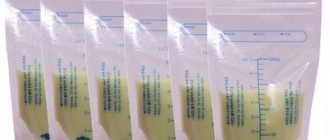
Colostrum color
Colostrum changes color after childbirth: from dark to light.
The female body begins to prepare nutrition for the unborn baby immediately after conception. Gradually, the mammary glands are rebuilt for lactation. Sometimes yellow spots appear on the bra, although there is still a lot of time left before the birth - this is the first production of colostrum. The main part of it is formed after the completion of childbirth.
Colostrum is the liquid that is secreted by a woman’s mammary glands in the first days after childbirth. It is distinguished by its thickness and yellow (cream) tint. Sometimes only a few drops of colostrum are released, but the baby does not require a significant amount of nutrition in the first hours of life, the main thing is fat content and richness.
After 2-14 days, the nutritional fluid changes: the color of breast milk becomes lighter and more transparent. There is no need to worry about this.
Composition of breast milk after one year
Breast milk is unique in that its composition adapts to the needs of the baby at different ages. WHO research suggests that after a year it covers 40% of daily calorie needs. Associated with this is the myth that children on breastfeeding eat worse. The volume of complementary foods is actually less, but this does not mean that the child is hungry.
Moreover, during this period the fat content of milk increases 2-3 times, and with it the amount of antibodies. Immunoglobulin A will help protect your baby, who explores the world and puts everything in his mouth, from intestinal infections, stomatitis and other diseases.
Breast milk plays a special role for children with allergies. It prevents the penetration of allergens into the blood through the intestinal mucous membranes.
The answer to the question of whether breastfeeding is useful after a year has been helped by research. Observations have confirmed that children receive a sufficient amount of:
- calcium, important for growth;
- potassium;
- gland;
- B vitamins;
- vitamins A and C;
- folates
Babies who drink breast milk at night are much less likely to suffer from tooth decay. It has virtually no effect on the acidity level in the mouth because it is swallowed immediately. Moreover, immunoglobulins IgA, IgG and lactoferrin inhibit the growth of streptococcal bacteria in the mouth. Night sucking stimulates salivation, which also enhances oral protection.
Regarding mental health, long-term observations confirm that long-term breastfeeding:
- promotes better adaptation of the child in the children's team;
- simplifies communication with a child during adolescence;
- provides a higher level of intelligence, including emotional intelligence.
Hind and foremilk

If you look at expressed milk that has stood in a transparent container, it will appear stratified into a translucent liquid below and a thick layer (cream) on top. Don't worry if there is not enough cream.
During feeding, with the first sips, the baby receives a pale, watery mixture - foremilk. Subsequent portions become fattier and thicker - this is hind milk. Its color is closer to cream.
Foremilk, watery, fills the baby's body with liquid, and hindmilk - with nutrients. It is important to use both types.
If the baby sucks on one breast for a long time, do not rush and offer the next one. The baby may not receive enough fatty hind milk, which will negatively affect weight gain. Sometimes it seems that there is nothing else in the chest, but the baby continues to suckle - it is worth giving the baby time to completely empty it. It is more difficult for a baby to obtain hind milk than fore milk. Sometimes this takes 20-40 minutes. It is important to be patient.
Healthy milk color

The color shade of milk is a variable characteristic. It changes during feeding, during the day and as the baby grows older.
Clear-colored breast milk is just as healthy as cream-colored breast milk.
Yellow color makes it clear about the presence of proteins and fats. They are necessary to saturate the child. Blue milk is no less important - it only seems useless, but it contains carbohydrates and water. Children under 6 months of age do not need to be given additional fluids, since foremilk replaces it. After six months, the composition and color of the milk changes as the child matures. He begins to eat complementary foods, and the mother’s body reacts to this by changing the nutrient fluid.
If the mother is worried that the baby is not eating enough, it is worth offering him the breast a little more often. It is important that the child empties it completely, reaching the fatty rear part.
Expert opinion
Sokolova L. S.
Pediatrician of the highest category
Only one breast should be given to the baby at one feeding. Otherwise, he will easily suck the foremilk from both mammary glands, but at the same time he will remain half-starved.
Protein in breast milk
Proteins are the basis for the growth of the body. Getting high-quality proteins plays a particularly important role in the first year of a child’s life, as he grows very quickly. Your milk contains proteins specially prepared for your growing baby.
The protein content of mature breast milk is approximately 1%. Proteins are represented by casein and whey fractions. Casein protein is synthesized directly in the mammary gland, and whey protein is filtered from the mother's blood. The ratio of these fractions in human milk is 20: 80 (30: 70).
Breast milk forms almost invisible flakes in the stomach, facilitating digestion and is quickly evacuated from the stomach. This makes it possible to frequently put the baby to the breast without fear of gastrointestinal overload and digestive disorders.
Whey proteins in human milk are mainly represented by alpha-lactoglobulin, an important component of the enzyme system in the synthesis of lactose. It should be noted that breast milk substitutes are made from cow's (goat's) milk and contain beta-lactoglobulin, which is a powerful allergen, as whey protein.
In human milk, a higher level of free amino acids is determined, among which the most important are cysteine and taurine, since their synthesis in young children is difficult. Cysteine is essential for the fetus and children born prematurely, and taurine is necessary for the maturation and development of the child’s central nervous system.
Remember that a child's intestines do not accept foreign proteins that are part of formula and contained in cow's milk well, because it is more difficult for him to digest casein.
What can affect color

Chemical elements from foods eaten by the mother enter the milk, so its composition is always different.
Reasons for milk coloring in different shades:
- orange - a woman eats a lot of foods with carotene, for example, carrots, pumpkin;
- pink - the influence of dyes from lemonade, jelly;
- green – consumption of a significant amount of green vegetation, drinks tinted with food coloring;
- blue – blueberries, blueberries and other berries can give milk a blue color;
- gray, black – drinking cola-based carbonated drinks. Certain medications can turn milk dark gray, almost black.
Normal milk is clear or thick and may have a yellowish or bluish tint. Don't worry about this. It’s another matter if red streaks are noticed in the milk. More often this occurs due to damaged blood vessels and cracks in the nipples. Such nutrition is acceptable for a child, but the mother needs to consult a gynecologist to eliminate the problem.
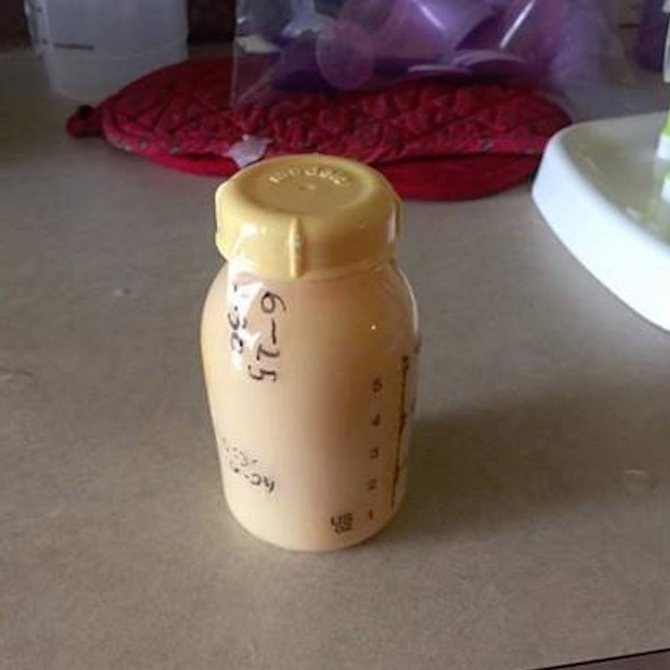

Why is breast milk yellow? If the child is not capricious and has normal bowel movements, there is no need to worry. But if, despite the presence of yellow streaks in mother’s milk, the baby’s stool becomes liquid and green in color, this is a reason to consult a doctor.
Most likely, mom has mastitis. It is accompanied by chest pain, body aches, drowsiness, and fever. You can check this by expressing milk onto a cotton pad. The liquid will be absorbed, normally the disc should remain clean. If yellow veins are visible on it, often with an unpleasant odor, go to the hospital immediately.
The development of mastitis is not a reason to stop breastfeeding. Modern medications can quickly solve the problem. The attending physician will develop an individual treatment plan that is compatible with feeding the baby.
Milk research
You can make sure that everything is fine with the milk or, conversely, there is pus or blood in it, through laboratory testing.
Milk must be collected correctly:
- wash your breasts;
- wipe dry;
- wipe with a semi-alcohol solution;
- express milk before feeding (the first drops on a napkin, the rest in a sterile container);
- submit the analysis within two hours from the moment of pumping.
A referral for examination is given by a pediatrician or therapist. There are laboratories that perform the procedure for a fee (without a referral). There is no need to draw conclusions based on the color of milk yourself. This should be judged by a specialist, not a friend, mother or grandmother.
Breast milk as a message
New research by American biologists has shown that mother's milk also contains a special hormonal “message” that regulates the growth and development of the child - in addition to the necessary nutrients, microelements, immune factors in the right proportions, as well as unique prebiotics that populate the initially sterile intestines of the baby and help him digest food. The results of the study were published in the journal Behavioral Ecology.
Katie Hinde, a biologist at Harvard University (USA), and her colleagues observed 108 lactating female rhesus macaques and their babies at the National Primate Research Center in California. The researchers took milk samples to assess the energy content and levels of the hormone cortisol contained in it. Cortisol has many functions in the human and animal body, but primarily it is known as the “stress hormone.” Cortisol produced in the mother's body also passes into breast milk. Scientists have found that baby macaques quickly develop specific receptors in the intestines responsible for the absorption of cortisol and they are extremely sensitive to its content in mother's milk. Hormone levels varied among different females. In females whose milk contained high levels of cortisol, the cubs quickly gained weight and were more irritable and restless.
Biologists have tried to establish factors influencing the level of cortisol in female milk. It turned out that young “mothers” had significantly higher levels of cortisol in their milk. At the same time, the level of cortisol in the milk of monkeys that had ten or more children was low, but it was higher in calories. Katie Hind suggested that cortisol provides a kind of information to the baby's body so that it does not expect a lot of milk and energy. He seems to be saying: “don’t waste your energy on games or walks, but gain weight quickly.” For this reason, the cubs of young females grow faster, despite receiving less nutritious milk from their inexperienced mothers.
It's tempting to draw analogies with human babies and their mothers' stress hormone levels. But, apparently, things are somewhat more complicated here. Scientists generally know much less about the effects of cortisol on human infants because it is impossible to conduct the same carefully controlled studies in humans as have been done in macaque monkeys. But at the same time, the few data that are available give us pause. Thus, studies conducted in 2013 indicate that children who received a lot of cortisol in milk grew up restless and difficult to calm down. But scientists can't say whether human babies react in the same way. Manufacturers of artificial formulas today almost exactly copy the quantitative proportions of human milk, but they do not have sufficient data on its hormonal composition.
Color of milk upon cessation of lactation

WHO recommends not stopping lactation until two years of age. Typically, women prefer to breastfeed until one year of age. When your baby rarely nurses, the fluid in the breast becomes thicker. The color of breast milk at the end of lactation is white or yellowish, but this is not necessary. The decision to stop feeding should be deliberate and not depend on the color of the milk. It’s good when the baby weans off the breast on his own, but this rarely happens.
When not to suddenly stop breastfeeding:
- summer - the baby needs a lot of fluid, he may completely refuse regular food;
- illness of the child - mother’s milk is important for maintaining immunity and for calming and distracting the baby from pain and discomfort;
- lactostasis - if milk stagnates in the breast, the child can best pump it out naturally;
- teething - mother's breasts are an excellent massager for swollen gums, milk relieves inflammation and calms irritability.
There are children who, during teething, can sleep only by calming themselves by sucking their mother's milk. When the teeth erupt, the child will switch to regular food on its own. Usually all teeth appear by two years. It is not for nothing that WHO recommends maintaining breastfeeding at least until six months of age, and the longer the better [1].
Breastfeeding is a reliable method of contraception
Argument: While you are breastfeeding, it is impossible to get pregnant.
Fact: Breastfeeding is an unreliable method of birth control, and the egg can mature before the first menstruation. There are contraceptives that are safe for nursing mothers: condoms, mini-pills, intrauterine devices.
Remember that most superstitions about breastfeeding have nothing to do with reality. Do not hesitate to seek help from certified consultants, breastfeed your baby and enjoy the process!