What does it look like
This substance is formed in the breast before childbirth and continues to be released in the first 3-5 days after, until transitional milk appears to replace it. Early colostrum can appear at any stage of pregnancy. Long before delivery, a small amount of yellow or whitish, translucent colostrum is sometimes released from the breast. This is considered a normal variant if it is not accompanied by pain and is not stained with blood.
To find out what colostrum looks like, just press on the nipple immediately after birth (this cannot be done before giving birth, so as not to stimulate the uterus earlier than expected). A thick substance will be released; it tastes salty and differs from milk. The color of colostrum is usually yellowish.
Composition and functions
Before birth, the child fed, receiving already broken down beneficial substances from the mother’s blood and the placenta. His stomach and intestines are sterile. But immediately after birth, the type of nutrition changes dramatically. The composition of colostrum, similar to human blood, is designed to solve several problems at once:
- Protect the child from an aggressive microbiological environment. From the complete purity of the uterus, immediately after birth he is attacked by bacteria, viruses and other microorganisms. To prevent pathogens from having a detrimental effect on the little person, the mother supplies immunoglobulins and other living immune cells of various types. Some enter the blood, others line the mucous membrane of the child’s intestines, nasopharynx, and respiratory organs.
- Colonize the digestive tract with bacteria. Their benefits are in the formation of one’s own immunity, assistance in the digestion of new food and the synthesis of substances necessary for the body.
- Give energy for life, growth and development. The beneficial properties of colostrum are such that with a smaller amount of food (after all, the stomach is not yet ready to work at full capacity), the baby receives the maximum benefit. There are still a few fats and carbohydrates, because they will not be fully digested. But there is enough protein, since the baby grows very quickly and gains weight.
- Provide the body with vitamins and minerals for organ development. Colostrum is yellow due to its high carotene content. These factors contribute to the development of vision. And a large amount of zinc promotes rapid brain growth. After all, the first task of a baby is to see and recognize the mother as the source of his nutrition.
- Adapt to a new life. The appearance of colostrum provides the newborn’s stomach and intestines with a painless transition from the previous type of nutrition to a new one. The chemical composition of the substance is similar to both blood and amniotic fluid, which he was accustomed to swallowing during pregnancy in the womb. At the same time, such nutrition protects the kidneys, which are not yet ready for the load: it contains a lot of calories, but little fluid. So gradually the organs become accustomed to milk.
- Discard meconium. Even in the prenatal period, the child’s intestines are filled with original feces, in which the products of the liver – bilirubin – have accumulated. It is important to remove it quickly, so colostrum has a laxative effect. Helps cope with newborn jaundice.

Burying
Use natural products in your nose:
- Propolis – cleanses the nose.
- Beetroot juice makes breathing easier and relieves congestion.
- Undiluted Kalanchoe or aloe juice (for small children it is better to dilute it with water 1:1) – disinfects and kills pathogenic flora.
- Onion juice (diluted with water 1:2; 1:3) – kills any bacteria, viruses, fungi.
The procedure is carried out in a sitting or lying position. First, the nose is cleared of mucus. The head is tilted back, 2-4 drops of medicine are injected into the nostril. In this case, you need to hold your breath so that the product does not enter the stomach. After the manipulation, the head is turned towards the instilled nostril for 2 minutes.
During pregnancy
Moderate release of colostrum from the nipples even before birth at any stage of pregnancy is normal. The mother's body is just training, preparing for the birth of a child. It is formed under the influence of hormones immediately after conception and can appear from the mammary glands when pressed. But you shouldn’t experiment with this, because... Stimulation of the nipples by the type of latching by the baby causes the mother's body to release hormones that are simultaneously responsible for the contraction of the uterus.
If you haven't noticed these white or yellowish spots throughout your pregnancy, don't worry, this is normal. Although in some cases it appears before birth, most often it begins to be released on its own immediately after the baby is born.
Deviations from the norm
The release of colostrum during pregnancy is a completely normal and natural process, but a woman should still discuss this issue with her gynecologist. Only the doctor leading the pregnancy knows the history of his patient, the characteristics of her body and is aware of current diseases.
Some symptoms of lactation, which are normal for some women, may be the first warning bell for others. These include:
- The color of early milk. In the later stages, bloody spots are found in the colostrum, and gynecologists do not believe that this is a pathology, but recommend undergoing additional examination, just in case. A pregnant woman should visit a mammologist and surgeon to rule out diseases of the mammary glands. You can also make an appointment with an oncologist to confirm or refute your preliminary diagnosis.
- Odor and feeling unwell. Colostrum has a pleasant aroma and sweet taste. An unpleasant odor, a green tint, and a bitter or salty taste to the milk may indicate an infection in the milk ducts. The disease is often accompanied by fever, weakness, poor health and engorgement of the mammary glands. A bacterial infection is dangerous for the fetus and can only be treated with special medications, so at the first symptoms you need to go to a gynecologist.
- Amount of milk. Intensive lactation is a normal option, but this does not mean that it is not dangerous. In some women, due to the flow of milk to the breast, the level of oxytocin increases and goes beyond acceptable limits. The hormone stimulates uterine contractions and can cause miscarriage or early labor. With strong lactation, a pregnant woman should get tested for prolactin and estrogen levels, and also think about what habits can stimulate the production of colostrum.
- Neoplasms. Breast enlargement, a feeling of heaviness and engorgement are the norm, but deformation of the mammary glands is a sign of pathology. Any depressions, bumps and seals are a reason to consult a doctor. Strange formations can be cysts, benign or malignant tumors, and the sooner a doctor makes a diagnosis, the easier it will be to treat the disease.
- Shape of the mammary glands. It is worth consulting with a gynecologist and mammologist if a woman has one breast that has become significantly larger than the other, although before pregnancy they were almost symmetrical. Asymmetry may indicate problems with glandular lobules and milk ducts, cysts and even hormone-dependent tumors.
- Uncomfortable sensations. Itching and tingling in the chest and nipples are normal. Nagging pain radiating to the uterus or lower back is an alarming symptom, especially in the early stages. Discomfortable sensations warn the pregnant woman that she may have a miscarriage or premature birth, so it is better for the expectant mother to consult a gynecologist and, if necessary, undergo conservatorship.
Strange symptoms are not a reason to panic. They may turn out to be a variant of the norm, so do not worry, because stress only worsens the situation and harms the child. It is better to visit a gynecologist, undergo all tests and follow the specialist’s recommendations.
Hygiene rules and feeding regime
It is important to feed your baby colostrum in the first hour of life. This starts the process of its additional secretion and the establishment of subsequent lactation. The milk will come only in a few days, and inexperienced mothers sometimes worry whether the baby is hungry. You should not express colostrum to check for its presence if the baby is close to the mother, has full access to the breast and is actively sucking. Just out of curiosity, you can’t squeeze out colostrum, because there’s not much of it, and everything should go to the baby.
Pumping is indicated in the following cases:
- The newborn is weakened and is under observation. He will not be able to suckle on his own; he must be fed colostrum from a bottle.
- The woman in labor received medications that were harmful to the baby. It's better to decant and discard.
- Rhesus conflict is possible. Colostrum should not be given to a child until the child’s blood type and Rh factor have been determined and a doctor’s opinion has been obtained. If a conflict arises, you should pump regularly to maintain lactation until the pediatrician allows you to start breastfeeding.
- There was a long break between feedings. It's better to express the portion. Colostrum is not stored, so it is useless to freeze it: the main – protective – function will be lost after thawing.
In order for the release of colostrum (and subsequently milk) to be regular and sufficient, you must follow the rules of breast care:
- Wear a special bra made from natural fabrics, selected according to size.
- Wash your breasts once a day, not before each application.
- If cracks occur, apply only special ointments recommended by pediatricians.
How much should there be
Feeding your newborn colostrum is very important. The benefit is mutual: the baby receives invaluable drops and learns to digest food, the mother’s uterus contracts, and during these short periods of sucking the breast prepares for full feeding. After all, breastfeeding will place a significant strain on the delicate skin of the nipples, soreness and cracks are possible. This short-term training is needed to adapt to the next period.
It is difficult for a woman to independently determine whether her baby has enough colostrum or not. Moreover, during this period, colostrum does not flow from the breasts, like milk in the very first days of the establishment of lactation, the breasts do not swell every 3 hours.
It is believed that a newborn eats up this amount of food if he sleeps a lot, does not cry, and often empties his intestines. In addition, in the first days of life, he is not yet able to suck for a long time; he needs to regain strength after childbirth.
Color of milk during cessation of lactation
When it's time to stop breastfeeding, mother's milk takes on a different consistency and color. The main function of this product is the formation of immune defense in the body of a newborn baby. During the involution stage of breastfeeding, milk becomes thick and yellow in color, reminiscent of colostrum.
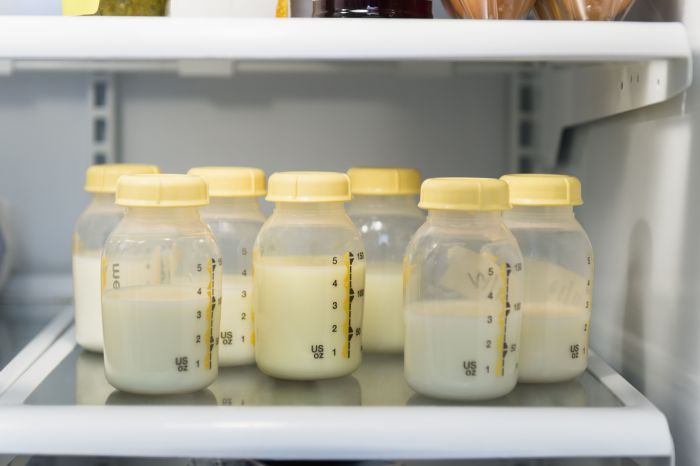

It is important to remember that taking certain medications can cause changes in the color of breast milk. Eating foods containing food coloring also affects the color of mother's milk.
When will it change to milk?
After colostrum (3-5 days after birth), the so-called transitional milk comes. It is necessary as another step, preparing the child’s gastrointestinal tract for the subsequent work - digesting mature maternal nutrition.
The composition of milk and colostrum is different. The amount of lactose and fat increases, the composition of proteins changes, enzymes, hormones are added, fewer immune factors and more substances for better digestion of food. Protection against the first introduction of microorganisms from the outside has already been solved; now it is important to grow quickly.
It is not difficult to distinguish colostrum from milk by appearance: the first is thick, viscous and yellowish, the second is white, more liquid and appears to be diluted with water. Milk, unlike its predecessor, flows noticeably, generously released from the mammary glands at the slightest stimulation: the sight of a child, his cry, latching on the nipple. Hot flashes are not typical for colostrum.

If there is no colostrum
Sometimes it seems to the mother that the colostrum has disappeared or was not there to begin with. Most often this turns out to be an illusion, because it may not appear from the nipples at all, even with pressure. And you cannot determine its presence on your own. The only indicator will be the condition of the child. Doesn't worry, soils diapers, sleeps peacefully - everything is fine.
If the birth was difficult, surgical intervention, premature or emergency, then there may be problems with the formation of colostrum in the glands. This is due to the body’s unpreparedness for childbirth itself and for the launch of hormonal support for breastfeeding. The following tips will help you start the necessary process or increase its intensity:
- It is important for the mother in labor to rest and regain strength.
- There should be enough liquid. Clean water is best.
- If possible, the child should always be nearby. Applying to the breast as soon as required is the key to establishing proper lactation.
But the most important thing in the process of establishing feeding is the calmness and balance of the mother. When she does not experience anxiety, nothing distracts her from the child, nature will do everything right itself.
Treatment of a pathological symptom
You can get rid of green discharge from the mammary glands only under one condition - to completely recover from the disease of which they are a sign.
Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor develops an individual therapeutic approach:
- Medication.
- Puncture (pumping out secretions).
- Operational.
For different diseases, individual treatment methods are used, taking into account the degree of neglect of the pathology, the general well-being of the patient and other important clinical aspects.
| State | Treatment methods |
| Ectasia | Antibacterial or anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out, or the damaged canal is excised. |
| Purulent discharge | It is recommended to take antibiotics or surgically open the abscess. |
| Mastitis | Treatment can be conservative or surgical, depending on the severity of the disease. |
| Intraductal papilloma | Only surgical intervention is indicated, in which the affected tissue is excised and histologically examined to exclude malignancy. |
| Paget's disease | A mastectomy is performed (removal of both mammary glands); in very rare cases, only one tumor may be removed. |
In addition, the features of treatment also depend on what factors provoked the underlying disease:
- Vitamin deficiency - vitamin and mineral complexes are prescribed.
- Problems of the thyroid gland - it is necessary to take iodine-containing, enzyme and homeopathic preparations, as well as herbal remedies.
- Hormonal imbalance – a course of hormonal medications is recommended.
Of the possible home remedies, diet therapy and giving up bad habits will provide invaluable help to the body.
Other folk options are permissible only after the final diagnosis has been determined and the doctor’s permission. However, they cannot be used as the main treatment due to their weak effect.
Alternative medicine recipes are suitable as an additional method to drug therapy or as a supportive measure after surgery.