From a medical point of view, mixed feeding is considered necessary when there is a lack of milk in the mother or a lack of the complex of nutrients necessary for the healthy development of the baby. Supplementary feeding is introduced on the recommendation of a doctor when it becomes clear that breastfeeding does not meet the needs of the child’s body.
It is important for the mother to know what signs indicate that it is time to start supplementary feeding and how to do it correctly. Distortion of the recommended formula feeding system can lead to gastrointestinal dysfunction in the infant and other health problems.
When to introduce supplementary food
Some young, inexperienced mothers begin to feed their baby immediately after birth, believing that there is not enough milk in the breast. In the first days it is not there at all, the mammary gland is filled with colostrum, a little of it is produced, but you should not worry about this. This is how nature intended. The newborn's kidneys have not yet formed, he is not able to process a lot of fluid, and his mother's colostrum is enough for him in full.
A misunderstanding about when to start supplementing with formula while breastfeeding is caused by the baby's anxiety, which the mother cannot explain.
Often a woman is alarmed by circumstances that do not indicate that the baby is not eating enough:
- The baby's crying at the breast, pushing out the nipple and painful latching do not mean that the baby does not have enough milk. The reason is incorrect or infrequent attachment, use of nipples and pacifiers.
- The cause of the baby's restless behavior when sucking may be an anatomical problem - a short frenulum in the newborn's oral cavity.
- A small amount of expressed milk is not considered a condition for starting early complementary feeding. If the mother only breastfeeds, the baby is full, then there is no need to pump.
- Baby's restlessness between feedings and calmness after breastfeeding. This does not mean that the baby is hungry, he needs maternal affection and warmth.
It is important to know: supplementary feeding of a newborn with formula while breastfeeding should begin after six months. According to WHO recommendations, early complementary feeding is possible only for medical reasons.
Until the age of six months, a child can be switched to complementary feeding with mixtures only as prescribed by a doctor.
From birth, babies need complementary feeding in certain cases:
- a weak child due to being born prematurely;
- neurological dysfunctions in a newborn, causing uncoordinated sucking reflex;
- lack of milk in the mother when it is impossible to normalize lactation by frequent breastfeeding;
- a mother’s illness in which the child cannot be fed to avoid infection or poisoning.
If the baby is able to suckle productively and eats enough, then the mother needs to take care that there is more milk. To do this, use the correct drinking regime and a balanced nutrition system. She should eat healthy foods containing vitamins and microelements, since along with milk the child receives the substances necessary for the development of the body.
Supplementary feeding methods
There are several methods of supplementary feeding, each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of one method or another depends on many factors, but in any case, the key to the success of their use is the patience and determination of the mother.
bottle
Advantages: Requires minimal effort and training.
Disadvantages: There is a risk of breast refusal.
To reduce the risk of breast refusal and improper latching on the breast by the child, leading to cracked nipples, you must:
- Choose the right bottle and pacifier. The bottle should be straight in shape without narrowing in the middle. The nipple should not have a wide base, as this causes the baby to squeeze his gums. The shape of the nipple should be round, as it is closer to the shape of the mother's nipple; the material of the nipple should be as soft as possible, otherwise orthodontic problems may occur. The hole in the nipple is made small so that the sucking process lasts 15-20 minutes.
- Correct feeding technique. If possible, give the baby the breast first and then the bottle. Place the baby on your lap, holding your hand and lifting the upper body. The bottle is held horizontally, and the nipple is placed in the baby's wide open mouth, almost up to the ring of the bottle. When everything is ready, the top edge of the bottle is raised so that air does not accumulate in the nipple. As the bottle is emptied, the baby is tilted back to completely empty the bottle.
A syringe without a needle or an extended syringe
Advantages: inexpensive, can be used once.
Disadvantages: the volume of the syringe is insufficient for older children, so supplementary feeding takes a lot of time. There is a danger of getting used to sucking a syringe instead of a breast.
For feeding, it is better to take a 5-10 ml syringe. The principle of milk supply is the same as for injections - when you gently press the piston, milk flows out of the syringe. The needle can be used to draw milk from a container with a narrow neck.
Methods of using a syringe can be different:
- The child sucks the syringe through which milk is injected;
- The milk flows through a tube at the end of the syringe into the corner of the baby's mouth.
- The baby sucks the mother's finger with the pad facing upward, and milk is injected with a syringe into the corner of the mouth.
- Milk enters the corner of the baby's mouth through a syringe with a tube directly during breastfeeding.
You can buy a syringe with a tube at a pharmacy or make it yourself. The pharmacy sells a “long cannula” syringe that is used by dentists. You can make it yourself by attaching a nasogastric tube or a venous catheter purchased at a pharmacy to a regular syringe.
Tea spoon
Advantages: does not require material costs. No interference with breastfeeding, as the spoon does not satisfy the need for sucking. The spoon can be used if the baby has a runny nose, since the sucking process is difficult at this time.
Disadvantages: its use requires skill, since at first most of the milk will spill past.
Usage. When the child opens his mouth, with a quick and confident movement, slightly tilt the spoon and pour its contents onto the middle part of the child’s tongue. You can also try pouring milk into your cheek. According to reviews from mothers who use this method of supplementary feeding, it only takes 2-3 days to learn how to use it effectively.
Soft spoon Medela
Advantages: it is more convenient to use than a teaspoon, since you do not have to scoop milk out of the container every time. It is one of the simplest and most effective supplementary feeding methods.
Disadvantages: relatively high price of the device.
Usage. It is a soft silicone spoon combined with a bottle. When you press on the protrusions located in front of the spoon, milk begins to flow into it. This way you can easily dose the amount of food. At the same time, there is a possibility that if a child does not like a teaspoon, then a soft one will not suit him.
Find out the price of a Medela soft spoon in the Obstetrics online store
Cup
Benefits: Easy to handle between feedings (Medela offers sterile cups with rounded edges and a scale for convenience). Feeding takes even less time than bottle feeding. Due to the fact that no air is swallowed while using the cup, the number of regurgitations and colics is reduced. Weight gain is greater, and the tongue and jaws learn to work correctly.
Disadvantages: cannot be used in newborns with a weak swallowing reflex. Just like using a spoon, it may take some time to adjust.
Any cup will do, but it is better with thin walls (coffee cup, shot glass). According to WHO, all babies, even premature babies, can be cup fed. Premature babies lap up the milk, while full-term babies sip.
Important! Supplemental feeding from a cup is optimal if the baby has not yet taken the breast. Otherwise, it is better to use other methods of supplementation.
Usage.
- Place the child upright or semi-sitting on your lap, supporting the head with your hand, which also serves as support for the child’s shoulders and neck.
- Using a light touch, place the edge of the cup on your child's bottom lip.
- Tilt the cup so that the milk touches the baby's lips. The baby will begin to lap or lightly sip the milk.
- The level of liquid in the cup should remain the same so that the child does not stop. To do this, you need to very smoothly gradually tilt the cup.
Attention! Never pour milk down your child’s throat! Let him control the slurping and swallowing.
Haberman's sippy cup
Advantages: after using the sippy cup, breast refusal does not occur.
A special system allows you to regulate the flow of milk, reducing the risk of swallowing air. Disadvantages: high price.
The main purpose of this sippy cup is to feed children who are unable to create a vacuum when sucking due to cleft lip and palate, Pierre-Robin syndrome and some neurological diseases.
Usage. Before feeding, milk is drawn into the bottle, air is released from the bottom of the nipple and the sippy cup is filled with milk after pressing the wide part of the tip using the pipette mechanism. When the tip is full, start feeding the baby. The flow of milk is regulated by turning the sippy cup.
Finger feeding
Advantages: the child works with his tongue as when sucking the breast. There is skin-to-skin contact between the baby and the mother. Suitable for sleepy newborns before breastfeeding and for cracked nipples to replace part of the feedings.
Disadvantages: personal hygiene rules are required. Not suitable for flat nipples, as breast rejection may occur in favor of the finger.
Usage. You will need a probe lowered into a container of milk. Its other end is attached to the finger. Alternatively, you can use a syringe with a tube at the end. When thumb sucking, food is delivered to the baby through a tube lowered into a container of milk. If a syringe is used, the milk is injected through a tube.
Supplementary feeding at the breast
The most commonly used systems for these purposes are the SNS (Supplementary Nursing System) and the Lact-Aid system.
Advantages: the most convenient and physiological method of supplementary feeding. The baby learns to suckle properly and stimulates milk production. Breast refusal is reduced to nothing.
Disadvantages: not suitable for children who refuse breastfeeding. Difficulties in processing the straws, since they cannot be boiled. Inconvenience associated with adding new portions of milk to the container. At the same time, excess milk will have to be poured out due to safety precautions. Some types of antireflux mixtures clog tubes.
It consists of a container into which supplementary food is poured and from which a long thin tube comes out. An important feature of this method is that the baby receives supplemental feeding while suckling at the breast, even if there is no milk at all. This method is often used in the case of adoption of very young children, which allows a woman to feel like a full-fledged mother, and in some cases even start lactation.
Several uses are possible.
You can breastfeed your baby first, and then carefully insert a tube into the corner of your mouth, or immediately start breastfeeding with a tube. When inserting the tube into the corner of the mouth, it is directed inward and slightly upward. Sometimes it needs to be supported during feeding as some babies may gradually push it out of their mouth. The flow of milk in the straw is regulated by raising or lowering the milk container. In 15 minutes of supplementary feeding, the baby sucks out 30 ml of milk. To maintain lactation, it is advisable to use a breastfeeding system at each feeding.
The Medela breastfeeding system consists of a graduated bottle that hangs on the mother’s neck and probes coming out of it - one per breast. The kit includes several probes of different sizes and a patch for fixing them on the chest.
If it is impossible to buy a ready-made system, you can make it yourself by inserting a thin probe through the nipple into a bottle (5-10 ml syringe) with milk. A nasogastric tube or venous catheter is used as a probe. You cannot boil them, just wash and dry them, and after 24 hours use a new straw. If there is no thin probe, then you can use a wide one after tying a knot on it to reduce the flow of milk.
Find out the price of the Medela breast supplementation system in the Obstetrics online store
Pipette
Used as a last resort if others do not work or for feeding newborns. The main difficulty is obvious - the volume of the pipette is very small, and the supplementary feeding process can take a long time.
Supplementary feeding from a Medela soft spoon video
Haberman's sippy cup video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nhIz9gWwpzA
How to drink from a glass video
Supplementary feeding with a spoon video
What to feed from
How and what to properly supplement with formula while breastfeeding is a question that requires certain skills and knowledge. There are several devices that make feeding your baby convenient and safe. They are specially created for this purpose; their design takes into account the optimal grip depth, sucking force, and the characteristics of the baby’s gums and tongue.
spoon
All mothers know how to supplement their baby with formula while breastfeeding using a spoon. There is only one secret - you need to buy a silicone soft spoon. The mixture should be given by the cheek, making sure that the baby has already absorbed the previous portion. A convenient model is a spoon plus a bottle. This device allows you to dose the amount of formula before putting it into the baby's mouth.

Syringe, pipette
How to administer formula while breastfeeding using a syringe - you need to learn this. The mixture is drawn into a reservoir with a dispenser, then the spout that delivers the portion is inserted into the baby’s mouth and the contents are poured out behind the cheek. Tubes for children's liquid medications can be used as such a device. Feeding with a pipette and syringe follows the same principle.
Cup
Before supplementing with formula from a cup while breastfeeding, you need to practice. This is not difficult, but the skill must be mastered so that the baby does not choke. It is better to use a beaker or a disinfected toy cup as a utensil. The main thing is that it is made from environmentally friendly material.
The feeding algorithm is as follows:
- first you need to tilt the cup towards your lower lip;
- Apply a small amount of the mixture to your lip;
- wait for the movements of the tongue and lips;
- then repeat the procedure.
This is a convenient way to supplement feeding for children in their first year of life. For a newborn baby, it is better to use the option with a syringe, pipette or spoon.

SNS system
The design is a silicone bottle equipped with a thin tube. The bottle filled with the mixture is placed on the mother's neck, and the end of the tube is attached to the nipple. When feeding, the baby takes the nipple and tube into his mouth, receiving milk and additional nutrition at the same time.
Pediatricians recommend combining breastfeeding and formula feeding, because the child feels an inextricable connection with his mother even during artificial feeding. If regurgitation occurs frequently, an antireflux mixture is administered in this way during breastfeeding.
Different methods of supplementary feeding contribute to the adequate nutrition of the child immediately after birth when the mother has a lack of milk. And when it dries up, they help switch to formula feeding.
How to supplement with formula while breastfeeding

Struggling with malnutrition of the baby, mothers begin to supplement their infants with artificial nutrition. This raises the question of how to supplement with formula while breastfeeding.
- Why is there not enough milk and is it worth continuing breastfeeding?
- Types of mixed feeding
- Supplementary feeding rules
- Pros and cons of supplementary feeding devices
- Is there any harm in mixed feeding?
Why is there not enough milk and is it worth continuing breastfeeding?
Sometimes a mother really wants to breastfeed her baby exclusively. But milk is not enough.
This happens for a number of reasons: from genetic, to hormonal and psychological. The last reason is the most common.
Initially, due to stress, a woman produces less milk. Then the worries intensify due to the baby’s malnutrition and feelings of guilt towards him. As a result, lactation remains just as weak.
Pediatrician Dr. Komarovsky advises not to fight for breastfeeding if it is only enough for one feeding per day.
He notes that in such quantities milk has little effect on the growth and development of the child. In this situation, it is more logical to feed the newborn exclusively with formula.
It makes sense to maintain lactation if the baby receives breast milk in 50% of feedings or at least 30% of them.
Types of mixed feeding
Like any other type of nutrition, mixed feeding must be clearly organized. There are two options: sequential and alternate.
Sequential feeding combines breast milk and formula feeding in one feeding. First, the baby is put to the breast, then a portion of the formula is given.
At the same time, artificial nutrition is offered only if there are signs of malnutrition: if the baby does not want to let go of the nipple, cries, smacks his lips. It is also important to monitor the number of servings to avoid overfeeding.
It can be helpful to weigh your baby before and after eating. This makes it easier to determine how much supplemental feeding he will need.
Alternate feeding is based on a different principle. Formula feeding and breastfeeding alternate. This gives the mammary glands time to fill up again.
Which method to prefer is best known to the mother. It depends on the amount of milk, feeding regimen, and daily routine.
Supplementary feeding rules
First of all, it is worth considering the interval between meals. The mixture takes longer to be processed by the body. So feeding on demand is out of the question.
At 1 month and beyond, the child should eat no more than once every 3-4 hours.
You should not experiment with different mixtures. If your child is happy to eat a certain food, continue giving it.
The body will have to adapt to the new product again. Undesirable reactions are possible.
If artificial nutrition clearly does not work (for example, allergies or problems with stool), you should try something else.
In order not to lose lactation, it is important to regularly feed the baby with your milk, offering both breasts. If the volume of milk allows, it should occupy at least half of the entire menu.
When you can’t choose a formula on your own, you can consult a pediatrician. Food must be prepared immediately before feeding. Under no circumstances should you leave it for another day.
At 2 months, most mothers prefer to supplement with formula from a bottle. In this case, it is necessary to choose a pacifier with a small hole.
So the baby will have to try to get food, as when breastfeeding. This increases the chances that the baby will not refuse mother's milk.
At 3 months you can give the mixture from a syringe. When using it, you should be especially careful. The baby's head should be raised and the flow of nutrition should be directed to the corner of the mouth.
This way there is no risk that the baby will choke. This method is used so as not to accustom the child to the bottle and not to provoke breast refusal.
At 4 months, you can try supplementing with formula from a spoon. Although it takes a lot of time. And it requires patience from mother and baby.
Useful tips for mothers: NUTRITION UP TO 3 YEARS OLD
From the age of six months you can try feeding your baby from a mug.
Another way of supplementary feeding is the supplementary feeding system. It consists of a cup and a small diameter tube.
The mixture is poured into a mug, and the tube is sent into the child's mouth. At the same time, he is given breasts. So the baby drinks the formula and mother’s milk at the same time.
Pros and cons of supplementary feeding devices
Each of the supplementary feeding options considered has its own positive and negative sides. The table provides a comparative analysis of all funds.
| Way | Advantages | Flaws |
| Bottle with nipple | The child gets full quickly, a convenient way to supplement feeding. | The baby may refuse to breastfeed. |
| Disposable syringe | Sterility and preservation of breastfeeding. | A long and labor-intensive process with a large volume of supplementary feeding. |
| Tea spoon | Accessibility, easy to wash, teaching your baby to eat from a spoon. | Requires dexterity and skills; you cannot feed on the road or on the street. |
| Cup | The child gets used to drinking like an adult and is easy to clean. | Without skill, milk will spill; it should not be used while walking or traveling. |
| System (tube) | Natural feeding, skin-to-skin contact, continued breastfeeding. | Expenses. The child may push the tube out. Cannot be used during forced breaks in breastfeeding; it is difficult to wash and clean. |
Is there any harm in mixed feeding?
Previously, it was believed that feeding formula and breast milk at the same time was harmful to the baby. Some experts still adhere to this opinion.
Dr. Komarovsky is confident in the safety of mixed feeding. Developers of baby food have brought its composition as close as possible to mother's milk.
Therefore, such supplementary feeding is safe for the child. The same cannot be said about regular cow's or goat's milk. They can cause great harm to the baby's health.
If a lack of milk or other circumstances forced the mother to switch to mixed feeding, do not be upset. A diet should be organized.
You can use alternate or sequential feeding. Give the mixture from a bottle, spoon, cup or other device. Choosing what is most convenient for mother and baby.
Do not forget that mixed feeding is justified only if there is sufficient volume of mother's milk.
Otherwise, it is better to switch completely to artificial feeding.
- about the author
- Recent publications
Arina Nagovitsyna
author of the publication (site editor)
JOURNALIST Higher education: Faculty of Journalism and Mass Communications
Arina Nagovitsyna recently published (see all)
- What can a child at 3 months - 09/12/2019
- What a 2 month old baby can do – 09/11/2019
- Which formula to choose when mixed feeding - 09/10/2019
Blend selection
Moms and dads should know how to switch to formula after breastfeeding, since feeding the baby becomes the responsibility of both. The first important task is the choice of mixture.
In order not to make a mistake in this matter, you need to fulfill several requirements:
- find out what formula was given to the newborn in the maternity hospital in the first days when the mother did not have milk;
- choose only fresh products and check the expiration date when purchasing;
- If your baby has digestive problems or allergic reactions, consult your pediatrician about which formula is best for you to use.
Note! If a child does not eat formula after breastfeeding, then contacting a doctor is necessary. You cannot experiment on your baby’s health; this can lead to serious consequences.
You need to switch to feeding a specific formula after observing the child’s reaction. If there is no colic, bloating, problems with stool, or rash, then the product is suitable for nutrition, it can be bought and given without fear.
Mixture volume
The quantity of the product must be calculated in accordance with how much breast milk the baby has eaten from his allotted portion. This is done by weighing before and after feeding. There is a table of milk consumption by age, you need to get acquainted with it and carry out complementary feeding according to the data given in it.
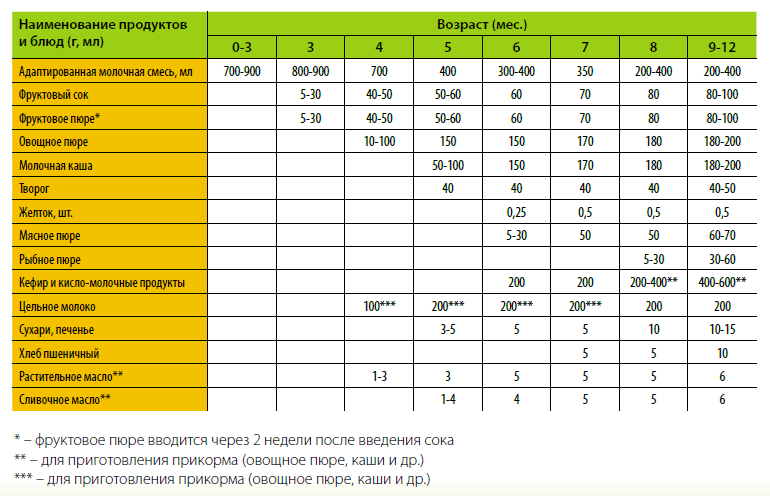
The first line shows how much formula the baby needs. Based on it and the results of weighing in the first months, you can accurately calculate the amount of additional nutrition. After six months, the mother needs to know how much milk is in the breast, and compensate for the lack of it with formula.
In addition, there is Zaitseva’s formula, according to which the daily volume of formula in the first week of a baby’s life is equal to 2% of body weight.
According to the Filkenstein formula, in the first ten days of life, the norm of the mixture is calculated based on weight and age in the following algorithm:
- weight up to 3.2 kg - 70 times the number of days (age)
- weight more than 3.2 kg - 80 multiplied by age in days.
The following daily nutritional intake is:
from 10 days to 2 months - a fifth of the mass, up to 4 months - a sixth part, up to 6 months - a seventh part, up to eight - an eighth part, up to nine - a ninth part. The norm is divided by the number of feedings per day. The daily volume of food should not exceed 1 liter. Everything that the child eats is taken into account, but not drinks, that is, except water, juices and tea.
Possible negative consequences of introducing supplementary feeding
- Changes in intestinal microflora and increased risk of allergic reactions when feeding with formula.
- Risk of developing diarrhea and infectious diseases if hygiene standards are not sufficiently observed.
- Decreased milk production due to insufficient emptying of the breast by the baby.
- If a child receives additional water or glucose in the maternity hospital, the risk of increased bilirubin levels and excessive weight loss increases.
- Formula feeding promotes a longer feeling of fullness in the baby and less frequent breastfeeding.
- Supplementary feeding may cause difficulty returning to breastfeeding.
- Before breastfeeding begins, supplementary feeding has a negative effect on its duration.
- The introduction of supplementary feeding in the early postpartum period leads to excessive breast engorgement associated with infrequent breastfeeding.
When should you stop supplementing?
If a baby develops symptoms of digestive system disorder during mixed feeding , then supplementary feeding with formula should be stopped until the functions of the gastrointestinal tract are completely restored. At this time, the baby should be fed only breast milk, putting it to the breast more often. The supply of milk depends on consumption; if the baby sucks more, lactation can be improved.
Be sure to refuse supplementary feeding if it causes an allergy. In such circumstances, the mixture must be replaced. Additional feeding is not required if the number of urinations corresponds to the established norm. In this case, the pediatrician does not recommend complementary feeding even if the weight does not reach the required age.