General blood tests
04/03/201801/24/2019 Yulia Martynovich (Peshkova) 2615 Views lymphocytes, general tests
It is very difficult to overestimate the role of lymphocytes in making a diagnosis and protecting a person. This is one of the first indicators that responds to infectious infection, the development of a malignant neoplasm, allergies or the negative effects of medications. Also, lymphocytes (normal in men and women) depend on the age of the patient.
Before you figure out what is the danger of lymphocytes deviating from the norm, you need to understand: what kind of cells are they and what functions do they perform?
- 1 Lymphocytes and their functions
- 2 Indications for analysis
- 3 Norms of lymphocytes in the blood of men 3.1 Norms of various types of leukocytes
Lymphocytes and their functions
Lymphocytes are one of the types of white blood cells (leukocytes). A common feature for all leukocytes: the presence of a formed nucleus and the absence of the cell’s own color. Depending on the morphology, it is customary to distinguish between large granular cells and small cells without granules. Each type of lymphocyte performs its own function, however, the general functionality is reduced to protecting the human body from infections and its own mutant cells.
According to the functional classification, lymphocytes are divided into three groups, which are presented in the table.
| Type | Functions | Place of synthesis |
| B cells | Production of protein antibodies that are strictly specific to foreign antigens | During fetal development - bone marrow and liver, after birth - bone marrow |
| T cells | T helper cells are involved in the activation of other immune cells; stimulate the production of antibodies | Thymus |
| T-suppressors determine the duration of the immune response and its severity | ||
| Natural killers | Destroy infected and cancer cells | Formed from lymphoblasts - cells that have not yet come into contact with foreign antigens |
The number of lymphocytes is determined as part of a general blood test (sodium lauryl sulfate method) or leukocyte formula (flow cytometry). The period for obtaining analysis results does not exceed 1 day.
Why are lymphocytes necessary?
B-lymphocytes, when in contact with foreign proteins, secrete protective immunoglobulins. They provide long-term, and often lifelong, immunity to diseases, including after vaccination.- T-lymphocytes destroy intracellular parasites, virus-infected cells, and are also responsible for the intensity of the immune response.
- NK lymphocytes attack cancer cells.
Indications for analysis
A man can receive a referral for testing from a general practitioner, infectious disease specialist, urologist, surgeon or hematologist. Determining the level of lymphocytes in the blood is relevant if necessary:
- general clinical routine examination;
- preparation for surgical intervention of any degree of complexity;
- symptoms of infectious or parasitic infection (fever, cough, nausea, weakness, pain of various localizations);
- primary diagnosis of an allergic reaction and determining the degree of its severity;
- identifying leukemia and assessing the effectiveness of selected treatment methods;
- suspected cancer;
- suspicion of various immunodeficiencies;
- diagnosing side effects of medications during long-term use.
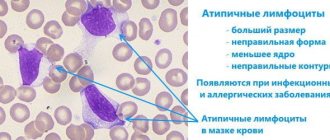
What causes the appearance of atypical lymphocytes?
When a person is sick and his body needs protection, the immune system must produce a sufficient number of lymphocytes so that together they can cope with the aggressor. Unfortunately, sometimes there are not enough immune resources for this. Cells are produced, but cannot fully mature and prepare to meet a pathogen or allergen. So it turns out that the number of such unusual lymphocytes in the blood increases. They perform the necessary functions, but their “appearance” is not very complete.
As soon as the patient gets better, the blood picture immediately, in just a few days, improves.
Sometimes high lymphocytes in the blood and the appearance of atypical forms are observed not only with ARVI and allergies, but also in more serious situations. Whooping cough, syphilis, tuberculosis, lymphocytic leukemia, brucellosis, toxoplasmosis, and serum sickness can lead to the appearance of large numbers of them.
The norm of lymphocytes in the blood of men
Important: decoding lymphocytes in the analysis is the task of the attending physician, while normal values are selected taking into account the gender and age of the subject.
Self-diagnosis is dangerous due to incorrect definition of the disease and the necessary treatment methods, which can subsequently lead to a significant deterioration in the man’s health.
The standard norms of lymphocytes in men by age, given in the table, are for informational purposes only and cannot serve as a basis for self-diagnosis of the patient.
| Age | The norm of lymphocytes in men as a percentage of the total number of leukocytes |
| 0 – 1 year | 40 – 75 |
| 1 – 2 years | 35 – 65 |
| 2-4 years | 35 – 60 |
| 4 – 6 years | 30 – 55 |
| 6 – 8 years | 30 – 50 |
| 8 – 10 years | 25 – 45 |
| 10 – 15 years | 25 – 40 |
| 15 – 50 years | 17 – 35 |
| Over 55 years old | 15 – 30 |
It should be noted that standard values for infants are significantly higher than for older children. An increase in the number of lymphocytes is necessary to provide natural immunity to the child until the acquired one is fully formed.
Starting from the age of 55, men may experience slight lymphopenia - a decrease in the content of white blood cells in the blood, which is a variant of the physiological norm.
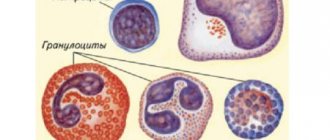
Norms of different types of leukocytes
Along with lymphocytes, patients are often interested in the question: what is the normal range of basophils and eosinophils, as well as other types of leukocytes?
The number of basophils in people should not exceed 1.5% of the total number of white blood cells; the value of the indicator does not depend on gender or age.
The eosinophil content up to 1 year is 1–5%, from 2 to 4 years – no more than 6%, and then the criterion should be in the range from 1 to 5% of the total leukocyte concentration.
The norm of monocytes for an infant is no more than 10%, for patients older than 2 years – from 3 to 13%.
Standard neutrophil values for children under 1 year of age are from 15 to 46%, from 1 to 16 years of age - from 25 to 60%, over 16 years of age - from 45 to 75%.
Read further: If neutrophils are low and lymphocytes are high in an adult
Designation of lymphocytes in blood tests
The designation of lymphocytes in a blood test varies depending on:
- quantitative content of blood elements;
- percentage compared to other bodies.
In the test results, protective bodies are designated by the Latin letters LYM with a “%” sign next to them. Knowing how lymphocytes are designated in a blood test, it is easy to compare their quantitative and percentage indicators with reference values.
In the test results of some laboratories, the level of cells may be indicated slightly differently, which does not change the essence of the results obtained. The quantitative indicator corresponds to the designation LY or LY “#”, and when designating the ratio, lymphocytes as a percentage of the norm look like LY% with the corresponding value.
Elevated lymphocytes in the blood of men - what does this mean?
It should be noted that a slight deviation of the criterion from normal values has no diagnostic value and can be caused by a number of reasons:
- improper preparation for the delivery of biomaterial;
- daily fluctuations of all laboratory criteria in the human body;
- errors at the preanalytical stage;
- errors of the instruments used.
In this case, an increase in lymphocytes in the blood of men is a variant of the physiological norm and has no diagnostic value. A repeat study is scheduled after 1–3 days.
If the number of lymphocytes exceeds the standard values by 10 or more units, then a comprehensive plan for examining the patient is determined to determine the presence of various pathologies. Possible causes of increased levels of lymphocytes in the blood in men:
- infectious disease of a viral, bacterial or parasitic nature;
- non-infectious inflammatory process;
- oncological pathologies affecting the functioning of the bone marrow, lymphatic and circulatory systems;
- acute stage of the allergic response of the human body;
- intoxication with carbon disulfide, arsenic, mercury or other substances, including psychotropic and narcotic substances;
- long-term use of medications related to anticonvulsants or antiepileptics.
Main article: What do elevated lymphocytes in an adult indicate, what are the reasons, and what to do?
How many lymphocytes should there be?
Throughout life, lymphocytes in the blood can increase or decrease. Factors on which the number of lymphocytes in the blood depends:
- Age. The difference between children and adults is obvious. But also in children there are differences in the normal lymphocytes by age;
- Floor. The reason is that in women, the number of lymphocytes can vary depending on how old she is and various conditions inherent in the female sex;
- Stress, heavy physical activity, the effects of drugs or other chemicals;
- Various illnesses or periods of recovery.
You can find out whether the number of lymphocytes in a person’s blood is normal in a very simple way. To do this, you need to take a general blood test, and then look at the numbers opposite the letters lym. There are two indicators: general (absolute) and differential. The normal level of lymphocytes in the blood of children ranges from 30 to 70%. This is due to the fact that the child was born very recently, the body begins to get used to the world around it, develop its own immunity, especially until he is one year old.
Organs associated with the production of immune cells work much more actively than in an adult.
Below is a table of lymphocytes and their quantitative dependence on age in children. The third column represents the absolute number of lymphocytes (x109/l):
| Age | Specific Gravity (%) | Norm lym |
| Up to a year | 45 — 70 | 2 — 11 |
| From 1 to 2 years | 37 — 60 | 3 — 9 |
| From 2 to 4 years | 33 — 50 | 2 — 8 |
| Up to 10 years | 30 — 50 | 1.5 — 6.8 |
| Teenagers | 30 — 45 | 1.2 — 5.2 |
| Adults | 18 — 40 | 1 — 4.5 |
The normal limits for lymphocytes in the blood of adults range from 18 to 40%, which in terms of absolute value will be from 1 to 4.5x109/l.
However, if a person feels well, and the analysis showed an increase in lymphocytes in the blood, this may be a consequence of recent physical activity, active sports, long exposure to the sun, drinking alcohol and other stresses on the body.
The norm of lymphocytes in the blood of women shifts slightly; it depends on the periods, which often change for various reasons. The well-known fact about changes in hormonal levels during pregnancy is one of the reasons for the deviation of the amount of LYM from the norm. During gestation, immunity decreases, the number of cells that increase protection decreases. The body, as it were, adapts to the situation and tries to prevent a reaction from occurring between the child and the mother (this can happen because the embryo contains half of someone else’s information). Despite the fact that this is not a deviation, it is necessary to monitor your health and tests due to decreased immunity.
You need to protect yourself from colds, all kinds of viruses, infections, because... any illness during pregnancy will harm mother and baby.
Another factor when deviations from the norm are allowed is the state before, before, and also during menstruation. The number of lymphocytes can rise to 50%. The fact is that at this time, slight swelling and inflammation occur in the endometrium. All this passes, is an absolutely normal physiological state, and is not taken into account as a full-fledged inflammatory process.
So what is the norm of lymphocytes in a woman’s blood? This number ranges from 20 to 40%.
Of course, if lymphocytes and their norm in women are very different, even taking into account the temporary hormonal disruptions inherent in the fair sex, one should look for the cause of the changes. Most likely, this is due to disorders in the body, diseases. If you take the tests again after the hormonal changes are completed and the leukocyte level in the blood is restored, there is no need to worry.
The norm of lymphocytes in the blood of men can deviate upward by more than 15% if their activity is associated with harmful chemical production.
Decreased lymphocytes
Patients ask themselves: what is the danger of a low lymphocyte count? The danger of this condition is due to the inhibition of the natural defenses of the human body. It can be a consequence of autoimmune pathologies, infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) or malignant lesions of the circulatory system.
It is important to note that during the acute stage of a bacterial or viral infection, the size of lymphocytes often decreases. The reason is the rapid death of protective cells when fighting infection, while new lymphocytes do not have time to be produced in sufficient quantities. In this case, in addition to antiviral drugs, the doctor prescribes immunostimulating drugs.
Read further: Lymphocytes are low - what does this mean and how to treat?
TABLE OF GENERAL CLINICAL BLOOD ANALYSIS INDICATORS WITH DECODING
- blood cells (RBC) are red blood cells, flattened cells without a nucleus, delivering oxygen to tissues and removing the main “waste” from them, a metabolic product - carbon dioxide. A decrease in the level of red blood cells, as red blood cells are also called, indicates a possible deficiency of oxygen in the tissues. If the number of red blood cells is increased, this may indicate blood thickening and the danger of thrombosis. Norms for men: 4.3 – 6.2 x 1012/l; for women: 3.8 – 5.5 x 1012/l; for children: 3.8 – 5.5 x 1012/l .
- Hemoglobin (HGB, Hb) is the main protein of the red blood cell, which has a high chemical affinity for oxygen and carbon dioxide. It is on it that molecules of vital gas are transferred to the tissues of the body, and the main “slag” of the body - carbon dioxide - from the tissues. Its decrease directly indicates the presence of anemia, and its increase is a consequence of dehydration or blood thickening. Norm : 120-140 g/l .
- Red blood cell distribution width (RDWc) is a percentage that determines how much the largest red blood cell in a blood sample differs in diameter from the smallest. A difference of more than 15% indicates anisocytosis, a characteristic sign of anemia. Norm : 11.5 – 14.5% .
- Cell volume (MCV) is a measure of the average size of red blood cells and another factor in the evaluation and differentiation of red blood cells that indicates anemia. A decrease in the indicator indicates iron deficiency or microcytic anemia, an increase indicates a deficiency of folic acid (aka vitamin B9), which indicates the presence of megaloblastic anemia. Norm for an adult: 80 – 100 fl.
- The content of hemoglobin in an erythrocyte (MCH) is a factor, a decrease in which indicates iron deficiency anemia, an increase in megaloblastic anemia. Normal value: 26-35 gu (pg) .
- The concentration of hemoglobin in an erythrocyte (MCHC) is an extremely important and rather rare indicator that reveals hidden inflammatory processes in the body, malignant tumors, and anemia in cases of its increase. A decrease may indicate an increased number of red blood cells. Norm : 330 – 370 g/l .
- Hematocrit (HCT) is an indicator that determines the volume of red blood cells in the total blood volume. An increased hematocrit indicates an increase in the content of red blood cells (erythrocytosis), which occurs with dehydration. A decrease in hematocrit is another factor in identifying anemia. It may also indicate an abnormal increase in the liquid fraction of the blood. The standards have gender differences: for men, normal hematocrit is 39–49% , for women 35–45% , which is associated with monthly blood loss.
- Platelets (PLT) - the indicator reports the number in a liter of blood of cells responsible for the clumping of red blood cells into dense conglomerates that prevent blood from flowing out of the vessels when they are injured. An increase in platelet levels is observed after removal of the spleen and in a number of other diseases. A decrease in the indicator indicates cirrhosis of the liver, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, aplastic anemia or congenital blood diseases. Norm : 180 – 320 x 109/l .
- White blood cells (WBC) - the indicator determines the number of white blood cells per liter of blood. Their main function is to protect the body from bacteria. An increase in the number of leukocytes indicates the onset and development of a bacterial attack in the body. White blood cell levels decrease in blood disorders, certain specific infections, and in response to certain medications. The normal indicator is: 4.0 – 9.0 x 109/l .
- Granulocytes (GRA, GRAN) - this indicator indicates the number of specific humoral immune cells per liter of blood. It increases during inflammatory events, the level of granulocytes decreases under the influence of certain drugs, with aplastic anemia and systemic lupus erythematosus. Normal : 1.2-6.8 x 109/l (sometimes indicated in quantity per microliter, then the standard is 1.2-6.8 x 103/µl) .
- Monocytes (MON) are a type of white blood cell, the number of which is calculated separately. These cells turn into macrophages - very large blood cells whose job is to absorb and process bacteria and dead body cells. An increase in the number of monocytes is a characteristic sign of infectious diseases, rheumatoid arthritis and some blood diseases. A decrease in the number of monocytes often occurs under the influence of immunosuppressants - drugs that suppress the immune system. A decrease is also observed after severe injuries, operations or fasting. Normal level : 0.1-0.7 x 109/l (or 0.1-0.7 x 103/µl) ; sometimes expressed as MON% 4 – 10% .
- Lymphocytes (LYM, LY%) are another type of white blood cell present in normal blood. The lymphocyte specializes in fighting viruses and some bacteria, and belongs to the cells of humoral immunity. The rate increases with viral infections, radiation sickness, taking certain medications, and blood diseases. Decreases with various immunodeficiencies characteristic of renal failure, taking immunosuppressants, prolonged fasting, fatigue, HIV). The normal value is 1.2 - 3.0 x 109/l (or 1.2-63.0 x 103/µl); sometimes expressed as LY% 25-40% .
These indicators are not limited to blood tests, but they are considered the main ones. By itself, each of them is not a sufficient basis for making a diagnosis and is considered only in conjunction with other indicators, data from a physical examination (examination by a doctor) and other studies.
How to prepare for the analysis?
The accuracy and reliability of the results obtained depends on the correct preanalytical preparation of the patient. The biomaterial for analysis is venous blood serum taken from a vein in the bend of the elbow. It is important to donate blood while sitting.
The biomaterial is collected strictly on an empty stomach (at least 8 hours break after the last meal), the optimal time is from 8 to 11 am. It is recommended to give up fatty, fried and spicy foods for 1 day; alcohol is prohibited. You are allowed to drink unlimited amounts of unsweetened water.
Physical and emotional stress should be limited as this may affect lymphocyte concentrations and lead to false test results. If you plan to go to the laboratory in the morning, it is not recommended to attend sports training the night before. Smoking is prohibited half an hour before blood collection.
For 2 days, the intake of any medications is limited, by prior agreement with the attending physician. This rule is especially important for drugs that thin the blood, for example, aspirin, phenylin, aspecard. The impossibility of discontinuing vital medications determines the need to notify the laboratory employee.