A detailed study of the hepatobiliary system using magnetic resonance imaging is necessary to clarify the diagnosis when other examination methods have failed. MRI scanning is an informative and safe way to visualize internal organs and structures.
Tomogram of the bile ducts
MRI cholangiography allows you to assess the condition of the gallbladder and ducts without the use of invasive measures. The exception is contrast-enhanced scanning, when the patient is intravenously injected with a drug based on soluble gadolinium salts (chelates). The substance is low toxic, hypoallergenic and is excreted from the body naturally.
Advantages of the method
MR cholangiography is not accompanied by radiation exposure to the body. Therefore, the procedure can be performed as many times as necessary. A magnetic resonance imaging scanner allows you to obtain high-quality images of the area under study in various planes with the necessary magnification. MR cholangiography can only be performed on devices whose power is more than 1.5 Tesla. Today, this procedure practically replaces the much more unpleasant and unsafe procedure of ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography).
An important advantage of MR cholangiography is the high accuracy of visualization of the gallbladder and pancreatic ducts. The method is based on the introduction of contrast, which makes it possible to identify the contours of all biliary tracts, as well as vascular anomalies. Special software makes it possible to obtain a three-dimensional image of the structures under study.
Diseases
The wide diagnostic capabilities of MR cholangiography allow the method to be used for the following diseases:
- cholelithiasis (acute or chronic version of cholecystolithiasis, stones in the bile ducts);
- acalculous inflammation in the biliary tract (cholecystitis, cholangitis);
- benign and malignant tumors of the hepatobiliary system;
- abnormal structure of the bile ducts;
- traumatic damage to the ducts with the formation of stenosis and strictures.
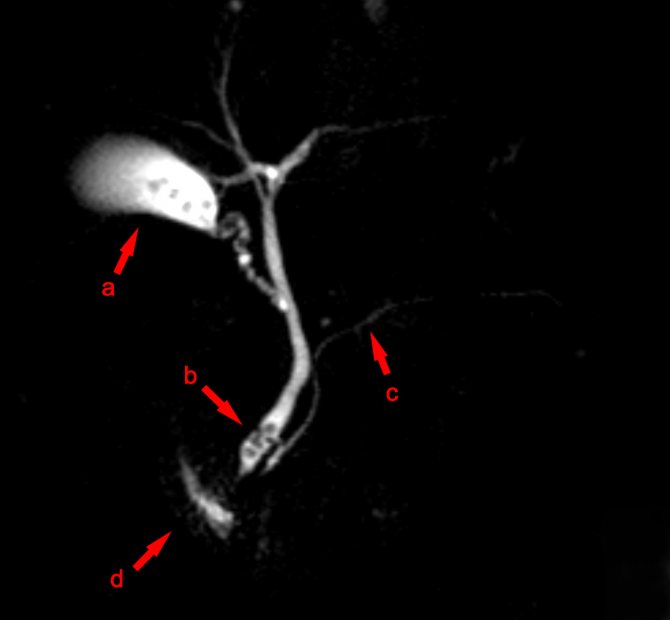
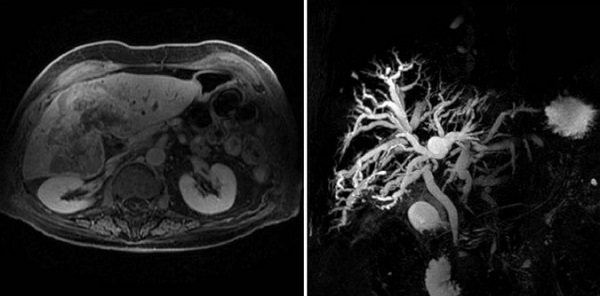
MR cholangiography image in 3D
The maximum diagnostic information can be obtained by using MR cholangiography in the following situations:
- preparation for surgery on the hepatobiliary system;
- control after bile duct surgery;
- diagnosis of the causes of jaundice;
- examination for postoperative complications.
The MR-CPG method is indispensable for oncological pathology. A tomographic image will show the presence of a tumor in the following organs:
- gallbladder;
- bile ducts;
- head of the pancreas;
- liver.
Often, it is during MR-CPG that the doctor, with a high degree of reliability, will be able to timely make the correct diagnosis and refer for surgical treatment.
Indications for MR cholangiography
- suspicion of stones in the bile ducts, gallbladder and pancreatic ducts;
- structural abnormalities of the development of the biliary system and ducts in the pancreas;
- pathological narrowing of the bile ducts;
- injuries of the ducts of the biliary system;
- preparation before surgery on the biliary system;
- assessment of the effectiveness of the treatment;
- pathology of the sphincter of Oddi and the major duodenal papilla;
- neoplasms of the biliary organs of a malignant and benign nature.
Cholangiography with MRI, what is it?
Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to study the state of anatomical structures that have a complex structure and are located in hard-to-reach places.
The bile ducts are tubular formations that pass both inside the liver and outside the organ. Pathological changes in the outflow tract have a negative impact on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. The hepatic and cystic ducts unite to form the common bile duct, which, in turn, merges with the pancreatic duct and opens into the lumen of the duodenum.
Scanning the biliary tract using radiation diagnostic methods is called cholangiography. The procedure involves a detailed study of the elements of the biliary system, assessment of the patency of the ducts, the condition of the walls and sphincters.
The research is based on the use of an induction field, under the influence of which hydrogen atoms in water dipoles perform oscillatory movements. In physics, the phenomenon is called magnetic resonance. The movement of charged particles is detected using sensitive sensors. The resulting signal is processed using complex algorithms and converted into a series of monochrome images of thin sections of the studied area.
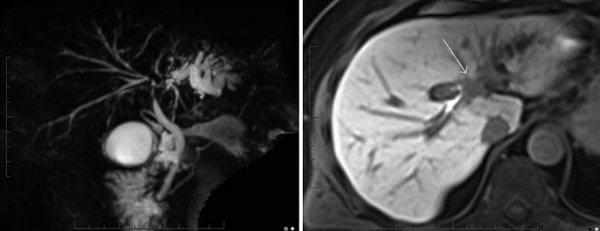
Klatskin tumor on MR cholangiography images
Layer-by-layer photos are transmitted to the computer screen, visualizing pathological changes in the scanned structures. To assess the blood supply to the area of interest and in case of suspected development of an oncological process, contrast MRI cholangiography is prescribed, which visualizes blood vessels and small tumors (from 3 mm) in size.
The patient is referred for a scan if the following symptoms are present:
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- nausea, vomiting;
- yellowness of the sclera and skin;
- dark yellow urine, light-colored feces;
- itchy skin.
With prolonged cholestasis (impaired bile drainage), signs of hypovitaminosis occur:
- weight loss;
- fragility of hair, nails, bones;
- decreased vision;
- bleeding, etc.
These symptoms are a consequence of impaired absorption of nutrients in the intestines.
As the liver increases in size, the patient notes increased pain; when examined under the rib on the right, the lower edge of the organ is palpated.
MRI cholangiography is necessary if there are deviations from normal biochemical blood test parameters, which indicates pathological changes in the hepatobiliary system. The method makes it possible to assess the functionality of the ducts, determine the condition of nearby structures, and identify the causes of obstruction of the biliary tract.
Contraindications to MR cholangiography
The study is not performed if there are metal objects in the patient’s body, for example, clips on blood vessels, a pacemaker, and so on. This is due to the fact that the magnetic field of the tomograph can disable the artificial pacemaker or heat up ferromagnets in the body. The presence of implants, braces and other dental structures is not a contraindication to MRI, since they are made of materials that do not react to the magnetic field.
If the patient suffers from claustrophobia, then the study should be carried out in a state of medicated sleep. During pregnancy, the study is not carried out, since the contrast can penetrate into the fetal tissue. Also, contrast-enhanced MR cholangiography is contraindicated in cases of intolerance to contrast agents.
MR-CPG with contrast
One of the advantages of MR cholangiography over computed tomography is the ability to diagnose without administering contrast: most of the pathology of the hepatobiliary tract can be detected without additional procedures. However, when a tumor is detected, it is necessary to do MR cholangiography with contrast, which will reveal:
- small tumors in places difficult to visualize (porta of the liver, neoplasms inside the liver or in the wall of the bile ducts);
- change in blood flow in the area of tumor formation;
- enlargement of nearby lymph nodes;
- relationship with neighboring organs (germination).
Contrast is administered according to strict indications. If there is no suspicion of a tumor, the doctor will not do MR-CPG with contrast.
How is MR cholangiography done?
At the preparatory stage before the procedure, the patient removes all metal objects. Next, contrast is introduced to improve visualization. The study is performed with the patient in a horizontal position, lying on his back. After this, the table with the patient is placed in the ring part of the magnetic resonance imaging scanner so that it is at the level of the upper abdomen.
During the scanning stage, the ring part of the device rotates around the table. Scanning with a magnetic resonance imaging scanner is accompanied by noise, which can create discomfort for the patient. Therefore, patients undergoing the study are asked to wear earplugs. To obtain accurate and high-quality images, the patient must remain motionless during the entire procedure.
Cholangiography with MRI, how is it performed?
For magnetic resonance imaging, a device consisting of a movable table and a wide tunnel is used. Inside the pipe there is a generator of an external induction field that will affect the area of interest.
Cholangiocarcinoma on MRI images
The patient lies face up on the table, the limbs and body are fixed using bolsters and fasteners. The measure allows you to ensure the immobility of the subject during the procedure, which helps to improve the quality of layer-by-layer photographs. For a detailed study of the liver and biliary system, gradient and radiofrequency coils are used, which are installed in the area of interest.
Special headphones provide protection from the noise of a working tomograph. During the scan, medical personnel are in the next room, observing the procedure through a transparent partition. Communication with the patient is maintained through an intercom.
The table with the patient moves into the tomograph tube, the detectors record the tissue reaction and transmit the information to the computer monitor. Scanning is carried out in sagittal, frontal and axial projections. Based on layer-by-layer images, the doctor can reconstruct a 3D model of the hepatobiliary system.
MRI cholangiography involves the use of contrast enhancement. In this case, after a series of native images, the doctor pauses the scan and the patient is injected with a gadolinium solution. The injection is carried out using a catheter inserted into a vein and connected to an automatic device. Bolus enhancement delivers contrast solution at a constant rate. The drug fills the vascular bed in the area under consideration, after which scanning is resumed.
The patient receives the MRI results in 15-20 minutes.
Contrast enhancement
MR cholangiography is always performed with intravenous contrast agents. Our medical center uses contrast agents, the main component of which is gadolinium.
The most commonly used drugs are:
- Magnevist;
- Omniscan.
These drugs do not have a toxic effect on the body and do not cause allergic reactions. The contrast initially spreads throughout all tissues, enters the liver and is excreted with bile, allowing the bile ducts to be clearly identified on images.
Indications
Bile, synthesized by liver cells, accumulates in the gallbladder, so to speak, the closest neighbor of the liver.
After eating, some time later, bile from the bladder enters the duodenum. There it interacts with food that is not completely digested. The task of bile is to break down food components into their component parts.
The bile duct connects the bladder and duodenum. It is where the pancreatic duct enters a little higher.
As we have already noted, the described procedure helps to understand what interferes with the normal functioning of the system. To do this, a contrast agent is used, and on the same x-ray the structure of the ducts, their patency and the interference created by the narrowings become visible. That is, the doctor gets the opportunity to understand what caused the system to malfunction.
Research is requested in the following cases:
- Jaundice of non-infectious nature;
- Pancreatic cancer;
- Inflammatory processes in the pancreas with frequent exacerbations;
- Suspicion of fistulas between the pancreas and duodenum.
When the exact cause of the disease is established, the procedure can develop from diagnostic to therapeutic.
How to prepare?
The considered method is completely safe. Does not require special training. However, the diagnosis is performed on an empty stomach, so the patient should eat 4-6 hours before visiting the clinic.
The Consultative Diagnostic Center (formerly the National Diagnostic Center) invites you to undergo MR cholangiopancreatography in the Primorsky district of St. Petersburg. The price of the study is from 5,600 rubles. The clinic is equipped with an expert-class tomograph and has a staff of experienced doctors. This is a guarantee of successful research and obtaining an accurate diagnosis.