What is a fertilized egg
The fertilized egg consists of embryonic membranes and an embryo.
This period of pregnancy is its first stage of development. And it all starts with the fusion of two cells – male and female. Then the fertilized egg actively begins to divide, first into two parts, then into four, and so on. The number of cells, like the size of the fetus, is constantly growing. And the entire group of cells that continue the division process moves along the fallopian tube to the zone of its implantation. This group of cells is the fertilized egg.
Having reached its goal, the fertilized egg attaches to one of the walls of the woman’s uterus. This occurs a week after fertilization. Until this time, the fertilized egg receives nutrients from the egg itself.
- The fertilized egg, 2 weeks after implantation into the uterine cavity, nourishes the swollen mucous membrane of this reproductive organ, which is already prepared for the process of development and nutrition of the fetus until the time of formation of the placenta.
- The baby's place, or placenta, is created from the outer membrane of the fertilized egg at 3 weeks, which at this time is already thickly covered with villi. These villi at the site of attachment of the fertilized egg destroy a small area of the uterine mucosa, as well as the vascular walls. Then they fill it with blood and immerse it in the prepared area.
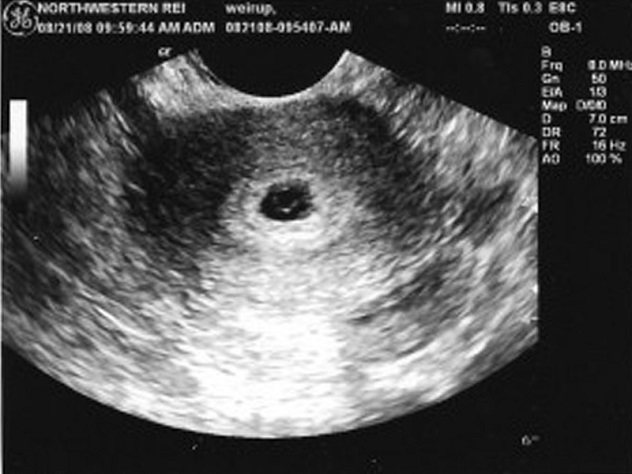
- In general, the fertilized egg is the very first sign of a normally ongoing pregnancy. It can be examined by ultrasound after two weeks of missed menstruation. Usually in this case the fertilized egg is visible for 3-4 weeks. The embryo becomes noticeable only at 5 weeks of pregnancy. However, if the doctor diagnoses the absence of an embryo in the fertilized egg of the 5th week - in other words, an empty fertilized egg, then the ultrasound is repeated again after a couple of weeks.
- Usually in this situation, at 6-7 weeks, the fetus and its heartbeat begin to be visualized. When the fertilized egg is still empty at 7 weeks, this indicates an undeveloped pregnancy. In addition to this complication, others may appear in the early stages of pregnancy - incorrect location of the fertilized egg, its irregular shape, detachments, and others.
- It is for this reason that it is important to undergo an ultrasound examination as early as possible, so that the situation can be changed if it can be corrected. Since in the first trimester (fertilized egg up to 10 weeks), there is a high probability of spontaneous miscarriage, detachment and other pathologies. However, enough about the sad things.
The fertilized egg at 6 weeks and before this stage of pregnancy has an oval shape. And an ultrasound examination usually evaluates its internal diameter - the SVD of the fetal egg. Since the size of the ovum at 7 weeks or at another stage of pregnancy is a variable value, there is an error in identifying the gestational age using this fetometric indicator.
On average, this error is 10 days. Gestational age is usually determined not only by this indicator, but also by the values of the coccygeal-parietal size of the fetus and other indicators, which are also very important
Why this name
A fertilized egg is called an egg because its shape and structure repeats the structure of a standard egg:
- shell;
- amniotic fluid;
- yolk sac;
- embryo
Over time, the egg transforms inside the uterus. The outer shell, called the chorion, has villi that serve to anchor it to the mucous membrane of the uterus. Later, the placenta is obtained from the chorion.
Amniotic fluid (analogue of egg white) is a nutrient medium produced by the amnion, that is, the inner membrane of the fertilized egg.
The yolk sac is the nutritional reserve that, when pregnancy occurs, the egg feeds the future embryo. It connects to the embryo in the area of the umbilical cord, and through a small tubule transfers nutrients to the zygote.
An embryo is produced by multiple divisions of a fertilized egg - a zygote. The first stage of zygote division is the morula, which looks like a small ball. Each cell of the morula has its own purpose. From these tissues will develop, and then organs, and then the baby’s organ systems. But that will come later.
For now, you can only see on an ultrasound what the fertilized egg looks like.
What does a fertilized egg look like?
Having learned about their pregnancy, many curious expectant mothers begin to ask the doctor questions about how and at what stage the fertilized egg is visible and what it looks like. We will try to answer them.
The fertilized egg, the diameter of which is very small in the first days of pregnancy, can be seen within two to three weeks after a missed period. The formed structure in most cases is located in the upper part of the uterine cavity, has a dark (gray) tint and a round or oval shape. The embryo at this time is still microscopic in size, so it is not detected by ultrasound.
Stages of fertilized egg formation
Cells move and differentiate. The formation of extraembryonic organs begins. At this stage, the following are formed:
- Amnion (future amniotic sac). The transparent membrane produces amniotic fluid, which is designed to be a nutritious and environmental medium for the embryo, promote the proper formation and growth of body parts, and protect against trauma.
- Chorion (future placenta). This is the outer membrane of the fertilized egg, in direct contact with the wall of the uterus. Through this shell, until the formation of the child's place is completed, the embryo receives nutrition and oxygen for breathing.
- Yolk vesicle. From it, the yolk sac is formed - the main hematopoietic organ until the formation of the placenta is completed, in which the first blood vessels appear and germ cells are produced.

On days 14–15 after fertilization, 3 germ layers, a neural tube and a notochord – the future spine – are formed. The allantois develops, from which the umbilical cord and bladder are then formed. From the 15th to the 20th day, the separation of embryonic tissues from extra-embryonic organs and the formation of the trunk fold continue.
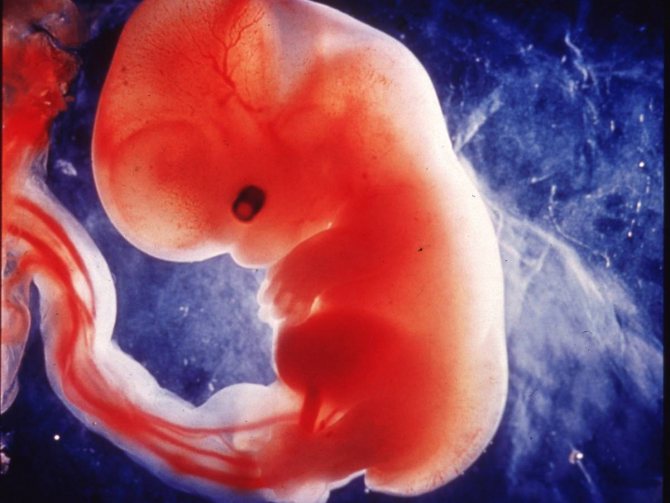
Until the 35th day, the cells of the embryo are divided and receive “specialization” - 43–44 segments are formed, from which the skeleton and rudiments of all organs will be formed before the end of the second month of intrauterine life. At 8–9 weeks, the embryo looks like a man and weighs about 5 g and is 40 mm tall.
Deviations from the norm and variant of the norm of the fertilized egg and embryo
It happens that the fertilized egg has formed and has even become embedded in the mucous wall of the uterus, but there is no embryo in it. There is such a pathological condition as anembryonia. That is, an ultrasound shows the presence of a fertilized egg and the absence of an embryo in it, regardless of what week it is. This happens as a result of exposure to infectious diseases, the influence of drugs, and genetic abnormalities at critical times, namely during the implantation period. Such a pregnancy will not grow, there is no embryo in the fertilized egg and it is considered “empty”, and sooner or later it will terminate on its own. Therefore, to avoid complications, this pregnancy is terminated. In the future, the couple needs a full medical examination.
The opposite picture of anembryonia also occurs, when an ultrasound examination detects one fertilized egg and two embryos in it. We are talking about a multiple pregnancy, which will be visible somewhere from six weeks of gestation. Data from the medical literature provide an answer to the question: “can two embryos grow and develop simultaneously in a fertilized egg?” Yes, of course they can, but the phenomenon is quite rare.
Timing of routine ultrasound diagnostics
Based on the results of the WHO, strict periods have been defined for conducting mandatory ultrasound examinations during the gestation period of the unborn baby.
At other time intervals, the examination is prescribed strictly according to individual indications from the mother and fetus:
- The first ultrasound examination is recommended to be carried out at 12–14 weeks;
- the second screening is prescribed at 20–24 weeks;
- A third ultrasound visit is necessary at 32–34 weeks of gestation.
It is not advisable to neglect the timing of the next examination, since it is during the specified period of gestation that it is possible to recognize fetal malformations. And if a forced need arises, an interruption for medical reasons. The last screening examination can also be carried out at a later time.
The results of the current diagnostics may be significantly outside the normal range, but this is far from a cause for concern. Do not forget that the development of each child has its own characteristics. However, you should not ignore the identified symptoms either.
The period of embryogenesis, that is, when the formation and development of the embryo occurs, lasts from the first to 11-12 weeks of pregnancy. After this period, the embryo is already called a fetus. In this case, the first day of the last menstruation is taken as the starting point.
The development of a new life begins from the moment the female egg is released. When a sperm and egg merge, a zygote is formed, which after 26-30 hours begins division and forms a multicellular embryo, the size of which, as they say, increases by leaps and bounds.
If in the first four days of its existence the embryo has a size of approximately 0.14 mm, then by the sixth day it reaches 0.2 mm, and by the end of the seventh - 0.3 mm.
On days 7-8, the embryo is implanted into the wall of the uterus.
On the 12th day of development, the size of the embryo is already 2 mm.
Change in embryo size by week of pregnancy
- at the 3rd week of embryo development, that is, at the 5th week of pregnancy, the ectoderm forms a groove at the site of the baby’s future spine. Then its edges close and a neural tube is formed - the future spinal cord and brain. By the end of this week, the embryo reaches 4 mm;
- in the fourth week, the basis of the central nervous system - the spinal cord and brain - is formed from the neural tube. The heart makes its first contraction. The rudiments of legs, arms, eyes and internal organs appear, blood begins to flow through the blood vessels;
- at 5-6 weeks the head and facial features of the embryo are formed. Its length is about 1 cm
- At week 7, the limbs lengthen and the lungs begin to form. The heart is fully formed. Embryo size – 1.5 cm;
- at 8 weeks, all vital organs are almost formed. about 2 cm;
- at 9 weeks the ears, nose, eyelids, mouth, and eyes are clearly visible. The baby's height is about 3 cm and he continues to grow quickly;
- at 10 weeks, that is, at 12 weeks of pregnancy, the skeletal structure fully corresponds to a person. Limbs lengthen. The child's blood acquires its own group. The size of the embryo, which is now becoming a fetus, can reach 7 cm.
When performing the very first ultrasound, which is done when menstruation is delayed and in order to accurately diagnose intrauterine pregnancy, you can see the fertilized egg. It is at this time, seeing this tiny formation on the monitor, that the doctor already informs you that you will soon become a mother. In the photo you can see the fertilized egg - a small oval formation. At an early stage, the embryo that will develop in the fertilized egg is not yet visualized, but soon it will grow and will be clearly visible.
An empty fertilized sac is an egg without an embryo when the pregnancy does not develop. The embryo is usually visible already from five weeks of pregnancy, but sometimes there are situations when the ultrasound doctor does not see the embryo even at this stage, in which case a repeat ultrasound is prescribed. Very often, a repeat ultrasound shows both the embryo and the heartbeat. If after six to seven weeks the embryo is not visible, then, unfortunately, there is a high probability that the pregnancy is not developing.
Diameter of fertilized egg by week
When the fertilized egg has a diameter of 4 millimeters, this indicates a fairly short period of time - up to six weeks.
- This is often the size of the fertilized egg at 4 weeks. Already at five weeks, the SVD reaches 6 millimeters, and at five weeks and three days the fertilized egg has a diameter of 7 millimeters.
- At the sixth week, the gestational sac usually grows to eleven to eighteen millimeters, and the average internal size of the gestational sac of sixteen millimeters corresponds to a period of six weeks and five days. At the seventh week of pregnancy, the diameter ranges from nineteen to twenty-six millimeters.
- At week 8, the fertilized egg increases to twenty-seven to thirty-four millimeters. At this stage, the fetus can be clearly seen on ultrasound.
- The fertilized egg grows to thirty-five to forty-three millimeters in 9 weeks.
- And at the end of the tenth week, the fertilized egg measures about fifty millimeters in diameter.
As you can see, the fertilized egg at the 4th week is very different in size from the tenth week.
The question of how quickly the fertilized egg grows can be answered with confidence: until the fifteenth to sixteenth week, its size increases by one millimeter every day. Further, the diameter of the fertilized egg increases by two to three millimeters per day.
Next you can see the increase in the ovum by week in the table:
Dimensions of the fertilized egg - norms by week
The size of the fertilized egg depends on the gestational age. In the absence of pathological processes, the diameter of the egg increases every day up to 15-16 obstetric weeks by 1 mm, and then by 2-2.5 mm daily. There are certain norms of indicators that allow one to judge the nature of the course of pregnancy; during an ultrasound, the thickness of the chorion is also determined.
Table of the size of the fertilized egg and the thickness of the chorion
| Gestation period (week) | Diameter of embryonic egg (mm) | Chorion thickness (mm) |
| 5 | 5 | — |
| 6 | 10,9–18,1 | — |
| 7-8 | 20,1–25,1 | 7–14 |
| 8–9 | 27,9–33,2 | 8–15 |
| 9–10 | 34,1–42,2 | 8,5-9,5–16,5–1,5 |
| 11 | 50 | 10–18,5 |
| 12 | 56-62 | 11,5-19 |
| 13 | 62–67 | 12,5–20 |
Accurate mass
Week of pregnancyHeight, cmWeight, grDB, mmDHA, mmBDP, mm
| 11 | 6,8 | 11 | 7 | 20 | 18 |
| 12 | 8,2 | 19 | 9 | 24 | 21 |
| 13 | 10,0 | 31 | 12 | 24 | 24 |
| 14 | 12,3 | 52 | 16 | 26 | 28 |
| 15 | 14,2 | 77 | 19 | 28 | 32 |
| 16 | 16,4 | 118 | 22 | 34 | 35 |
| 17 | 18,0 | 160 | 24 | 38 | 39 |
| 18 | 20,3 | 217 | 28 | 41 | 42 |
| 19 | 22,1 | 270 | 31 | 44 | 44 |
| 20 | 24,1 | 345 | 34 | 48 | 47 |
| 21 | 25,9 | 416 | 37 | 50 | 50 |
| 22 | 27,8 | 506 | 40 | 53 | 53 |
| 23 | 29,7 | 607 | 43 | 56 | 56 |
| 24 | 31,2 | 733 | 46 | 59 | 60 |
| 25 | 32,4 | 844 | 48 | 62 | 63 |
| 26 | 33,9 | 969 | 51 | 64 | 66 |
| 27 | 35,5 | 1135 | 53 | 69 | 69 |
| 28 | 37,2 | 1319 | 55 | 73 | 73 |
| 29 | 38,6 | 1482 | 57 | 76 | 76 |
| 30 | 39,9 | 1636 | 59 | 79 | 78 |
| 31 | 41,1 | 1779 | 61 | 81 | 80 |
| 32 | 42,3 | 1930 | 63 | 83 | 82 |
| 33 | 43,6 | 2088 | 65 | 85 | 84 |
| 34 | 44,5 | 2248 | 66 | 88 | 86 |
| 35 | 45,4 | 2414 | 67 | 91 | 88 |
| 36 | 46,6 | 2612 | 69 | 94 | 89,5 |
| 37 | 47,9 | 2820 | 71 | 97 | 91 |
| 38 | 49,0 | 2992 | 73 | 99 | 92 |
| 39 | 50,2 | 3170 | 75 | 101 | 93 |
| 40 | 51,3 | 3373 | 77 | 103 | 94,5 |
Although you can find out the weight of the fetus by week of pregnancy from the table, you are unlikely to be able to weigh your own baby before birth. And doctors can’t do it either. After all, it is in your tummy. And it’s hardly worth taking it out of there to weigh it.
The baby's body weight is important to determine the degree of its intrauterine development. But its exact definition is impossible. Therefore, the doctor uses other indicators to understand whether the weight corresponds to what it should be at a given gestational age. To identify possible lag, the doctor evaluates the various sizes of the hearth, determined using ultrasound.
But in obstetric practice, an indicator such as estimated fetal weight (EFW) is used. Why is she speculative? Yes, because no one weighs the fruit. This is a calculated figure. Body weight is calculated based on several dimensions. True, this indicator is not always reliable. It can give an error of up to 25%. Especially in cases where the weight of the fetus by week of pregnancy does not correspond to the gestational age. A number of factors influence the error in calculating the estimated mass. This is the amount of amniotic fluid, the ratio of muscle and fat tissue, and even presentation.
If there is an urgent need to more accurately determine the child's weight, MRI can be used. It gives results that are as close to real as possible.
Features of embryonic development after IVF
In the first 20 days from conception, the embryo undergoes major changes, ranging from gastrulation to organogenesis. During the embryonic period, which begins from the moment of fertilization until the 10th week of obstetrics, the embryo rapidly increases in size.
At 2 and 3 weeks of gestation, the embryo does not resemble a baby and only at the stage of organogenesis gradually acquires characteristic shape and structure. In the last week of the embryonic period, the gill arches and tail disappear in the fetus.
Embryos at 20 days after conception
- On the ninth day after implantation into the wall of the uterus, the process of cell division of the embryo continues, as a result of which it is transformed from a single-layer blastosphere into a gastrula with several embryonic petals;
- On days 20-21, the embryo enters the neurula stage, which is characterized by the formation of the neural plate;
- At the beginning of the 4th week of gestation, the process of placenta formation begins. The chorion and amnion arise from the ectoderm and trophoblast, in which amniotic fluid subsequently begins to accumulate.
The chorion is a villous formation that produces hCG. With the participation of the mesoderm, a fetal place is formed from it, in which the fetus continues further development. By the end of the third week of gestation, the fetus reaches only 4-5 mm in length and looks more like an oblong cylinder.
Possible pathologies
In the presence of unfavorable factors, the shape and size of the formation with the embryo change, which indicates pathological processes that can cause miscarriage and developmental abnormalities.
Possible pathologies may be detected in the image of the ovum
Pathologies and possible causes
| Pathology | Possible reasons | Provoking factors |
| Small fertilized egg | Frozen pregnancy, fetal development abnormalities. | Taking antibiotics, infections, genetic pathologies, hormonal imbalance. |
| Large fertilized egg | Death of the embryo, chromosomal pathologies. | Infections of the genitourinary system, gene pathologies, deficiency of sex hormones. |
| The egg shell is uneven and has corners | Hypertonicity of the uterus, if the cervix is closed and there is no dark vaginal discharge, then this condition is not considered dangerous, but requires constant medical supervision. | Low progesterone levels, high levels of male hormones, prolactin, endometriosis, fibroids, polyhydramnios. |
| Flat shape | Frozen pregnancy. | Hormonal imbalance, genetic abnormalities in the fetus, addictions, acute infectious diseases. |
| The amniotic sac is located very low | This arrangement is not dangerous, but requires constant medical supervision. If the egg has attached very close to the cervix, there is a high probability of developing cervical pregnancy; with such a pathology, removal of the uterus is often required. | Pathological changes in the mucous layer of the uterus, structural features of the amniotic egg. |
| The amniotic sac is empty, the embryo is not visualized | Ectopic or frozen pregnancy. | Genetic abnormalities, infections, endometriosis, endocrine and hormonal disorders. |
| Two fertilized eggs, one empty | The problem arises when conceiving twins, when the development of one fetus has stopped for some reason. The empty egg gradually dissolves on its own. | |
| Elongated shape | In the absence of other negative symptoms, the condition is not considered dangerous. | Severe stress, infectious pathologies of the genitourinary system, viral and bacterial diseases, hormonal imbalance. |
Thickening of the chorion occurs in diabetes, with the development of hemolytic pathologies, thinning is a sign of placental insufficiency. During inflammatory processes, a chorionic cyst is formed, and the blood supply in some areas of the membrane is disrupted. If the structure of the chorion becomes heterogeneous, hypoplasia develops, and the risk of detachment of the fertilized egg is very high.
If the size of the egg does not correspond to the gestational age, a repeat examination is required; often errors can be caused by an incorrectly determined gestational age.
Deviations from parameters
The growth and size of the fertilized egg and embryo must correspond to the duration of pregnancy. If the fetus is less than 2 mm in size at 5 weeks, a developmental disorder can be stated. Fetal size less than 4 mm at seven weeks also indicates a disorder. With these parameters, you need to make sure that the set deadline is correct.
A large fertilized egg with a small embryo often indicates a frozen pregnancy. But re-examination is necessary to confirm. A frozen pregnancy can also be indicated by a too small fertilized egg. However, again we need to observe the dynamics of development.
Irregular shape
We can also talk about a violation when the structure surrounding the embryo has a non-standard shape. If the angles of the membrane are uneven, then the specialist may suspect increased uterine tone. In many cases, this condition is harmless, however, if there is pain, dark vaginal discharge, or dilatation of the cervix, then there is a possibility of miscarriage.
To correct the situation, doctors remove the tone of the uterus, after which the egg takes the correct shape. What the fertilized egg looks like during a miscarriage depends on the gestation period. At 1-2 weeks, a miscarriage may look like menstrual bleeding. At later stages, the formation looks like a blood clot. If a miscarriage occurs at 7-9 weeks, the woman may find pieces of fetal tissue.
If the structure is oval and at the same time flat, this may also indicate a frozen pregnancy. However, in the absence of pain and other ailments, it makes sense to continue monitoring the pregnancy. A repeated examination will allow the doctor to draw the correct conclusion.
Wrong location
A low gestational sac does not indicate a serious pathology, but requires more careful monitoring throughout pregnancy. If the formation is very close to the cervix, then cervical pregnancy may occur, which can lead to removal of the uterus.
Empty fertilized egg
With an ectopic pregnancy, you can find an empty ovum when the cavity contains only fluid or a blood clot.
Other abnormalities of the ovum
In addition to such pathology as “irregularly shaped fertilized egg,” there are a number of pathological processes that can provoke fading of pregnancy or miscarriage.
Small fertilized egg.
When establishing this diagnosis, specialists correlate the size of the fertilized egg with the gestational age, as a result of which the development of the fetus in the womb is determined and how correct it is. The time of gestation is determined based on the same size of the egg, so this developmental anomaly often has no basis, but is only a consequence of an inaccurate determination of the gestational age. However, there are cases when the fertilized egg slows down the rate of growth and development due to a frozen pregnancy. In this situation, it is necessary to conduct a number of additional studies aimed at determining the level of hormones in a woman’s blood.
Large fertilized egg.
This anomaly of the ovum is a type of frozen pregnancy and is called anebryonal pregnancy. With a pathology such as a large ovum, an ultrasound image can show all the signs of fertilization, the formed membranes of the ovum, the normal growth of the ovum, but in the absence of an embryo. An ultrasound examination, during which this condition can be established, should be done no later than 6-7 weeks of pregnancy. But even in this case, you should not rush to disappointing conclusions and set yourself up for an artificial abortion, since this diagnosis is sometimes made erroneously, due to an incorrectly determined gestational age or the small size of the embryo, which the machine simply cannot “see.”
Elongated fertilized egg.
The normal shape of the fertilized egg is considered round or oval. An elongated ovum may signal a possible risk of losing the baby. The reason for this phenomenon is, as a rule, increased muscle tone in the walls of the uterus. Timely diagnosis of this type of deformation of the ovum, provided the woman strictly follows the doctor’s recommendations, will prevent termination of pregnancy, saving the life of the child.
Women with this pathology are recommended to be prescribed medications that reduce the tone of the uterus, as well as bed rest and a stress-free, calm environment until the fertilized egg takes its original correct shape. The dynamics of the development of the ovum, positive or negative changes, must be monitored using ultrasound.
Bubble drift.
With this disease of the fetal egg, the chorionic villi are transformed into vesicles that are filled with a light-colored liquid. The bubbles are located on cord-like stalks, and particles of the decidua are found between them. Their size can vary from the size of a millet grain to a cherry, conglomerates of bubbles are cluster-shaped. Three forms of hydatidiform mole are known, depending on the degree of proliferation and anaplasia:
- benign: characterized by the absence of proliferation and anaplasia;
- malignant (potentially): characterized by the presence of hyperplasia and persistent anaplasia of the chorionic epithelium;
- malignant: with the presence of pronounced proliferation and anaplasia of the chorionic epithelium.
One of the main symptoms of a hydatidiform mole is uterine bleeding, which begins during the first weeks of pregnancy. Periodically weakening and intensifying, it ends at the moment of the birth of a mole. The blood is dark in color, and in rare cases it contains mole bubbles. The nature of the bleeding is light, increasing during the birth of a hydatidiform mole. Diagnosis of the disease is carried out on the basis of the above-mentioned manifestations of hydatidiform mole. An additional remedy that can be prescribed to confirm the diagnosis is biological reactions to determine pregnancy, due to the fact that with a pathology such as hydatidiform mole, a large amount of gonadotropic hormones are formed in the woman’s body.
Due to the fact that these diagnoses are established in the first trimester of pregnancy, i.e. in the very early stages of gestation, thanks to careful research and observations of the development of the embryo, women have a considerable chance to correct the situation and allow the child to be born.
What to do?
Gynecologists believe that increasing the tone of the uterus does not always have serious consequences. Danger to pregnancy occurs when other symptoms are added to it:
- the cervix dilates;
- pain;
- the appearance of discharge (a characteristic symptom of chorionic detachment).
The patient is prescribed antispasmodic drugs, sedatives and hormonal therapy. During treatment, the deformed structure returns to normal. If there is a threat of complications, the woman is sent to a hospital to continue the pregnancy (for more details, see the article: How to save a child in the early stages of pregnancy if there is a threat of miscarriage?). Bed rest and complete peace of mind help to survive an unpleasant period and successfully carry a child.
An important point in prescribing treatment is listening to the fetal heart: if it is present, the chances of success increase significantly. Hospitalization is mandatory if there is a clear threat of miscarriage. Using various medications, doctors relieve the tone of the uterus, after which the fertilized egg returns to its normal shape. If the diagnosis of a frozen pregnancy is confirmed, curettage of the uterus is performed.
Early fetal death is not a death sentence. In 90% of cases, a woman retains the ability to become pregnant and bear a child. In recurring situations, a deep examination of the body is required to determine the main cause of the problem. If the deformation of the ovum leads to the loss of the fetus, pregnancy planning should be postponed for six months.
The capabilities of modern gynecology make it possible to identify negative changes in the early stages of pregnancy. Minor deformities do not require urgent medical intervention. The prognosis is quite favorable. Women with this diagnosis usually feel normal during pregnancy and give birth successfully. If the ultrasound shows a problem, try to strictly adhere to the doctor’s recommendations and follow them strictly.
Is the pathology treatable?
As a rule, a deformed fetal element at a very early stage does not affect the woman’s well-being. But if such a condition is detected during the study, the doctor must immediately take action. Tests are required, including tests for progesterone, to rule out hormonal imbalance.
If this diagnosis is confirmed, the gynecologist prescribes Duphaston or Utrozhestan. Reviews about the drugs are the best, which indicates the high effectiveness of the products. As for the dosage, it is always individual and determined by the degree of hormone deficiency.
If the cause is uterine hypertonicity, then antispasmodics are prescribed, the most popular ones include:
- No-Shpa;
- Papaverine.
In addition, medications with magnesium and iron and sedatives are prescribed to relieve tension. With timely and proper treatment, the pathology can be dealt with by the 13th week of pregnancy or a week or two later. But treatment must be carried out under strict medical supervision.
If necessary, you need to go to the hospital. Here it is important not only to follow the doctor’s recommendations, but also to feel comfortable. In the latter, women are helped by a set - a robe with a “Mamalandia” shirt. Very comfortable clothes for staying at home and in the hospital
You can wear a shirt, and if you need to go out, just throw a robe on top and tie it with ribbons. No buttons, rough locks! The kit is designed for any stage of pregnancy, thanks to just this mounting option. Clothes will also be indispensable when feeding your baby.
As you have learned, a deformed ovum is a completely understandable and, most importantly, not dangerous condition in some cases. But prompt research and treatment are important.
Useful tips
You should not draw conclusions based on the tables and standards indicated as indicative. If now the egg size is lower or higher than normal, this does not mean that in a week or two the deviation will persist. Sometimes it is enough to calm down, stop worrying, take a weekend and lie down at home with a book, drinking warm tea and No-Shpu, so that the muscles of the uterus relax, the deformation is eliminated, and the size becomes normal.
If a serious anomaly is discovered (anembryonia, hydatidiform mole, etc.), you should not give up. It didn’t work out with the birth of the baby this time - it will work out next time, because these anomalies do not affect the subsequent ability to get pregnant, carry and give birth to a fully-fledged child.
Types of ultrasound during pregnancy
Transvaginal and transabdominal diagnostics are considered the most effective in the initial stages of pregnancy. These types of ultrasound make it possible to clearly see the location of the concentration of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity. In addition, the procedure makes it possible to determine the presence of an ectopic pregnancy.
But, there are cases when it is not possible to examine the egg shell even within the planned time frame. However, an experienced diagnostician can only determine the thickening of the uterine walls characteristic of pregnancy. What to do in such a situation and when can you see the fertilized egg on an ultrasound for sure?
A repeat ultrasound should be performed after a couple of weeks, having previously agreed on this issue with the leading specialist.
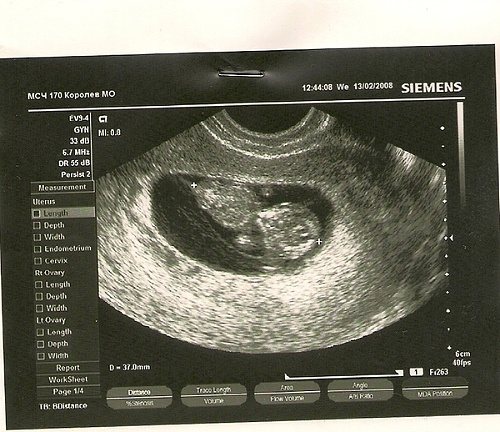
What are SVD and KTR?
SVD and KTR are the most important measuring indicators up to 12-14 weeks of pregnancy. It is by them that it is determined whether everything is okay with the embryo and whether there is a risk of developing pathologies and birth defects.
SVD is the average internal diameter of the fertilized sac. The unit of measurement is millimeter. An error in setting the period of up to 1.5 weeks is acceptable, as it may depend on individual characteristics.
KTP is the coccyx-parietal size. The unit of measurement is similar. Errors in determining the period are not allowed; this is a more accurate indicator than SVD. The error may be no more than 3 days. CTE has an advantage over SVD in accuracy; it is measured after 5 weeks, when the embryo is visible.
Tables of ovum sizes by week of pregnancy can help the expectant mother obtain information.
Sources
- https://endo1med.ru/beremennost/plodnoe-yaytso/
- https://its-kids.ru/plodnoe-yajtso.html
- https://mama66.ru/pregn/plodnoe-yajjco
- https://www.OldLekar.ru/beremennost/plod/stroenie-plodnogo-yajca.html
- https://kidbooms.ru/tablica-razmerov-plodnogo-ajca-po-nedelam-beremennosti-priciny-otklonenij/
- https://MoePuziko.ru/beremennost/techenie/razmer-plodnogo-yajca-po-nedelyam.html
[collapse]
Parameters of the ovum are normal by week of pregnancy
The size of the fetal egg by week has an important diagnostic value until the 7th–10th week of pregnancy, when the embryo is poorly visible (see also: what does the fetus look like at the 9th week of pregnancy: what does ultrasound show?). After 12–14 weeks, it acquires the status of a fetus, and the placenta begins to form, their indicators are monitored. The fruit shell grows quickly. Until 15–16 weeks, it grows by 1 mm per day. For example, at 9 weeks its diameter is 35 mm, and at 11 it is more than 47 mm. The table shows what the SVD of the fetal egg should be from 4 to 13 weeks.
| Duration, weeks | Diameter at the beginning of the week, mm | Diameter at the end of the week, mm | Yolk sac size, mm |
| 4 | 1 | 4 | – |
| 5 | 5 | 11 | – |
| 6 | 11 | 18 | 3 |
| 7 | 19 | 26 | 4 |
| 8 | 27 | 34 | 4,5 |
| 9 | 35 | 43 | 5 |
| 10 | 44 | 50 | 5,1 |
| 11 | 50 | 56 | 5,5 |
| 12 | 56 | 62 | 6 |
| 13 | 62 | 67 | 5,8 |
As can be seen from the table, from 1 mm in 14 days the diameter increases to 17–18 mm, and after another 7 days it reaches 20–24 mm. At the same time, the coccygeal-parietal size of the fetus is informative only from 8 weeks.
The first days after embryo transfer
The period after transfer of the embryo into the uterine cavity before the hCG test is the most critical in the IVF procedure. To increase the chances of successful implantation of blastomeres and their normal development, women should strictly follow the doctor's recommendations regarding:
- bed rest;
- nutrition rules;
- work and rest schedule;
- taking medications.
During the first 12-14 days after embryo transfer, life proceeds with certain restrictions, compliance with which increases the likelihood of implantation of the embryo into the endometrium for further development.
The embryo is hard to see on an ultrasound: should I worry?
The mere absence of an embryo on ultrasound imaging does not mean anembryonia, even if the study was performed at 6 weeks or later. The equipment may not detect the embryo for the following reasons:
- Imperfection of ultrasound. Ultrasound diagnostics has long been firmly established in medical practice, but this method has its limitations. The resolution of some devices (even modern ones) is too low to detect a fetus, which in the early stages of pregnancy is only a few millimeters in size. Therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, a repeat examination is carried out after 6-8 days, which will confirm or refute the initial result.
- Excess weight. During ultrasound, an image of the organs being examined is formed using reflected high-frequency signals passing through the tissue. Some of the sound waves are absorbed, which distorts the data. Since during abdominal ultrasound the sensor is located on the surface of the patient’s abdomen, if she has a thick sound layer, the weakened signal may simply not detect the embryo. To increase the accuracy of this method, a transvaginal examination is used, in which a sensor is inserted into the patient's vagina - this reduces distortions caused by the tissues surrounding the embryo.
- Too early. Often, during natural conception, a woman cannot determine exactly when it occurred. In such cases, routine ultrasound can be performed earlier than the time when the embryo reaches a size sufficient for its visualization. To accurately determine the presence or absence of an embryo in the fertilized egg, you need to undergo the examination again using more sensitive equipment.
If, when diagnosing pregnancy, ultrasound “does not see” the embryo, doctors combine it with other examination methods - in particular:
- Dopplerography is a type of ultrasound that records dynamic processes in the body of the mother and fetus (for example, blood flow, fetal heartbeat);
- With cardiotocography - the essence of this method is to record electrical impulses accompanying the heart contractions of the embryo.
In addition to these methods, a gynecological examination, blood tests for progesterone or hCG are also used. In general, at 6-8 weeks of pregnancy, doctors can already confidently state the normal or abnormal development of the embryo.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!