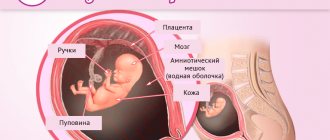
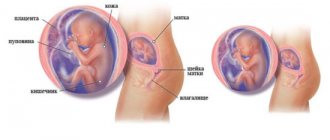
Baby development at 37 weeks of pregnancy
At 37 weeks of pregnancy, the baby is ready for birth, but his body continues to change and prepare for childbirth. The baby's body gradually becomes plump due to the accumulating subcutaneous fat, the skin smoothes out, becomes elastic and acquires a pink tint. The fetus at the 37th week of pregnancy is fully developed: all systems of its body are ready to start working, the hormone cortisol is produced, which promotes the maturation of the lungs. Meconium has accumulated in the baby's intestines - original feces, which will be released on the first day, from 3 to 20 hours after birth. By the way, the removal of meconium from the newborn’s intestines will be facilitated by colostrum secreted from the mother’s breast in the first time after childbirth.
What's happening
At 36–37 weeks of pregnancy, the baby’s body produces hormones important for life. One of them, cortisone, is necessary for the full maturation of the lungs. Iron actively accumulates in the liver. Without this microelement, the proper functioning of the body is impossible. In the last trimester of pregnancy, the fetal liver contains five times more iron than adults. This supply will be enough for the baby for the first six months of life.
At the 37th week of pregnancy, the main systems of the body continue to improve. Neurons in the brain begin to be covered with a myelin sheath, which helps nerves transmit signals. This process will continue throughout the first year of the child's life.
The ear and nasal cartilages harden, but the bones of the skull, due to the fontanelles, will remain flexible, so that it is easier for the baby to overcome the obstacles of the birth canal. The fontanel is an area where there is no bone tissue. A newborn baby has as many as six of them, but most close immediately after birth. As the cranial bones grow, the fontanelles will gradually disappear.
How a woman’s body changes by the 37th week of pregnancy
By the 37th week of pregnancy, the uterus has reached its maximum size: it weighs about a kilogram, its volume is 4-5 liters. The pressure on the bladder increases, the pregnant woman has back pain, and shooting pain in the legs and perineum is also possible. At the 37th week of pregnancy, the abdomen hardens several times a day - training contractions occur. At this stage, the aging of the placenta is noted, and harbingers of imminent birth
: release of the mucus plug (yellowish discharge with streaks), lowering of the abdomen (the child takes the position of the presenting area in the pelvis), slight dilution of the stool.
Risk factors
One of the risk factors at 36–37 weeks of pregnancy is group B streptococcus. This is a bacterium that can settle in the vagina or area around the rectum. Group B streptococcus occurs in almost 35% of healthy adults. But if its colonies are present in a pregnant woman, the child may become infected during childbirth. And infected newborns need serious antibiotic treatment and close monitoring in the hospital because group B streptococcus can cause dangerous complications in babies, such as meningitis, pneumonia and blood poisoning. If you test positive for this bacterium, your doctor will likely prescribe antibiotics before and during labor. This measure will prevent transmission of the infection to the baby.
Childbirth at 37 weeks of pregnancy no longer poses a serious danger. If you have cramping pain in the abdomen and lower back, or early loss of amniotic fluid, you should call an ambulance. Sometimes a woman even needs premature birth - for example, if she is diagnosed with:
- Fetal hypoxia;
- Infection;
- Placental abruption;
- Entwining the baby with the umbilical cord.
In these cases, the method of delivery is chosen by the attending physician.
Fetal activity at 37 weeks
At 37 weeks, the baby’s movements often bring painful sensations to the expectant mother; now his stomach is very crowded: there is even less amniotic fluid, the baby’s size and weight are increasing. It turns out that the uterus at 37 weeks of pregnancy now puts pressure not only on the mother’s internal organs, but also pinches the baby. Fetal movements must also be monitored at 37 weeks of pregnancy: there should be at least 10 movements per day. In the last days of pregnancy, the baby's activity decreases, he calms down a little and prepares for his birth.
Weight gain at 37 weeks of pregnancy ranges from 8.2 kg (with a BMI of more than 26) to 14 kg (with a BMI of less than 19.8). To calculate your individual weight gain at 37 weeks, use the pregnancy weight gain calculator.
Feelings of the expectant mother and changes in her body
General state. This period is the starting point before the birth of a child. Mommy begins to feel herself in a completely new way, both physiologically and morally. Impatience increases, and frequent questioning, sometimes even of close people, can easily throw you out of a state of psychological balance.
Right now, the hormonal background is actively being restructured, and the birth canal is preparing for the passage of the fetus.
The uterus begins to descend. If you were previously suffering from constipation, now you may experience stomach upsets. But this is only for the good. Everything that is superfluous and unnecessary comes out, which would create additional difficulties during the birth process.
Weight. By this time, women gain an average of 10-13 kg. The fruit itself weighs the most, up to 40%. Approximately the same amount, 10% each, is occupied by the placenta and amniotic fluid. The rest comes from the uterus, breasts, hips, blood and excess fluid. From this point on, weight gain should practically stop. The average weekly norm is 150 grams. A week before giving birth, your appetite may disappear on its own, and you will lose a couple of kilograms.
Pain at 37 weeks of pregnancy can be:
- sharp;
- pulling.
These are some of the main signs that you will soon see your little one. It puts pressure on your perineum, the pelvic bones become softer and begin to separate.
The stomach also becomes hard. One of the reasons is the cessation of uterine growth. Considering the psychological changes and concern for the baby, do not hesitate and seek advice from a gynecologist.
When walking or standing in one place for a long time, discomfort in the legs may worsen. Now you need to take care of yourself and rest more, lie down.
Sex . Previously, doctors recommended abstaining from intimacy. But today the situation has changed dramatically. If you do not have serious contraindications or psychological barriers, then you should not deny yourself pleasure. The main thing is to choose a position that is comfortable for you, so that your stomach does not create severe discomfort. Sperm promotes greater elasticity of the uterus. This, in turn, helps her open up more easily during childbirth.
Discharge. Milky and whitish discharge is considered normal. They can be either liquid or have a mucous structure. Abundant yellowish discharge makes it clear that it is time to immediately go to the maternity hospital. If you notice blood in them, this may be a signal of placental abruption.
What should you be wary of? If the discharge has acquired an earthy, green tint and looks more like pus or has become cheesy, immediately go to the hospital for additional examinations. This may be an alarming indicator of the presence of an infection that needs to be treated urgently so that your child does not become infected with it. If the discharge becomes watery, it means your water has started to break.
What does a baby look like at 37 weeks of pregnancy?
At 37 weeks, the baby is about the size of a melon.
At week 37, the Baby’s height is about 46-47 cm, and his weight ranges from 2700 to 2800 g. What happens to him:
- Baby's skin becomes lighter than before;
- the fluff that covered the body disappears;
- the central nervous, endocrine and immune systems grow and improve;
- the heart has formed well and is working, the blood now circulates differently than in an adult, since the Baby does not breathe on his own, but receives oxygen from the umbilical cord, and not from the lungs;
- your Baby is preparing for his first breath: he is increasingly trying to make breathing movements;
- Some Babies have hair actively growing on their heads, reaching 5 centimeters by the time of birth;
- The marigolds continue to grow, and it’s time to prepare special scissors to cut the nails after birth.
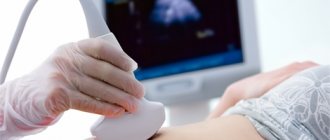
How often should fetometry be done?
Fetometry is scheduled to be performed 3 times throughout the entire pregnancy period. Moreover, during each examination, the obstetrician-gynecologist sets a very specific goal, correlated with the characteristics of fetal development.
1 fetometry - 11-12 weeks
This is an ultrasound screening at 11-12 weeks. Helps clarify the expected due date and determine whether the child has chromosomal developmental disorders. The choice of this particular time is not accidental: before the 11th week, the thickness of the fetal collar space is still so small that it cannot be measured, and after the 14th week, the surrounding space is filled with lymph, distorting the results.
The main measurements that are carried out during the first ultrasound are CTE, BPR, PY. The first fetometry is very important, as it becomes the starting point for subsequent examinations that confirm or clarify the first data on the condition of the fetus.
Useful advice for future parents
For the healthy development of a child, from the very moment of conception, love and sincere relationships between the expectant mother and father are very important.
At first glance, it seems that only when the Baby is born, your attitude towards each other, towards life, towards the people around you, your worldview, deeds, words and actions will begin to have a direct impact on the development of character, attitude, spiritual and moral qualities of the child. But it's not that simple. It turns out that all of the above affects the Baby even before birth! What to do, because nine months from conception to the birth of a child is a period of trials and problems for both the mother and the future father. How will the transformations taking place in a woman, frequent mood changes, irritation or even despondency, affect the Baby? Do the father's experiences affect a very tiny person? In general, are the feelings and moods of his parents transmitted to him, so tiny? And if so, how do they affect the pace of its development and overall well-being?
So, the child who is expected:
- more viable, since positive emotions of parents are one of the conditions for the successful bearing of a child and the development of all its organs and systems, as well as motor and intellectual activity;
- has a much greater chance of being born healthy, since his parents take care of his “nutrition”;
- develops better before birth, since its cells receive sufficient oxygen;
- smiles often (as Babies “repeat” their mother’s emotions);
- can respond with active movements to touches through the walls of the abdomen, as well as to affectionate words addressed to it.
Objectives
The use of an ultrasound method for diagnosing the fetus at the thirty-seventh week is necessary to determine its degree of maturity and assess the compliance of the child’s physiological development with all relevant normative values, as well as determine the approximate date of birth. An ultrasound diagnostic doctor provides invaluable assistance in the management of a pregnant woman and answers a number of the following questions:
- fetal heart rate and its compliance with the norm;
- location of the baby in the uterine cavity;
- degree of maturity of the placenta;
- the state and level of maturity of the child in the womb;
- the total amount and volume of amniotic fluid, its condition;
- cervical condition;
- correspondence between the size of the pelvis and the size of the child;
- the location of the umbilical cord and the presence of its entanglement around the fetal neck.
When ultrasound is supplemented with color Doppler mapping, it becomes possible to visualize blood flow in the vessels. This determines the blood flow in the arteries of the umbilical cord, the vessels of the uterus and the ratio of utero-placental blood flow.
Tests and studies during pregnancy
Ultrasound (ultrasound examination) - 35-36 weeks after the first day of the last menstruation.
The condition of the placenta, the height and weight of the child, its position in the uterus, and the quantity and quality of amniotic fluid are assessed. Blood test for AIDS (HIV), syphilis (RW) - 35-36 weeks after the first day of the last menstruation. These diseases can complicate pregnancy and childbirth.
Biochemical blood test - 35-36 weeks after the first day of the last menstruation. Gives an idea of the general health of the pregnant woman.
Vaginal smear - 35-36 weeks after the first day of the last menstrual period. Assessment of microbial flora before the baby passes through the birth canal.
Visiting a doctor monitoring pregnancy: once a week. Weighing, measuring blood pressure, measuring the height of the uterine fundus, listening to the fetal heartbeat.
General urine test - before each visit to the doctor. Indicates the quality of kidney function.
Dopplerography (a study that allows you to evaluate blood flow in the vessels of the uterus, placenta and main vessels of the child) - 33-34 weeks after the first day of the last menstruation, according to indications . The study allows you to find out whether the child is getting enough oxygen and nutrients.
Cardiotocography (CTG, synchronous recording of fetal heartbeats and uterine contractions) - 33-34 weeks after the first day of the last menstruation, according to indications. The child’s condition is assessed and intrauterine hypoxia is excluded.
Receive an exchange card with the results of tests and examinations - 30 weeks after the first day of the last menstruation. It is recommended that you always carry this document with you, which is required for admission to the maternity hospital.
Registration of maternity leave for workers - 30 weeks after the first day of the last menstruation.
Medical observation
At the appointment, the gynecologist will examine you in the chair to see if your cervix is ready for childbirth, because starting from the 36th – 37th week of pregnancy, the baby can ask to be born at any minute. During a vaginal examination, the doctor pays attention to the location, density and length of the cervix.
While the baby lives in the mother’s tummy, the lower segment of the uterus has thick walls, which during childbirth begin to stretch, becoming softer and thinner. This is called "smoothing". Before the onset of labor, it is zero; during active labor, the walls of the cervix are smoothed by 50%, and just before the birth of the baby - by 100%.
Also, at 37 weeks of pregnancy, the doctor checks the degree of dilatation (stretching) of the cervix. This indicator is determined in centimeters. When fully dilated, the width of the pharynx reaches 10 cm. If during the examination it is discovered that the cervix is not ready for childbirth, the doctor prescribes medicinal or non-medicinal means to increase its maturity.
When examined at 37 weeks of pregnancy, the gynecologist takes a smear. The test results will allow us to judge the presence or absence of infection in the birth canal. If necessary, treatment is prescribed, because at the moment of birth the child should be maximally protected from possible infection. Also during this visit, the doctor will listen to the baby's heartbeat, measure your weight and blood pressure, and assess the width of the pelvis and the presentation of the fetus.
Ultrasound is usually not done at this stage. It may be needed only if any abnormalities were identified during pregnancy.
Good to know
How to give birth without tearing: preparing the perineum for childbirth
How to sleep during pregnancy in the 3rd trimester?
“Pregnant” and maternal fears: how to stop being afraid
What to name the girl? Women's names and their meanings
Types of “pregnant” husbands
What to name the child? Choosing names according to the church calendar
All texts for pages about mother and baby were kindly provided by RAMA Publishing - these are chapters from the book by Svetlana Klaas “Your Favorite Little Man from Conception to Birth”, reviewer Irina Nikolaevna Kononova, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology of the Ural State Medical Academy (Ekaterinburg).
How is fetometry performed?
So, fetometry is a detailed examination of the condition of the mother and baby using an ultrasound machine. For pregnant women it is performed in two ways:
- transvaginally - with insertion of the sensor tip into the vagina;
- transabdominal - the contents of the uterus are viewed through the external abdominal wall.
Transvaginal ultrasound is recommended for women in early pregnancy. It allows the doctor to get a good look at the condition of the woman’s internal organs and the developing fetus. There is no need for special preparations for such an ultrasound, and it does not cause discomfort. And the aseptic effect is achieved through the use of a condom, which is placed on the sensor.
Transabdominal ultrasound is indicated in advanced pregnancy. The mother's belly is lubricated with a special gel that ensures good contact between the tip and the skin. And amniotic fluid makes it possible to examine the baby in detail and determine its gender, weight, size, and in the 3rd trimester even facial features. If for some reason a transabdominal diagnosis is carried out at an early stage of pregnancy, the woman will need to come to it with a full bladder - do not go to the toilet for 3-4 hours or drink about a liter of plain water half an hour to an hour before the procedure.
The advantage of ultrasound is that the woman herself can see the picture appearing on the screen or receive it in the form of an image. And all fears that sound waves can harm the child are completely unfounded. No one has yet discovered anything but benefit from an ultrasound procedure.
Ultrasound standards at 37 weeks

In addition to a standard examination of the fetus and assessment of all its indicators, the pregnant woman must undergo Doppler sonography to study blood flow and timely diagnosis of placental insufficiency. The arteries of the uterus, umbilical cord and blood flow in the placenta are studied. The amount of amniotic fluid is also measured, which begins to decrease from the 37th week. If the volume of amniotic fluid is insufficient, problems may arise with the development of pregnancy, so the woman will be prescribed the necessary treatment.
Important indicators for the mother’s body at 37 weeks are (in brackets - the norm):
- Presentation (cephalic, sometimes pelvic).
- Placenta maturity (2-3).
- Neck length (more than 3 cm).
- Location of the placenta (not lower than 7 cm from the cervical canal).
- Amniotic fluid index – 75-244.
- The thickness of the placenta is 27.8-45.8 mm.
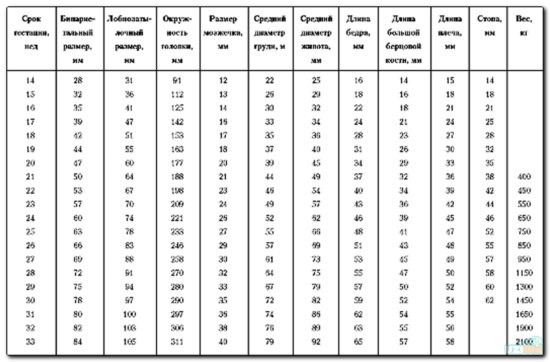
Ultrasound at this stage records a decrease in fetal movements, which is normal due to its large size. During an ultrasound, fetometry is performed, or calculation of the baby’s main parameters and comparison with the norm - how much he should weigh, what height he should be, etc. The main indicators for a baby at 37 weeks are:
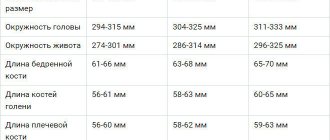
- The biparietal size of the head is about 90 mm.
- The head circumference is about 325 mm.
- Fronto-occipital size – 106-126 mm.
- The diameter of the chest is 93-94 mm.
- Abdominal circumference – 300-361 mm.
- Femur bone (length) – 66-76 mm.
- Shin bone – 59-67 mm.
- Shoulder bone – 59-69 mm.
- Forearm bone – 59-67 mm.
Based on these figures, by the 37th week the baby looks just like a newborn, so he will be born soon. Using an ultrasound scan at this time, the doctor will draw all conclusions about the upcoming birth and the method of delivery, and if there are deviations in the health of the mother and child, he will recommend procedures and treatment to eliminate them.