this, for some time the tests give false results, showing a normal pregnancy. Only after some time the chorion stops secreting hCG, the level of which gradually begins to decrease.
The reasons for embryonic growth arrest, leading to an empty fertilized sac, are not fully understood. Today these include:
- Genetic abnormalities. In most cases, anembryony is caused by pathological chromosomal mutations, either originally characteristic of the parents, or appearing as a result of unsuccessful recombination of genes in their body. Genetic disorders in the embryo itself are also possible, occurring in the early stages of its development.
- Infections. Among them, the most dangerous for embryogenesis are the diseases included in the TORCH complex - rubella, herpes, cytomegalovirus, toxoplasmosis, syphilis, hepatitis B and C, etc. Infectious pathogens can affect the maternal body, disrupting its reproductive function (for example, causing chronic endometritis) , or the embryo itself, leading to disruptions in its development.
- External factors. This primarily applies to ionizing radiation (radiation) and toxic chemicals (poisons, some medications). They cause functional disorders of the mother's reproductive system or genetic mutations in the embryo, stopping its normal development.
- Endocrine disorders. Disorders of a woman's endocrine glands can also lead to anembryonia. The appearance of a fertilized egg without an embryo is especially likely if there is a deficiency or disturbance in the metabolism of progesterone, a sex hormone that plays an important role in the decidualization (morphological change) of the endometrium at the point of implantation of the embryo.
- Immune disorders. Quite often, the cause of improper development of the embryo is damage to it by the protective system of the mother's body. This can happen indirectly - for example, when the embryo gets caught in the “crossfire” of immune cells attacking the infection. Sometimes the embryo itself is regarded by the woman’s immune system as a foreign object, because its genetic code is half composed of the genome of another person (the father).
Anembryonia can be caused by either one of these factors or their complex effects. It is impossible to predict the development of this pathology - it is observed even in absolutely healthy women who have already had experience of successful pregnancy.
This anomaly should be separated from a frozen pregnancy. With anembryony, the embryo does not form at all, and in the second case, its development stops at an early stage. Moreover, in terms of external manifestations and ultrasound, these pathologies may look the same.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
Fetal size in the sixth week of pregnancy
The fetus at the sixth week measures 6.6 mm. It still weighs less than one gram, but two tubercles are already appearing on the sides, which will later become arms. Several days will pass and the same tubercles will appear in the back of the embryo, becoming the prototype of the legs. The arms develop faster than the legs. By the end of the sixth week, the rudiments of the hands will form.
At the proximal end of the neural tube, at the beginning of the sixth week, a thickening appears, which is nothing more than the rudiment of the brain. By the middle of the week there will be a division into sections and hemispheres of the brain.
The fetus begins to develop a face. The rudiments of the lower and upper jaws, ears, nose, and eyes are formed.
The heart is actively functioning, the formation of ventricles and atria occurs in it. During an ultrasound, the fetal heartbeat can be clearly heard.
The yolk sac and the already formed liver begin to produce blood cells. In the sixth week, the rudiments of the large and small intestines, as well as the stomach, are formed.
The formation of the baby’s genital organs continues and very soon it will be possible to determine the sex of the unborn child.
The formation of the placenta will soon end. In the sixth week, chorionic villi and the umbilical cord are formed, which will later become the umbilical cord. All these processes prepare the child’s body for the rapid supply of oxygen and nutrients from the mother.
6 weeks Your baby is the size of a lentil grain
Starting point: how to find out when pregnancy started
The obstetrician calculates the date when a woman is expecting a baby during her first visit to the antenatal clinic.
- The doctor performs a manual examination to determine the size of the uterus. This will help him understand what stage of pregnancy the uterus corresponds to.
- Also, the local doctor must specify the date of the first day of the last menstruation. This point is taken into account, because The uterine mucosa begins to prepare for pregnancy from this period of time.
- You can find out the most reliable information about the duration of pregnancy using an ultrasound examination. An ultrasound examination can tell with precision down to the day when a small life was born. The examination, even at the earliest stages (starting from 4-5 weeks), assesses the size of the embryo, which allows the obstetrician-gynecologist to calculate the exact date of pregnancy.
In the first week after conception, the embryo actively moves along the fallopian tube. After six days of active “journey”, it enters the uterine cavity. Under the influence of progesterone (also called the pregnancy hormone), the unborn baby attaches to the lining of the uterus, this process is called implantation .
If the attachment of the embryo has taken place successfully, then the next menstruation will not occur - the pregnancy has begun.
Signs of pregnancy in the sixth week
This week the symptoms of pregnancy are already quite clearly expressed. Due to the restructuring of the body, which now has to work for two, the woman feels a loss of strength, constantly wants to sleep and gets tired quickly.
She begins to react extremely acutely to certain odors, and increased salivation may occur. Women who, due to toxicosis, have already experienced morning sickness and vomiting, note an increase in these phenomena in the sixth week. Those who have not had these symptoms before can become familiar with toxicosis this week. Nausea and vomiting can be caused by both food intake and odors, which a pregnant woman begins to perceive very acutely.
In the sixth week of pregnancy, changes continue in the mammary glands, which are prepared by the body for future breastfeeding. Blood supply to the chest increases. It increases in size, the nipples become more sensitive, and when touching them the woman feels a tingling sensation. The nipple areas darken.
The uterus also continues to grow. She is already the size of a plum, but outwardly the increase in her belly is not yet visible. The body actively produces progesterone, which prevents the tone of the uterus from increasing, preventing abortion.
Mom's feelings
At this stage, the expectant mother already feels all the signs of early pregnancy. Morning sickness is very typical: weakness, nausea, possible vomiting. Very often women feel drowsy. Due to the increased content of progesterone, which causes relaxation of the internal muscles, problems with stool may begin. Therefore, a woman must include in her daily diet foods that help improve digestion, as well as maintain an adequate drinking regime.
Changes in the mammary glands are characteristic: enlargement, soreness, darkening of the areolas is possible, and a venous pattern appears. The uterus has grown somewhat and puts pressure on the bladder, so women notice frequent urination.
Painful sensations in the lower abdomen are possible, and if they occur, you should definitely consult a doctor to eliminate the risk of miscarriage.
The most characteristic symptoms are signs of early toxicosis. Normally, symptoms of toxicosis are observed until the end of the first trimester of pregnancy, but they can last longer. Their intensity is individual for all women, and quite often expectant mothers do not feel nausea or malaise at all.
A typical sign is also a change in taste preferences. A woman may crave foods that were not previously on her list of favorite foods. But nutrition should now be taken very seriously: the baby needs to receive all valuable nutrients, all harmful foods containing preservatives and dyes must be excluded from the menu, and alcohol should absolutely not be consumed.
Feelings of the expectant mother in the sixth week of pregnancy
A pregnant woman’s health in the sixth week is not the best. She feels weak in the morning and constantly wants to sleep. The unfortunate toxicosis fully manifests itself. Its manifestations can be different. Some women experience a loss of strength and morning sickness, while others experience toxicosis with daily painful vomiting, which can even lead to fainting.
A small percentage of women experience virtually no symptoms of toxicosis, which greatly facilitates the course of pregnancy.
Almost all pregnant women become very sensitive to odors during the sixth week. Their salivation increases, and their taste habits change dramatically. In most cases, this goes away over time, but if a severe deterioration in well-being occurs, this is a reason to consult a doctor.
Brown discharge in the sixth week of pregnancy may appear due to a lack of hCG. In this case, the doctor prescribes drugs that are synthetic analogues of the missing hormone and support pregnancy (Duphaston, Utrozhestan). These medications are usually taken for up to twelve weeks, after which there is no need to use them. In some cases, your doctor may recommend continuing to take these medications.
If a woman has a stomach ache in the sixth week, this may indicate a threat of miscarriage.
Body changes and new sensations for women
Most expectant mothers who did not feel any changes before will now probably encounter new sensations.
The fact is that week 6 is characterized by dramatic hormonal changes. At this time, the level of the hormone progesterone increases significantly. On the one hand, this is very good. It strengthens the mucous walls of the uterus, isolates it from the penetration of various infections from the vagina, and also inhibits muscle contractions, which is necessary to prevent miscarriages. On the other hand, excess progesterone negatively affects the digestive system and can cause nausea (usually in the morning) and even vomiting. Toxicosis during pregnancy is a very unpleasant phenomenon. But you should not despair, since morning vomiting, as a rule, is temporary. In addition to toxicosis, at the beginning of pregnancy some women's taste preferences change and sensitivity to various odors increases. Pregnant women notice darkening of their nipples, enlarged and sore breasts, they are worried about weakness in the body, dizziness and headaches. Some people experience whitish discharge in the form of flakes. There is no need to worry too much about this either - this happens due to an increase in the activity of the vaginal microflora. However, heavy discharge during pregnancy often indicates the development of candidiasis (thrush).
Examinations in the sixth week of pregnancy
During a visit to a gynecologist, a pregnant woman is examined and, based on the results of the examination, is prescribed the following tests:
- Blood test for hCG. A positive result allows you to establish the fact of pregnancy with 100% probability. If the hormone is not produced in sufficient quantities, the doctor prescribes a course of replacement therapy to prevent miscarriage.
- Ultrasound at 6 weeks of pregnancy. Prescribed according to indications.
- Blood test for hepatitis B, syphilis, HIV.
- Analysis to determine blood group and Rh factor. It is carried out to prevent Rhesus conflict.
- General blood and urine analysis. Helps determine the health status of a pregnant woman.
- Vaginal smear. This analysis is necessary to identify possible urogenital infections.
Visiting an obstetrician-gynecologist

Visiting a doctor for examination and tests
At the 6th obstetric week of pregnancy, it is not yet necessary to visit an obstetrician-gynecologist, but it is necessary in a number of cases:
- to confirm pregnancy;
- to exclude the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy: in the presence of pain, bleeding, improper attachment of the embryo in previous pregnancies;
- for consultation with severe manifestations of toxicosis;
- in the presence of complex chronic, infectious, bacterial diseases;
- for long-term pregnancy planning, IVF, etc.
At an appointment with a gynecologist, the doctor will calculate the obstetric period, conduct an examination in the chair, and give directions for tests for registration.
At the current stage, during a vaginal examination, the doctor can already notice changes that have occurred in the uterus; he will assess the condition of the breasts (noticeably rounded, with darkened nipples).
Additionally, he will ask about your feelings and recommend the necessary vitamin complexes. If you are concerned about any sign of pregnancy or changes in your health, be sure to discuss this with your gynecologist to get the most appropriate recommendations.
At the 6th week of pregnancy, the woman will be given directions for tests necessary to create an exchange card (a special journal in which all changes occurring with the expectant mother and baby are entered to assess and track the timeliness of the appearance of all necessary parameters). The exchange card contains information about the woman’s current health, previous diseases, allergic manifestations, etc.
Among the tests required in the first trimester of pregnancy, at your first appointment with a gynecologist you will receive a referral for:
- general blood analysis;
- blood test from a vein for sexually transmitted diseases;
- blood chemistry;
- measuring blood sugar levels (taken strictly on an empty stomach);
- analysis for the level of hCG and progesterone (to confirm the normal course of pregnancy);
- general urine analysis.
In addition to tests, a gynecologist can refer a woman for examination to specialists:
- ophthalmologist;
- cardiologist;
- otolaryngologist;
- endocrinologist;
- dentist.
At the 6th week of pregnancy, an examination by specialists is usually prescribed for consultation purposes for early detection of possible complications for the mother’s health. For example, women suffering from diabetes mellitus should be additionally monitored by an endocrinologist throughout their pregnancy to exclude possible complications. For myopia, monitoring by an ophthalmologist is necessary. Heart defects or diseases in an expectant mother are an indicator for thorough monitoring by a cardiologist.
If the doctor suspects a multiple or ectopic pregnancy (if there is bleeding and pain), the woman will be referred for a transvaginal ultrasound.
If the pregnancy is developing successfully, there is no need for an ultrasound examination of the fetus.
Ultrasound and tests
In most cases, at the 6th obstetric week of pregnancy, an ultrasound scan is performed on women with suspected complications. At the current stage, the study will show how enlarged the uterus is and where the fertilized egg is located. You can already clearly hear the fetal heartbeat. It is impossible to examine possible defects or developmental features at the current stage, therefore, if a woman has no symptoms or features of the course of previous pregnancies, an ultrasound scan is not prescribed.
If you take a hormone test at the 6th obstetric week of pregnancy, you can see a steady increase in progesterone (the pregnancy hormone). This important element performs a protective function: it helps to relax the muscles of the uterus, which prevents its contraction and prevents miscarriage. Progesterone promotes the growth of the uterus and ensures intense blood flow to its walls.
There should be no changes in normal blood and urine tests. If standard indicators increase or decrease, consultation with a gynecologist is necessary, and hospitalization is possible. In order for the tests to show the real picture, you must carefully follow the rules for taking them:
- before testing for sugar, blood biochemistry, you should not eat at night and before the procedure. These tests are taken strictly on an empty stomach;
- Urine analysis must be collected in a sterile container; before collection, you must wash yourself thoroughly to prevent the ingress of foreign bacteria;
- before taking tests, try not to drink coffee or tea, avoid stress and physical activity, get good sleep;
- It is best to take tests in the morning. Values may vary throughout the day, and laboratory values are based on morning averages.
Pain in the abdomen and other parts of the body
In the 6th obstetric week of pregnancy, there should normally be no pain. There may be unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen caused by the growth of the uterus and stretching of the abdominal muscles.
If you experience abdominal pain, especially on the right or lower left, you should consult a gynecologist. If the pain is very strong, growing, aggravated by palpation, but an ultrasound was not done to rule out an ectopic pregnancy, call an ambulance.
Discharge
Normally, at the 6th week of pregnancy (according to obstetric calculations), the discharge should be light, colorless and odorless.
Contact your gynecologist if you notice that the discharge:
- red or brown;
- yellow or greenish;
- have an unpleasant odor;
- curdled structure.
Bleeding and menstruation
At the 6th obstetric week of pregnancy, there should normally be no bleeding or menstruation. If slight or severe bleeding from the vagina occurs, you should consult a gynecologist. In rare cases, this is a normal process associated with the characteristics of the female body, but more often it is a symptom of an incipient miscarriage.