Computed tomography is a modern high-tech diagnostic method, the essence of which is to scan the patient’s body with X-rays and create a computer image of internal organs. Thanks to the use of this painless and safe study, data on the presence of inflammatory processes, tumors, abscesses, injuries and developmental abnormalities is obtained.
You can get a computed tomography scan in Moscow at an affordable price at one of the leading medical centers - the Yusupov Hospital. Radiologists perform computed tomography using the latest equipment from leading global manufacturers. Examination of patients and interpretation of study results are performed by doctors who have undergone special training and have extensive practical experience. If a complex pathology is determined during a CT scan, the results of the study are discussed at a meeting of the Expert Council with the participation of doctors and candidates of medical sciences, doctors of the highest category.
Indications and contraindications
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use computed tomography as a routine examination and for emergency indications (for injuries, suspected bleeding, cerebrovascular accident). During the examination, the patient bears radiation exposure. For this reason, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe a computed tomography scan only if there are the following indications:
- Diseases of the brain and spinal cord;
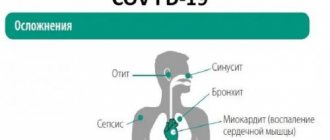
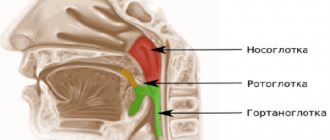
- Pathologies of ENT organs;
- Traumatic injuries and diseases of the spine;
- Vascular pathology;
- Diseases of internal organs (heart, lungs, kidneys, liver, pancreas, mediastinal organs and reproductive system).
Despite the well-tolerated procedure by patients and the absence of absolute contraindications, the study is prescribed by the doctor after a detailed assessment of the patient’s complaints, objective examination data, results of laboratory and instrumental studies (except in emergency cases).
CT scans are not performed on pregnant women. The radiation exposure to the body during a computer scan significantly exceeds the dose received by the patient during a standard x-ray examination; the risk of developing defects in the fetus increases. For the same reason, small children are prescribed a computed tomography scan only if other research methods fail to establish an accurate diagnosis. If contrast agents are planned to be administered during a CT scan, doctors will find out whether the patient has previously had allergic reactions to iodine-containing drugs. If you have an allergy to iodine, computed tomography with contrast is not performed.
Contraindications to CT examination are the patient’s severe general condition caused by decompensated diabetes mellitus, renal failure, multiple myeloma, diseases of the thyroid gland and other organs. CT scans are not performed on patients with mental health disorders (claustrophobia - fear of closed spaces). CT examination cannot be performed on patients whose weight exceeds the load for which the device is designed. Before a CT examination, radiologists obtain the patient’s motivated consent to conduct the examination.
Make an appointment
Contrast enhancement
The need to constantly improve examination results complicates the diagnostic process. Increasing information content due to contrast is based on the ability to distinguish tissue structures that have even slight differences in density, which are often not determined during conventional CT.
It is known that healthy and pathological tissue have different intensities of blood supply, which causes a difference in the volume of incoming blood. The introduction of an X-ray contrast agent allows for increased image density, which is closely related to the concentration of iodine-containing X-ray contrast agent. Injection into a vein of 60% contrast agent in an amount of 1 mg per 1 kg of patient weight can improve the visualization of the organ under study by approximately 40–50 Hounsfield units.
There are 2 ways to introduce contrast into the body:
- oral;
- intravenous.
In the first case, the patient drinks the drug. Typically, this method is used to visualize hollow organs of the gastrointestinal tract. Intravenous administration makes it possible to assess the degree of accumulation of the drug in the tissues of the organs being studied. It can be carried out by manual or automatic (bolus) administration of the substance.
Important! The rate of bolus administration of the drug fully corresponds to the operating mode of a modern tomograph, so it is almost impossible to obtain a similar result using a manual one.
Preparing for the study
At the start of the examination, the patient must provide all the necessary clinical information, as well as data from previous examinations to the radiologist. Doctors recommend wearing loose clothing without metal devices and removing jewelry. If you are planning a computed tomography scan with contrast, you must first discuss with your doctor the possibility of using a contrast agent if the patient is taking the following medications:
- b-blockers;
- Glucophage (metformin);
- Interleukin;
- Guanidines;
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
In the presence of chronic kidney disease, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital evaluate the state of kidney function (blood plasma creatine should be in the range of 60-130 microns per liter).
If renal function is impaired, other alternative research methods (ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging) are considered. When planning a CT examination, preliminary preparation is carried out depending on the degree of risk, which is prescribed by the anesthesiologist. If a patient has diseases of the thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism, papillary or follicular cancer of the thyroid gland), when planning scintigraphy (studies with iodine intake) or treatment with radioactive iodine, consider the possibility of using other alternative research methods, prepare for the examination, consult with the attending physician and the doctor. anesthesiologist. If hyperthyroidism is suspected, the levels of the hormones T3, T4 and thyroxine in the blood serum are examined. Active hyperthyroidism is a contraindication to the use of contrast media.
In patients suffering from diabetes mellitus (diabetic nephropathy), the state of renal function is assessed (blood plasma creatine should be in the range of 60 -130 µm/l). If renal function is impaired, alternative research methods are used. On the eve of computed tomography, preliminary preparation is carried out depending on the degree of risk, which is determined by the anesthesiologist.
Caution should be exercised when performing computed tomography using contrast in patients suffering from bronchial asthma and polyallergies. If a patient has heart disease with stage 3-4 heart failure and has recently suffered a heart attack, ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging is preferred. If there is still a need for a computed tomography scan, patients are first consulted by a cardiologist and an anesthesiologist.
If there is information about allergic reactions to iodine, the presence of itching, urticaria, the anesthesiologist prescribes premedication. In case of an examination with intravenous contrast, the patient is advised not to eat food 4 hours before the examination. When examining bones, soft tissues, head, neck, spine and chest cavity, special preparation for the examination is usually not required. Medicines, medical procedures and drinks can be taken as usual.
Before performing a CT scan of the heart, the heart rate is counted. It should not exceed 70-75 beats per minute. On the day of the examination, patients should stop smoking and drinking alcohol, avoid taking atropine, caffeine, and administering N-butylscopolamine and theophylline. At a higher heart rate, first discuss with the anesthesiologist or attending physician the possibility of taking medications (beta-blockers). These drugs are not used if the patient has bronchial asthma, blockade, severe hypotension, severe heart failure, or there is information about intolerance to beta-blockers.
When preparing for a computed tomography scan of the abdominal cavity, the patient drinks 1-1.5 liters of non-carbonated purified water in portions within 1-1.5 hours before the examination. The radiologist must also be informed if surgery is planned immediately after the examination, if there is a suspicion of perforation of a hollow organ or the presence of a fistula. Computed tomography of the abdominal cavity and pelvis is carried out no earlier than three days (and for constipation or more) after an X-ray examination of the intestines or stomach with a barium suspension.
During a CT examination of the pelvic organs, the patient is asked to drink 1-1.5 liters of non-carbonated plain water in small portions within 1-1.5 hours before the examination. It is necessary to have a moderately full bladder. If the patient has a catheter installed, it is closed 30 minutes before the examination.
If dual contrast is planned to be used during a CT scan, the patient should arrive at the hospital one hour before the procedure. The laboratory assistant gives the subject a contrast agent diluted in a certain way. The patient drinks it within an hour immediately before the test. This does not affect the cost of a CT scan.
Summarizing
It is difficult to say which of the modern diagnostic methods is better for examining the lungs. Everyone has their own strengths and weaknesses.
MRI does not show the condition of tissues that are in constant motion well enough. But when studying functional changes in hemodynamics, perfusion, assessing pulmonary ventilation, and their work, it is better to use magnetic resonance imaging.
Computed tomography is considered more informative in examining the hollow structures of the lungs and assessing the condition of small vessels of the respiratory tract, but its results in the study of neoplasms are inferior to MRI data.
The choice of lung diagnostic method should be left to specialists.
Progress of the procedure
During a CT scan, the patient lies motionless on a special mobile table.
The most accurate image can be obtained by periodically holding your breath, which the radiologist warns the patient about during the procedure via speakerphone, observing the subject through the viewing window. The tomograph ring moves along the patient’s body, while X-rays illuminate the required area. Computed tomography is characterized by high scanning speed and low x-ray load on the body. High quality images ensure the detection of pathologies at the earliest stages of their development.
Make an appointment
Image rendering
To visually determine tissue density during computed tomography, a black-and-white Hounsfield scale is used, which has 4096 units of change in radiation intensity. The starting point in the scale is an indicator reflecting the density of water - 0 НU. Indicators that reflect less dense values, for example, air and fat tissue, are below zero in the range from 0 to -1024, and more dense values (soft tissue, bones) are above zero, in the range from 0 to 3071.
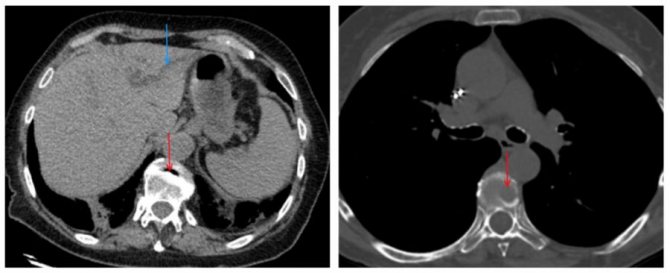
Changing image contrast to improve visualization of structural abnormalities in the intervertebral disc
However, a modern computer monitor is not capable of reflecting so many shades of gray. In this regard, to reflect the required range, a software recalculation of the received data is used into the scale interval available for display.
With a conventional scan, tomography shows an image of all structures that differ significantly in density, but structures that have similar indicators are not visualized on the monitor; a narrowing of the “window” (range) of the image is used. In this case, all objects located in the viewed area are clearly visible, but the surrounding structures can no longer be seen.
What does a CT scan show?
Computed tomography of the skull and brain allows for a comprehensive assessment of soft tissues, blood vessels, bones, and cavities.
It is used for traumatic brain injuries, tumors of the meninges and brain, vascular pathologies, hemorrhagic strokes. Computed tomography of the temporomandibular joint is a reliable non-invasive method for diagnosing minor disorders of the musculoskeletal structures. Prescribed for marking and planning dental implantation, it allows you to identify and clarify the nature of the malignant tumor, and identify the consequences of injury.
Computed tomography of the abdominal cavity is performed to detect appendicitis, intestinal abscesses, tumors, cysts, abdominal aortic aneurysm, abdominal blood clots, ascites. CT scan of the liver allows you to obtain not only standard data on tissue density, identify neoplasms and pathologies, but also assess the iron content in the organ.
Computed tomography of the mediastinal organs and lungs provides the most accurate visualization of structures that cannot be distinguished using fluorography and radiography. Before a CT scan of the lungs, a plain radiograph is required.
Computed tomography of the spine is prescribed to determine the presence and extent of damage to cartilage and bone tissue. Used to diagnose the following diseases:
- Osteoporosis;
- Osteomyelitis;
- Osteochondrosis;
- Arthritis;
- Injuries, spinal curvatures;
- Vertebral displacements;
- Tumors of cartilage and bone structures.
Computed tomography of the kidneys and urinary tract helps to identify and study infectious processes, tumors, and the consequences of injury.
Kidney CT is prescribed for patients with complaints of lower back pain, if pyelonephritis, cancer, or cyst are suspected. The study is not carried out in patients with renal failure. Computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses is used in otolaryngology for inflammation of the lacrimal ducts, paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity, suspected tumors, as well as traumatic lesions of the nose. Considered the gold standard for diagnosing chronic sinusitis. Computed tomography of the chest is prescribed for the diagnosis of infectious, oncological, inflammatory and other pathologies affecting the lungs and pleura, heart, esophagus, ribs, sternum, mammary glands, etc.
Computed tomography of joints allows you to identify injuries, inflammatory and degenerative diseases of the joints. CT scan of joints is used to assess the size of joints and joint spaces, the quality of articular surfaces, identify diffuse, focal or degenerative changes in cartilage and bone tissues, the volume of synovial fluid in the joint capsules, the presence of cartilaginous growths and osteophytes, swelling and effusions in the joints.
Computed tomography of the pelvis allows for primary and differential diagnosis of oncological and surgical pathologies, identification of injuries, gynecological and urological diseases, and vascular pathologies. Often, CT scans of joints require the use of contrast. The study allows you to detect fluid, blood, pus in the pelvis, assess the nature of congenital pathologies, size, location and structural features of organs, bone structures of the pelvis and identify the presence of pathological processes in them.

Diagnostic results
The results obtained during a computed tomography scan will be ready within 24 or 48 hours.
The norm is:
- normal size, position and patency of internal organs and blood vessels;
- absence of foreign bodies;
- absence of foci of inflammation and neoplasms;
- no bleeding or cavities filled with fluid.
Pathologies may be indicated by:
- internal organs are too large or small;
- damage to organs;
- abscesses, cavities of fluid or air in the abdomen, lungs, or chest;
- the presence of foreign bodies and stones;
- tumors in the intestines, lungs, ovaries, liver and other organs;
- aneurysms of blood vessels;
- obstruction of the intestines or bile ducts;
- the presence of foci of inflammation or diverticula in the intestine;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- blocked blood vessels;
- fractures, infections, bone growths.
CT in Moscow: addresses and prices
CT scanning is included in the list of medical services that are provided by the state free of charge to every citizen of Russia. Therefore, undergoing an examination is possible only if there is a special referral from the attending physician at the clinic at the place of residence. If the institution itself does not have a machine for performing CT scans, the doctor may indicate in the referral a clinic or medical center where a CT scan can be performed in Moscow (prices for additional services can be checked independently with the center administrators).
The patient is placed in a special queue, where he must wait no longer than one month, and in case of suspicion of a malignant tumor - no longer than two weeks. If the disease progresses during the waiting period, every patient has the right to find out where a CT scan can be done in Moscow inexpensively and with high quality. Almost every private medical center in the capital provides a paid CT service. The price in Moscow for computed tomography depends on the part of the body that is planned to be scanned and ranges from three to seven thousand rubles. The cost of CT with contrast is higher than without it.
Due to the lower flow of patients in private medical centers, which includes the Yusupov Hospital, doing a CT scan will be much easier and faster. To undergo the examination, the patient is given the opportunity to sign up on any day and time convenient for him. The quality of the procedure does not suffer at all, as the Yusupov Hospital has installed a modern fifth-generation computed tomograph. The cost of the procedure in Moscow is slightly higher than in other regions of Russia.
How much does a CT scan cost at Yusupov Hospital?
Thanks to the high quality of diagnostic services, comfortable conditions created for the convenience of each patient and competitive prices, the Yusupov Hospital enjoys well-deserved trust. The study is carried out on a modern new generation computed tomography scanner; the results of computed tomography are interpreted by competent specialists, which together guarantees a high quality of the procedure, an accurate diagnosis and the most effective treatment regimen for the established disease.
The results of the study are given to the patient in hand and electronically, so that in the future it is possible to provide the attending physician with information about what the computed tomography showed. The price of a CT scan at the Yusupov Hospital is quite affordable for everyone and depends on the area of study and the type of tomography (with or without contrast). To find out the cost of computed tomography, call the contact center of the Yusupov Hospital.