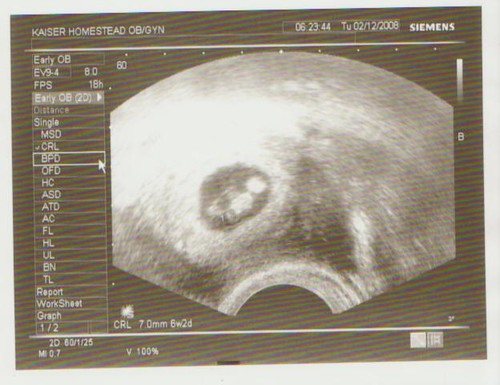
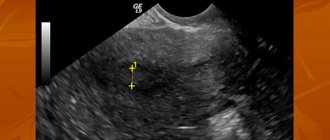
Ultrasound in gynecology is a study that is used to study the condition of female organs, the periuterine space and the ligaments that support the uterus. Accurate, safe and affordable ultrasound diagnostics can be used the required number of times without any damage to the female body.
At the MedicCity clinic, gynecological examinations are performed using expert-class equipment. The Voluson 10 ultrasound scanner, due to its excellent visualization quality and automated measurement technologies, ensures diagnostic accuracy of up to 85-95% even in the most clinically complex cases.
1 Ultrasound in gynecology

2 Ultrasound scanner Voluson 10
3 Transabdominal ultrasound
The history of the use of ultrasound in gynecology dates back to 1958. Then the British doctor D. Donald carried out the first measurement of the fetal head in the uterus using ultrasound.
In the 1980-90s, new, well-equipped ultrasound systems appeared that made it possible to obtain a clear three-dimensional image of the female organs and the developmental features of the unborn baby. Previously, such diagnostics could only be dreamed of.
Types of ultrasound in gynecology
Ultrasound in gynecology can be performed in three ways. The following types are distinguished:
- transrectal ultrasound (performed through the rectum in girls who are not sexually active);
- transvaginal ultrasound (carried out by inserting a sensor into the vagina for an accurate examination of diseases of the pelvic organs);
- transabdominal ( or simply abdominal) ultrasound , or simply abdominal ultrasound (performed through the abdominal wall when signs of inflammation of the pelvic organs are detected or in girls who are not sexually active).

1 Ultrasound in gynecology
2 Ultrasound scanner Voluson 10
3 Ultrasound in gynecology
For what indications is an ultrasound of the pelvic organs performed in women?
- identifying the causes of infertility;
- menstrual irregularities;
- assessment of pathology of the uterus and ovaries;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs: endometritis, parametritis, vulvovaginitis, salpingoopharitis;
- vaginal discharge;
- study of the nature of pelvic tumors (bladder cancer, fibroids, uterine cancer);
- inflammatory diseases of the urinary system (cystitis, pyelonephritis, urolithiasis);
- study of the condition of the ovaries and uterus during IVF;
- surgical manipulation of the bladder, uterus, fallopian tubes or ovaries;
- complications of pregnancy;
- monitoring the installed intrauterine device (see methods of contraception).
What diseases and conditions can ultrasound detect in gynecology?
- tumor processes in the pelvic area;
- torsion of ovarian cyst; ovarian cyst;
- complications after pregnancy and childbirth;
- pathology of the development of the uterus and appendages (duplication of the fallopian tubes, underdeveloped “infantile” uterus, bicornuate, saddle-shaped uterus);
- endometrial polyps;
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes (formation of adhesions and constrictions);
- the presence of fluid in the pelvic organs;
- uterine fibroids;
- pelvic inflammatory diseases, endometriosis;
- pregnancy (uterine and ectopic).

1 Ultrasound in gynecology

2 Ultrasound scanner Voluson 10
3 Ultrasound in gynecology
A female ultrasound will help determine the following indicators:
- ovarian size;
- the presence and type of ovarian cysts (follicular, luteal, endometrioid);
- size and shape of the uterus;
- thickness of the uterine mucosa (varies depending on the day of the cycle);
- the presence of tumors of the uterus and appendages, their location and the nature of the formation (benign or malignant).
How men are examined
The study is mandatory for patients with complaints of various urinary problems, unpleasant or even painful sensations in the pelvis, with impaired potency, as well as for preventive purposes after 40 years.
What do they look for on a pelvic ultrasound in men? Depending on the preliminary diagnosis, the doctor examines the bladder, seminal vesicles, prostate, and looks at the lymph nodes located nearby.
For diseases of the bladder, ultrasound is performed transabdominally - through the anterior abdominal wall. The patient lies on a medical couch, exposes the lower abdomen, onto which the doctor applies a special gel to improve the signal from the sensor. The procedure lasts approximately 20 minutes. Before the examination, it is often necessary to fill the bladder, and after the examination, carry out a second examination, but with an empty bladder.
In cases where it is necessary to examine the prostate and/or seminal vesicles, an ultrasound examination of the organs is done by inserting a special sensor through the anus - the so-called transrectal ultrasound or TRUS. This method causes a somewhat uncomfortable feeling in the patient, however, with this type of examination, the device’s sensor is in close contact with the prostate gland, which means a detailed examination of the organ by the doctor and the most accurate conclusion.
Features of preparation for gynecological ultrasound
Preparation for an ultrasound of the pelvic organs in women will differ depending on the method of examination.
Transabdominal ultrasound
In order for the study to be as high-quality as possible, you will need a little preparation. It is necessary to adhere to a diet for three days that excludes foods that cause fermentation (carbonated drinks, black bread, cabbage, sweets, fresh berries and fruits, fatty foods).
If you have a morning study planned, then your last meal should take place no later than 18.00-19.00, and you can drink some water in the morning.
If a gynecological ultrasound takes place in the evening, then the last time before the procedure you can eat something light until 12.00, no less than 5 hours before the examination.
1 hour before the test you need to drink 1 liter of clean, still water.
Preparing for a transvaginal ultrasound
A vaginal ultrasound also requires some preparation. For 1-2 days before the test, try to eliminate foods that cause gas. You should not eat food 4 hours before the test. The procedure is performed on an empty bladder, so you will need to urinate before the procedure.
Preparation for transrectal gynecological ultrasound
A diet is also indicated for 1-2 days before the procedure. The night before, it is necessary to cleanse the intestines (using a glycerin suppository or a small microenema).
Progress of the procedure
This type of ultrasound is performed with an empty bladder. If the procedure is combined with a transabdominal ultrasound that requires filling of the bladder, it is necessary to interrupt the examination and empty the bladder.
The patient undresses from the waist down and sits on a special couch, lying on her back. The doctor puts a nozzle on the sensor (a special condom), lubricates it with gel and inserts it into the patient’s vagina. For a better view, it can move the sensor from side to side. The information is recorded on the screen and assessed by a specialist. The diagnostic procedure takes no more than 10 minutes.
When is it better to perform an ultrasound of the pelvic organs in women?
In normal cases, the procedure is best performed in the first half of the menstrual cycle. Ultrasound for uterine fibroids will be effective if performed on days 5-10 of the cycle, since at this time the endometrium becomes quite thin and all changes are visible on it. At the same time, formations such as polyps, synechiae or adhesions in the uterine cavity, and malformations of the genital organs can be found in the mucous membrane of the uterus.
If an ultrasound of the pelvic organs in women is performed in the second half of the cycle, then distortions are possible. By the middle of the menstrual cycle, a follicle forms in the ovary, which may look like a small cyst on the monitor. The corpus luteum (luteal) can also give the same picture on an ultrasound.
If the following symptoms occur, the examination is carried out regardless of the cycle:
- more heavy discharge during menstruation than usual;
- the appearance of blood outside of menstruation;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- bloody discharge with pus;
- painful sensations in the lower abdomen.
Indications for diagnosis
Indications for performing a vaginal ultrasound include:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- suspicion of tumors and neoplasms (based on palpation results);
- menstrual irregularities;
- infertility;
- bloody discharge from the genital tract;
- complicated course of pregnancy and the postpartum period, etc.
In some cases, the examination is carried out for preventive purposes. It allows you to accurately evaluate:
- asymptomatic diseases of the female genital organs;
- anatomical and functional features of the uterus and appendages;
- growth rates and features of fetal development (screening studies of the 1st, 2nd and 3rd trimesters).
Ultrasound of small pelvis organs occupies a special place when planning pregnancy. It allows you to monitor the process of formation and release of eggs, assess the condition of the inner layer of the uterus (endometrium) and the patency of the fallopian tubes (using special contrast solutions). The first study is carried out on days 5-7 of the menstrual cycle, then from days 10 to 14 the growth of the follicle and the moment of ovulation are monitored (slight shifts in timing are possible due to the individual characteristics and length of the patient’s cycle). Echo-hysterosalpingography (assessment of fallopian tube patency) is performed on days 8-12 of the cycle.
What is pelvic ultrasound
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs is a diagnostic procedure aimed at visualizing the structure of organs, mainly the genitourinary system. Based on the properties of ultrasonic waves emitted by a special sensor, as well as on the basis of the reflectivity of body tissues, when conducting a study on the monitor screen, the doctor sees an image of the organs and tissues of the area being examined.
Provided the doctor has the required level of knowledge and practical skills, he can immediately interpret what he sees, suspecting or ruling out pathology of the pelvic organs.
Based on the ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, the doctor issues a conclusion, on the basis of which a final diagnosis will be made in the future and an appropriate treatment regimen will be prescribed.
Today, doctors use several options for ultrasound in this area: transabdominal, transvaginal and transrectal examination. Each method has its own characteristics, which we will discuss in more detail.
What will a vaginal ultrasound examination show?
Vaginal ultrasound allows you to determine:
- the size of the uterus and ovaries, their location in the pelvis and relative to each other;
- echogenicity (structure) of tissues;
- the presence of pathological changes in the pelvic organs.
With the help of transvaginal examination it is possible to identify:
- the presence of free fluid behind the uterus, in the fallopian tubes (pus, blood, etc.);
- endometriosis is a pathological change in the walls of the uterus and ovaries;
- fibroids - a benign tumor of the muscular layer of the uterus;
- PCOS is a disease associated with hormonal imbalance and characterized by the formation of multiple cysts;
- ovarian cysts are benign formations;
- cervical and endometrial polyps;
- inflammatory diseases (salpingoophoritis, endometritis, etc.);
- anatomical features of the female genital organs (duplication, presence of an additional horn, absence of a uterus, etc.);
- oncological diseases;
- pathological formations of neighboring organs (bladder, intestines, soft tissues of the pelvis;
- the presence of an ectopic pregnancy (attachment of the fertilized egg in the fallopian tube, on the ovary, in the abdominal cavity, cervix);
- varicose veins of the small pelvis.
During pregnancy, such a study allows you to evaluate the development of the fertilized egg, the condition of the cervix, etc.
What are the benefits of uterine ultrasound?
The undeniable advantages of ultrasound examination as a method for diagnosing the condition of the uterus and its appendages include the following:
- in the vast majority of cases the procedure is painless;
- does not require special training other than following simple doctor’s recommendations regarding diet, genital hygiene and a number of additional procedures (gastric lavage or drinking plenty of fluids to fill the bladder - depending on the diagnostic method);
- efficiency of implementation and versatility;
- accessibility for a wide range of patients (due to the simplicity of the procedure, it is not expensive);
- the ultrasound method is absolutely harmless for women of any age, since it does not involve exposure to any significant radiation on the body;
- allows you to obtain reliable results in real time, which is why it is used to monitor the state of organs over time.
Today, ultrasound of the uterus and appendages remains one of the most informative methods for diagnosing various diseases of the female reproductive system. This method is also relevant in oncological practice; it allows identifying various neoplasms in the early stages of the clinical course of various etiologies. It often becomes an important part of diagnostics in reproductive medicine.
Author of the article: general practitioner Valentina Vasilyeva
How to properly prepare for an ultrasound examination of the uterus?
The first rule of almost any ultrasound is the absence of intestinal gases, which interfere with the correct passage of ultrasound waves and, accordingly, can significantly distort the results of the study. It is recommended to stop consuming foods that increase gas formation - in particular, carbonated drinks and foods rich in fiber - at least two days before the procedure. To eliminate excess gases in the body, a day before the ultrasound, take the recommended dose of activated carbon (or another drug aimed at eliminating excess gas formation). Other preparation features depend on the specific method (transvaginal or transabdominal), as well as the time of day for which the study is scheduled.
When is an ultrasound of the uterus performed?
|
| arincrumley flickr |
Ultrasound examination of the uterus, ovaries and appendages is also carried out in the following cases:
- during a routine examination of the female body;
- to determine early pregnancy;
- painful or irregular periods;
- uterine bleeding, including during menopause;
- pain in the pelvic organs - both during sexual intercourse and regardless of its presence;
- when planning pregnancy;
- if you suspect an ectopic pregnancy;
- to establish the causes of infertility - if attempts to get pregnant for six months or more have not been successful;
- to monitor the condition of the uterus after installation of an intrauterine device;
- to monitor the condition of a woman’s body and the development of the fetus during pregnancy - in order to promptly identify possible pathologies and take measures to eliminate them;
- in order to monitor the condition of the uterus after childbirth, mandatory if the birth was carried out by caesarean section.
- when a patient applies for an abortion or if there are medical indications for this.
How to properly prepare for a transvaginal ultrasound procedure?
It is very important to sign up for an ultrasound scan at a certain time - given the characteristics of the female body, you will get the most complete picture with this method of examination for prevention at the very beginning of the menstrual cycle. Therefore, in this case, you need to sign up for the first day without menstruation. If you are going to do an ultrasound because you suspect endometriosis, it is optimal to choose the second half of the cycle. For pregnant women, transvaginal ultrasound is prescribed exclusively in the first trimester, if there are direct indications for this. The only reason why you should undergo this procedure without delay and as soon as possible is bleeding of an unknown nature.
Ultrasound of the mammary glands
Until the age of 40, women are recommended to undergo annual preventive ultrasound examination of the mammary glands. Ultrasound helps identify a number of serious diseases:
- mastitis;
- mastopathy;
- cysts;
- fibroadenomas;
- cancerous tumor.
It is recommended to undergo this examination if:
- injuries;
- inflammatory diseases of the breast;
- detection of volumetric or diffuse formations during examination.
The study is highly informative when identifying the initial manifestations of pathological processes in the mammary glands, studying the vascular pattern and architectonics of the mammary glands, assessing the condition of silicone and gel implants, as well as when examining nursing and pregnant women.
Sign up for a study