Computed tomography of the lungs is a highly sensitive method for detecting inflammatory diseases (pneumonia, abscesses), specific infectious processes (tuberculosis), traumatic changes, neoplasms in the lungs and mediastinum, abnormalities of the skeleton and soft tissue structures.
Unlike radiography, fluorography, CT of the lungs is not:
- mass, cheap and simple research method;
- in most cases it is used as a subsequent diagnostic procedure.
Features of computed tomography of the lungs in children
Young children almost never assist staff in performing the examination, as a result of which they must be restrained and use restraints.
With a young patient it is necessary:
- talk and calm him down;
- distract with a toy or watching cartoons.
It is possible, and sometimes necessary, for parents to be present during the study.
In a hospital setting, in restless children with severe pathology, for example, polytrauma, the use of anesthesia is acceptable.
However, tomography under anesthesia is performed extremely rarely, only in exceptional cases:
- due to the speed of the procedure - compared to MRI;
- low value of motion artifacts.
Older children tend to be more cooperative with staff. Their tomographic studies are closer to CT scans in adults.
Since children have a small body weight and smaller volume, special protocols are used with different voltage and current values, section thicknesses, etc. than in adults.
These protocols help:
- optimize radiation exposure;
- achieve greater resolution with a minimal dose;
- improve the quality of visualization.
So what to do?
Children are sick. And often the symptoms are such that it is difficult for a doctor to make a correct diagnosis without conducting examinations. In such cases, you can proceed according to the following scheme :
- Before performing a CT scan, it is necessary to use any other less informative, but safe for the child, examination methods, such as ultrasound, MRI, ECG, FGDS, etc. (in most cases, these methods provide the information necessary to make a diagnosis);
- CT is never performed as the first and only method of diagnosing a suspected disease, nor is it performed “just in case” or “to make sure everything is in order”;
- for examination, it is better to give preference to MSCT (multispiral computed tomography), since the radiation dose of such a tomograph for the patient is half that of a spiral one;
- It is best to conduct a targeted examination: the smaller the area being examined, the less harm there will be to the child’s body;
- Before carrying out the examination, it is necessary to find out what settings of the device are set by the staff: special settings are set for children, since half the radiation dose, or even less, is sufficient to “examine” a small child’s body in terms of volume and weight.
According to American researchers, in approximately 60% of cases the risk for the child is not justifiably high, since the indications for CT are not serious enough and/or it is possible to obtain the same information using other methods. In another 25% of cases, the harmful effects of X-rays can be reduced by choosing the correct radiation parameters sufficient to obtain clear and informative images of the child’s body.
Visualization approaches
Currently, spiral tomography using devices with 4-64 rows of detectors is considered a routine imaging method. Step-by-step CT scanning of a child is performed much less frequently.
Children cannot perform most respiratory tests or hold their breath. Therefore, it is necessary to perform the study as quickly as possible to avoid the appearance of artifacts. These conditions are well met by spiral tomography with a large step.
Keep in mind: the more rows of detectors the tomograph has, the higher the resolution of the scans, but the longer the examination time and dose.
Preparing for a chest CT scan
As a rule, the procedure does not require special preparation. But if a chest CT scan is performed on a child 3 years of age or older, general anesthesia may be required. Anesthesia is administered because children cannot remain still during the examination, which affects the clarity and information content of the images. A chest CT scan can be performed on a child 6 years of age or older without anesthesia if the parent or guardian can persuade the child to remain still while the examination is performed.
Pathological changes detected on CT
Most often, computed tomography is performed on children for inflammatory diseases (pneumonia, abscesses).
- Up to 90% of all tomographic studies in childhood are caused by pneumonia.
- The second most common cause is pulmonary tuberculosis (5-8%).
- The third reason is injuries to the bone frame of the chest, spine, soft tissues, as well as wounds.
- The fourth reason is neoplasms in the lungs and mediastinum. This can include enlargement of the thymus gland.
- The study is also performed to evaluate anomalies, for example, accessory or wedge-shaped vertebrae, fusion of ribs, and developmental disorders of soft tissue structures.
- Relatively rarely, a CT scan of the lungs is performed to assess postoperative changes. Changes detected on tomograms have higher specificity compared to traditional radiography.
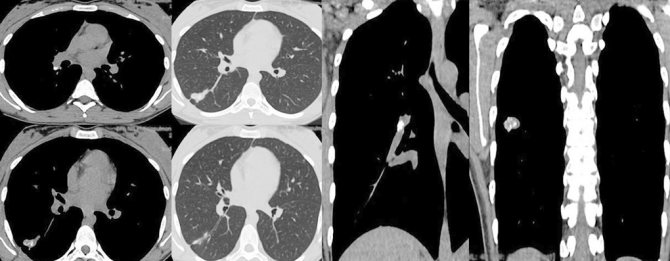
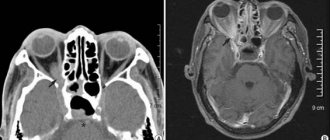
CT scan of a child with a positive test for recombinant tuberculosis allergen
Indications for lung tomography
The main indication is the presence of respiratory symptoms (cough, shortness of breath) against a background of elevated body temperature, detection of wheezing when listening to the lungs and changes in blood tests indicating inflammation.
Other main indications:
- injuries;
- injuries;
- suspicion of a tumor;
- contact with people sick with tuberculosis against the background of specific skin tests;
- previously identified anomalies in the development of the skeleton and soft tissues;
- enlargement of the thymus.
For the purpose of early detection of diseases in healthy children, tomographic methods are not used in Russia.
Lung CT is much more informative than radiography, but is not used for screening in children.
Types of CT scans and diseases diagnosed using the method
- Head (brain, vessels, sinuses) - diagnosis of aneurysm, atherosclerosis, hematoma, tumor, cyst, sinusitis, sinusitis, abscess, fracture, foreign body, developmental anomaly, the stroke area is specified, etc.
- Spine - osteoporosis, scoliosis, hernia, trauma, tumor, etc.
- Neck - tumors, pathologies of the cervical lymph nodes, great vessels of the neck, identification of diseases of the pharynx, larynx and thyroid gland.
- Chest - detection of tumors, tuberculosis, pneumonia, malformations, chronic nonspecific diseases, foreign bodies, control after surgery, assessment of mediastinal structures.
- Joints and bones - detection of inflammation, tumors, trauma (cracks and fractures), changes in tissue density, monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
- Abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space - diagnosis of diseases of the abdominal organs (stomach, liver, kidneys, adrenal glands, gall bladder, spleen, pancreas, intestines), pelvic organs (uterus, ovaries, prostate gland, urinary tract), heart and blood vessels and etc.
Methodology of the procedure
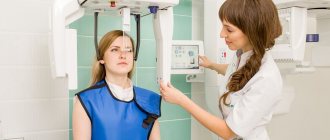
- First, parents are explained how the study is performed.
- After signing the consent or other documents, which depends on the clinic, the patient is placed on the tomograph table.
- Small children are additionally fixed on it using standard devices, older children usually lie freely, like adults.
Parents are in the same room or outside it. Then the scanning begins. The patient is asked through a loudspeaker to inhale and not breathe while the CT scanner takes preliminary scans used for marking.
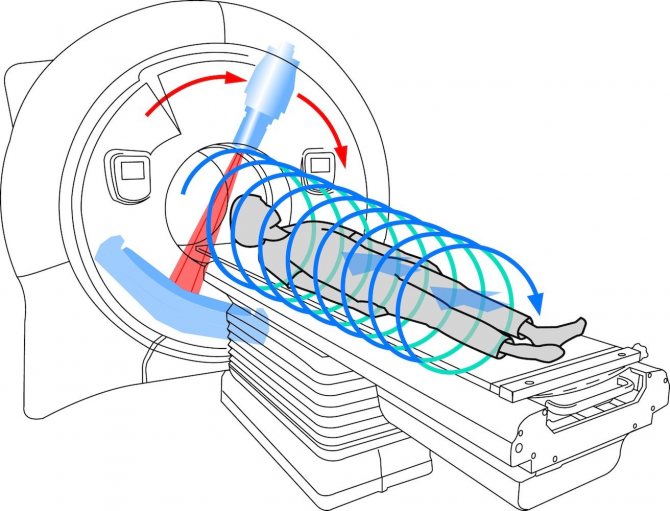
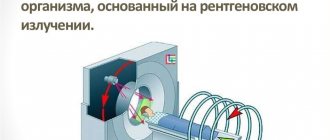
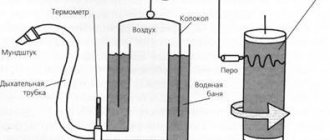
The principle of operation of a computed tomograph
Further:
- a series of transverse scans of the body is performed;
- the images are transmitted to the workstation, where they are analyzed and the detected violations are described;
- After the above steps, the doctor forms a conclusion.
Occasionally, the study is performed with the introduction of contrast. This is more difficult and requires special training.
Preparing for tomography
In most cases, no special preparation is required. Necessary:
- remove all metal objects, such as jewelry, from the scanning area, which may cause image distortion;
- remove thick and tight clothing,
- remove items with metallic threads and buttons.
If CT is performed with contrast, you must first:
- exclude a history of allergic conditions to any drug, especially iodine;
- undergo laboratory tests to rule out renal dysfunction.
Study execution process
You need to lie on the tomograph table - most often on your back, much less often on your side or stomach - and follow the commands given.
The table moves inside the tomograph ring, where there is a tube on one side and a row of detectors on the other. During the examination, you will need to repeatedly hold your breath for short periods of time - from a few seconds to a minute.

The procedure will take no more than five minutes, in many cases less. The doctor or laboratory assistant will notify you of the completion of the study. All that remains is to get up from the table and wait for the results.
Recommendations after the procedure
If the tomography was performed with contrast, it is necessary to drink more of any liquid (water, juice, tea) in order to quickly eliminate the contrast agent by the kidneys. If contrast was not administered, the only thing to do is wait for the conclusion and follow the recommendations given by the doctor.
Presence of contraindications
There are no absolute contraindications to CT without contrast. Relative ones are:
- increased excitability of the child;
- unmotivated refusal to study.
For the most part, all contraindications are related to contrast, which can lead to:
- to allergic reactions;
- impairment of excretory renal function.
However, even with a high level of creatinine in the blood, it is possible to perform a test after it has stabilized.
Possible risks in children
The risks associated with radiation are small, but they do occur. Thus, there are several foreign studies that reliably prove an increase in the appearance of tumors in the brain (gliomas, neurofibromas, etc.) and the blood system (leukemia) when a certain cumulative dose is reached.
- The younger the age, the higher the risk.
- The older the patient, the lower the risk due to a decrease in the number of actively dividing tissues.
Thus, a CT scan is more dangerous for a three-year-old child than for a 17-year-old teenager. Other risks are associated with the introduction of contrast, which provokes:
- allergic reactions;
- kidney damage.
In addition, there is a risk of injury to the child when performing a CT scan, which is extremely rare, only if there is improper fixation and lack of control.
Attention! Do not perform a CT scan on a child without the recommendation of a clinician!
Price
Costs may vary between clinics. Each institution sets its own prices:
- depending on age;
- the need for contrast;
- discount policies, etc.
On average, prices for CT scans of the lungs in Moscow and St. Petersburg start at the beginning of 2021 from one and a half thousand rubles - without contrast, and can reach up to five thousand rubles or more if contrast agents are used.
Recently, CT scanning of the lungs for children has been gaining popularity as a method for diagnosing pneumonia, which is likely due to the expansion of the network of tomographs in the country. The transition from traditional radiography to layer-by-layer studies is clearly visible.
Protocols are constantly being improved, in some cases it is possible to reduce the dose to 0.1-0.2 mSv, which is not much higher than with radiography, fluorography, etc.
Where can I get a CT scan of the lungs?
The cost of performing a computed tomography scan of the lungs is determined by several factors: whether a contrast agent will be used, what device will be used for the study, whether the patient needs to record data on an external medium, and in which clinic the examination is taking place.
Today, prices in Moscow for CT scans of the lungs vary from 3 thousand to 7 thousand rubles. To carry out the procedure, you must have your passport, directions and medical card with you:
- Health Clinic. Open daily from 09:00 to 21:00, located at: st. Maroseyka, 2/15, building Kitay-Gorod metro station.
- SM-Clinic. The multidisciplinary medical center allows you to undergo examinations at night and on weekends, with a 15% discount. You can find the clinic at two addresses: st. Klara Zetkin, 33 building 28 (metro station Voikovskaya), Volgogradsky Prospekt, 42, building 12 (metro station Tekstilshchiki).
- Diagnostic. Open on weekdays from 08:00 to 21:00, on Saturday – from 09:00 to 21:00, on Sunday – from 09:00 to 18:00.