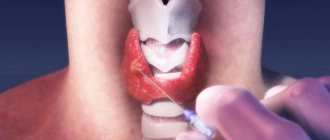
Ultrasound of the thymus
(thymus) in children is an absolutely safe, painless procedure with which the diagnostician determines the condition of the thymus. The study helps to identify organ diseases, congenital or developing anomalies, and pathologies.
The thymus gland is located at the top of the chest, in the upper mediastinum. It consists of 2 lobes, fused or tightly adjacent.
The gland is the central organ of the immune system and performs an extremely important function - it differentiates and clones T-lymphocytes responsible for human immunity. In addition, the gland is responsible for the production of hormones - thymosin polypeptides, thymulin, thymopoietin, insulin-like growth factor-1, thymic humoral factor. Thymus peptides affect the functionality of the central nervous system, reducing anxiety and increasing useful activity. The thymus is directly related to human longevity: its proper functioning slows down biological aging.
ultrasound of the thymus gland
Indications for ultrasound diagnostics of the thymus
The doctor prescribes ultrasound diagnostics of the thymus for those children who get sick very often. The cause of pain is often childhood thymomegaly - an enlargement of the thymus gland.
The pathology is caused by hereditary factors, infectious diseases of the mother during pregnancy, late pregnancy, nephropathy, living in a region with an unfavorable environmental situation, and other reasons.
Symptoms of the disease appear up to 3-6 years of age. It is very important to pay attention to them, because thymomegaly forms immunodeficiency, thymus-adrenal insufficiency. After 6 years, it becomes the cause of chronic diseases: rheumatism. Bronchial asthma, pyelonephritis, chronic pneumonia.
Diagnosis of the gland is carried out in the presence of the following symptoms:
- the child regularly, almost every month, and sometimes several times a month, gets sick;
- a common cold can be complicated by bronchitis, sinusitis, pneumonia;
- temperature without signs of disease can rise to 37-37.5 ° C and stay at this level for several days;
- chest pain, chronic weakness and fatigue;
- in babies - frequent regurgitation is observed, they breathe heavily and frequently;
- clear display of the vascular network on the chest (marble pattern);
- heart rhythm is disturbed;
- hyperhidrosis, constantly cold feet, hands;
- adenoids, tonsils, lymph nodes enlarge;
- tendency to allergic manifestations - diathesis, urticaria, hay fever, bronchial asthma.
Children under 1 year of age are recommended to undergo ultrasound diagnostics of the thymus if they were born with a large weight, if they are stressed, cyanosis is observed (the skin and mucous membranes turn blue), and an unreasonable cough occurs, which becomes stronger when lying down.
Diagnosis of diseases
Knowledge of the age-related size and structural features of the normal thymus helps to eliminate errors in identifying diseases and tumors of the thymus. European doctors have carried out a lot of work to study the condition of the gland at the age of two.
The most accurate characteristic is to determine the width of the lobe. The criterion applies to CT and MRI.
Lymphoid hyperplasia of the thymus
In patients with myasthenia gravis, the proliferation of lymphoid elements may be activated. Differential diagnosis between hyperplasia and tumors is required for thyrotoxicosis, when the process is triggered by an increased concentration of thyroid hormones.
Primary MRI diagnosis of lymphoid hyperplasia of the thymus is difficult, since there is no increase in the size of the gland. The disease is characterized by degeneration of the structure.
A volume increase does not always indicate a tumor, since histological analysis shows the normal structure of the cells.
Visual diagnosis of the thymus in myasthenia gravis
Autoimmune damage to neuromuscular transmission occurs through the formation of antibodies to the own structures of the thymus parenchyma. Immunoglobulins block the functioning of acetylcholine receptors, which leads to disruption of muscle function.
Radiation neuroimaging methods are prescribed for double vision of objects inside the eye in the evening. Overload of speech muscles, pathological fatigue, difficulty swallowing are the first symptoms of myasthenia gravis.
The extreme degree of pathology is crisis. The disease is characterized by severe motor disorders, swallowing disorders, and speech disorders. Lack of early diagnosis and emergency care leads to death.
Lymphangioma of the thymus
Benign proliferation of lymphatic vessels increases the volume of the organ. The child has an excess amount of lymphocytic tissue, so neoplasms of this origin are more common.
Lymphatic neoplasms are provoked by viruses, chemical and physical factors (the effect of radiation). There are scientific works regarding the genesis of thymic lymphangiomas in children with hereditary developmental anomalies. The formation of thymic cysts in the fetus during embryogenesis disturbances has been proven.
How the research works
Like any ultrasound examination, diagnosing the thymus is simple and does not cause discomfort. You need to remove clothes from the upper body and take the desired position.
The position of the child depends on his age:
- a baby up to one year old is held in the arms of adults;
- a child from 1 year to adolescence is examined in a lying position;
- adolescents are examined standing.
The diagnostician applies the gel to the area to be examined and scans the upper part of the chest with a sensor. On the monitor he sees the condition of the thymus gland, its size. Based on these data, conclusions are drawn about the state of the thymus.
Diagnostics lasts about 10-15 minutes.
Functions of the thymus
The thymus is a lymphatic system that produces thymic hormones that activate the immune system, improve skin condition and promote rapid cell restoration. In a word, the thymus (thymus gland) helps.
Also functions of the thymus in the body:
- Maintaining peak immune system protection
- Helping the pituitary gland and hypothalamus
The thymus gland regulates and ensures good and correct growth of the child’s skeleton
What does ultrasound of the thymus gland reveal in children?
Ultrasound diagnostics of the thymus reveals the following disorders and diseases:
- thymomegaly;
- aplasia (underdevelopment);
- developmental pathologies;
- neoplasms of different nature (cystic, tumor, benign and malignant);
- Nezelof syndrome associated with gland dysfunction;
- Bernard-Horner syndrome;
- congenital aplasia of the thymus and parathyroid glands, in which the production of T-lymphocytes is significantly or critically reduced.
During the procedure, the diagnostician assesses the size of the thymus gland, which must correspond to age standards. The contours of the organ are determined - their clarity and uniformity, the structure of the gland tissue.
If during the procedure suspicious changes are detected or the diagnostic result is ambiguous, the doctor may prescribe additional tests - blood tests, ECG, and others in accordance with the symptoms.
The thymus gland and vitality
Children differ from adults not only in size and mental characteristics. Even their internal organs work in their own way, and some stop functioning when the child grows up. This refers to the thymus gland, or thymus, which begins to disappear after the age of 20, and by the age of 40, for most, not a trace remains of it.
How does the thymus work?
The name of the organ was given because of its resemblance to a two-pronged fork, but translated from ancient Greek the word thymus means “life force.” The Greeks guessed about the function of the thymus gland, but modern scientists have long considered it a minor or vestigial organ that modern humans do not need. About 60 years ago, it was discovered that the thymus is the central organ of the immune system, without which normal development of the body and even survival are impossible.
After the baby is born and for 6-12 months, it is protected by antibodies and immune cells from the mother’s body. Then your own immunity comes into play, but the greatest activity appears at 2-3 years. It manifests itself in the training and differentiation of a huge number of T-lymphocyte cells.
These cells come from the bone marrow, but they are not able to protect the body. Their final maturation occurs in the thymus gland. Once there, T-lymphocytes acquire the ability to detect foreign proteins that can harm the body, as well as viruses, bacteria and cancer cells. Learning also occurs due to the child’s constant exposure to new infections. Therefore, small children under 5 years old often catch colds; their body learns to resist diseases.
By the age of five, a sufficient number of immune cells and antibodies are formed, so the activity of the thymus begins to decrease. This process accelerates in adolescents; by the age of 20, the size of the organ is several times smaller than in childhood, and at 30 it practically does not function.
Thymus involution: good or bad?
But the reverse development of the thymus, or involution, does not occur in everyone. Research shows that in some people it does not disappear completely; adipose and lymphoid tissue remains in its place. There is no explanation why this happens. They suggest a connection with a certain lifestyle or heredity. This affects health and vitality. Such people suffer less from senile pathologies and remain active and alert longer.
Maintaining vitality and longevity is associated with the production of biologically active substances and hormones. Target cells influenced by thymic hormones are found in all tissues. It has been experimentally proven that the following processes depend on the thymus gland:
• correction of immunodeficiency conditions associated with age or long-term illnesses;
• maintaining the work of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus - the main regulators of the endocrine system;
• production of the hormones prolactin, somatotropin, follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones, estradiol and progesterone in women;
• normal functioning of the thyroid gland;
• increasing resistance to stress;
• weakening of feelings of anxiety and improvement of behavioral reactions.
The introduction of artificial thymus hormones does not replace the function of the organ. And the long-term preservation of its natural activity makes it possible to restrain the processes of biological aging.
Ways to maintain thymus function
If it is not possible to avoid stress and harmful factors, then the activity of the thymus decreases and immunity decreases. A person becomes more susceptible to diseases. Synthetic substances can temporarily replenish hormone deficiency, but they will not restore the functioning of the thymus gland, and can sometimes cause harm.
But you can safely support the functioning of the thymus gland if you take short peptides orally. The best option is to use specially selected complexes combining 3-5 peptides. Such drugs were developed by the Vitual company together with Professor V.Kh. Khavinson.
With age, there are no more peptides, and the need for them increases. Therefore, the function of the thymus and other organs suffers. If you compensate for the deficiency of peptides, the thymus gland will independently produce the necessary hormones, its function will be restored, which will allow you to maintain active longevity and slow down the aging process.
Professor V.Kh. Khavinson has been studying the peculiarities of the regulation of the thymus by short peptides for 40 years. These are natural substances that are found in any living organism. Cells need them to synthesize proteins, hormones and other substances. The results of many years of research are reflected in the monographs:
• Korkushko O.V., Khavinson V.Kh., Butenko G.M., Shatilo V.B. Peptide preparations of the thymus and pineal gland in the prevention of accelerated aging. // St. Petersburg: Science. – 2002.
• Khavinson V.Kh., Morozov V.G. Peptides of the pineal gland and thymus in the regulation of aging. // St. Petersburg: IKF “Foliant”. — 2001.
• Morozov V.G., Khavinson V.Kh., Malinin V.V. Peptide thymomimetics. // St. Petersburg: Science. - 2000.
• Khavinson V.Kh., Kuznik B.I., Ryzhak G.A. Peptide Bioregulators: A New Class of Geroprotectors. Message 1: Results of Experimental Studies. // Advances in Gerontology. — 2013. — Vol. 3, N 3.
• Khavinson V.Kh., Pendina AA, Efimova OF, Tikhonov AV, Koltsova AS, Krapivin MI, Petrovskaia-Kaminskaia AV, Petrova LI, Lin'kova NS, Baranov VS Effect of Peptide AEDG on Telomere Length and Mitotic Index of PHA- Stimulated Human Blood Lymphocytes. // Cell Technologies in Biology and Medicine. – 2021. – N 3, November.
Preparing for an ultrasound
Preparing for ultrasound diagnostics of the thymus is not difficult. During the initial examination after prescribing the study, the doctor must be informed what medications the child is taking and his weight. The diagnostician must know the exact weight in order to determine the normal volume of the gland in accordance with age standards.
The child (if he is already able to understand), the teenager needs to be told how the procedure is going, what he should/should not do, and eliminate his fears about the painfulness of the process.
To visit a medical facility on this day, you should choose clothes that are easy to take off and put on - this will save the time and nerves of the accompanying adult.
ultrasound examination
MRI of the thymus: what diseases and tumors does it show?
The location of the thymus gland in the anterosuperior mediastinum in children does not normally allow the organ to be observed on radiographs due to the projection of the sternum.
Only an enlargement of the thymus in children leads to the appearance of an additional shadow on the image, located above the cardiac shadow on the right or left. Hyperplasia on MRI of the brain in infants is visualized by neuroimaging methods due to its increased size compared to adults.
Gradually the organ drops lower and decreases in size, which is the norm.
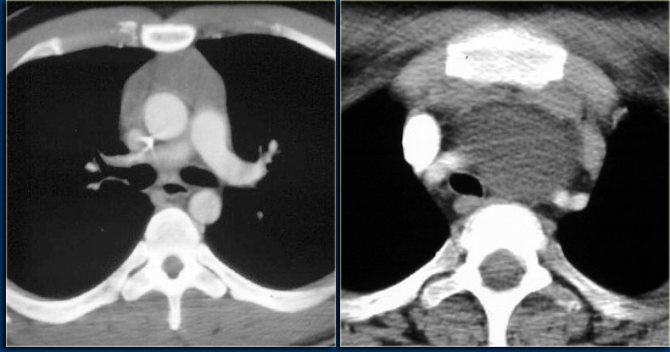
Tomogram of the thymus gland
Diagnostics
If thymoma is suspected, the patient is examined by an endocrinologist, surgeon, or oncologist. The main role belongs to visualization methods. This:
- digital radiography of the chest organs. High-quality X-ray images are available for additional digital processing and highlighting of particularly important details;
- computed tomography with the possibility of three-dimensional reconstruction of mediastinal organs, thymoma and their topographic-anatomical relationships. This possibility is very important for planning surgery to remove the tumor;
- Magnetic resonance imaging. A layer-by-layer study of the smallest features of the structure of a tumor of the thymus gland gives an idea not only of its relationship with other organs of the mediastinum, but also of its benign or malignant nature, the degree of spread and involvement of surrounding tissues - everything that is important for prognosis and treatment planning;
- mediastinoscopy - examination of the mediastinal cavity using a mediastinoscope (an optical endoscopic instrument that also allows you to perform a biopsy of a tumor);
- biopsy of regional lymph nodes;
- histological and cytogenetic analyzes of tissue samples obtained during biopsy;
- electromyographic study if symptomatic myasthenia gravis is suspected;
- laboratory diagnostics for tumor markers of immune cells.
The main method of treatment for thymoma is surgical removal of the tumor, and the operation is performed as soon as possible after diagnosis, since compression of the mediastinal organs even by a benign tumor poses a threat to life.