Dangers and consequences of high amylase levels.
Elevated enzyme levels are dangerous for the development of diabetes mellitus
The growth of the enzyme in the bloodstream is a marker of a number of diseases. It is necessary to accurately determine the cause of the deviation from the norm. The doctor may order additional tests that will help establish an accurate diagnosis. Timely treatment will eliminate the increased concentration of the enzyme.
If the increase in enzyme units continues, a possible complication may be a disturbance in carbohydrate metabolism. Changes in carbohydrate metabolism provoke excess or sharp fluctuations in blood glucose. This can lead to the development of diabetes mellitus, disruption of the entire metabolism (including the metabolism of proteins and fats), and the occurrence of fermentation processes.
Reasons for increased alpha amylase in the blood
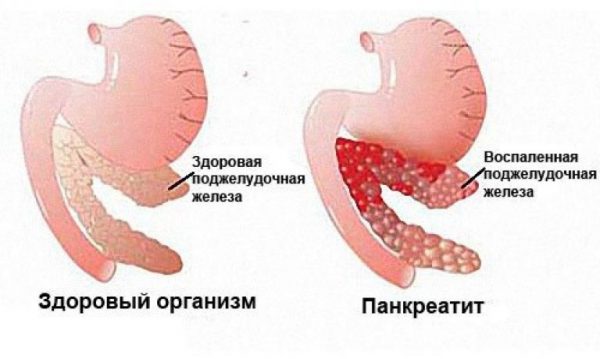
If the concentration of alpha amylase in the blood is elevated, this may indicate the development of pancreatitis. The enzyme level is significantly higher than normal.
It happens that alpha amylase does not increase with pancreatitis or increases, but only slightly. This is explained by the fact that the severity of the pathology does not affect the concentration of the enzyme.
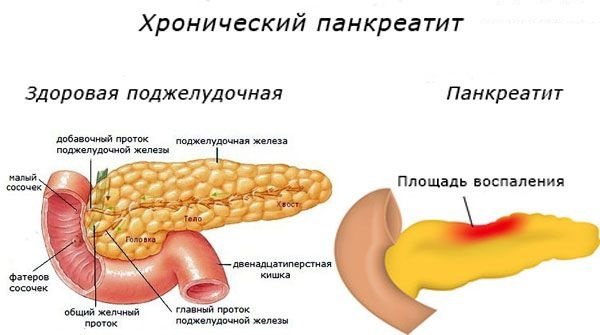
If extensive destruction of the soft tissue of the pancreas occurs, the bulk of the alpha amylase cells are destroyed. For this reason, with pancreatitis, the enzyme level may not exceed its normal value.
If chronic pancreatitis is diagnosed, then initially the concentration of amylase increases, but due to the destruction of soft tissues, the level of the substance returns to normal.
Important! If, during an exacerbation of pancreatitis with pronounced pathological symptoms, it turns out that the enzyme level is not elevated, the prognosis for the patient will be disappointing. This condition indicates significant destruction of the soft tissue of the pancreas.
There are other reasons for increased alpha amylase in the blood:
- Amylase. Normal blood levels in women, men, children by age, table. What does it mean increased, decreased, treatment
- Oncological pathology of the pancreas of a malignant nature. Cancer of the head of this organ is usually diagnosed. If this particular disease caused an increase in the concentration of the enzyme, then the norm will be exceeded four times.
- Diabetes mellitus of any type. This pathology is characterized by metabolic disorders. Incorrect enzyme consumption occurs. As a result, the pancreas begins to synthesize more alpha amylase and its concentration increases.
- Kidney failure. Here, the activity of this internal organ is disrupted and because of this, the enzyme is retained in the blood, which provokes a deviation from the norm in a larger direction.
- Peritonitis. With such an illness, the patient’s well-being deteriorates sharply. The pancreas also suffers, which begins to synthesize an increased amount of alpha amylase.
- Mumps. This is a pathology that occurs in an acute form. Most often children suffer from it. Inflammation occurs in the salivary glands, which provokes an increase in the concentration of the enzyme in the blood.
- Stones present in the gallbladder and ducts.
Other reasons for an increase in enzyme deviation from the norm upward:
- abdominal injury due to mechanical impact - impact, fall, etc.;
- pathologies in which microamylase appears in the blood;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- fourth type of herpes virus;
- intestinal obstruction;
- complications after operations on the abdominal organs;
- poor nutrition;
- unstable emotional background;
- alcohol abuse;
- taking certain medications.
Indications for analysis, or why test amylase?
Since these enzymes perform the same function in the body of an adult and a child, the indications for studying amylase levels in children and adults are the same. The pancreatic variety is examined for suspected acute and chronic pathology of the pancreas, as well as for acute and girdle pain in the upper abdomen, which may indicate acute pancreatitis.
In early childhood, there is a dangerous, severe hereditary pathology associated with impaired carbohydrate metabolism, which is called cystic fibrosis. If cystic fibrosis is suspected, one of the first tests performed is to determine the concentration of both types of amylase.
In early childhood, there is such a well-known infectious viral disease as mumps, or mumps. The virus causes inflammation of the salivary glands (and the pancreas too) and a sharp change in the concentration of the corresponding enzymes.
Decreased amylase concentration
The reasons for the decrease in enzyme concentration are usually hepatitis, occurring in acute or chronic form. With such diseases, disruptions in carbohydrate metabolism occur, which causes an increase in the load on the fermentation system and changes in the parameters of a biochemical blood test. The second reason for the decrease in the level of the substance is neoplasms of the pancreas.
Typically, tumor processes cause an increase in the concentration of amylase (especially in the initial stages), but after the degeneration of its tissues, the secretion of enzymes is disrupted. Due to organ injuries, intoxications of the body and poisoning, it is also possible for the enzyme concentration to change either down or up.

Normal indicator
The alpha norm is very strict. If there is a low amylase level, or, conversely, an increased one, it means that the digestive system cannot work as it should. Based on the alpha norm test results, you will be given a form within which the normal values for the laboratory that performed the testing are indicated. However, in most cases the rules are as follows.
The alpha norm indicator depends on age. So in children under two years of age, the norm is numbers from 5 to 65 U/l. Adults should see a reading between 25 and 100 U/L when receiving results. If we are talking about the older age group, when a person has crossed the threshold of 70 years, then the normal figure will be 20-160 U/l.
It is important to note that the alpha norm indicator can be called total amylase, since it also contains pancreatic amylase. Its quantity is separately measured by modern laboratories. When it comes to this particular compound area, it is important to note the new regulations. For children under six months of age, the norm is no more than 8 U/ml. For children aged 6 to 12 months, the norm is below 23 U/ml. Everyone who has reached one year of age must adhere to the limit of 50 U/ml.
- Tests for rheumatoid arthritis: what tests to take and their meanings
It is worth noting that, despite the difference in the functioning of the male and female body, experts did not find any strong differences in the activity of the component, therefore, increased amylase in the blood of a woman will be considered increased in a man.
It is important to note that sometimes the indicator increases by about two units. In this case, there is no reason for serious concern. These are not pathological values. You need to think about how to lower amylase if its level is increased two to three times.
Often, when amylase should be reduced, a person experiences such unpleasant symptoms as causeless pain in the abdominal area. Therefore, doctors always check the amylase level in case of such complaints.
Normal blood amylase level in children
It is somewhat more complicated with the pancreatic fraction. Its age-related indicators largely depend on age and the development of the pancreas. That's why:
- in babies under 6 months of age, the normal value ranges from 1 to 12 U/l;
- at the age of up to one year - this value increases to 23 U/l;
- in children older than one year, gender should be taken into account: in boys under 2 years of age this concentration does not change (1-23 U), and in girls the figure is slightly higher: from 3 to 38 U/l;
- finally, from the age of two until the age of puberty (19 years), the concentration of the pancreatic form in boys and girls is again comparable and ranges from 4 to 31 units per liter.
As for the enzyme that is produced by the salivary glands, everything is simpler here:
- the norm of amylase in the blood of children under one year of age is 5 – 65 U/l;
- starting from the age of one, and throughout life, up to the age of 70 years, the norm is from 25 to 125 units per liter.
In order to pass the test without errors and without retaking, to determine this enzyme, you must take blood on an empty stomach in the morning. You can drink water, and, as a last resort, you can feed the baby, but no later than 4 hours before taking blood. This applies, first of all, to infants who are fed “by the hour.”
What is amylase in a biochemical blood test?
Amylase is a glycoside hydrolase enzyme that is synthesized by the body. The main part is produced by the pancreas. A small amount of the enzyme is synthesized by other internal organs, as well as the salivary glands.
Amylase takes an active part in carbohydrate metabolism. The main function of the enzyme is to regulate the activity of the digestive system, break down starch and modify it into a digestible substance.
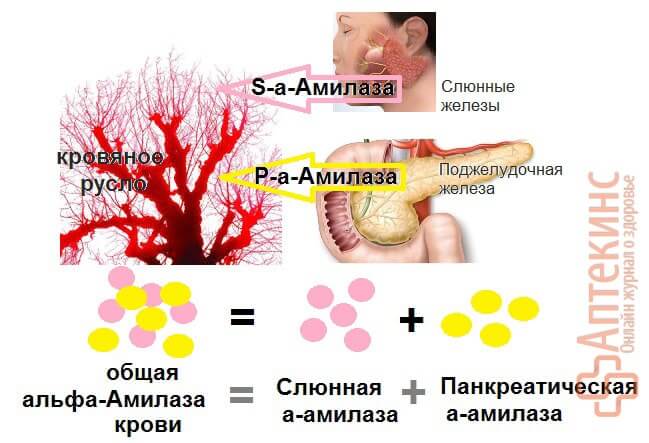
The enzyme is divided into two types:
- Alpha amylase. Another name is salivary amylase. This is an enzyme that is synthesized in the salivary glands and pancreas. The digestion process depends on its concentration.
- Pancreatic amylase. This is part of alpha amylase. This enzyme is synthesized only in the pancreas. It has a direct effect on the digestive process occurring in the duodenum.
Amylase is not only synthesized by the pancreas, but is also part of pancreatic juice. Here she takes an active part in the breakdown of complex substances.
If we talk about what an enzyme shows in a blood test, then its deviations from the norm indicate various pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Leukocytes in the blood - normal by gender and age, increased and decreased values
Serum total amylase
Amylase is one of the enzymes of digestive juice, which is secreted by the salivary glands and pancreas.
Synonyms Russian
Diastase, serum amylase, alpha-amylase, serum amylase.
English synonyms
Amy, alpha-amylase, AML, diastase, 1,4-?-D-glucanohydralase, serum amylase, blood amylase.
Research method
Kinetic colorimetric method.
Units
U/L (unit per liter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not eat for 12 hours before the test.
- Avoid physical and emotional stress and do not smoke 30 minutes before donating blood.
General information about the study
Amylase is one of several enzymes that are produced in the pancreas and are part of pancreatic juice. Lipase breaks down fats, protease breaks down proteins, and amylase breaks down carbohydrates. From the pancreas, pancreatic juice containing amylase passes through the pancreatic duct into the duodenum, where it helps digest food.
Normally, only a small amount of amylase circulates in the bloodstream (due to the renewal of pancreatic and salivary gland cells) and enters the urine. If the pancreas is damaged, as in pancreatitis, or if the pancreatic duct is blocked by a stone or tumor, amylase begins to leak into the bloodstream in large quantities and then into the urine.
Small amounts of amylase are produced in the ovaries, intestines, bronchi and skeletal muscles.
What is the research used for?
- To diagnose acute or chronic pancreatitis and other diseases involving the pancreas in the pathological process (together with a lipase test).
- To monitor treatment for cancer affecting the pancreas.
- To ensure that the pancreatic duct is not compromised after removal of gallstones.
When is the study scheduled?
- When the patient has signs of pancreatic pathology: intense pain in the abdomen and back (“girdling pain”),
- temperature increase,
- loss of appetite,
- vomit.
What do the results mean?
Reference values: 28 - 100 U/l.
Reasons for increased activity of total amylase in serum
- Acute pancreatitis. With this disease, amylase activity can exceed the permissible level by 6-10 times. The increase usually occurs 2-12 hours after injury to the pancreas and persists for 3-5 days. The likelihood that acute pain is caused by acute pancreatitis is quite high if amylase activity exceeds 1000 U/L. However, in some patients with acute pancreatitis, this indicator sometimes increases slightly or even remains normal. In general, amylase activity does not reflect the severity of pancreatic damage. For example, with massive pancreatitis, the death of most cells that produce amylase may occur, so its activity does not change.
- Chronic pancreatitis. In chronic pancreatitis, amylase activity is initially moderately increased, but then may decrease and return to normal as damage to the pancreas worsens. The main cause of chronic pancreatitis is alcoholism.
- Trauma to the pancreas.
- Pancreas cancer.
- Blockage (stone, scar) of the pancreatic duct.
- Acute appendicitis, peritonitis.
- Perforation (perforation) of a stomach ulcer.
- Decompensation of diabetes mellitus – diabetic ketoacidosis.
- Impaired flow in the salivary glands or salivary ducts, for example with mumps (mumps).
- Operations on the abdominal organs.
- Acute cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Aborted tubal pregnancy.
- Ruptured aortic aneurysm.
- Macroamylasemia is a rare benign condition where amylase binds to large proteins in the serum and therefore cannot pass through the glomeruli, accumulating in the serum.
Reasons for decreased activity of total amylase in serum
- Decreased pancreatic function.
- Severe hepatitis.
- Cystic fibrosis (cystic fibrosis) of the pancreas is a severe hereditary disease associated with damage to the exocrine glands (lungs, gastrointestinal tract).
- Removal of the pancreas.
What can influence the result?
- Serum amylase activity increases:
- in pregnant women,
- when taking captopril, corticosteroids, oral contraceptives, furosemide, ibuprofen, narcotic analgesics.
- Elevated cholesterol may decrease amylase activity.
Important Notes
- In acute pancreatitis, an increase in amylase is usually accompanied by an increase in lipase activity.
- Amylase activity in children is low in the first two months of life; it rises to adult levels by the end of the first year.
Also recommended
- Total amylase in daily urine
- Pancreatic amylase
- Lipase
Who orders the study?
General practitioner, therapist, gastroenterologist, surgeon.