Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the female genital organs is one of the most informative types of diagnostics. Among its advantages are the complete absence of pain or discomfort for the patient, the absence of contraindications (safety), efficiency, instant receipt of data for prescribing treatment or detection of pathologies. Another definite plus is the minimum requirements for preparation for a gynecological ultrasound. A woman is not required to follow strict diets, preliminary manipulations, any training, etc. It is enough just to follow a number of simple rules.
When is it prescribed?
Ultrasound examination is actively used both for the diagnosis of various diseases and for preventive examinations. In the first case, an appointment for an ultrasound is issued if there are complaints:
- for pain in the lower abdomen and groin;
- prolonged tugging or other discomfort;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- spotting (not during menstruation);
- uncomfortable urination (accompanied by aching or acute paroxysmal pain);
- burning sensation in the urethra;
- too much (scanty) discharge during menstruation;
- the presence of blood or bloody mucus in the urine, etc.
Preventive ultrasound of the female organs is prescribed when planning pregnancy to monitor its course or progress of treatment (confirm recovery); before installing or removing an intrauterine device. An ultrasound examination is mandatory after operations on the organs of the woman’s reproductive system and during the recovery period. In addition, all women are strongly recommended to undergo preventive examinations to identify so-called female diseases at an early stage with a frequency of once every 1–2 years.
How to prepare for an abdominal ultrasound?
It is used for navigation, for cutting and joining materials, for disease recognition and treatment. All this is ultrasound.
Today we are talking about its use for examining the abdominal organs with Anna Viktorovna Poskrebysheva, an ultrasound diagnostics doctor at Clinic Expert Orenburg LLC.
Now patients of the Expert Orenburg Clinic have the opportunity to undergo not only MRI, but also ultrasound. Anna Viktorovna, in connection with which we turn to you with questions that concern our readers. Tell us, what is the essence of this method?
Ultrasound (or ultrasound) is a modern method for diagnosing diseases. You may remember from your physics course: ultrasound is mechanical vibrations, waves of a certain frequency, namely more than 20,000 Hertz. Unlike sound waves, we no longer hear it.
Ultrasound is widely used in medicine. Its different modifications are used for different purposes.
The principle of the research is as follows. An ultrasound machine generates ultrasound waves. The doctor, using a special sensor, directs them to the area under study. Along the way, the waves reach tissues and organs, are reflected from them and return back. The sensor picks up the return signals, from which the image is formed. It allows the ultrasound diagnostic doctor to make a conclusion.
What are the advantages of this method?
These include:
- non-invasiveness;
- painlessness;
— safety for the patient and doctor;
- high information content - with the help of ultrasound you can detect diseases at the earliest stages and, accordingly, consult a doctor in time;
- availability;
— the procedure can be performed as often as required.
What organs can be examined using this method?
Ultrasound allows you to examine most internal organs. The exceptions are hollow organs containing air (such as the stomach, intestines, lungs), as well as very dense tissues (in particular, bone).
What exactly is included in an abdominal ultrasound?
Here we include studies of the liver, gall bladder, bile ducts, portal vein, spleen, and pancreas. In addition, during diagnosis we also look at the kidneys, although strictly anatomically they do not belong to the abdominal organs.
We also examine the abdominal aorta, inferior vena cava, and different groups of lymph nodes.
Anna Viktorovna, how to properly prepare for an abdominal ultrasound? Do I need a special diet before performing this type of ultrasound?
The preparation is relatively simple. A routine examination of the abdominal organs is usually performed on an empty stomach. This means that the last meal is a light dinner the night before the test. If the study is planned for the afternoon, a light breakfast is allowed no later than 8 a.m.
3 days before the study, you need to exclude from the diet foods that cause intense gas formation in the intestines, which may complicate the study. These are, for example, cereals, whole grain bread, legumes, milk and dairy products, fresh vegetables and fruits, carbonated drinks.
The diet during preparation for an ultrasound examination allows boiled lean meat and fish, various cereals (for example, rice, buckwheat), low-fat cheeses, eggs (but not more than one soft-boiled per day).
Do I need to take any medications before an abdominal ultrasound?
Yes, in some cases this is necessary. For example, we can additionally prescribe activated carbon or some other drugs when the patient, despite changes in diet, experiences increased gas formation.
Are there any contraindications to ultrasound?
There are no absolutes. Among the relative ones are significant changes in the skin at the location of the sensor. For example, an open or fresh postoperative wound. A limitation to performing an ultrasound scan may be intestinal bloating - it complicates the examination and interpretation of the results.
Anna Viktorovna, can ultrasound cause harm to the body?
No. Ultrasound used in diagnostic ultrasound machines is harmless to both the patient and the doctor.
How often can an ultrasound be performed?
As often as your attending physician deems necessary. There are no recommended restrictions on the frequency of examinations, as, for example, in the case of radiological methods, for ultrasound.
Can ultrasound be used in children? From what age and how often?
Yes, you can. The first ultrasound examination of a newborn can be done already 2-3 days after birth to exclude any congenital pathology.
Which research method is better - ultrasound or MRI of the abdominal cavity?
I would not say that this or that research method is better or worse. Each of the methods is valuable and has its own indications for use, even if it is the same area of research, the same organs. In some cases, methods can complement and clarify each other. The decision about what kind of examination is needed - MRI of the abdominal cavity or ultrasound - is made by the doctor in each specific case.
You can find out the cost of an abdominal ultrasound in your city here or by calling
For reference
Poskrebysheva Anna Viktorovna
Graduate of the Orenburg State Medical Academy in 2007 (currently Orenburg State Medical University).
In 2007-2009 she completed clinical residency in the specialty “Skin and sexually transmitted diseases”.
In 2011, she underwent professional retraining at the Faculty of Education and Training of Nizhny Novgorod State Medical Academy in the specialty “Ultrasound Diagnostics”.
Since 2021, he has been working as an ultrasound diagnostic doctor at MRI Expert Orenburg LLC.
What diseases are determined using ultrasound of the female organs?
The list of pathologies that an examination can confirm or refute is very large. A specialist can evaluate several indicators at once: position, size, structure of organs, and compare the obtained indicators with normal ones.
Based on the results of the ultrasound, the doctor can state:
- polycystic disease;
- oncology (indicated by various neoplasms, thickening of organ walls);
- ovarian cysts;
- fibroids;
- endometriosis and much more.
The research data is obtained immediately (no need to wait for processing), but it must be deciphered by a qualified doctor (urologist, oncologist, gynecologist, obstetrician). The patient’s area of responsibility is proper preparation for a gynecological ultrasound, on which the correct diagnosis largely depends.
How to prepare
To prepare for the procedure, you need to know which method will be used. Today in gynecology, three types of ultrasound examinations are prescribed. As the frequency of use decreases, this series looks like this:
- transabdominal method;
- transvaginal ultrasound;
- transrectal examination.
Preparation for transabdominal gynecological examination
The easiest and fastest option is transabdominal. Almost every woman aged 16 years and older underwent such examination. Its essence is to gradually move the ultrasound sensor along the lower abdomen to study the projections of the internal organs displayed on the screen. For better sliding of the sensor, a special “conductive” gel is applied to the patient’s abdomen. It is non-allergic and does not contain aggressive elements, so it can be used without the slightest risk.
Rules for preparing for this type of gynecological ultrasound:
- 3-4 days before the procedure, it is advisable to start following a simple diet, which involves: Avoiding foods that increase gas formation. This includes fatty meat or fish, rich broths, dairy products, white bread, and sweets. It is undesirable to eat dishes with a pronounced taste - salty, spicy, fried, smoked and spicy.
- Avoid drinking alcoholic beverages and alcohol-containing products.
- Avoiding carbonated drinks.
- It is advisable to include lean soups, lean meats and poultry, buckwheat, rice, and oatmeal in the menu.
- It is not forbidden to eat up to 1 egg per day and drink no more than 1 glass of kefir (milk).
- Ensure that the bladder is full. To do this, you can refrain from going to the toilet (urinating) for 2–3 hours or drink 0.8–1 liters of clean still water 60–90 minutes before the procedure at your usual pace.
Transvaginal method
For transvaginal examination, a special sensor with an elongated end, the diameter of which does not exceed 3 cm, is used. The end of the sensor is inserted into the vagina. The examination itself does not differ in technique from the transabdominal examination (projection of organs on the screen, assessment of their condition in the protocol).
The patient experiences no more pain and discomfort during the transvaginal examination than in a gynecological chair. The entire procedure takes 5-20 minutes (very rarely does the doctor need more time) and is performed on an empty bladder. Preparation for a gynecological ultrasound is simpler here (only diet and quitting smoking for a few hours).
An important point: for hygienic purposes, the ultrasound doctor puts a latex condom on the end of the sensor. If the patient may be allergic to latex, this must be reported in advance.
Transrectal ultrasound
Transrectal ultrasound is performed much less frequently than transabdominal and transvaginal ultrasound, but the preparation rules are similar, only the mandatory emptying of the rectum is added immediately before the procedure.
General recommendations for ultrasound
To properly conduct an ultrasound examination, general rules must be followed. They are:
- if there are open wounds, it is better to postpone this procedure for another time;
- It is not recommended to smoke three days before the procedure;
- diagnostics are always carried out on an empty stomach;
- It is better to take special medications that eliminate gas formation 2-3 days before the procedure;
- It is better to wear clothes that are easy to remove during the procedure.
Using ultrasound, you can examine the thyroid gland, eyes, scrotum, and joints. And here no special preparatory measures are required.
Publication date: 2019-08-11
Ultrasound for expectant mothers
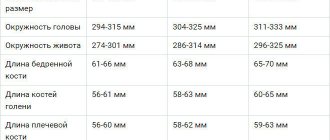
Pregnant women may undergo preventive or therapeutic ultrasounds up to 5–6 times. The mandatory minimum is a three-time study, which is prescribed at 11-14, 19-21 and 30-34 weeks. Ultrasound in the first trimester is the most effective and safe way to detect serious disorders/anomalies in fetal development (including Down syndrome).
In the second trimester, the normal development of vital organs and their systems in the fetus is monitored (sex is also determined here). The latter procedure is aimed at identifying late developmental abnormalities of target organs (heart, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, central nervous system, etc.). During this study, the doctor can draw conclusions about whether the speed of fetal development is normal.
General information about ultrasound
If a woman has no health complaints during pregnancy, then she will need to undergo 3 scheduled ultrasounds: at 12, 20-22 and 30 weeks of gestation. Screening examinations are mandatory because they allow you to monitor the child’s condition and development.
The study is carried out in two ways:
- Transabdominal, when the sensor is installed on the patient’s abdomen lubricated with a special gel. The specialist moves along its surface, receiving an image of the baby on the monitor.
- Transvaginally, i.e. by inserting a sensor into the vagina. This allows you to examine not only the fetus, but also the structure of the woman’s genital organs.
The second method is applicable only for pregnant women up to 12 weeks - during this period, examining the fetus using a transabdominal sensor is problematic due to the small size of the embryo. In the 2nd and 3rd trimesters, it is prohibited to perform an ultrasound with a vaginal probe, as this can cause uterine tone.
Diagnostics has a number of purposes:
- confirmation or denial of the fact of pregnancy;
- determining the number of embryos;
- identification of fetal development pathologies;
- assessment of the baby’s position, placenta, amount of amniotic fluid;
- establishing the length and weight of the child’s body;
- checking the general condition of the mother’s genital organs.