In the womb, the baby is surrounded by membranes and amniotic fluid. They play an important role in the development of the fetus: they serve as a shield from damage and infection, a source of nutrition and create favorable conditions for movement and development. Each gestational stage (gestational age) is characterized by a certain volume of amniotic fluid, the assessment of which allows us to assess the condition and development of the fetus. The volume of water determines the amniotic fluid index (AFI) - it is calculated in different ways.
Consultation with a doctor based on the results of tests or ultrasound - 500 rubles.
Methods for diagnosing IAF
The content of the article
There are two ways to determine the volume of amniotic fluid:
- Subjective: Ultrasound of the uterus transverse and longitudinal
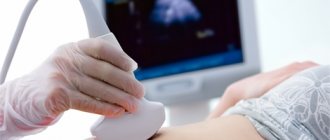
. The examination is carried out using ultrasound. Using ultrasound, the doctor performs transverse and longitudinal scanning and determines the amount of water. Using this method, you can make a mistake, so ultrasound with the calculation of the amniotic fluid index is considered more accurate.
- Objective: Ultrasound of the uterus with measurements by quadrants.
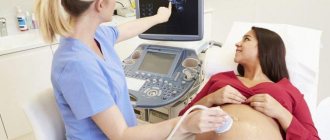
This method is the definition of IAF. The doctor scans the entire uterine cavity using an ultrasound sensor, conditionally dividing it into 4 quadrants by two perpendicular lines. Then in each "compartment" he identifies and measures a vertical pocket, i.e. the deepest pocket free of fetal limbs and umbilical cord. The resulting 4 indicators in total determine the amniotic fluid index. It is approximate, but it can be used to accurately judge the presence of polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios.
This diagnostic procedure is important for all pregnant women, as it allows timely detection of anomalies and pathologies of fetal and placental development. If deviations are detected, the gynecologist takes the necessary measures. In severe cases, it is recommended to terminate the pregnancy. But it is important to understand that the result depends on two components - the quality of the device and the qualifications of the doctor.
Diagnosis of polyhydramnios
With the development of polyhydramnios, a significant increase in the size of the uterus is observed: the abdominal circumference and the height of the uterine fundus (the distance from the womb to the fundus of the uterus) significantly exceed those at the expected stage of pregnancy. The uterus is tense, parts of the fetus are difficult to palpate, while the fetus easily changes its position, and its excessive motor activity may be observed. Fetal heart sounds are not heard clearly.
Ultrasound plays an important role in the diagnosis of polyhydramnios. During the study, the size of the vertical pocket is determined (ultrasound criterion for assessing the amount of amniotic fluid): with a mild degree of polyhydramnios, its value is 8-11 cm, with a moderate degree - 12-15 cm, with severe polyhydramnios this figure reaches 16 cm or more. If the diagnosis of polyhydramnios is established, then it is necessary to exclude the presence of possible fetal malformations using additional research methods, in particular amniocentesis - taking a small amount of amniotic fluid (by puncture of the anterior abdominal wall, uterine wall) for biochemical, hormonal, immunological, genetic research. Determining the concentration of alpha-fetoprotein in the amniotic fluid is of great diagnostic importance. This protein is produced in the fetal liver and then enters the amniotic fluid along with urine. A high concentration of alpha-fetoprotein indicates fetal developmental abnormalities, mainly in the nervous system. Amniocentesis is always performed under ultrasound guidance. The most important information about the condition of the fetus can be obtained from the results of direct examination of its blood obtained by taking it from the umbilical cord (cordocentesis). This procedure is carried out strictly according to indications, such as diagnosis of congenital and hereditary pathologies, intrauterine infection, etc. Cordocentesis is performed after 18 weeks of pregnancy under ultrasound guidance.
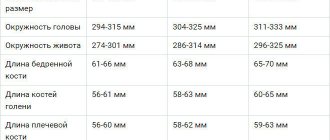
Amniotic fluid index table
The gynecologist must take into account the IAF to assess the quality of pregnancy, since a deviation from the norm indicates an anomaly or pathology of the fetus. Data is collected and entered into a table.
For the most accurate and correct research results, the following preparatory activities are carried out:
- cytological and biochemical analysis of amniotic fluid;
- assessment of transparency and shade of amniotic fluid;
- accounting of hormones contained;
- check, volume measurement.
For each stage of pregnancy, a certain norm of the amniotic fluid index is shown. By comparing the normal value with those obtained during examination of a pregnant woman, it is possible to determine the lack or excess of fluid.
| Gestational period (weeks) | Average value (cm) | Range of possible fluctuations (cm) |
| 16 | 12,1 | 7,3 – 20,1 |
| 17 | 12,7 | 7,7 – 21,1 |
| 18 | 13,3 | 8 – 22 |
| 19 | 13,7 | 8,3 – 22,5 |
| 20 | 14,1 | 8,6 – 23 |
| 21 | 14,3 | 8,8 – 23,3 |
| 22 | 14,5 | 8,9 – 23,5 |
| 23 | 14,6 | 9 – 23,7 |
| 24 | 14,7 | 9 – 23,8 |
| 25 | 14,7 | 8,9 – 24 |
| 26 | 14,7 | 8,9 – 24,2 |
| 27 | 15,6 | 8,5 – 24,5 |
| 28 | 14,6 | 8,6 – 24,9 |
| 29 | 14,5 | 8,4 – 25,4 |
| 30 | 14,5 | 8,2 – 25,8 |
| 31 | 14,4 | 7,9 – 26,3 |
| 32 | 14,4 | 7,7 – 26,9 |
| 33 | 14,3 | 7,4 – 27,4 |
| 34 | 14,2 | 7,2 – 27,8 |
| 35 | 14 | 7 – 27,9 |
| 36 | 13,8 | 6,8 – 27,9 |
| 37 | 13,5 | 6,6 – 27,5 |
| 38 | 13,2 | 6,5 – 26,9 |
| 39 | 12,7 | 6,4 – 25,5 |
| 40 | 12,3 | 6,3 – 24 |
| 41 | 11,6 | 6,3 – 21,6 |
| 42 | 11 | 6,3 – 19,2 |
Table of values
Different modulations of the norms of the AF-amniotic fluid index by week indicate the development of an anomaly or pathology in the fetus. To avoid unfavorable situations, pregnant women need to be constantly examined.
Check with a gynecologist
To ensure correct diagnostic results, doctors carry out a number of preparatory measures.
- Analysis of the cytological and biochemical composition of amniotic fluid.
- Checking transparency and shade.
- Accounting for hormones contained.
- Checking, studying the volume. The gestational period affects the volume of amniotic fluid, which is calculated relative to the trimesters of pregnancy.
There is a special table that describes the norms of the amniotic fluid index by week in mm.
| Gestation period (weeks) | Lower limit of normal | Average value | Upper limit of normal |
| 16 | 73 | 121 | 201 |
| 17 | 77 | 127 | 211 |
| 18 | 80 | 133 | 220 |
| 19 | 83 | 137 | 225 |
| 20 | 86 | 141 | 230 |
| 21 | 88 | 143 | 233 |
| 22 | 89 | 145 | 235 |
| 23 | 90 | 146 | 237 |
| 24 | 90 | 147 | 238 |
| 25 | 89 | 147 | 240 |
| 26 | 89 | 147 | 242 |
| 27 | 85 | 156 | 245 |
| 28 | 86 | 146 | 249 |
| 29 | 84 | 145 | 254 |
| 30 | 82 | 144 | 258 |
| 31 | 79 | 144 | 263 |
| 32 | 77 | 143 | 269 |
| 33 | 74 | 142 | 274 |
| 34 | 72 | 140 | 278 |
| 35 | 70 | 138 | 279 |
| 36 | 68 | 135 | 279 |
| 37 | 66 | 132 | 275 |
| 38 | 65 | 127 | 269 |
| 39 | 64 | 123 | 255 |
| 40 | 63 | 116 | 240 |
| 41 | 63 | 110 | 216 |
| 42 | 63 | 110 | 192 |
As can be seen from the table, the calculation principle is quite simple. For example, you need to find out the normal amniotic fluid index at 19 weeks of pregnancy. The table values show 83-137-225, where the first value is the minimum, then the average value and the maximum allowable quantity are indicated.
At 20-21 weeks, the lowest limit of the AF index - amniotic fluid is 86-88, this is a deviation from the norm. If such indicators occur, you should see a doctor.
There are two ways to diagnose IAF.
- Subjective: examination using ultrasound, when longitudinal and transverse scanning is performed.
- Objective: the diagnostician, using the method of certain calculations, summarizes 4 indicators that determine the amniotic fluid index by week in cm. At week 16 it is a value of 12 cm.
This is what a baby looks like in the mother's womb
Additionally, the size of the amniotic fluid pocket is diagnosed, which is determined in two perpendicular planes. An additional test analysis is possible, which is carried out at 16-18 weeks.
Such an analysis is useful for the timely detection of anomalies, pathologies of fetal or placental development. After diagnosing a pregnant woman’s body, doctors take the necessary measures. In rare acute cases, termination of pregnancy is recommended.
Deviations from the norm
Measuring the amniotic fluid index allows you to identify dangerous problems during pregnancy:
- polyhydramnios – increased volume of amniotic fluid;
- oligohydramnios – reduced amount of amniotic fluid.
Polyhydramnios can be of different types:
| View | Internal pocket size |
| Moderate | 7-18 cm |
| Expressed | 18-24 cm |
| Chronic | the figure is slightly higher, but stable |
| Borderline/acute | the index value varies between the average and the highest indicator |
Reasons for deviations from the norm of the AF index
Polyhydramnios, which occurs in 1-3% of cases, can be caused by the following factors:
| Diagnosis of mother | immunization based on Rh factor and blood group; infectious and inflammatory processes; presence of diabetes mellitus. |
| Diagnosis of the placenta | swelling of the placenta; benign neoplasm of the fetal membrane (the size of the tumor affects the outcome of pregnancy). |
| Diagnosis of the fetus | several fetuses in the uterine cavity; abnormal fetal development; genetic characteristics; chromosomal pathologies. |
According to statistics, oligohydramnios occurs in 0.3-5.5% of cases. The reasons for its occurrence may be:
- abnormal fetal development;
- pathological changes in the fetus (developmental delay, chromosomal disease, infection);
- diseases of women (cardiovascular disorders, infectious and inflammatory processes, gestosis);
- kidney pathologies (dysplasia, Potter's syndrome, cystomas);
- developmental disorders of the placenta (placental insufficiency, placental defect and infarction);
- post-term pregnancy;
- placental rupture;
- frozen pregnancy.
What is oligohydramnios?
Oligohydramnios is a decrease in the amount of amniotic fluid to 500 ml or less, associated with a violation of their formation and absorption.
This condition occurs in approximately 0.3-0.5% of pregnant women. Among the causes leading to oligohydramnios, the most common are gestosis and maternal hypertension, and the severity of oligohydramnios and the frequency of its development depend on the duration of this pathology and the degree of its severity. A decrease in the amount of amniotic fluid also occurs against the background of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the mother, such as toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, mycoplasma infection and other sexually transmitted diseases, as well as chronic inflammatory diseases of the mother (chronic tonsillitis - inflammation of the tonsils, kidney disease, gynecological diseases and etc.). Insufficient production of amniotic fluid occurs with lesions of the fetal excretory system, such as blockage of the urethra, ureters, as well as with impaired renal function due to a decrease in the amount of primary fetal urine. Chronic hypoxia (oxygen deficiency) of the fetus is also one of the reasons for the development of oligohydramnios.
The mechanism of development of oligohydramnios during chronic fetal hypoxia has not been fully studied, but it is assumed that against the background of oxygen deficiency, a reflex redistribution of blood flow occurs in favor of vital organs: the brain, fetal heart, adrenal glands, while bypassing the lungs and kidneys, which are the main ones. sources of amniotic fluid production at the end of pregnancy.
It should be noted that the appearance of oligohydramnios does not depend on the age of the patients - it occurs with equal frequency in both primiparous and multiparous women.

Amniotic fluid index: possible complications
Non-compliance with the norms of the amniotic fluid index indicates not only the presence of oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios. The occurrence of such conditions poses a danger to the health of the woman and her unborn child and even threatens with serious consequences. And it is precisely thanks to the calculation of the AF index that it is possible to prevent the development of possible complications.
Polyhydramnios threatens:
- placental abruption;
- infection of the birth canal;
- impaired fetal development;
- miscarriage.
Oligohydramnios, first of all, poses a danger to the fetus and threatens it with serious diseases.
This pathology can lead to:
- disruption of the respiratory and genitourinary systems of the fetus;
- hypoxia;
- hypodynamics and pressure on the fetus, which can provoke developmental disorders of the fetus (weight changes, dislocations, deformation of bones, spine);
- miscarriage;
- postpartum bleeding.
Management of pregnancy and childbirth with polyhydramnios
Pregnant women with polyhydramnios are subject to hospitalization and a thorough examination to identify the cause of its occurrence (diabetes mellitus, the presence of a chronic infection, fetal malformations, etc.). The method of treatment depends on the identified pathology - in the presence of an infectious process, immunoglobulin therapy (intravenous administration of immunoglobulin preparations) is used; it is also possible to use antibacterial therapy. If the examination reveals fetal malformations that are incompatible with life, the pregnancy is terminated regardless of the term.
Childbirth with polyhydramnios is often complicated. One of the common complications is weakness of labor, which is associated with overstretching of the uterus due to excess amniotic fluid. As a result, the excitability of the uterus and its contractility are reduced. The course of labor can be protracted.
Due to the fact that the rupture of amniotic fluid can be complicated by the prolapse of the umbilical cord, small parts of the fetus, as well as premature detachment of the normally located placenta, there is a need for artificial opening of the amniotic sac (amniotomy) when the uterine pharynx is not fully dilated (3-4 cm), in order to release the amniotic fluid by holding back its flow with the hand inserted into the vagina.
To prevent bleeding in the afterbirth and early postpartum period (in the first 2 hours after birth), bleeding is prevented by intravenous or intramuscular administration of drugs that increase uterine contractility (oxytocin, methylergometrine).
In conclusion, it should be noted that for timely diagnosis, and therefore treatment of the described conditions, it is necessary to promptly follow all the recommendations of the doctor managing your pregnancy. This will avoid serious complications and help give birth to a healthy baby.
Amniotic index is broken: what to do next
Deviation from the norm of the amniotic fluid index provokes developmental disorders of the fetus, therefore, if the indicators do not correspond, careful monitoring by a gynecologist is necessary throughout pregnancy. You cannot self-medicate, since the safety of the mother and child is at stake. And only qualified assistance from doctors and compliance with all their instructions guarantee a successful outcome for the health of both.
The specialist must determine the reason for the deviation of the index from the norm. If it turns out to be a serious pathology in the development of the fetus or an amniotic cord incompatible with the life of the fetus, then it is recommended to terminate the pregnancy. If deviations do not pose a threat to the child’s life, doctors prescribe appropriate treatment aimed at getting rid of the causes of discrepancy with the AF index and normalizing the condition of the fetus, and determine tactics for managing pregnancy and childbirth.
Traditionally, antibiotics are used to restore hypodynamic functions, immunomodulators in the presence of infection, as well as diuretics.
With moderate oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios, a woman should follow the following recommendations:
- taking Curantil, Actovegin (as prescribed by a doctor);
- limiting physical activity;
- healthy eating and adherence to the regime;
- taking a vitamin complex;
- therapy that prevents the development of infectious and inflammatory processes;
- in post-term pregnancy - stimulation of labor.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Optimal treatment
The optimal treatment is determined individually for each pregnant patient, taking into account the diagnosis, characteristics and cause of the problem.
Let's say you are 32 weeks pregnant and your amniotic fluid index is 77. This means you have borderline oligohydramnios.
Polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios are far from a tragedy, but with oligohydramnios you will have to spend most of your time in hospital.
If you take medications correctly and strictly follow the doctor's recommendations, the level of polyhydramnios will decrease, and the value of oligohydramnios will increase to the required numbers. In this case, your index of AF - amniotic fluid will remain at a stable value.
A good mood, positive emotions, a positive attitude, and strict adherence to all doctor’s recommendations guarantee minimal risk to the mother’s health and the normal development of the child.
| Medical Center | Address | Price |
| 1st Clinical City Hospital | Minsk, Nezavisimosti Ave., 64 | 6200 rub. |
| Medicine plus | Moscow Volgogradsky pr., 64 | from 1500 rub. |
| Alpha Health Center | Ekaterinburg, st. Maxim Gorky, 17 | from 1500 rub. |
| Nadiya Reproductive Medicine Clinic | Kyiv, st. Maxim Krivonosa, 19 A | from 490 rub. |