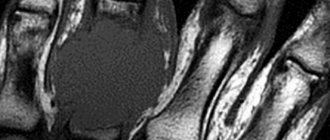
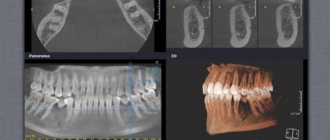
The shoulder joint is the most mobile and susceptible to dislocation. When traumatic force is applied to the shoulder joint, fractures, dislocations and subluxations can occur, especially in young and active people. Instability in the shoulder joint can be classified in various ways, including depending on the etiology and pathogenesis (traumatic or atraumatic), the direction of displacement (posterior and anterior) or based on the severity of the process (acute or chronic).
A final judgment about the type of damage to the soft tissue structures of the shoulder joint can only be formed on the basis of arthroscopy - the introduction of optical instruments into the joint cavity, allowing one to accurately see changes in the ligaments, tendons and cartilage. At the same time, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) plays an important role in preoperative diagnosis, as it allows the traumatologist to detect various types of injuries at an early stage and correctly plan the operation, or make a conclusion about maintaining conservative treatment. Interpretation of MRI of the shoulder joint is carried out by radiologists. You can get an expert opinion on the results of an MRI of the shoulder joint using the service of the National Teleradiological Network.
Get an MRI of the shoulder joint in St. Petersburg
This article is devoted to an analysis of the most common types of instability of the shoulder joint, as well as the principles of their diagnosis using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It will be shown how different types of shoulder joint injuries look on MRI, and typical MRI signs of shoulder labral tears, rotator cuff injuries, and other types of injury will be discussed.
What is an MRI of the shoulder?
The human shoulder joint is perhaps one of the most complex and therefore the most mobile. However, you often have to think about this in certain cases, namely when it loses its normal functions. Therefore, it is extremely important not to allow unpleasant symptoms to develop and to undergo prompt diagnosis. MRI will help show a complete and reliable picture of the condition of the shoulder joint. MRI is a modern and effective diagnostic method that allows you to obtain not just a photo, as with an x-ray, but to examine in detail all components of the shoulder joint: tendons, ligaments, bones, muscles.
What determines the price of a shoulder tomography?
The price of an MRI of the shoulder joint is largely determined by three factors: the power of the tomograph, the qualifications of the personnel and the need to use contrast. A good way to reduce diagnostic costs without losing the quality of the examination would be to use the MRI service at night, when the maximum discounts apply.
| Service | Price according to Price | Discount Price at Night | Discount Price During the Day |
| Shoulder MRI | 4000 rub. | 2990 rub. | 3690 rub. |
| Appointment with an orthopedist | 1800 rub. | free after MRI | free after MRI |
| First aid program for joints (8 studies + appointment with an orthopedist + MRI of the joint) | 13000 rub. | 7500 rub. | 7500 rub. |
What determines the cost of tomography?
Tomograph power
![]()
Applying Contrast
Personnel qualifications
![]()
Promotions and discounts
Indications for MRI
The main indications are: unbearable pain, immobility, swelling of the soft tissues of the shoulder. They may be a consequence of reasons that we will discuss below.
Diseases of muscle fibers, shoulder ligaments
Mainly manifested by an inflammatory process in the soft tissues of the shoulder. They can appear as a result of stress, hypothermia, or infection. MRI of the shoulder joint accurately determines the structure of the tissues and the nature of the damage.
Injuries to the shoulder joint as a result of playing sports
Occur mainly due to excessive stress or a fall. More often they occur in the form of a dislocation, less often - a fracture. A fracture of the shoulder joint is one of the most complex and almost always requires surgical intervention. Examination of the shoulder joint using MRI allows you to accurately determine the extent of damage.
Muscle/ligament/tendon ruptures
They can be obtained either independently due to loss of elasticity of the joint and sudden movement, or as a result of a dislocation or fracture. An MRI of the shoulder joint can detect either complete or partial rupture of ligaments or tendons, which is difficult to detect using other procedures.
Clamping of nerve fibers in the shoulder joint
Occurs both with injuries and with prolonged exposure to an uncomfortable position. It manifests itself as local pain during movement. Can lead to neuralgia and neuritis - inflammation of the nerve. Any of these manifestations requires additional examination. An MRI of the shoulder joint shows any changes in the tissues, which is necessary to make a correct diagnosis.
Indications
The shoulder joint is one of the most loaded joint systems of the musculoskeletal system. It is not surprising that regular stress on it can lead to degenerative pathologies and inflammatory diseases. If a person puts a lot of physical stress on his shoulder joints, their bone and cartilage structures begin to wear out quickly, and pain occurs. In addition, shoulder injuries are a common reason for visiting an orthopedist or traumatologist. In order to make an accurate diagnosis and identify the causes of shoulder dysfunction, the attending physician usually prescribes an MRI of the shoulder joint. The following symptoms may lead the patient himself to the idea that he urgently needs to undergo magnetic resonance imaging:
- pain and crunch in the shoulder;
- injuries in the shoulder joint, fractures;
- ligament ruptures, periodic dislocations;
- swelling in the shoulder area;
- improperly fused bones, the presence of bone spurs;
- pinched nerves, tendons;
- visually noticeable tumor.
Initial appointment with an ORTHOPEDIST
ONLY 1800 rubles!
(more about prices below)
What diseases does the procedure diagnose?
Bursitis
This is an inflammation of the periarticular bursa with possible accumulation of fluid, pus, salts, stones, and protein. Based on the nature of the accumulations, several types of bursitis are distinguished and they resort to one or another treatment. An MRI of the shoulder joint can detect not only the inflammation itself, but also what caused it. Bursitis occurs due to injury, infection, or with constant, monotonous load on the joint (during sports or work). It has both acute and chronic forms.
Shoulder arthritis
This is also inflammation, but of the articular cartilage or connective tissue itself. It occurs most often as a result of injury, nervous diseases, allergic reactions, and even intestinal or stomach infections. It can also be hereditary. Without proper attention and treatment, it can lead to complete immobility and, as a result, atrophy of the limb.
Osteoporosis
It is a lesion of bone tissue and its depletion. Leads to destruction of the shoulder joint and immobilization. Before carrying out treatment, it is important to understand the causes of the disease, and they can be different: from previous infectious diseases to kidney failure and poor lifestyle. An MRI of the shoulder joint will help reveal the full picture of the disease.
Hass disease
A very rare disease. It is the death of the head of the bone of the shoulder joint. The causes of the occurrence have not been precisely established, but there is an opinion that this occurs due to poor blood supply to the joint. Without proper diagnosis, it is difficult to accurately identify a specific ailment, because all diseases in this area manifest themselves in the same way: pain, redness and swelling of soft tissues, dysfunction of the shoulder. MRI reveals a complete picture of the condition of the shoulder joint.
Procedure
The tomography procedure of the shoulder joint takes on average 20-40 minutes. The duration of the scan depends on the tomograph model. In the diagnostic room, the patient is placed on a tomography table. Then a special coil is placed over the examination area. The table is moved into the scanning part of the device and the screening procedure is started.
The main task of the patient during the examination is to remain completely still. This is largely a guarantee of quality research. The fact is that the tomograph is very sensitive to any movement. If the patient moves the shoulder during the scan, motion artifacts appear on the tomograms. They reduce the effectiveness of the study and the overall quality of diagnosis.
Questions about diagnostics
Dress code
You can enter the MRI room in any clothing that does not contain metal. When going to the clinic, it is best to wear loose, non-restrictive clothing without metal elements (zippers, rivets, hooks), in which you can lie comfortably. For women, we recommend bringing a T-shirt or not wearing a bra with metal wires or hooks.
Preparation
This tomography does not require any preparatory steps from the patient.
Is MRI harmful to health?
MRI is a completely harmless diagnostic method for the human body. This method of examination can be carried out at any age and for any disease an unlimited number of times, unless you have contraindications.
Contraindications
Some pacemakers and foreign objects in the body may pose serious limitations to tomography. In particular, cochlear implants, vascular clips, stents, heart valves and insulin pumps, pacemakers, neurostimulators, steel screws, staples, pins, plates, joint endoprostheses may be a contraindication to diagnosis. The patient must notify the radiologist about all implanted objects in the body. The diagnostician will be able, based on information about the composition and model of the implant, to assess the possibility of conducting diagnostics.
If you are having an MRI with contrast, be sure to report any allergies to medications or kidney problems. It is also necessary to inform the radiologist about a possible pregnancy.
Is it possible to do an MRI with braces and dental implants?
Dental implants and crowns are not a contraindication to magnetic resonance imaging. The magnetic field does not have any negative effect on them. Fixed brace systems can produce artifacts on tomograms during MRI of the head. If the light effect is too strong, the doctor will stop the study and offer the patient alternative diagnostic methods.
Is the device noisy?
Any MRI machine in working condition makes noises reminiscent of tapping. The open tomograph is one of the quietest installations. The noise from its operation is significantly lower compared to closed tomographs. If the sounds of the operating unit cause you anxiety, you will definitely be offered special noise-canceling headphones.
What should I do if I have claustrophobia?
An open tomograph is the optimal solution for patients suffering from panic attacks in a closed space. It is open on the sides on three sides and does not create a claustrophobic feeling.
Can I take sedatives before an MRI?
If you are a little nervous, before the tomography you can take mild sedatives, for example, valerian, motherwort infusion or afobazole. Taking sedatives does not have a negative impact on the quality of MRI.
Why is it important not to move during the test?
Any movement during the examination reduces the quality of the resulting images. Multiple motion artifacts may appear on the images, and the MRI results will be uninformative.
Can I do the research with an accompanying person?
Absolutely yes. You can invite any accompanying person from among your family and friends to the MRI room. It is important that your companion does not have metal implants or artificial pacemakers in his body.
Contraindications for MRI of the shoulder joint
Despite the proven harmlessness, unlike X-rays, there are still a number of contraindications for MRI of the shoulder joint: • the presence of metallic foreign objects; • claustrophobia; • pregnancy (first trimester) and breastfeeding (when performing MRI with contrast); • weight exceeding 120 kg.
MRI of the shoulder joint is now done in both closed and open apparatus. The second option is optimal for claustrophobia. However, open scanners are rare. We provide this information as a reference. Due to the complex anatomy of the shoulder joint, MRI is one of the most effective and safe methods for diagnosing diseases of this organ. At our center, we perform MRI of various body systems, including the shoulder joint.
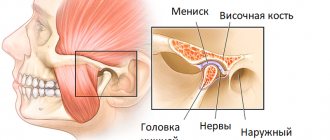
The structure and anatomy of the shoulder joint
The shoulder joint is the most mobile joint in humans, formed by the head of the humerus and the scapula. His lack of powerful ligaments is compensated by the muscles of the shoulder girdle and upper limbs surrounding the shoulder like a corset. On the one hand, this provides greater mobility, on the other hand, it explains why the shoulder joint is easy to dislocate.
Along the periphery, the joint is surrounded by short ligaments that form the articular capsule. It unites the joint into one whole and holds the articular surfaces of the head of the humerus and scapula in optimal position. The inner surface of the joint capsule is covered with a synovial membrane that produces fluid into the joint cavity, acting as a lubricant and nourishing the cartilage.
An MRI of the shoulder joints clearly shows all the anatomical structures that form the joint. The method allows you to assess the condition of the soft tissues and cartilage of the shoulder, ligaments, joint capsule, joint cavity, tendons and muscles.
Decoding
The radiation diagnostics doctor interprets the results obtained. Deciphering usually does not take more than 2 hours, but when the radiologist is busy, patients have to wait for results within 24 hours. What does an MRI of the shoulder joint show:
- inflammatory foci, destructive and degenerative changes in bones and hyaline cartilage are visualized as intensely colored areas;
- inflammation is indicated by cavities formed around the tissues;
- benign and malignant neoplasms look like areas with a denser structure. They are intensely colored and localized at the border between bones and muscles;
- when the ligaments rupture, there is a noticeable displacement of the torn parts into the articular cavity;
- overgrown edges of bone plates and calcified areas signal the irreversible destruction of cartilage tissue and the development of osteoarthritis;
- complete or partial fusion of the joint space indicates ankylosis (immobility of the joint) and the need for surgical intervention;
- the formation of sequestra (dead tissue) is a characteristic sign of infectious arthritis;
- the accumulation of fluid in the synovial bursa indicates bursitis, and the presence of effusion in the joint cavity indicates synovitis;
- changes in heat exchange, also determined during examination, accompany many diseases of the shoulder joint.
During interpretation of the results, the condition of the bone surfaces lined with cartilage tissue is assessed. Normally, there should be no obvious defects on them. Ligaments, tendons, nerve bundles, and muscle fibers located near the joint are also examined. Changes in soft tissue structures often indicate a low-grade inflammatory process.
What does an MRI of the shoulder show?
MRI scanning allows you to accurately visualize the area of interest layer by layer. During the test, tissue layers up to 1 mm are scanned. This allows you to fully assess the condition of the shoulder, identifying vulnerable or damaged areas:
- soft fabrics,
- vessels,
- bones,
- nerve roots.
The study allows timely detection of compression or dilation of blood vessels, identification of inflammatory processes, neoplasms, cracks and thinning of cartilage tissue.