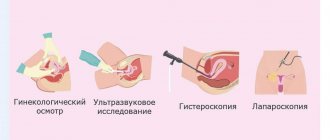
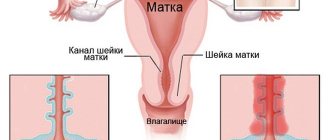
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs for fibroids is the most common diagnostic method, which allows identifying the disease at an early stage of development. It is deservedly considered safe and allows you to obtain a range of information about the state of women's health. In order for the procedure to be as successful as possible, ultrasounds are performed on a certain day of the menstrual cycle. The procedure itself will require simple preparation from the woman.
Causes
The most common cause of this pathology is considered to be a hormonal imbalance, in particular an increase in the amount of estrogen. This dysfunction is facilitated by disturbances in the system of regulation of reproductive functions, from the brain to the ovaries and uterus. These can be both hereditary diseases and inflammatory processes of the genital organs, endocrine diseases and concomitant pathologies.
The formation of myomatous nodes is also influenced by the condition of the uterine receptor apparatus, which worsens after abortion, postpartum complications and chronic infection of the reproductive system.
Causes
Experts around the world cannot name the cause of the pathology with 100% accuracy. Damage to ovarian tissue can affect the growth of the tumor. This impairs their basic function, which leads to increased production of female sex hormones. Studies have shown that estrogens promote tumor growth. As soon as women stopped taking oral contraceptives, the growth of fibroids stopped, and subsequently it completely resolved. But this is not the exact cause, since uterine fibroids can develop in the absence of endocrine disorders. Among other reasons, experts identify:
- Genetic predisposition.
- Lack of pregnancy until 30-35 years of age.
- Diseases of the immune and endocrine system.
- Endometriosis.
- Inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
- Abortion.
- Difficult birth.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
Uterine fibroids during pregnancy
Women with this pathology are capable of conceiving and developing pregnancy. The exception is when fibroids grow into the uterine cavity, thereby reducing its lumen, deforming the uterus and preventing the attachment of a fertilized egg to the uterine wall. Myoma and pregnancy are incomparable phenomena when the myomatous node grows towards the abdominal cavity, which compresses the fallopian tubes and prevents sperm from moving to the egg.
During pregnancy, this pathology can be asymptomatic. A pregnant woman has no idea about the presence of such nodes and learns about them only after the first ultrasound.
Endometriosis – when to perform an ultrasound examination
Unlike diagnosing fibroids, the second phase of the cycle is more suitable for endometriosis, when the uterus prepares to shed the mucous layer.
The following facts indicate the presence of endometriosis:
- uneven thickness of the walls of the uterus;
- round shape of the organ;
- increase in the size of the uterus;
- in the muscle layer, the doctor will see areas with increased echogenicity.
Examination of the ovaries for the presence of cysts should also be carried out in the second half, since cysts gradually increase in size closer to menstruation.
Manifestations of uterine fibroids during pregnancy
In this case, the symptoms depend on the size of the nodes, their number, the nature of their growth and the presence of concomitant pathology from the ovaries or other organs.
Many women who have intermuscular nodes up to 4 cm in size, which are located in the body of the uterus and do not deform its cavity, successfully bear a child and have no complications during childbirth.
Despite such cases, myomatous nodes affect the condition of the pregnant uterus, namely the amount of estrogen entering the uterus, thereby contributing to an increase in the size of fibroids. The influx of progesterone is significantly reduced. This phenomenon is explained by a violation of the receptor apparatus of the uterus, which becomes more sensitive to estrogens. The longer the course of the disease, the more significantly the blood flow in the uterus deteriorates, its volume increases due to the myomatous node, and the risk of complications during pregnancy increases.
MYTH 7: If you have fibroids, forget about the bath and tanning!
In fact.
For patients with uterine fibroids, tanning, baths, saunas and massage are not contraindicated, since there is no scientific evidence of the influence of these factors on the growth and development of fibroid nodes.
We were unable to find a single reliable scientific study that would show a connection between the listed physical effects and the growth of myomatous nodes. All speculation on this matter is purely speculative. This does not mean at all that having learned about this, you need to sunbathe all day under the scorching sun without reasonable restrictions or sit for hours in a sauna. It’s just that if you have uterine fibroids, you shouldn’t make significant changes to your usual lifestyle and limit yourself; try to observe moderation in everything and avoid abuse.
Complications of pregnancy with fibroids
Pregnant women with this disease at any stage have a high risk of developing complications: the threat of miscarriage, impaired trophism of the myomatous node, which can lead to its death and tissue disintegration, increased uterine tone.
The threat of interruption in the early stages and an increase in the tone of the uterus in the second and third semester is possible due to a decrease in the elasticity of the uterus, the low ability of the muscle layer to stretch, while a decrease in blood flow in the myomatous node and the development of an inflammatory process in it are also observed.
During pregnancy, this pathology leads to fetoplacental insufficiency (the inability of the placenta to provide the fetus with the necessary amount of oxygen and nutrients), gestosis in the second half of pregnancy, which is manifested by edema, high blood pressure, decreased kidney function and fetal hypoxia. Women planning to have a child with this pathology should remember the frequent cases of abnormal fetal position (oblique, transverse), breech presentation, as well as complete or partial placenta previa. The most common cause of such pathologies is fibroids, which grow into the uterine cavity and deform it, which does not allow the fetus to be positioned head down and longitudinally. The placenta is also located in the part where there is free space (as a rule, the placenta should be on the back wall of the uterus).
Large myomatous nodes disrupt the uteroplacental circulation if they are located at the site of attachment of the placenta to the uterine wall, which leads to intrauterine growth retardation and chronic hypoxia.
Expectant mothers with fibroids very often experience complications such as: accelerated growth of the tumor, the reasons for which are still completely unknown, premature placental abruption, disruption of the “migration” of the placenta (with increasing gestational age, fibroids also grow, which prevents the normal movement of the placenta from the pharynx to the bottom uterus, and causes its detachment).
Pregnancy and large fibroids are incomparable phenomena. In such cases, an interruption of up to 12 weeks is recommended to avoid life-threatening complications for the woman. Among the possible ones are spontaneous miscarriages, which cause heavy bleeding, since the uterus is not able to contract due to large fibroid nodes; necrosis of myomatous nodes, which causes tissue breakdown; the development of severe placental insufficiency threatens congenital defects of the fetus and its nervous system.
How pregnancy affects uterine fibroids
In the first trimester, due to hormonal changes in the body, there is an increase in the blood supply to the uterus and, accordingly, to the fibroids, which leads to an increase in its size. But, fortunately, this trend is rarely observed. It also happens that the tumor does not grow during pregnancy. Due to the enlargement of the uterus and stretching of the walls, myomatous nodes change their location, and if the node is attached to the wall of the uterus with the help of a thin stalk, then its torsion is possible, which leads to necrosis of the node. Torsion of the leg of the myomatous node is manifested by symptoms of an “acute abdomen”: severe acute pain in the lower abdomen, increased body temperature, symptoms of general intoxication, as well as changes in the general blood test. This complication requires immediate hospitalization and surgical treatment.
In the second and third trimester of pregnancy, it is also possible to develop processes that disrupt the nutrition of fibroids: swelling, necrosis, impaired circulation and lymphatic drainage, which also manifest themselves as symptoms of an “acute abdomen.”
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of uterine fibroids are varied and depend on the location of the fibroids, size and individual characteristics of the body. The most typical manifestations are:
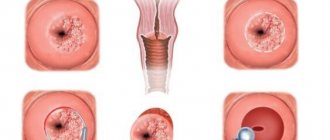
- for submucosal (submucosal) fibroids - heavy and prolonged menstruation; metrorrhagia - uterine bleeding leading to anemia; pain resembling contractions;
- for intermuscular fibroids - often asymptomatic at first, and with increasing size - lengthening and increasing pain of menstruation; bleeding; with significant growth - compression of the organs adjacent to the uterus, resulting, for example, in an increased urge to urinate, sometimes - the development of inflammatory diseases; if the nodes are located on the back wall of the uterus - difficulty defecating and constipation;
- for subperitoneal (subserous) fibroids - disturbances in the menstrual cycle; pain in the lower abdomen; increased temperature and severe pain due to poor nutrition (blood supply) of the myomatous node; with growth - compression of internal organs with difficulty urinating and defecating.
Nonspecific symptoms accompanying uterine fibroids in some cases are infertility, inability to bear a child. They are not always signs of a tumor, but often are its consequence with a pronounced increase in nodes.
Diagnostics
Examination of the expectant mother for fibroids requires a careful approach and is carried out in the following periods:
- I trimester
– examination must be carried out within 7-10 weeks; - 2nd trimester
– 14-16 and 22-24 weeks; - III trimester
– 32-34 and 38-39 weeks.
The examination evaluates fetal development, excludes intrauterine growth retardation and malnutrition in myomatous nodes, and evaluates blood circulation in the placenta, uterus and fetus. At the last examination, the location of fibroids and placenta, the position and presentation of the fetus are clarified in order to decide on the method of delivery.
In the first trimester, pathology can be palpated through the anterior abdominal wall during a vaginal examination. To confirm the diagnosis, ultrasound diagnostic methods are used. Moreover, with the help of ultrasound, it is possible to diagnose small myomatous nodes in the early stages of their development, as well as monitor treatment and the dynamics of fibroid growth. Ultrasound during pregnancy helps to assess the structure, size and number of myomatous nodes, their localization relative to the placenta, as well as the degree of deformation of the uterine cavity, blood supply to the myomatous node. At the same time, measurements of the anatomical structures of the fetus are carried out to exclude intrauterine growth retardation, respiratory parameters, the degree of maturity of the placenta and blood circulation in the fetal-uterine complex are assessed.
To assess the cardiac activity and motor activity of the fetus from the 32nd week of pregnancy, it is advisable to conduct cardiotocography before the onset of labor. Fibroids and pregnancy require CTG every 5 days in recent weeks.
Treatment
During pregnancy, radical measures to treat fibroids are not carried out. It is mainly aimed at avoiding complications of fibroids during this period.
The goal of treatment is to reduce the tone of the uterus, prolong pregnancy for the birth of a full-term fetus, avoid premature birth and the appearance of a healthy baby.
Since fibroids impair the blood supply to the fetoplacental complex, the choice of drug therapy falls on drugs that help improve blood flow in the vessels and prevent fetal hypoxia.
Treatment of fibroids is carried out after the birth of the child, but in acute conditions, not only conservative therapy, but also surgical intervention may be required.
In the IVF Center clinic in Kaliningrad, it is possible to perform a conservative myomectomy - removal of a tumor while preserving the uterus. Pregnancy after this removal of fibroids is possible, and if myomectomy is performed during the gravid period, it is possible to save the fetus.
Timing and method of delivery
A week before the expected date of birth, a pregnant woman should be hospitalized in the maternity ward so that obstetricians and gynecologists can plan and choose a method of delivery. Pregnant women at low risk of complications can give birth vaginally, but using adequate analgesia to avoid vasospasm, as this can lead to fetal hypoxia.
Complications of pregnancy with fibroids:
- earlier discharge of amniotic fluid due to increased uterine tone or pathological location of the fetus;
- bleeding in the postpartum period due to reduced contractility of the uterus in the area of fibroids;
- premature placental abruption.
In case of complicated pregnancy, childbirth is carried out by cesarean section and removal of fibroids.
Pregnancy after fibroids: is it possible?
Often, in order to have a child, it is necessary to undergo conservative treatment with the removal of myomatous nodes, while preserving the uterus. This is an organ-saving operation. Pregnancy after such removal of fibroids is possible; it proceeds without complications, provided that no new tumor foci develop. Its management requires close attention from the doctor, because during gestation, due to hormonal changes, a relapse may develop.
You can plan a pregnancy after fibroids after a 6-month rehabilitation course. This term is due to the peculiarity of the healing of the walls of the uterus, because only the resorption of the sutures occurs after three months.
Prognosis and prevention
If pathology is detected at an early stage and treated conservatively, then further complications are excluded. If a safe surgical operation is prescribed while preserving the integrity of the organ, it is possible to preserve reproductive function. But this applies only to the initial stages of pathology. If the fibroid grows strongly and the patient’s condition worsens, then complete removal of the uterus is required, even at a young age. This is why you need to visit a specialist twice a year for diagnosis, as the disease can lead to infertility.
To avoid relapse after surgery, you need to take hormonal medications. Regular visits to a specialist and MRI and ultrasound are recommended in order to detect tumor formation at an early stage. It is important to avoid severe disruptions in the hormonal system and mechanical damage to the vagina and uterus. The specialist must select the optimal method of contraception to avoid abortion or complicated childbirth. People over 35 years of age should not sunbathe for a long time if surgical treatment of the pathology has been performed.
The multidisciplinary CELT clinic employs experienced specialists.
After a comprehensive examination, the gynecologist will choose the optimal treatment method or (most often) a sequential combination of methods, i.e. will develop an individual treatment program for uterine fibroids. Our doctors try in most cases to resort to organ-preserving laparoscopic operations, which are the least traumatic and allow you to preserve the uterus and ovaries and have children in the future. We answer the most popular questions from patients about uterine fibroids on our website.
Is it possible to confuse fibroids with pregnancy?
Many women's websites report stories of how fibroids were confused with pregnancy on an ultrasound. Indeed, in the early stages, the fertilized egg is similar in size to a myomatous node and there is a risk of confusing the disease with pregnancy if the ultrasound machine is old, the image is of poor quality, and the doctor himself is incompetent. But any highly qualified specialist will not allow himself to confuse fibroids with pregnancy, because in addition to ultrasound, there are other diagnostic methods that allow you to determine an accurate diagnosis.
- Pregnancy can be diagnosed during a routine gynecological examination, based on the size and consistency of the uterus, as well as the appearance of its cervix.
- In addition, the gynecologist prescribes an analysis to determine the level of hCG. Myoma does not affect the amount of this hormone, and during pregnancy it will be increased.
- The menstrual cycle with fibroids is preserved, which is impossible during pregnancy.
Make an appointment by calling +7
or
use the registration form: Make an appointment
Our services
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Preoperative hysteroscopy | 35 000 |
| Embolization of the uterine arteries without taking into account the cost of embolic agents and consumable instruments (radial access) | 86 000 |
| Endoscopic conservative myomectomy | 100 000 — 145 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions