Ultrasound diagnostics is a universal diagnostic method that is used in various fields of medicine. Until recently, examining the intestines was quite difficult, and ultrasound was practically not used in proctology. This is explained by the fact that the intestinal lumen contains gas that distorts the image. The development of ultrasound technology has made it possible to overcome this drawback, and now ultrasound examination of the intestine is considered one of the most popular measures for examination and diagnosis. This method plays a special role in identifying oncological processes.
Types of intestinal ultrasound
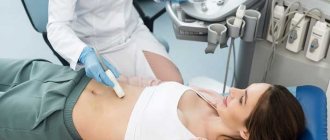
Two ultrasound methods are used to visualize the intestines: transabdominal and rectal. The transabdominal method involves ultrasound examination through the abdominal cavity. This method is used without filling the intestines, while contrast is introduced, and the bladder must be full.
The rectal method uses a rectal sensor. You can also do an intracavitary examination using a vaginal probe. This method is optional and is only possible for women.
Content:
- Types of intestinal ultrasound
- Indications for ultrasound diagnostics
- Preparing for an ultrasound examination
- Carrying out an ultrasound
- What can you find?
- Ultrasound examination of the intestine in children
- Preparing a child for an ultrasound
- Advantages of intestinal ultrasound
To maximize coverage of the intestines, most often 2 methods are used at once. Transabdominal ultrasound does not always give 100% results, since in 15% of cases the bladder is not full enough. Rectal ultrasound is more informative, but may be contraindicated in some people. Such a study is not carried out for people who have been diagnosed with stenosis of the terminal part of the gastrointestinal tract. Based on this, it becomes clear that none of the methods is ideal, so only their combination can give the most accurate result.
Benefits of Ultrasound Examination
Often, if it is necessary to identify diseases of the abdominal cavity, computed tomography or other diagnostic examinations are prescribed, however, the use of the ultrasound method has a number of advantages:
- Ultrasound diagnostics are carried out in real time, which allows you to obtain the most relevant data;
- it is possible to conduct an examination of a specific area of the organ in which discomfort or pain is felt;
- in order to clarify the results, duplex scanning can be performed;
- there is the possibility of conducting a compression examination - with the help of pressing movements in the abdominal cavity and the use of a special sensor, it is possible to identify disturbances in the processes of compression of the walls of organs, which will indicate a particular disease;
- the possibility of using the method for severe diseases due to its complete painlessness for the patient.
Separately, it should be noted the benefits of conducting research if appendicitis is suspected: ultrasound allows you to show the exact location of appendicitis, which helps in determining an effective treatment regimen.
Preparing for an ultrasound examination
It is important to understand that any intestinal examination should be carried out only after preparation. Ultrasound also requires preliminary preparation. This procedure is performed after an enema and on an empty stomach. If the patient has constipation, then it should be eliminated and gases should be removed from the intestines.
If a person has severe flatulence, then it is necessary to refrain from foods that cause increased gas formation. You need to give up this food for 2-3 days. The list of these products includes: dairy products, yeast products, legumes, as well as products containing a large amount of fiber.
In addition, you should take enterosorbents: charcoal, smecta, espumizan. In order for food to be better digested in the stomach, you can take enzyme preparations, which can be prescribed by your doctor.
The process of preparing for an intestinal ultrasound also depends on the examination method.
During a superficial examination, it is important to give up food and drinks 5-7 hours before; 1 hour before the procedure, you need to drink 1 liter of still filtered water without gas or unsweetened tea. Immediately before the procedure, you should give up smoking, chewing gum and lollipops.
If you have an ultrasound with contrast, you should take an enema before the procedure in the evening. Ultrasound examination through the rectum is possible with a cleaned intestine and an unfilled bladder. It is worth noting that the cleansing procedure can be done using an enema or using an osmotic laxative. At the same time, there is no need to observe long breaks between meals.
As for nutrition, these questions should be clarified with your doctor immediately before the study. Quite often, the intestines are examined together with the stomach and gastrointestinal tract. In such a case, it is not allowed to have food residues in the digestive tract. If there is a possibility that double research will be required, then it is better to approach this issue as seriously as possible.
What can an intestinal ultrasound reveal in children?
- Ultrasound of the intestines in children, the picture (image) of which is displayed on the monitor, can show various types of neoplasms in it, as well as tumors;
- Inflammation occurring in the intestines;
- Intestinal damage and complications caused by them;
- Intestinal malformations;
- The doctor also studies the size and structure of the intestines, its shape and tissue structure.
Carrying out an ultrasound
Ultrasound examination of the rectum through the abdominal wall is a procedure that is familiar to many. The patient should bare his stomach and lie down on the couch. The doctor must apply a special gel to the skin of the abdomen and then examine the organ using a sensor.
Ultrasound with contrast is performed in another way:
- The patient should remove clothing below the waist and take a comfortable position on the couch. The doctor should first examine the intestines in the usual way, using a probe (through the abdominal wall).
- Next, the patient should lie on his side, with his back to the doctor. The doctor must inject sterile saline solution (2 liters) into the intestines through a catheter, and then perform the usual transabdominal examination. This is done so that the intestinal walls can expand under the pressure of the fluid and make it possible to examine all parts of the organ.
- After bowel movement, the doctor should examine the organ again using ultrasound diagnostics.
While a conventional ultrasound examination is familiar to everyone, a procedure with an endorectal probe may cause fear and questions in a person. There is nothing dangerous or scary about an ultrasound through the anus. A thin sensor, which is specially designed and intended for such manipulations, is inserted into the anus at a distance of 10-13 centimeters. This does not cause pain to the patient and is completely safe. The divisions on the sensor allow the doctor to control the depth of its insertion. During the procedure, the patient should lie on his side and keep his knees to his chest.
How is an intestinal ultrasound done?
Patients are most concerned about how bowel ultrasound is performed in women and men and how unpleasant or painful the procedure is. It all depends on what type of ultrasound is supposed to be done, as well as on the gender of the patient. Ultrasound of the intestine for women and men can be performed differently. In some cases, both methods are used for a more detailed study.
Transrectal ultrasound
The patient is asked to lie on his side and bend his knees so that they rest against the abdomen.
Transrectal ultrasound of the intestine is performed using a special thin sensor, which is inserted into the anus, then into the colon at a distance of no more than 10-12 cm. The procedure is painless and safe, but requires ideal cleanliness of the intestinal walls.
Transabdominal ultrasonography
With transabdominal ultrasonography, the procedure is more complex as it is carried out in three stages. At the first stage, the patient exposes his stomach, the doctor examines the abdominal cavity in the intestinal area in the usual way using a sensor. In the second stage, the patient is asked to lie on his side, after which saline solution is injected into the intestines.
Fluid in the intestine, straightening its walls, will improve visibility on ultrasound. After a bowel movement, the bowel is scanned again through the abdomen to assess movement status.
What can you find?
A healthy rectum on ultrasound is a round, slightly elongated organ with a rim that extends from the muscle layer. Ultrasound scans it in transverse and longitudinal sections. During the examination, the doctor can evaluate the condition of the intestine on the monitor of the device: its size and shape, the location of the organ relative to others, the thickness and structure of the walls, the length of the intestinal segments, the condition of the tissues, the size and structure of the lymph nodes, the presence of neoplasms, scars, and inflammatory foci.
Normally, the intestines should not contain scars, lesions and neoplasms; the size and structure should also correspond to the norms.
During the study, the doctor must make a detailed description of the intestines and make a tentative diagnosis. Further study of the results should be carried out by the proctologist who prescribed the tests and examination to the patient.
The examination can confirm the previously made diagnosis or refute it. In addition to possible neoplasms and noticeable changes in the size of the organ, ultrasound can reveal the following pathologies: appendicitis, colitis, intestinal bleeding, hematomas in the walls of the colon, tumors, paraproctitis, intestinal obstruction, diverticula, intussusception, etc.
If an oncological formation is detected in a person’s intestines, ultrasound can help clarify its location, extent and the presence of metastases, including lymph nodes.
When preparing for surgery in the case of an oncological tumor, ultrasound examination allows you to determine the location of the upper pole of the tumor and its size. This information is necessary before planning surgery and to determine the optimal approach to the tumor.
After surgery, an ultrasound is done to monitor the organ and to identify possible relapse.
There is also an ultrasound screening of the intestines. It is carried out not for direct indications, but for preventive purposes. Indirect indications include: heredity, old age.
In such cases, it is recommended to carry out ultrasound diagnostics using the endorectal method, since neoplasms in the rectum can be clearly seen with a cavity sensor. The purpose of a preventive study is to exclude an oncological process in the organ. Regular scanning allows you to assess the possible risk of developing cancer and promptly notice changes.
What does an ultrasound of the small intestine show?
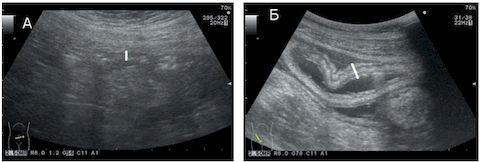
Ultrasound of the small intestine begins with visualization of the initial section - the duodenum. The homogeneity of the structure, clarity of contours, echogenicity, and the presence of fluid accumulation are determined. Then the shape, size, position and structural features of the jejunum and ileum are assessed. Additionally, Doppler sonography can be used to evaluate the vascular bed, blood supply to the rectum, and intraorgan blood flow.
The following diseases of the small intestine are diagnosed using ultrasound:;
- enteritis (functional dysfunction and dystrophy of the small intestine),
- duodenal ulcer;
- duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum),
- intestinal obstruction,
- Crohn's disease (granulomatous inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract),
- structural anomalies,
- consequences of injuries.
An ultrasound is also performed to detect free fluid in the intestine. When performing a repeat study, you can evaluate the dynamics of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment.
Preparing a child for an ultrasound
Before the procedure, the child must prepare for it. First of all, this concerns nutrition. Parents should provide the child with dietary nutrition 2-3 days before the ultrasound, and also give medications that reduce gas formation. The name of the drug and dosage must be stated by the attending physician. If the child does not suffer from constipation, then an enema is not necessary.
Immediately before the ultrasound examination, the child should fast for a while. The duration of such a “hunger strike” depends on age:
- if the child is an infant, then you need to skip one feeding before the procedure;
- if the baby is 1-3 years old, then the break in eating should be reduced to 4 hours;
- if the child is from 3 to 14 years old, then the last meal should be 6 hours before the procedure.
It is worth noting that you need to stop drinking 1 hour before the procedure.
Preparing for an ultrasound of the intestines
It is necessary to begin preparation 3 days before the study, following a diet. The diet should consist only of dietary dishes (boiled chicken breast, porridge with water, lean fish, boiled eggs, etc.), legumes, vegetables, fried foods, and flour products are excluded. You cannot drink alcoholic and carbonated drinks, as well as juices and coffee.
Before an ultrasound of the intestines, the doctor individually prescribes medications that support the digestion process and neutralize gas formation.
On the eve of the study, bowel cleansing is carried out. You can do a light enema or choose a medicinal method - the choice depends on the indications, the state of the gastrointestinal tract and the wishes of the patient himself. The group’s doctors will take care of your physical and psycho-emotional comfort, offering the most suitable preparation plan for your intestinal ultrasound.