The role of bilirubin in the body
The analyzes take into account not only the overall indicator of the pigment, but also its fractions - direct and indirect. Exceeding the total concentration may indicate intoxication in the body, cirrhosis, viral hepatitis, malignant neoplasms in the liver or genetic disorders.
An increase in concentration is due to dysfunction of the gallbladder and biliary tract, or indicates a malfunction of the pancreas.
An increase in the level of indirect pigment can be explained by the presence of Gilbert's syndrome, past infections, hemolytic anemia, and spleen dysfunction. The value of this chemical element is indicative for recognizing anemia and jaundice in newly born children.
Bilirubin standards for adults
A blood test for bilirubin is carried out quickly, within a couple of hours; normal values for adults will be:
- total bilirubin level - from 5.1 to 17 mmol/l,
- indirect bilirubin level from 3.4 to 12 mmol/l,
- direct bilirubin level from 1.7 to 5.1 mmol\l,
In this case, the level of direct bilirubin should be about 70-75% of the total level.
During pregnancy, the level of bilirubin corresponds to that of ordinary people; in the third trimester there may be a slight increase in bilirubin levels due to some disruption of the outflow of bile, but there should not be a sharp increase in values.
A sharp increase in bilirubin levels requires immediate exclusion of hepatitis, anemia and cholecystitis in pregnant women.
What test should be taken for bilirubin?
Most often, a biochemical blood test is performed to determine the concentration of bilirubin. Analysis will help determine the overall meaning of the dye and its associated species. And the indirect view is simply calculated from these two values.

Bilirubin is measured in micromoles per liter with very high accuracy, making it possible to detect problems in the body even before painful symptoms appear. Most often, the result of the study is ready the next day, but it is possible to conduct an urgent analysis, in which all indicators will be known within a few hours.
Indications for testing
Due to improper functioning of the liver and biliary tract, bilirubin is not completely eliminated from the body, toxicity occurs, and the tissues of the internal organs acquire a characteristic icteric color. This does not necessarily mean that the person has hepatitis.
A study is prescribed to determine the level of pigment if:
- hepatitis or cirrhosis is suspected;
- jaundice;

- liver cancer is suspected;
- the patient abuses alcohol;
- there are stones in the gallbladder;
- malfunction of the spleen;
- hemolytic anemia must be confirmed.
Preparing for the test
Bilirubin - the norm for women by age (table below) - indicates the proper functioning of organs such as the spleen, liver and bile ducts. But sometimes research results can be distorted. This occurs due to violation of certain conditions before taking the test.
Reasons that may affect the results of the study:
- abuse of coffee, alcohol, fatty foods before analysis;
- long exposure to the sun;
- taking hormonal medications and contraceptives;
- taking diuretics;
- taking medications containing codeine, caffeine, alcohol;
- taking sedatives containing barbiturates;
- heavy physical activity or a strict diet before taking the test;
- taking the test after completing a course of chemotherapy or after the last dose of antibiotics (at least 14 days must pass).
Blood is donated from a vein in the morning before breakfast . If it is not possible to refuse food for any reason, it is given 4–5 hours after the morning meal.
The rules for passing urine for bilirubin are no different from the usual ones applied to passing a general analysis. Before the examination, you must take a bath or shower. The initial portion of urine is passed, and the next one is collected in a sterile container.
Increased indirect bilirubin
The reason is the rapid breakdown of red blood cells. It can occur as a complication of sepsis, acute intestinal infection, congenital, toxic, acquired autoimmune anemia.
An increase in the indirect form of bilirubin also occurs with Gilbert's syndrome. This is a benign, chronic disease caused by disruption of the intracellular transport of bilirubin. Among the causes of hyperbilirubinemia, Crigler-Najjar syndrome is a disruption of the process of combining bilirubin with glucuronic acid, formed during the oxidation of D-glucose.
The Lucy-Driscol symptom is unusual. It occurs exclusively in infants due to breastfeeding. Breast milk contains an enzyme that disrupts the conjugation of bilirubin. With the transition to artificial feeding, the disease goes away. However, indirect bilirubin is very dangerous, so the occurrence of jaundice after 3-5 days of life requires urgent medical examination.
Types of bilirubin
Red blood cells, whose “lifespan” (approximately 90 days) ends, begin to decompose. The main task of bilirubin is to remove the waste protein component of hemoglobin from the body. Initially, an indirect type of bilirubin is formed, which cannot leave the body on its own and is toxic to it.
The indirect species then travels through the bloodstream to the liver, where, after its further breakdown is complete, it combines with readily soluble glucuronic acid. There is a transformation of the indirect form into a direct form, which is easily excreted along with urine and feces.
What is bilirubin and what types are there?
Total bilirubin is the total amount of direct and indirect fractions of bile pigment, which is formed after the breakdown of iron-containing blood components (erythrocytes). Direct bilirubin is excreted along with bile. It makes up approximately 25% of the total amount of the substance. Indirect is toxic to the body, as it penetrates into cells and disrupts their functioning. Its content in the blood is about 75% of the total volume of bilirubin.
The permissible amount of total bile pigment depends on the age and health of the woman.
Exceeding the norms of indicators indicates that changes are occurring in the body that need to be paid attention to and treated.
How is the amount of bilirubin determined?
There are several ways to determine the level of this chemical element in the blood:
The colorimetric method consists of identifying the amount of pigment, taking into account the color intensity of the resulting solution of pigment and diazotized sulfate acid.
This method is also called the Van Den Bergh method. The direct type reacts quite quickly, and the indirect type only after the introduction of an auxiliary substance - acetic acid, sodium benzoate, caffeine, methanol, urea or other reagents.
Medical diagnostic devices - bilirubinometers - are also used to calculate the concentration of bilirubin.
The work of some of them is based on the photometric research method.
The advantage of such devices is the speed of analysis and the minimal error of the results, since in this case the human factor can be completely eliminated.
To carry out an analysis with a bilirubinometer, it is enough to donate a small amount of blood from a finger (capillary). To operate such a device, special small disposable vessels containing anticoagulants are required. The biological material for research contained in this vessel is placed in a centrifuge, where the red blood cells are deposited.
After which the device calculates the amount of bilirubin in the patient’s blood. Modern devices can provide results in 7–15 seconds.
Reasons for decreased direct and indirect bilirubin
Any non-compliance with performance standards should raise concerns. There should also be no exceptions regarding the concentration of bilirubin. Therefore, if one of the types of bilirubin in the blood - direct or indirect - is reduced, you should find out what this means, what are the causes and consequences of such changes for the body and human life as a whole. A significant reduction in various fractions of the substance is also of great clinical significance.
Direct bilirubin is reduced
Direct, or bound, bilirubin is formed in the liver as a result of the combination of free bilirubin with glucuronic acid. Having turned into a water-soluble fraction, it can freely leave the body along with feces and urine.
The normal level of direct bilirubin in an adult is 3.4-5.1 µmol/l.
The reasons for the decrease in the direct indicator are:
- Consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- Taking glucocorticosteroids (prednisolone);
- Treatment with antibiotics (penicillin);
- Ascorbic acid and Phenobarbital.
Indirect lowered
Indirect, free or pure bilirubin cannot be removed directly from the body. It is poisonous to humans; the lower its content in the blood serum, the better.
The normal level of indirect bilirubin in an adult is 3.4-12.0 µmol/l.
The free fraction may decrease:
- During pregnancy, increased load on the kidneys due to edema and changes in blood pressure can cause such a decrease;
- In children - in newborns, the indicator changes literally by day of life. A decrease in the amount of the indirect component may indicate the presence of renal failure.
Today, a reduced level of direct or indirect bilirubin indicates the general condition of a person and has not yet been fully studied.
The normal level of bilirubin in the blood of women
Bilirubin, normal for women by age, table:
| Age | Indirect view, µmol/l | Direct view, µmol/l | General indicator, µmol/l |
| Premature baby | 3 – 3,5 | 27 – 31,5 | 30 – 35 |
| Newborn | 5 – 6 | 45 – 54 | 50 – 60 |
| 1 – 7 days | 5,45 – 25,6 | 49,05 – 230,4 | 54,5 – 256 |
| 7 – 14 days | 6 – 10 | 54 – 90 | 60 – 100 |
| 30 days | 2,25 – 5 | 6,75 – 15 | 9 – 20 |
| 18 – 20 years old | 2,62 – 12,75 | 0,88 – 4,25 | 3,5 – 17 |
| 21 – 30 years old | 3 – 13,5 | 1 – 4,5 | 4 – 18 |
| 31–40 years old | 2,85 – 13,35 | 0,95 – 4,45 | 3,8 – 17,8 |
| 41 – 50 years | 2,95 – 13,2 | 0,98 – 4,4 | 3,9 – 17,6 |
| 51 – 60 years | 2,77 – 13,05 | 0,93 – 4,35 | 3,7 – 17,4 |
| 61 – 70 years | 2,55 – 12,82 | 0,85 – 4,28 | 3,4 – 17,1 |
| Over 70 | 2,32 – 4,23 | 0,78 – 4,23 | 3,1 – 16,9 |
The ratio of direct and indirect bilirubin in newborns is normally approximately 90% to 10%, and by the 1st month of a child’s life it is already 75% to 25%. In adult women, these values change diametrically opposite - the amount of insoluble pigment is 75%, the direct type is 25%.
When the pigment concentration increases to 33–35 µmol/l, the whites of the eyes acquire a characteristic yellow tint. When the value exceeds 50 µmol/l, the mucous membranes and skin also begin to turn yellow. Increased bilirubin accumulates in organ tissues, poisoning them and affecting the central nervous system.
Bilirubin and pregnancy
The amount of pigment should be carefully monitored during pregnancy. When a woman is pregnant, the body may experience an exacerbation of chronic diseases acquired before pregnancy (cholecystitis, anemia). Normally, the concentration of bilirubin should not increase.
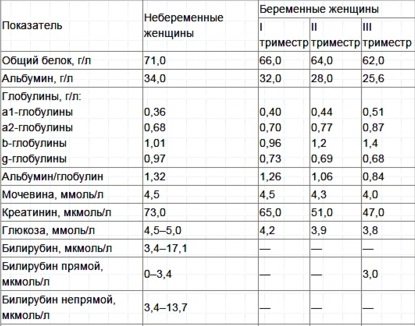
In the table you can see the rate of bilirubin in women during pregnancy (but without depending on age)
Some past infections can also increase bilirubin levels. Toxicosis in the 1st trimester signals that the norm of pigment in the body of a pregnant woman is exceeded. If the amount of pigment in the mother’s body reaches a critical value, early delivery is performed.
A growing embryo is able to put pressure on the liver and gallbladder, thereby disrupting the circulation of bile and causing a rise in pigment levels.
Bilirubin in pregnant women
During the period of gestation, it is very important to constantly monitor the level of bilirubin, which should be in the range from 8.4 to 20.5 µmol/l. It is very important not to exceed the maximum value, since in this case the woman may experience jaundice, since the level of this substance is always related to the functioning of the liver and bile.
In most cases, during pregnancy, the level of bilirubin in women is normal, but sometimes there may be fluctuations in one direction, both minor and very noticeable. If, when deciphering the analysis, it is clear that the amount of pigment does not meet the established standards, the woman must undergo a full examination.
It is important to remember that high bilirubin levels can have a very negative impact on the health of a developing baby, which may indicate a possible illness.
Some diseases, such as hemolytic anemia, can have very serious consequences, including leading to premature birth and sometimes stillbirth. Therefore, it is important to detect and treat any diseases on time.
Reasons for deviation from the norm
Basically, pathological conditions leading to the growth of pigment in the body are acquired (hepatitis, oncology, cirrhosis, cholecystitis), but there are also disorders transmitted genetically - Gilbert's syndrome and Crigler-Najjar syndrome.
In addition to diseases that lead to dysfunction of the gallbladder and liver, there are factors that do not in any way affect the functioning of these organs, however, they contribute to the growth of bilirubin in the body.
These include:
- anemia of various etiologies;
- diseases associated with accelerated destruction of red blood cells - malaria, blood poisoning;
- taking certain medications (penicillin antibiotics, diazepam, furosemide);
- receiving serious soft tissue injuries, accompanied by hematomas and bone fractures.
As can be seen from the table, the level of bilirubin in newborns can increase on days 3–4 and reach its maximum – 256 µmol/l. In children born prematurely, this value should not exceed 170 µmol/l.
Increased bilirubin
A sharp increase in bilirubin levels usually occurs:
- for cholecystitis,
- with a hereditary disorder of bilirubin metabolism,
- with mononucleosis,
- with hepatitis,
- with cirrhosis of the liver,
- for liver tumors,
- for hemolytic anemia, toxic hemolysis
- for pancreatic tumors,
- when transfusion of incompatible blood,
- in case of reaction to medications (antibiotics, contraceptives, diazepam, etc.).
Decreased bilirubin
A decrease in bilirubin can be caused by taking vitamin C, theophylline, or phenobarbital.
Symptoms of abnormal bilirubin levels and when to see a doctor
Some factors may indicate an increase in the concentration of pigment in the blood even before the test results are obtained.
What to pay attention to:
- pain in the left hypochondrium after physical activity or sports training;
- feces become light-colored and urine darkens;
- the appearance of vomiting and nausea;
- yellowing of the whites of the eyes, skin and mucous membranes;
- dizziness and weakness;
- nausea, vomiting and lack of appetite;
- chronic fatigue and anxiety.
What drugs are prescribed
Bilirubin, the norm for women by age (the table above) should not exceed the limit value; in case of deviation from the norm, it gives a direct reason for prescribing therapy. If the cause of increased bilirubin is liver dysfunction, hepatoprotectors are used.
These remedies are not able to completely solve the problem in such serious diseases as hepatitis, cirrhosis, disorders caused by excessive use of alcohol or drugs, obesity, however, they can alleviate the patient’s condition.
Hepatoprotectors are pathogenetic agents for treating the liver. They restore cells, reduce inflammation, prevent fibrosis, and help cleanse the body of toxins.
Almost all drugs related to hepatoprotectors do not have proven medical effectiveness.
The exception is products containing ademetionine - Heptral, Heptor.
The detoxifying effect of ademetionine has been studied and proven scientifically. The herbal drug Karsil is also well known.
If the pigment concentration rises due to poisoning, therapy is prescribed with adsorbent agents that successfully absorb and remove toxins from the body. These include activated carbon, Smecta, Enterosgel.
If the cause of an increase in the amount of bilirubin is gallbladder dysfunction, choleretic drugs are prescribed. Diagnostics will allow you to determine the cause of the disease - a disorder in the liver, gallstones or pathological changes in the biliary tract.
The action of such drugs is aimed at enhancing the secretion of bile and facilitating its entry into the intestines, which helps speed up the digestion process and reduces the risk of gallstones.
Choleretic drugs differ in their effects - cholekinetics activate the work of the gallbladder, promoting its more frequent contraction, and cholespasmolytics, which affect the biliary tract, relaxing them; choleretics make bile less viscous. Choleretic drugs can also be of mixed type.
The composition of choleretic drugs can include not only synthetic, but also natural components. Chemicals have an analgesic effect, kill pathogenic bacteria and eliminate inflammatory processes, lower cholesterol levels. The effect of such drugs also affects the functioning of the intestines - digestion improves, and the decomposition process is suppressed.
The use of natural choleretic drugs, which may include not only medications, but also herbal decoctions and infusions, is based on the action of essential oils, resins, phytoncides, vitamins and some other substances included in their composition.
Herbal medicines have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the liver, dilute bile, stimulate the functioning of the stomach and pancreas, accelerate metabolism, and have an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect. The most famous natural choleretic drugs include Allohol, Holosas, Hofitol.
In case of serious disorders, choleretic drugs are prescribed in combination with antibiotics. In addition to medications, some types of mineral waters also have a choleretic effect.
To reduce the load on the liver and gallbladder, the doctor may prescribe medications containing enzymes that help improve the functioning of the pancreas and speed up metabolic processes. Examples of such drugs are Mezim, Pancreatin, Festal.
The consequence of some infectious diseases may be an increase in the concentration of bilirubin. To stop the inflammatory process, the doctor may prescribe treatment with antiviral drugs.
Pigment growth may be associated with vitamin B12 deficiency. It will be enough to compensate for the lack of this vitamin to reduce bilirubin.
With anemia, there is a decrease in the concentration of bilirubin, since the body does not produce a sufficient number of red blood cells, and, accordingly, the level of hemoglobin also drops. The tissues of the internal organs do not receive the oxygen necessary for normal functioning.
This also entails a decrease in bilirubin levels. Then iron-containing drugs are prescribed, such as Maltofer, Ferlatum, Aktiferrin.
In some cases, a similar effect of lack of hemoglobin can be caused by a strict low-calorie diet.
Bilirubin (the norm for women by age - the table is given above), namely its indicators, may deviate from the norm if parasites are present in the human body.
They feed on useful substances that come with food, process them and remove toxic products of their vital activity into the human body, which tend to accumulate in the tissues of internal organs, thereby poisoning them and causing an increase in the concentration of pigment.
A stool analysis will help determine what type of worms the patient has, after which the doctor will prescribe treatment. The most well-known means for combating helminths are Pirantel, Vormil, Helmintox, Nemozol.
Diet
People suffering from diabetes mellitus are at risk of exceeding the norm of pigment in the body . In this case, the doctor most often prescribes a special diet.
The essence of such a diet is to completely eliminate overeating. You need to eat in fractional portions, 4-5 times a day. At least 2–2.5 hours should pass between the last meal and sleep. The amount of water, juices, and liquid soups consumed should be at least 2 liters per day. Fried foods are completely excluded from the diet. Salt should be limited and not consumed more than 10 g per day.
Products that cause an increase in pigment concentration:
- sausages and smoked products;
- legumes;
- sorrel, radish, onion, garlic;
- hard cheeses;
- buns, chocolate, ice cream, cakes and pastries;
- lamb and pork, poultry – duck;
- types of fish with high fat content;
- berries or fruits that have a sour taste;
- alcoholic and carbonated drinks;
- hot seasonings and sauces;
- pickles;
- mushrooms;
- canned food
There is another group of products that help reduce bilirubin in the blood.
These include:
- low-fat fermented milk products;
- light dietary soups with vegetables;
- boiled eggs (the yolk must be omitted);
- sweet fruits and berries;
- cereal porridge;
- veal, rabbit, as well as turkey and chicken meat;
- honey;
- teas, homemade compotes and jelly;
- some vegetable crops such as beet and carrots;
- a small amount of butter or vegetable oil;
- stale bread or homemade crackers.
These products will relieve the liver and gallbladder, relieve pain and increase the effectiveness of taking medications.

In medicine, this diet is called table No. 5.
For breakfast, you can prepare porridge with milk or water - semolina, buckwheat, rice or oatmeal. Products with cottage cheese are also added to the diet - cheesecakes, casseroles, dumplings. It is recommended to drink tea or weak coffee with milk.
The next meal should be in 2-3 hours. It is recommended to eat a baked apple, sweet fruit or a handful of berries.
For lunch you should eat a bowl of vegetable soup. Meat and fish, cutlets, vegetables should be either stewed or steamed. The second course can be puree or vegetable stew. They drink fruit juice, compote or jelly.
After 2-3 hours, you can eat a small amount of marshmallows or cookies, drink a glass of heated milk or freshly squeezed juice.
Dinner must be eaten no later than 7 pm. For dinner you can eat a casserole, pasta, mashed potatoes, stewed cabbage or porridge of your choice.
The diet can be supplemented with a small piece of chicken fillet or steamed fish and a salad of fresh vegetables. You can also prepare a vinaigrette by omitting the pickled cucumbers and beans. Half an hour before bedtime, you can drink a cup of low-fat yogurt or kefir. The principle of the diet for pregnant women remains the same.
Phototherapy
After birth, the child’s body no longer needs such a large number of blood cells, which leads to their increased destruction and an increase in bilirubin in the newborn’s blood. This manifests itself in the form of jaundice 3–5 days after birth.
Phototherapy is used to treat jaundice and hemolytic disease in newborns. It is carried out using special ultraviolet lamps, which contribute to the transformation of indirect toxic bilirubin into its direct form, which is not dangerous for the child’s body. Such light therapy is safe for the child, which cannot be said about drug treatment.

To carry out phototherapy, the child is placed in a box where lamps are installed. The genitals are covered with a bandage, and the eyes are protected with glasses. Usually the course of treatment is 4 days. You can take short breaks of 2–3 hours if the jaundice is not pronounced. Irradiation is carried out from all sides, periodically shifting the child, changing his position.
Breastfeeding should not be canceled, as it helps remove pigment from the child’s body. If it is not possible to attach to the breast, use a bottle. During phototherapy, a biochemical test of the child’s blood is performed every day to determine the effectiveness of the procedure.
Undesirable reactions include dryness and flaking of the skin, diathesis, diarrhea, and rashes. Phototherapy is mainly used in the treatment of newborns, but sometimes it is also used to treat adults.
Detailed description of the study
Bilirubin is a reddish-yellow pigment formed from hemoglobin. Total bilirubin is a combination of direct and indirect fractions of this pigment.
Indirect - unbound, free - bilirubin is formed from destroyed red blood cells. It is poorly soluble in water and is toxic to the body, especially when its permissible concentration in serum is exceeded. Normally, indirect bilirubin joins albumin - serum proteins - in the blood and is transported to the liver, where it is converted into direct (bound, non-free). This process is associated with a conjugation reaction - a molecule of glucuronic acid is added to free bilirubin.
The direct fraction of bilirubin is soluble in water and is not toxic to the body. Direct bilirubin enters the lumen of the small intestine along with bile, where it is divided into two parts. The first part of the pigment is absorbed into the blood and excreted from the body along with urine in the form of urobilin pigment. The second part, during biochemical reactions under the influence of enzymes of the intestinal microbiota, is converted into the pigment stercobilin, which is excreted along with feces.
Many diseases are characterized by a syndrome of increased total bilirubin in the blood, or hyperbilirubinemia. This condition is potentially dangerous due to the fact that bilirubin is toxic to the organs of the central nervous system: the brain and spinal cord.
The main clinical symptom of a pronounced increase in the concentration of bilirubin in the blood is jaundice. It is characterized by skin changes from lemon yellow, orange yellow to greenish. Jaundice is a nonspecific syndrome; its development can be caused by many diseases. In clinical practice, there are three types of jaundice:
- Hemolytic, or suprahepatic;
- Parenchymal, or hepatic;
- Mechanical, or subhepatic.
Prehepatic jaundice develops against the background of hemolysis - destruction - of red blood cells, which leads to the release of a large volume of indirect bilirubin into the bloodstream.
Hepatic jaundice is associated directly with damage to liver cells. This type of jaundice occurs with hepatitis of various origins: viral, autoimmune, medicinal, toxic, etc.
Subhepatic jaundice is associated with a violation of the outflow of bile from the liver along the bile ducts. This variant of jaundice is associated with cholelithiasis and pathologies of the pancreas, including tumors. This type of jaundice usually requires surgery.
The best biological material for determining the concentration of total bilirubin is venous blood. This study reveals the amount of pigment in capillary blood. It may be relevant for diagnosing hyperbilirubinemia in newborns (up to 1 month of life), as well as in children under 7 years of age.
Elevated serum bilirubin levels may occur as part of physiological jaundice. It occurs in most babies in the first week of life. The origin of physiological jaundice is based on the characteristics of bilirubin metabolism in newborns. However, an increase in bilirubin concentration during this period can also be a manifestation of a disease, such as hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN). This pathology is characterized by the destruction of the baby's red blood cells, associated with the reaction of immunological intolerance to the red blood cells of the mother and child during pregnancy.
Other indications for testing bilirubin in capillary blood include:
- Large area burns;
- Small/hard-to-reach veins;
- Excessive obesity;
- Proven tendency to thrombus formation in venous vessels.
In the absence of the above indications, it is strongly recommended to study the concentration of this pigment in venous blood. In combination with the analysis of total bilirubin, it is recommended to take bilirubin fractions, liver enzymes (ALT and AST), a complete blood count and compare the results with clinical symptoms.
Folk remedies
It is possible to normalize bilirubin levels, in accordance with the table, in a woman’s body at any age through the use of traditional medicine recipes.
An infusion prepared from corn silk stabilizes the functions of the liver, biliary tract and kidneys. Take 1 d.l. stigmas, pour 200 ml of boiling water, then keep in a steam bath for 15–17 minutes.
Then the infusion is allowed to cool for 45–50 minutes, after which it is filtered and water is added so that the volume is 200 ml. Before use, the infusion is heated and shaken. Drink it every 2–4 hours, 1–3 tbsp. for adults, and 1–2 d.l. for children for a month.

Tea made from chamomile flowers effectively reduces bilirubin. For this, 1 tbsp. the herbs are placed in a teapot and 200 ml of boiling water is poured in, left for half an hour and filtered. The liquid is then divided into three equal parts, which should be taken after each main meal.
Adding 1 tsp. mint leaves in tea help normalize digestion, improve the functioning of the liver and gall bladder. This tea can be drunk for 1.5–2 months.
A decoction of birch leaves effectively reduces the level of bilirubin in the blood. 3 tsp you need to pour 1 tbsp. boiling water and leave for 25–30 minutes. The resulting broth is divided into 8 equal parts. Drink 1 part 4 times a day. Store in the refrigerator.
For the infusion of St. John's wort, you need to take 2 tbsp. herbs and pour 200 ml of boiling water over them. Leave for 30 minutes and then filter. You need to drink the infusion in the morning and evening after meals, 100 ml. The course of treatment is usually 1 month.
Surgical intervention
Before any surgical interventions, the level of pigment in the blood is also examined. If it reaches 55 µmol/l, but other liver test parameters do not exceed normal values and there are no signs of disturbances in the functioning of the liver and gallbladder, then the operation is not cancelled.
In some cases, if the cause of increased bilirubin is gallbladder dysfunction, surgery may be performed. Gallstones or the gallbladder itself are removed. Stones are formed due to the fact that the consistency of bile becomes more viscous, which complicates its outflow from the body.
Prerequisites for the development of gallstone disease are:
- lack of physical activity and obesity;
- pregnancy;
- inflammatory processes in the biliary tract;
- female;
- elderly age;
- excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- operations performed on the stomach and intestines.
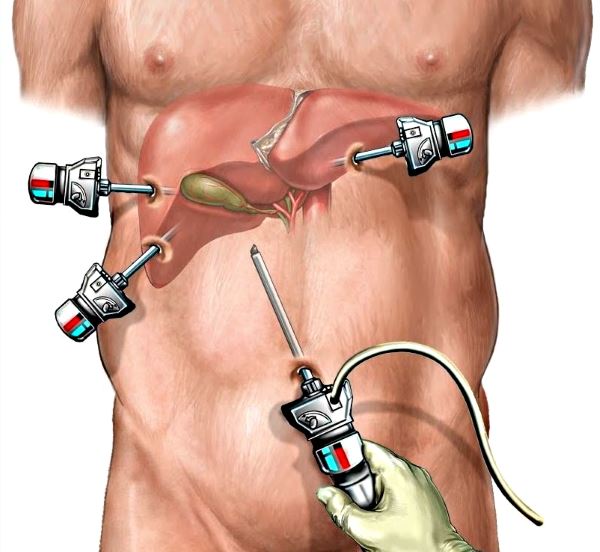
Surgical intervention is performed in several ways. The laparoscopic method is based on the use of special medical equipment - a laparoscope.
This method is the least traumatic and the safest for the patient, since the incisions on the abdomen are very small and other internal organs are not affected during the operation. The duration of such an operation is on average 40–50 minutes.
Under certain conditions, only the stones are removed, and the gallbladder itself is preserved. This operation is performed if there are no disturbances or inflammatory processes in the functioning of this organ, and the diameter of the largest stones does not exceed 3 cm.
An experienced doctor will be able to quickly establish the reason for the excess bilirubin value in a woman’s body at any age, based on the data in the table and finding out which type of pigment indicators exceeded the norm. It is important to recognize the symptoms of the disease in time and conduct the necessary research, which will determine an effective course of treatment.
Article design: Mila Friedan
Symptoms
Abnormalities in the chemical reactions of bilirubin are detected by determining its level in the blood. If the concentration is higher than normal, but does not exceed 85 µmol/l, this is a mild form of hyperbilirubinemia, up to 170 µmol/l is moderate, and from 170 µmol/l is a severe form of the disease. External signs manifest themselves differently, depending on the cause of the increase in bilirubin concentration.
- Liver problems are expressed in the following symptoms:
- Discomfort and heaviness due to liver enlargement.
- Change in urine color (it becomes like dark beer), lightening of stool.
- Heaviness after eating, drinking alcohol, frequent belching.
- Periodically occurring dizziness, general weakness, apathy.
If the cause of the pathological condition is viral hepatitis, then elevated body temperature is added to the symptoms.
- Violation of bile outflow:
- Yellowness of the skin and sclera.
- Itchy skin.
- Intense pain in the right hypochondrium.
- Flatulence, constipation or diarrhea.
- Dark urine, light stool.
A common cause is gallstone disease. The list functions normally, neutralizes incoming bilirubin, but its removal from the body is difficult.
Prehepatic jaundice
- a condition caused by the rapid destruction of red blood cells. Expressed by the following symptoms:
- Anemia.
- Dark stools with normal urine color.
- Extensive hematomas that form without external causes.
- Skin itching, worse at rest and after warming up.
- Yellowish skin color.
Also, sometimes, regardless of the cause, symptoms such as bitterness in the mouth, changes in taste, weakness, impaired memory and intelligence may be observed.