Is it allowed to treat teeth during pregnancy?
Of course yes, and sometimes it’s simply necessary. A problematic oral cavity is not only decayed teeth, bad breath and unbearable pain in an inflamed tooth, but primarily the cause of the appearance and spread of infection, which must be prevented and treated at an early stage of pregnancy.
If the situation has already become complicated, the infection will spread throughout the body with pieces of food, saliva and blood. A particularly dangerous situation is when the inflammation is already located near the tooth roots, where blood vessels and bone tissue are located.
Even if during pregnancy a dental infection did not harm either the woman or the child in any way, this can happen after childbirth. After all, every mother loves to kiss and hug her newborn baby, and along with tenderness, the mother passes on her microflora to the child, including a tooth infection. If bacteria enter a child's body that is still fragile after birth, this can lead to many serious problems.
MRI during pregnancy
MRI during pregnancy is not performed as often as ultrasound, but there are situations when only magnetic resonance imaging can help make a diagnosis. It is important that MRI will not harm either the mother or the child, which means that if you have a choice, give preference to magnetic resonance imaging.
Our experienced radiologists at the Elena Malysheva Diagnostic Center will do everything to quickly, efficiently and in the most comfortable atmosphere for the patient to identify possible pathologies.
Sign up for an MRI at the Elena Malysheva Diagnostic Center near the Baumanskaya metro station (see map) by phone or leave a request on the website.
Baumanskaya metro station (see map) 8
leave a request on the website
Effect of anesthesia
Sitting at the dentist's office, people are afraid of the discomfort and pain that always accompany dental treatment. But a solution has long been found - pain relief. How do pregnant women tolerate anesthesia? Are they allowed to take painkillers? Many dentists answer that such an injection is simply necessary. After all, expectant mothers will experience unnecessary anxiety and fear of feeling pain while waiting for their turn to see a doctor. And stress negatively affects the well-being and development of the baby in the womb, so she does not need worry at all and is even contraindicated.
Is it safe to give a painkiller injection to pregnant women? If we are talking about general anesthesia, then its influence can still negatively affect both the child and the expectant mother. But local anesthesia can be done using modern medications. They will perfectly anesthetize a small area of the gum, since they act in a targeted manner, and will limit the pregnant woman from terrible torment in the dental chair during the treatment process. In addition, the dose of the drug is very small, so you should not be afraid that the drug gets to the baby along with the blood; its components will still not pass through the placenta.
Anesthesia, painkillers and antibiotics
Anesthetics during pregnancy are dangerous because they can penetrate the placenta and also increase blood pressure due to the high content of adrenaline. However, its concentration in a ratio of 1:200,000 has been proven to be safe for both mother and child. It is recommended to use ultracaine and ubistezin as pain-relieving injections during pregnancy. And it is better not to use lidocaine, which is more popular in dentistry, as a “freeze”: it causes cramps and muscle weakness. Also, during pregnancy, anesthesia is strictly prohibited. If complex treatment or tooth extraction cannot be avoided, the doctor may prescribe painkillers to the patient. Ibuprofen and paracetamol are considered the safest during pregnancy, but you need to keep in mind that taking ibuprofen is not recommended in the 3rd trimester. Antibiotics should also be avoided by expectant mothers, but if there is a risk of complications and the development of bacterial infections, drugs from the group of penicillins and cephalosporins are acceptable.
Effect of X-ray
X-rays are another factor that frightens not only pregnant women, but also ordinary people. There are a lot of myths about the negative impact of x-rays on the human body, and since a woman during pregnancy must take care not only of herself, but also of the new life within herself, it is often because of these myths that she refuses dental treatment, for fear of harming the baby.
Of course, the X-ray procedure must be approached with all seriousness, but in this case you should not be afraid of it. After all, we are talking about a targeted effect, which is strictly aimed at a small area in the oral cavity, while the woman’s chest, neck and stomach are reliably protected by a lead apron. Therefore, we can say that exposure to X-rays is minimized and cannot in any way harm either the baby or the expectant mother.
Is it possible to do x-rays?
It is not advisable for pregnant women to undergo X-rays, and it is strictly contraindicated in the first trimester. But at a later date, if there is evidence, such a procedure is possible. Fortunately, modern dentistry uses equipment with highly sensitive sensors and minimal radiation. During the examination, the patient’s chest and abdomen are covered with a lead apron.
Attention!
To avoid the risk of complications in the fetus, it is worth taking care of prevention at the stage of pregnancy planning. Before deciding to expand the family, a woman needs to consult a dentist, cure all carious lesions, chronic diseases of the gums and periodontal tissues, and, if necessary, undergo procedures to strengthen tooth enamel. Those who are preparing to become a mother need to pay special attention to hygiene and proper oral care, because during pregnancy the risk of developing caries increases.
Dental treatment and pregnancy
Women in special situations should visit the dentist more often than ordinary people. This will increase the chance of catching the problem early and fixing it quickly and safely. The dentist must first explain in detail and gently what he will do, what medications to use, and how this procedure will somehow affect her body or her fetus. It is important that the doctor helps the pregnant woman choose good products for cleaning her mouth, tell her what vitamins she needs to take while the baby is growing and how to properly care for her teeth.
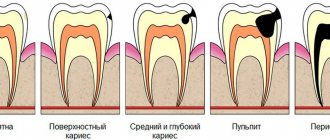
Do pregnant women need to have their teeth pulled out or inserted? When the problem is detected at the initial stage, it will not be difficult to solve it. You will just need to clean the affected area with a drill and close it with a special solution (seal). Modern fillings do not affect a pregnant woman or her child in any way, since their components are absolutely safe.
But if the situation has already started and the infection has reached the roots of the tooth, then the doctor will have to work a little. You must first take a picture to determine how damaged the roots are, remove them, take a few more pictures, and only then proceed with filling. Since the root removal procedure is unpleasant and painful, you cannot do without an anesthetic injection.
It is much easier to restore a damaged tooth than to create a new one in its place. But if the tooth cannot be saved, then there is only one option - removal. Is it possible to have teeth removed during pregnancy? The answer is yes, if there are no contraindications. But doctors still try to save the tooth and carry out treatment with all available methods, and resort to removal only when there is no longer a chance.
As for inserting a new tooth during pregnancy, there are also no contraindications to this procedure. If the gums are healthy and there is no infection, then it is better to postpone such a procedure for a while, since the process of creating a new tooth is quite labor-intensive and will require frequent visits to the dentist.
Can pregnant women have their wisdom teeth removed? It is possible, but if the situation is not critical, then it is better to postpone such a procedure. After all, removing a healthy tooth is not an easy process, and if it is even slightly covered by gum, it will have to be cut. Such an intervention risks causing complications, for example, bleeding from the gums, pain after or increased body temperature, which is undesirable for the mother and her fetus. But if the tooth is damaged and hurts, then it is better to remove it as soon as possible.
Safe anesthesia options for pregnant women
Dental treatment under anesthesia during pregnancy is clearly prohibited - only local painkillers can be used. However, local anesthesia for dental treatment during pregnancy is very important: severe pain during treatment can cause a surge of adrenaline, which can dangerously affect the unborn baby and even cause premature birth.
Novocaine and lidocaine should be excluded from local anesthetics - they can cause muscle weakness, cramps, pressure changes, dizziness and vomiting. Ubistezin, ultracaine, artifrin, alfacaine are considered safer painkillers for dental treatment during pregnancy, because they do not have a vasoconstrictor effect and almost do not penetrate the placenta.
When is the best time to treat teeth for pregnant women?
When the problem is critical, you need to consult a dentist at any time, and as soon as possible. But first, a pregnant woman needs to find out from her gynecologist whether there are any restrictions on dental treatment. If you can be patient, it is better to carry out treatment procedures in the second half of the term, since in the first and third the formation and intensive growth of the baby’s internal organs occurs, so there is a possibility that any intervention and medication will have a detrimental effect on the child’s development.
Tooth extraction during pregnancy
It is not advisable to undergo tooth extraction during pregnancy. This is always associated with a heavy burden, both psychological and emotional, as well as physiological - after all, this is a surgical operation. In addition, with such an operation there is a high probability of infection and the development of inflammation, which may require the use of antibiotics, the use of which is extremely undesirable during pregnancy.
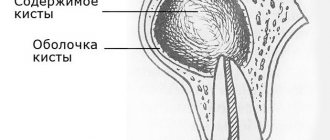
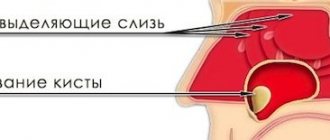
Therefore, planned extractions (for example, wisdom teeth) are not carried out during this period, and only emergency extractions are performed, associated with severe acute pain, dangerous inflammatory processes, fracture of the root or neck of the tooth, the formation of a large cyst (more than 1 cm) or a purulent focus of inflammation.
Is it possible to take an X-ray of a tooth?
A lot of questions arise about whether it is possible to take dental x-rays during pregnancy. In the first trimester, X-rays are prohibited. Dental X-rays in the early stages of pregnancy pose a high risk of dangerous effects on the woman’s body and the developing fetus. In the second and third trimester, x-rays can be taken (preferably radiovisiography, characterized by lower radiation intensity) using a protective apron and according to strict indications.
When is dental treatment in a clinic considered safe during pregnancy?
The first trimester of pregnancy is considered the most dangerous in terms of treatment, all kinds of procedures and complex interventions. Thus, for the safety of mother and child, dental treatment should, if possible, not be performed until the end of the first trimester, i.e. until the thirteenth week. After the thirteenth week and up to the twenty-eighth, such intervention is permissible. In the third trimester, that is, from the twenty-eighth to the fortieth week, treatment will be less safe, since it can provoke severe stress for the mature fetus and negative consequences.
Note! Oral sanitation is included in the mandatory monitoring program for women in labor at the antenatal clinic. Even if a pregnant woman has certain dental problems, she will, one way or another, be recommended treatment by a doctor.
Implantation and prosthetics during pregnancy
Prosthetics in themselves are not prohibited during pregnancy. You can install removable and fixed dentures, and even crowns. But implantation will have to wait until the baby is born. Dental implantation during pregnancy requires a huge expenditure of vitality and body resources, and most importantly, the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, strong painkillers, and sometimes antibiotics.
Inserting an implant into bone tissue requires surgical cutting of the gum and drilling into the bone. And then the body must form new bone tissue around the implant. And all this during the period when the skeleton of the unborn child is intensively formed, when every milligram of calcium counts - so much so that the mother’s body is ready to weaken its own bone tissue and the structure of the enamel and dentin of the teeth so that the baby’s body does not experience a lack of calcium.
Therefore, during such a period, it is extremely unwise to further weaken the mother’s body and endanger the unborn child through the most complex surgical implantation operation. It is better to wait a few months and have implantation done after birth, without endangering the baby.
Benefits of CT
CT scanning of the jaw has many advantages. That is why this diagnostic method has found wide application in dental practice.
Advantages:
- Safety. Radiation exposure during the study is minimal.
- Information content.
- Image clarity.
- The ability to zoom in on a computer monitor and examine the desired area in detail.
- Fast execution (less than one minute).
- Comprehensive examination of the entire dentofacial apparatus.
- Possibility of saving received data on electronic media.
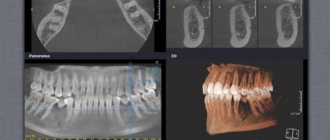
On the left is a panoramic image of the jaws, on the right is a CT image
How does pregnancy affect teeth?
Ideally, the expectant mother should plan her conception and at this time eliminate all dental pathologies. But even in this case, problems can arise at any time.
This is due to powerful changes in the body:
- immunity decreases, which suppresses the activity of pathogenic bacteria;
- the composition of saliva changes - due to increased viscosity, it protects less well from pathogenic microorganisms and poorly enriches the enamel with minerals;
- the body lacks calcium and magnesium, so bone tissue becomes more fragile;
- soft gum tissues become loose and prone to infections.
For these reasons, patients develop caries, gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease, and epulis. It is impossible to spread infectious diseases, because pathogenic microflora easily penetrates the blood, which means it can infect the fetus and lead to developmental abnormalities. At the first signs of disturbances, you should immediately contact a dentist, who will decide how best to cope with this or that disease.