Reasons for viral activation during lactation
Hipes, as this pathology is also called, during lactation gives the mother a general deterioration in well-being, and rarely an increase in temperature. Its causes are the entry of viruses into the mother’s body; they can be of several types, according to which the types of the disease differ.
The virus is activated during lactation if the defenses weaken for various reasons:
- A woman has to refuse to eat foods that cause allergies and intestinal disorders in the baby. As a result, the mother’s body does not receive the necessary substances for the proper functioning of the immune system.
- A mother can suffer stress from lack of sleep and worry about the baby. This also weakens the security functions.
- A nursing mother, without the advice of a doctor, takes medications or dietary supplements to strengthen the immune system. Uncontrolled use of medications and biological supplements often gives the opposite result.
The period of breastfeeding is a dangerous time for taking unnecessary medications, especially without medical supervision. Only a doctor prescribes medications and warns about the need to stop breastfeeding. The cause of genital and shingles diseases lies in hormonal changes in nursing mothers.
Is milk feeding allowed?
Feeding a child during herpes is not only possible, but also necessary.
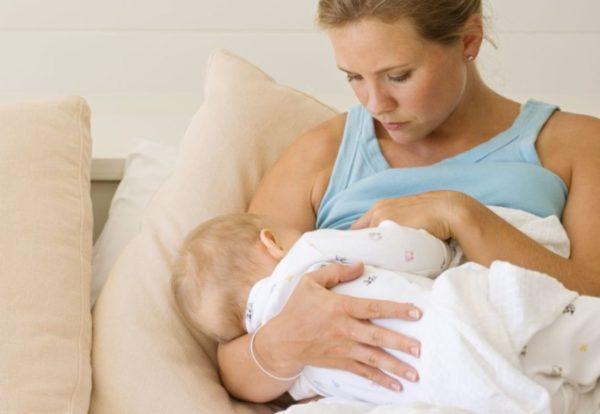
During lactation, a woman's body releases antibodies that can destroy the virus. They block it 3-5 days from the onset of the disease. They also pass into milk and are passed on to the baby, which is an excellent way to prevent infection with the virus.
If a rash appears on the nipples, it is better to interrupt feeding, since the virus is transmitted through contact.
The most important thing is to prevent the child from coming into contact with the site of herpes infection.
Types and locations of localizations
There are several types of disease based on the location of the skin rash:
- herpes type 1 in a simple form;
- herpes type 2 simple form;
- Herpes Zoster – shingles type.
The first form is expressed by rashes on the lips, nose, and face. The second form develops on the genitals. The shingles type is caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox and gives a typical picture of a childhood illness. Exposure to any type of illness leaves the virus in the body forever. In case of immunity disorders, herpes is expressed by rashes along the nerve endings, always with severe pain.
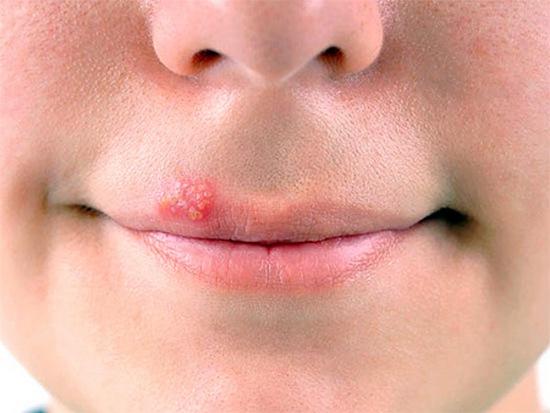
On the lips
Herpes on the lip during breastfeeding is not dangerous for the child; to prevent infection, the baby should not be kissed; contact of the mother’s affected lips with the baby’s skin should be avoided. Before breastfeeding, you need to thoroughly wash your hands with disinfectants and treat your nipples.
You can cure a rash on the lips with home remedies, patiently treating the affected area with water in which they are diluted: per glass of water - 1 level teaspoon of salt and baking soda, 5 drops of iodine. Carry out the treatment 5-6 times a day, lubricate the rash with brilliant green at night.
Herpetic rash on the lips is a common form of the disease. Its causative agent is the herpes virus type 1. It is transmitted through household contacts using shared utensils. You should protect your baby from infection, carefully handle his bottles and pacifiers, and store them separately from adult utensils.
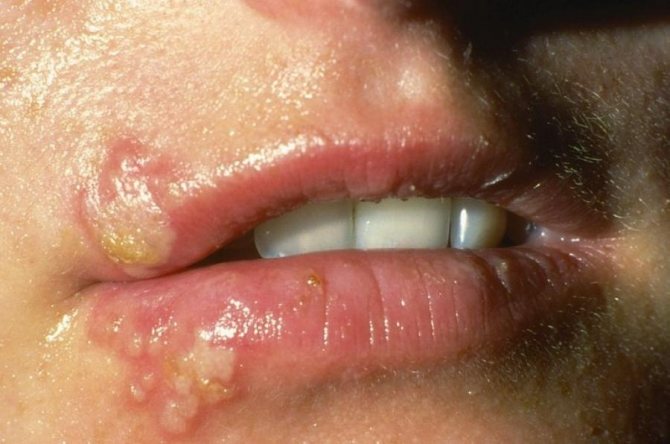
On the genitals
Type 2 virus manifests itself in the perineum, which is why it is called genital. Accompanied by a deterioration in health, the appearance of general weakness, and fever. At the first signs, the mother may think that an acute respiratory infection is beginning. Then itching and burning from a blistering rash in the area of the external genitalia and perineum are added. The rash penetrates the vagina, causing the woman significant discomfort.
Genital herpes, which often appears after childbirth, is not dangerous if the mother follows the hygiene requirements during breastfeeding. Dr. E. Komarovsky recommends not washing your breasts with water before feeding your baby - this does not reduce the risk of transmission of the virus and leads to dry nipples and cracking. A woman with genital hipes should use personal towels and change bed linen frequently.
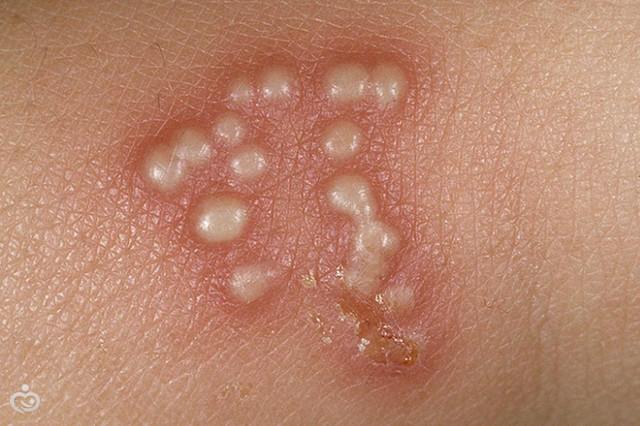
girdling
The most dangerous type of disease is the 3rd type, which causes shingles. When the body is infected, this virus negatively affects the nervous system. Active rashes cause weakness and severe pain; this dangerous condition is treated with oral medications.
Prevention
Herpes during breastfeeding can be prevented (both primary infection and its exacerbation). This requires:
- observe the rules of hygiene;
- limit contact with carriers of the disease;
- Healthy food;
- devote enough time to sleep and rest;
- walk in the fresh air every day, etc.
If immunity decreases, the body becomes vulnerable to the herpes virus. Therefore, the main rule of disease prevention is to avoid suppression of the body’s natural protective function.
How dangerous is herpes and what complications does it cause?
After penetration or activation of its virus, the mother’s body begins to intensively produce antibodies that kill pathological agents. Frequent feeding of the baby increases the release of antibodies that fight viruses. This is why doctors recommend not interrupting breastfeeding. Mother's milk transfers passive immunity antibodies to the baby.
For a young mother
Often herpes in a nursing mother goes away easily or takes on a moderate form. In such situations, it does not cause complications and is treated with local remedies. If the viral infection develops into a protracted, severe form, the mother may develop headaches and her overall health may deteriorate. The virus is capable of infecting tissues of the nervous system, penetrating internal organs and ENT organs, causing an exacerbation of existing somatic diseases. Visual perception deteriorates from exposure to viruses. Against this background, dizziness occurs.
Genital Herpes simplex virus type 2 is dangerous for a nursing mother. In addition to rashes on the genitals, it causes sore throat and stomatitis.
If the rash affects the breast tissue near the nipples, the baby must be protected from infection by stopping breastfeeding.

For a child
Labial herpes type 1 is considered the simplest, but it carries the threat of dangerous consequences when transmitted to a baby, including the death of the child. Defeat is dangerous for the baby:
- eye areas;
- genital areas;
- internal organs.
The most dangerous virus is that it affects the baby’s brain, leading to herpetic encephalitis. Type 4 virus, Epstein Barr, leads to the development of oncological tumors, damage to lymph nodes, and diseases of the organs responsible for the formation and flow of blood. Once in the baby's body, this virus causes inflammation of the throat and fever.
DNA virus type 6 causes roseola in infants with pronounced symptoms and fever. This pathology is not dangerous to the health of children, but is very contagious.
Type 8 virus, HHV-8, is very dangerous, it causes the development of skin malignant neoplasms and disruption of the gastrointestinal tract. This virus affects the lungs, oral mucosa, and disrupts nutrition and digestion.

Treatment method
Treatment for hippes should begin when the first symptoms appear. You should immediately consult a doctor; self-medication is contraindicated here. The doctor will prescribe local remedies to act on the affected areas. Genital and herpes zoster are treated with oral antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs. They stimulate the production of interferon, a protein that resists viruses. When prescribing each drug, the doctor explains the likelihood of the drug affecting the baby and decides whether it is necessary to stop breastfeeding during treatment.
Timely treatment under the supervision of a doctor relieves a woman of viruses within a week; properly selected drugs prevent the occurrence of possible complications, the formation of a stable remission without relapses. WHO experts recommend not stopping breastfeeding for any strain of herpes. Breastfeeding is an excellent prevention of infection in infants.
How to treat an infection
For hepatitis B, the use of topical medications – gels, ointments with antiviral properties – is allowed. For moderate and severe cases of the disease, oral medications are used.
Breastfeeding allows you to take medications:
- Zovirax;
- Acyclovir;
- Penciclovir;
- Valacyclovir;
- Fukortsina.
These products are compatible with GW. The doctor prescribes antiviral and immunostimulating drugs, assessing the severity of the disease, accordingly choosing the dose of the drug: Fenistil, Viferon, Laferobion, Cycloferon. They significantly increase the body’s ability to resist the disease; with their use, the remission stage is quickly achieved.

Acyclovir
Acyclovir ointment does not penetrate into milk, breastfeeding is not stopped with it. If you need to take Acyclovir in tablets, the doctor prescribes it up to 5 times a day for 7 days. This medicine passes into milk, so breastfeeding should be stopped during treatment. To maintain lactation, the mother must constantly express milk during feeding. During treatment with Acyclovir tablets, the child is transferred to infant formula.
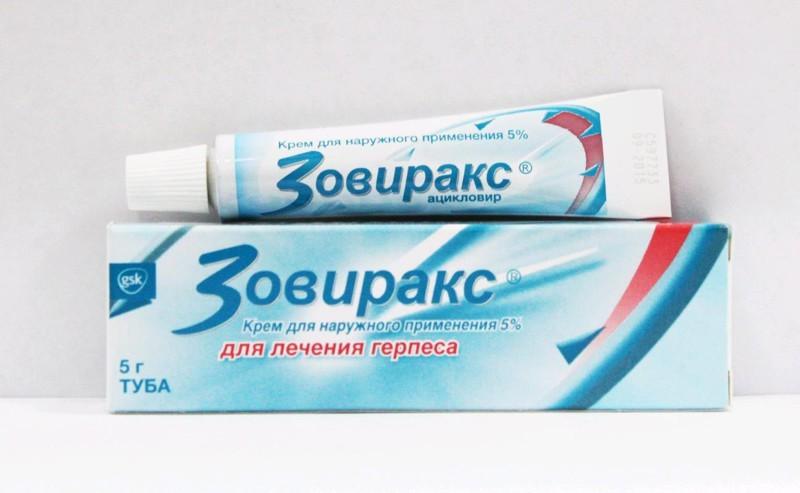
Zovirax
The drug Zovirax is produced as an analogue of Acyclovir. It has the same antiviral properties and quickly cures the disease. It differs from its analogue in that it practically does not penetrate into milk. The drug belongs to a new generation of drugs; in the treatment of a viral infection it gives pronounced results, since pharmacologists in its creation removed the negative properties of the primary drug. The composition of Zovirax is somewhat different from the structure of Acyclovir, taken as the basis for its release. But if these are analogues, then the new drug must be used carefully.
Action of Zovirax:
- penetration of the virus into cells;
- penetration into the cellular structure;
- modification of cell structure.
After this, the virus loses activity, freezes, but does not leave the body. The medicine does not affect the baby; breastfeeding can be continued.
Traditional methods
Traditional recipes can be used, but consultation with a doctor is also required.
You need to know some nuances:
- folk remedies do not have antiviral properties;
- do not have an effective effect on the pathogen;
- are used as additional treatment.
Not all folk recipes are safe for a nursing mother. Only external products can be used.
The affected areas are treated:
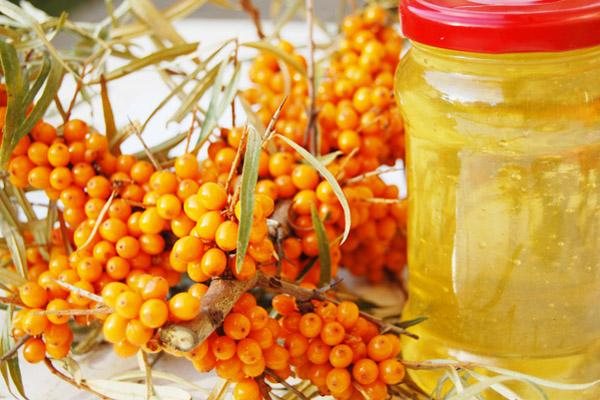
- tea tree essential oil;
- fresh aloe juice;
- sea buckthorn oil.
They reduce itching, pain, relieve inflammation, and accelerate skin regeneration. At the same time, many doctors have a negative attitude towards the use of folk remedies by women during breastfeeding.

Precautionary measures
Protective mask
To prevent the baby from getting sick, mommy must follow the following rules.
- Be sure to wear a protective mask when feeding (if there are sores on the lips) so that the child cannot come into contact with the affected area of the body, and you should also refrain from kissing.
- Be sure to treat your hands with a disinfectant solution before approaching your child.
- If the breast is affected, you should not feed from that breast under any circumstances. When feeding, it should be covered with a towel, and the baby should be given only a healthy breast, not forgetting to express milk from the breast affected by herpes, so as not to get mastitis and so that the milk does not disappear.
It should be remembered that herpes can occur in an infant if a woman does not follow basic hygiene rules.