Electroencephalography (EEG)
Electroencephalography, also called EEG, is a method that is used to study the state of the human brain and is based on recording its electrical activity.
This examination allows you to detect the spread of pathological processes and signs of epilepsy. The average duration of the procedure is about an hour, but it is highly informative and makes it possible to track any changes in the brain, the dynamics of the disease, and evaluate the impact of the therapy. Since the procedure does not cause any pain or discomfort, EEG can be called not only the most accurate, but also the most gentle method of examining the brain.
Types of EEG
- Routine recording , in which paroxysms are diagnosed. The procedure takes no more than 20 minutes. In this case, the bioactivity of the patient’s brain is studied. Photostimulation (exposure to flashing light) and hyperventilation (frequent, prolonged breathing) are performed. This way you can identify hidden changes.
- Monitoring with sleep deprivation is carried out as prescribed by a doctor to in-depth study the state of the patient’s brain. The person needs to stay awake for a long time before the procedure.
- Long-term recording recording the patient's daytime sleep. Prescribed for changes observed during sleep.
- Recording during night sleep is the most informative and expensive EEG. This examines the state of the brain during wakefulness, falling asleep, resting and waking up. The process is accompanied by video recording and is carried out in a dark room with the connection of various sensors for electrooculogram, respiratory recursion, electromyogram, electrocardiogram.
Many people believe that MRI can replace the electroencephalogram. But that's not true. EEG is based on recording the activity of neurons and reveals mental and functional abnormalities. MRI studies brain structures and tissues and allows one to diagnose organic pathologies at the earliest stages. These two methods complement each other perfectly in diagnosing neurological diseases.
The advantages of the electroencephalogram include the availability of the procedure, which does not require anesthesia and stay in a confined space. Disadvantages include the influence on the result of a person’s emotional state during the examination period.
How EEG works
The human brain consists of millions of special cells called neurons. Each of them generates its own electrical impulse. Within individual areas of the brain, impulses must be consistent. They can also strengthen each other or make each other weaker. Their strength and amplitude are not stable and are constantly changing.
This is the bioelectrical activity of the brain. To register it, special electrodes can be applied to the intact scalp, which will pick up vibrations, amplify them and record them in the form of special curves, so-called waves. The latter, depending on their shape, frequency and amplitude, are divided into five types: α- (alpha), β- (beta), δ- (delta), θ- (theta) and μ- (mu) waves. Each of the waves reflects the work of a specific part of the brain and is named by the first letter of its Latin name.
Their registration in real time is the essence of encephalography.
Cost of EEG and certificate validity period
On average, the price of an EEG is 1000–1500 rubles, depending on the region of the Russian Federation. These prices for this type of examination are established in public clinics. But admission to them is by appointment and with a referral from a doctor.
In a private clinic you can make an appointment at a convenient time and come without a referral. The cost of the service here ranges from 1.5–5 thousand rubles. However, you should first clarify whether the medical institution has a license for examinations for reference to the traffic police.
Please note that the new type of certificate from the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate with an encephalogram is valid for only 1 year and after its expiration you will have to undergo a medical examination (if you need a certificate of form AF No. 003-B/u) again. As for the EEG result, it does not have a specific validity period.
How to get tested for free
According to current legislation, a citizen who receives or reissues a driver’s license independently bears the costs of training, medical examination and paperwork. Therefore, no one will conduct an electroencephalogram for the traffic police for free, even in a public clinic upon a doctor’s referral. An exception is made only for persons who have health insurance that includes the EEG procedure, or those whose employment contract with the employer states that the medical examination is carried out at the company's expense.
Historical reference
One of the founders of the electroencephalography method is considered to be the physiologist and psychiatrist from Germany Hans Berger. In 1924, using a device for measuring small currents called a galvanometer, he was the first to perform a procedure resembling an EEG recording.
Later, a special device called an encephalograph was created to conduct an electroencephalogram. Today, there are stationary encephalographs, which make it possible to conduct research exclusively in a special room, and portable ones, which can be moved.
It is noteworthy that initially EEG was considered exclusively as a method for identifying mental disorders in a person. Only over time, scientists found out that the technique also makes it possible to detect deviations not related to psychiatry.
Benefits of an Electroencephalogram
Today, electroencephalography is widely used in neuropathological practice.
It makes it possible to clarify a huge number of problematic situations that are associated with the diagnosis and differentiation of neurological diseases. One of the undeniable advantages of encephalography is the fact that it not only helps to identify certain problems, but also helps to distinguish true disorders from hysterical manifestations or simulation. In addition, the procedure is not as expensive as examination using a tomograph or other similar devices. EEG equipment is available in most hospitals.
The procedure does not have any negative impact on human health and condition. The patient remains fully functional. At the same time, the study can be carried out even on patients in serious condition, children and adults of any age, since it does not cause deterioration of the condition, discomfort or pain.
Contraindications
It is noteworthy that there are no absolute contraindications for electroencephalography.
If a person suffers from convulsive attacks, is diagnosed with coronary heart disease, hypertension, or mental disorders, an anesthesiologist must be present during the diagnosis. The procedure should be postponed if there are open wounds, traumatic injuries, postoperative sutures or any signs of an inflammatory process in the area where it is necessary to install electrodes. Also, the study is not carried out for patients with ARVI.
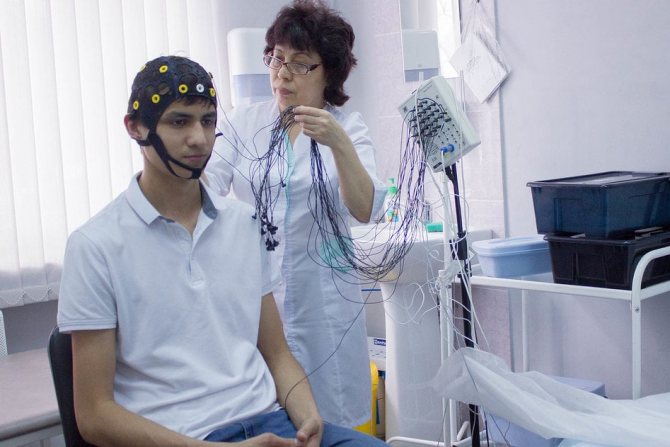
Performing an EEG
Electroencephalography is performed in a special room, which is completely isolated from light and sound. The patient sits in a chair or is asked to lie on the couch. A special cap with electrodes is first placed on his head. During the procedure, the patient is alone in the room, contact with doctors is maintained using a camera and microphone. If the diagnosis is performed on a child, one of the parents remains in the office.
Before starting the procedure, the patient is asked to close and open his eyes several times to adjust the equipment. During the diagnosis, the eyes must be closed. If during the procedure the patient needs to change position or visit the restroom, he can inform the doctors about this, after which the diagnosis will be suspended.
It is extremely important that the patient lies with his eyes closed and does not move during the procedure. In the event that a person opens his eyes slightly or moves, the doctor makes a corresponding note, since these actions must be taken into account when deciphering the electroencephalogram.
After the resting EEG is recorded, so-called “stress tests” are performed. Their goal is to test how the brain will react to situations that are stressful for it.
So, a hyperventilation test can be performed. The patient is asked to breathe frequently and deeply for three minutes. Photostimulation with a stroboscopic light source can also be used. It flashes frequently, and this allows you to evaluate how the brain reacts to bright light.
Stress tests can trigger convulsions or an epileptic seizure. The doctors who conduct the study have the appropriate skills to provide emergency care to the patient if necessary.
After the study is completed, the physician should remind the patient to resume taking medications that were stopped the day before the EEG.
The total duration of the procedure is from forty minutes to two hours.
How to do it for adults
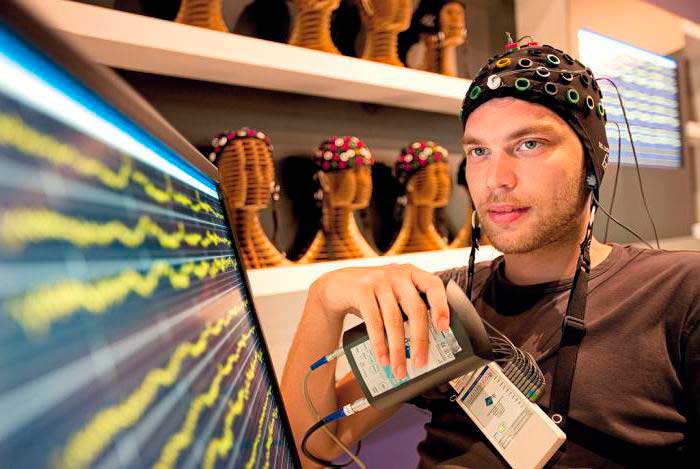

For routine recording, a person sits in a comfortable chair or lies down on a couch. A cap connected to a recording device is placed on his head. A special computer program records brain bioactivity and compares it with video.
A person coming to a session for the first time is explained what an EEG of the head is, what kind of procedure it is, and how to behave.
- During the session, the doctor asks you to open and close your eyes to record the error caused by blinking.
- Then the subject closes his eyes, sits quietly and does not move.
- It takes several minutes to breathe deeply (for epilepsy or for occasional convulsive episodes).
- The light flashes about 20 times per second, which can provoke an attack in patients predisposed to light irritation.
At the end of the procedure, the patient is given a conclusion about the presence or absence of brain disorders.
What does an EEG of the brain show in adults?
Electroencephalography is a modern diagnostic method that helps determine the parameters of the brain.
At the Yusupov Hospital, functional diagnostic doctors perform all types of EEG studies: standard daytime electroencephalography, EEG monitoring of day and night sleep, 24-hour study of bioelectrical activity of the brain. Thanks to the neurology clinic being equipped with modern diagnostic equipment, the quality of the research complies with European protocols.
Where can I get an EEG done?
To have an electroencephalogram done, you can go to a public clinic at your place of residence or a private clinic.
The main thing is that the medical institution has permission to conduct medical examinations of drivers and the appropriate equipment.
You can get this information on the clinics’ websites or by calling their contact number.
Usually, a neurologist informs you about where to get an EEG for reference to the traffic police when scheduling an examination. In this case, the doctor only gives a recommendation - the choice of the clinic is yours.

Normal EEG readings
Neurologists and neurophysiologists interpret the EEG using a computer program.
The EEG determines the basic rhythms of the brain:
Rhythms correspond to types of activity. On the EEG you can see special types of bioelectrical activity of the brain:
Pathological images of the electroencephalogram include:
The EEG can record complexes (spike-wave, peak-wave, wave-spike, slow spike-wave, helmet wave), flash, paroxysm and burst of hypersynchronization. Neurophysiologists evaluate each frequency component of the EEG based on its amplitude and severity on the electroencephalogram over time.
Normally, the alpha rhythm predominates in the occipital regions of the brain. It decreases in amplitude from the back of the head to the forehead. In the frontal regions it is not recorded during bipolar leads from electrodes that are placed along sagittal lines with small interelectrode distances. Symmetrical in amplitude and frequency in the left and right hemispheres. On a normal EEG, functional asymmetry is observed with a predominance in filling the surface facing the bones of the skull, and a slight excess of amplitude is greater in the right hemisphere of the brain. This is a consequence of functional asymmetry of the brain. It is associated with greater activity in the left hemisphere.
Beta activity is observed in the frontal regions of the brain and at the junctions of the alpha spindles. It is symmetrical in amplitude in both hemispheres of the brain. The beta activity index in the frontal regions can reach 100%. Its absence is not a sign of pathology.
In a healthy adult who is in a state of passive wakefulness, theta and delta rhythms are not normally recorded. They are observed only in a state of anesthesia or sleep. In a normal electroencephalogram, the alpha rhythm dominates. Low-frequency beta activity is recorded at the junctions of the alpha rhythm spindles and in the frontal regions of the brain. In the posterior parts of the brain, functional diagnostic doctors can observe rare, not exceeding the alpha rhythm, bursts of theta rhythm of 2-4 waves. Rare single scattered low-amplitude delta waves are also recorded here.
Encephalogram rhythms

Many people do not know what exactly an electroencephalogram of the brain records, what it is, and how the resulting recording is deciphered.
The EEG records impulses (rhythms) that are determined by the functionality of the brain. There are rhythms:
- Alpha (reflecting a state of rest with eyes closed). It should be with a frequency of 8 to 14 Hz. It is not detected during motor stimulation. Pathologies of this rhythm can be caused by tumors, cystic neoplasms, or stroke. If the alpha rhythm is unstable, concussions, injuries, and bruises occur.
- Beta with a frequency of 13 to 30 Hz reflects irritability and depression. If the rhythms are short, the development of encephalitis or inflammation of brain structures is suspected.
- Theta with a frequency of 4 to 7 Hz. Most pronounced in young children. Shows the state in a dream.
- Delta with a frequency of 0.5 to 3 Hz indicates the state of normal sleep and should account for up to 15% of the existing rhythms. If the indicator is too high, then it is considered abnormal. It is in the area where the delta rhythm is elevated that profound brain changes are noted.
Brain bioactivity should be without paroxysmal phenomena. This is a complex indicator that describes all the rhythms of the brain.
Other EEG indicators include:
- Dysfunction of the middle brain structures , in which the disturbance of neuroactivity is weakly expressed, which may be a consequence of experienced stress, shock, or excitement.
- Interhemispheric asymmetry is observed in a disorder that requires observation by a neurologist.
- The focus of epiactivity indicates the excitability of a particular area of the brain and susceptibility to seizures.
- Irritation of brain structures is associated with impaired cerebral blood flow resulting from traumatic brain injury.
- Paroxysms indicate a tendency to episyndrome or an existing disease in previously recorded attacks.
- Organic changes in brain structures in children are considered a consequence of infectious diseases that arise during childbirth. This requires serious therapy and additional examinations.
- Changes in regulatory function are noted in hypertension.
- Inhibition of the alpha rhythm, which has a significant manifestation, indicates parkinsonism.
Pathologically altered EEG
Pathological manifestations on the EEG are slow rhythms - theta and delta. The lower their frequency and higher the amplitude, the more pronounced the pathological process. Slow wave activity appears in the following pathological processes:
Unilateral local slow-wave activity is a sign of local damage to the cerebral cortex. Flashes and paroxysms of generalized slow-wave activity in waking adults appear in the presence of pathological changes in the deep structures of the brain. High-frequency rhythms (beta-1, beta-2, gamma rhythm) are also a criterion for pathology. Its severity is greater, the more the frequency is shifted towards high frequencies and the more the amplitude of the high-frequency rhythm is increased. The high-frequency component of the EEG occurs due to irritation of brain structures (irritation of brain centers).
Polymorphic slow activity with an amplitude below 25 μV is often considered as a possible activity of a healthy brain. If its index is more than 30% and its occurrence is not a consequence of successive indicative reactions (in the absence of a soundproof chamber), then the presence of polymorphic slow activity in the EEG indicates a pathological process in the deep structures of the brain. The dominance of low-amplitude polymorphic slow activity may be a manifestation of activation of the cerebral cortex, but it may also be a sign of deactivation of cortical structures. In order to carry out differential diagnosis, neurophysiologists at the Yusupov Hospital carry out functional exercises.
High-frequency asynchronous low-amplitude activity may be a consequence of processes of excitation of areas of the cortex or the result of an increase in activating influences from the reticular system. Pathological images of the electroencephalogram (sharp waves, spike, peak, slow spike, complexes) are a manifestation of synchronous discharges of huge masses of neurons in epilepsy.
Who undergoes EEG
In 2014, changes were adopted to the legal framework regulating the procedure for issuing driver's licenses. They provided for an EEG to be taken by everyone who received their first driver's license, had their license restored, or opened a new category. But at that time, too few clinics with the appropriate license had the necessary medical equipment, so this clause in the legislation was changed.
In accordance with Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated June 15, 2015 No. 344n “On conducting mandatory medical examination of vehicle drivers (candidate vehicle drivers),” the answer to the question of whether an electroencephalogram of the brain is needed for a certificate from the traffic police is affirmative in two cases:
- when drivers open category C or D, including all their subcategories. That is, it is needed for everyone who decides to drive a truck or bus;
- if an EEG was prescribed by a neurologist, regardless of driving category. Indications for examination may include frequent headaches, sleep disturbances, past illnesses, etc.
Let's take a closer look at the second case. If a doctor has grounds to prescribe an EEG and you refuse to undergo it, then by law he has the right to not allow you to drive a vehicle for health reasons.
The question of whether it is necessary to do an EEG for a certificate from the traffic police in 2021 for all groups of drivers can be heard often today. So far the legislator has not announced such intentions.