Why is genetic testing performed during pregnancy?
Testing is carried out to obtain the following information:
- How genetically compatible are partners who want to have a child together?
- Is there a hereditary predisposition in the child to certain diseases?
- Are infectious agents present in the body of the mother or unborn baby?
- To obtain a genetic passport of a person, which is a combined DNA analysis with information about the uniqueness of a particular person.
During a frozen pregnancy, increased attention is paid to analysis. Miscarriage often occurs due to congenital thrombophilia, the presence of which, analysis, will allow us to identify and take the necessary actions to save the child. In case of repeated cases of a non-developing fetus, an analysis should be done to find out the karyotype with the chromosome set of the embryo. The doctor will check the pregnant woman’s level of cytokines, the level of which is significantly reduced when the fetus freezes.
Nutritional Features
Nutrient levels
Good eating habits help us get the vitamins, minerals and fatty acids we need. These elements enter the body with food and are converted into substances necessary for the body. In this they are helped by proteins, for which genes are also responsible - some accumulate the substance in excess, while others may lack it.
For example, some people have a genetic predisposition to accumulate iron in their tissues. The human body is not able to get rid of iron on its own, and an oversaturation with it can cause health problems such as arthritis, liver and heart problems, and diabetes.
Sometimes the body cannot extract enough iron from foods on its own, even when eating the recommended intake (RDA), which can cause anemia.
Genetic test results include taste perception, nutrient response, vitamin and mineral levels, omega 3 and 6 fatty acids. All this is reflected in the Nutrition section in your personal account.
Response to nutrients
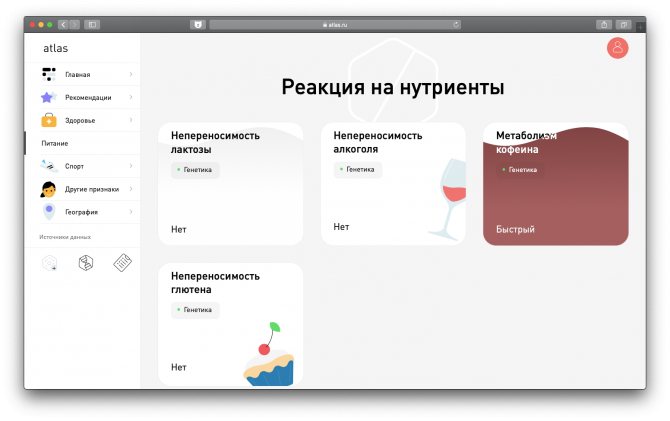
Our body uses proteins to break down the food and drinks we consume. Alcohol, gluten or lactose intolerance occurs when the body does not produce the enzymes needed to break them down.
In this case, such compounds provoke a series of responses that cause discomfort or more serious problems. In fact, alcohol, gluten or lactose intolerance is a genetic trait that is common in certain populations.
Gluten is a naturally occurring protein that is formed in wheat, barley and other grains. Its use in some people causes an immune response - the body's reaction to a potentially dangerous substance, against which special cells are mobilized to destroy it.
The test helps identify genetic factors that predispose you to gluten intolerance.
Caffeine is found in coffee, tea, cocoa, chocolate, and energy drinks. Most often, consuming caffeine in moderation is safe. However, there are times when drinking caffeine can cause unpleasant symptoms: irritability, insomnia, headaches and heart rhythm disturbances.
This is due to the fact that in some people the activity of proteins responsible for caffeine metabolism changes at the genetic level. As a result, caffeine has a longer lasting effect on the body and leads to unwanted effects.
Taste

You probably have friends who don't like cilantro or think your favorite vegetables taste terrible. There are a large number of eating behavior patterns embedded in us at the genetic level.
Eating behavior influences your food choices, which in turn can have a positive or negative effect on your health. For example, if you don't like bitter-tasting foods, you'll likely avoid iron-rich, dark green vegetables and strong-tasting drinks like coffee. This can lead to a decrease in dietary diversity, which negatively impacts the gut microbiota.
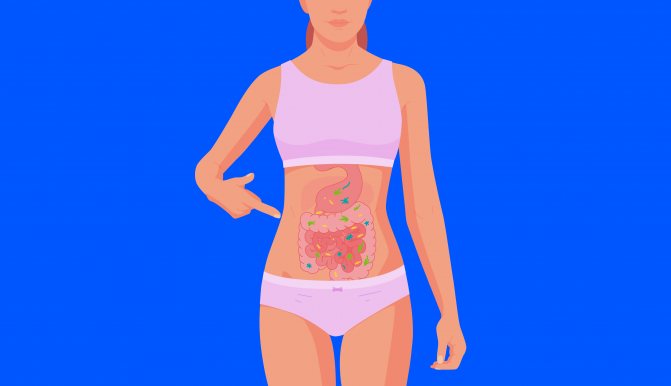
Microbiota. What kind of organ is this and why do we need it?
The gut microbiota is an ecosystem consisting primarily of bacteria that inhabit the large intestine. A healthy microbiota protects the body from disease and supports physical and psychological health.
Indications for analysis
If a pregnant woman is at risk, a genetic test is a desirable procedure that the doctor will recommend first. The list of indications includes:

- Age over 35 years.
- The woman has previously given birth to children with abnormal features or serious developmental defects.
- The expectant mother suffered a health-threatening infection.
- The lady suffered from alcohol or drug addiction.
- During previous pregnancies, there have been cases of fetal failure, miscarriage or stillbirth.
High risk group
Some women are at higher risk. In this case, you will have to do an analysis:
- The woman has hereditary diseases.
- During a previous pregnancy, a child was born with developmental defects or congenital anomalies.
- A woman, a man, or both partners suffer from dangerous infectious or viral diseases (hepatitis, HIV, herpes).
- A woman suffered from chickenpox or rubella during pregnancy.
- The lady used potent medications that are undesirable to take during pregnancy.
- In the early stages of pregnancy, a radiation dose was received during a fluorographic or x-ray examination.
- The woman was involved in strength and extreme sports.
- The expectant mother suffered an increased dose of UV radiation.
Types of Genetic Tests
Many parents wonder why genetic testing is needed. Doctors answer unequivocally: testing, which is preferably carried out while planning a future child, will minimize the risk of having a baby with genetic developmental pathologies. If tests are carried out before conception, the doctor will be able to determine whether there is a risk and suggest effective ways to solve the problem. When testing, doctors take tests to identify monoheme diseases and chromosomal rearrangements.
The basis of modern medicine has been and remains the early detection of diseases. Prenatal diagnosis occupies a fairly significant niche among diagnostic studies, thanks to which it is possible to identify most developmental anomalies and chromosomal mutations at the stage of intrauterine life. One of these examinations during pregnancy is the “double test”, or “genetic double test”.
Genetic twin - what is it? Simply put, this is a standard screening test that is carried out in the first trimester of pregnancy to identify a group at risk for genetic disorders. No matter how scary this definition may sound, to carry out a “genetic match” a banal blood sample is taken from a vein, so such a procedure will not cause any harm to expectant mothers.
“Genetic two” - what is this action and who is involved in it?
To find a pregnant woman who is not worried about the health of her unborn child, you will have to work hard, because almost every expectant mother is, to one degree or another, concerned about the general condition of her child. Prenatal screening was invented, first of all, to identify the risk of chromosomal diseases, severe malformations in a given fetus, as well as to eliminate anxiety in a caring mother who wishes her “blood” happiness and good health.
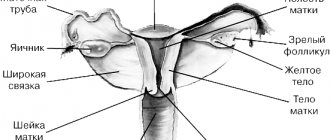
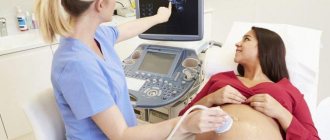
Genetic pairing is a biochemical study of specific blood proteins, namely beta-hCG and plasma protein PAPP-A, which are markers of certain hereditary diseases. As a rule, “genetic pairing” is carried out in combination with an ultrasound examination of the uterus, during which special attention is paid to the collar area of the fetus (cervical fold, width of the cervical translucency).
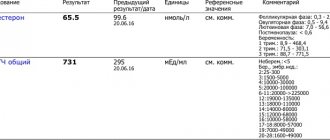
IMPORTANT! Determining the concentration of beta-hCG and PAPP-A in the mother's blood allows us to judge the health of the fetus. The values of these indicators are determined depending on the duration of pregnancy and are compared with generally established standards.
Testing for a “genetic double”: how does it happen?
According to the protocols of the antenatal clinic, all pregnant women up to 12 weeks are sent for a screening examination to the medical genetic center. This method of prenatal diagnosis is very effective, as it allows you to identify the most common genetic mutations.
The optimal time for “genetic twinning” is from 10 to 13 weeks of pregnancy. The first stage of screening is an ultrasound examination of the fetus, the purpose of which is to identify gross developmental anomalies incompatible with life. Along with this, the doctor assesses the thickness of the fetal neck fold and the size of the nasal bone - diagnostic criteria for Down syndrome.
After the ultrasound, the woman is sent to the second stage - biochemical screening. Taking blood from a vein with subsequent analysis of this biological material makes it possible to determine the level of plasma pregnancy protein PAPP-A and the free beta subunit of human chorionic hormone.
Question answer.
Genetic doubles - what is it and who is it shown to?
According to WHO recommendations, a double genetic test is strongly recommended for:
- pregnant woman over 35 years of age;
- taking large doses of medications shortly before conception;
- presence of children with genetic disorders;
- presence of cases of chromosomal disorders in the family;
- radiation exposure before conception, etc.
What chromosomal diseases can a “genetic double” be suspected?
A double genetic test is necessary to exclude chromosomal pathologies such as trisomy 21 (Down syndrome), trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome). To identify neural tube defects, that is, pathology of the development of the central nervous system of the fetus, a triple genetic test is required from 16 to 18 weeks.
At what stages of pregnancy is prenatal screening performed?
- Conducting a “genetic twin”: 11-13 weeks (up to 14 weeks is acceptable).
- Carrying out a triple test: 16-18 (permissible up to 20 weeks).
“Genetic double” - what is it, a pre-planned examination or a standard trip to the hospital?
No special preparation is required before this examination. To obtain the most reliable results, it is recommended:
- conduct an ultrasound examination no earlier than a week before the “genetic twin”;
- draw blood from a vein in the morning, preferably on an empty stomach.
What factors can influence the result of the “genetic pairing”?
The level of prenatal markers (b-hCG, estriol, PAPP, AFP) may not correspond to standard values due to:
- the presence of a chromosomal mutation in the fetus;
- pathologies of development of the brain and spinal cord;
- threats of abortion;
- intrauterine developmental delay of the fetus;
- disturbances of fetal-placental blood flow;
- development of severe toxicosis;
- taking Utrozhestan or Duphaston;
- multiple pregnancy.
What parameters are taken into account when assessing the results of “genetic pairing”?
- Age and ethnicity of the woman;
- Having bad habits (smoking);
- History of pregnancy and childbirth;
- Pregnant body weight;
- Presence of somatic diseases;
- Metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, obesity).
How to interpret the results of the “genetic double”?
Test results vary depending on the stage of pregnancy. The unit of measurement, MoM, indicates the degree of deviation of a given analysis from the norm. As a rule, MoM fluctuates between 0.5-2 throughout pregnancy. A deviation from the average value in one direction or another may indicate a high risk of developing chromosomal diseases.
What is the threshold value for a double test?
The results of biochemical screening are obtained by using special programs designed to determine the most reliable values. The threshold value for conducting a “genetic match” is 1:250, that is, it means that the probability of having a baby with genetic disorders corresponds to 1 case in 250 births. The lower the number in the “denominator” (for example, 1:150 or 1:30), the higher the risk of the presence of a genetic pathology.
It must be remembered that prenatal screening is one of the methods for determining the risk of chromosomal disorders. Regardless of the results of the “genetic double”, the final diagnosis can be made only after additional studies of the fetal condition.
Monohemeic diseases
Monogeneic diseases are understood as failures caused by certain types of mutations. Each person is a carrier of approximately seven mutations. But this does not mean that everyone is sick. There is a second copy of the gene in the body that does not have abnormalities. The risk of having a child with pathologies increases only if both partners have the same mutation in the same gene.
The likelihood of mutations increases in certain nationalities living within a single population for a long time. Indigenous Europeans often suffer from cystic fibrosis and spinal muscular atrophy. Almost three percent of Europeans have a gene with similar mutations.
PAPP-A – protein
PAPP-A is needed for the growth and development of the placenta, so this level increases as pregnancy progresses. If the fetus has a chromosomal abnormality, then this enzyme often decreases between 8 and 14 weeks of pregnancy - precisely at the time of the first screening.
The lower the PAPP-A level, the more severe the child’s defect may be - from trisomy 21, 18 or 13 (Down, Edwards and Patau syndrome, respectively), to Cornelia de Lange syndrome - a severe genetic pathology with multiple developmental defects. The nuance is that after 14 weeks, even with serious disorders and anomalies in the fetus, the level of PAPP-A is in accordance with the norm in the specified period. Therefore, this substance must be analyzed within a certain period of time.
Chromosomal rearrangements
Chromosome rearrangements mean the process in which normal chromosomes, without abnormalities or mutations, change places. The presence of chromosomal translocations cannot be determined by external signs, but such people often have problems in the reproductive sphere. It is because of chromosomal rearrangements that miscarriages occur, children are stillborn or children with serious developmental defects are born.
To determine the presence of chromosomal rearrangements, karyotyration is performed. Further actions are carried out depending on the result obtained.
If the doctor finds abnormalities in the same gene in both parents, two options will be offered:
- Preimplantation diagnosis or PGD is a manipulation that is included in the IVF program to identify genetic disorders even before the embryo is transferred into the uterine cavity.
- Non-invasive prenatal test or NIPT - a blood test performed on a pregnant woman to detect chromosomal abnormalities after 10 weeks.
Menu (Meal Schedule)
Menu for every day of the Deuce diet
It is best to eat at the same time, finishing meals before 19:00. A couple of days before the start, you can spend a fasting day on kefir or another product (pomelo, buckwheat), and then eat a menu of up to 1200 calories for two days. Then for 10 days you have only “two foods” and a certain serving size at your disposal:
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|