Antibiotic sensitivity testing is widely used in pediatrics and therapeutic practice. It is indicated for prescribing adequate treatment for infectious processes.
Pathogenic bacteria are not sensitive to all types of antibacterial drugs, so it is so important to choose an appropriate antibiotic that inhibits the viability of the microflora.
Rapid suppression of the activity of pathogenic microflora reduces the risk of chronic disease and the development of secondary complications.
An antibiotic sensitivity test is a laboratory test that determines the type of pathogen and the total volume of pathogenic media. Before taking the test, you need to prepare.
Usually the test is scheduled for the morning. Patients are not recommended to wash themselves, rinse their nasal passages, or wash their face. Antibiotics should not be taken due to the risk of false results.
Your attending physician will tell you how to take the test correctly.
An antibiotic sensitivity test is indicated to study the type of bacteria and determine drug therapy.
The main goal is to determine the type of bacterium, its resistance or sensitivity to various groups of antibiotics.
Indications and test samples
The main indications for prescribing the analysis are acute inflammatory processes of a bacterial nature and drawing up a plan for further management of the patient. The analysis is used in surgery, urology, nephrology, oncology and other branches of medicine.
The biological material studied depends on the patient’s current clinical history and the location of the inflammatory focus. In case of extensive sepsis, a detailed study of all biological materials is recommended. Suitable for research:
- Blood. A biochemical detailed hemotest helps determine not only the type of pathogen, but also the general condition of the body as a whole.
- Urine. Urine culture is carried out to clarify sexually transmitted infections, inflammation of the kidneys, and urogenital tract organs.
- Stool analysis. It is used for patients with inflammation of the intestinal tract, complications of acute intestinal infections, and suspected parasitic infections. At the same time, the physical and chemical parameters of feces are studied.
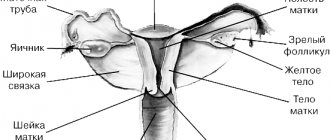
- Cervical smear in women. The research method helps to identify genital tract infections.
- Sperm examination, urethral smear, prostate secretion. Bacterial culture tests are used to clarify infections of various locations in men.
- Sputum analysis. Helps in the diagnosis of respiratory diseases, pulmonary tuberculosis, pneumonia. At the same time, the amount of impurities - pus, blood, mucus - is assessed.
For chronic pathologies of the respiratory tract and respiratory system, it is possible to take a smear from the nasal passages and larynx. The analysis is widely used in pediatrics due to the ease of collecting biological material.
Materials Study Methods
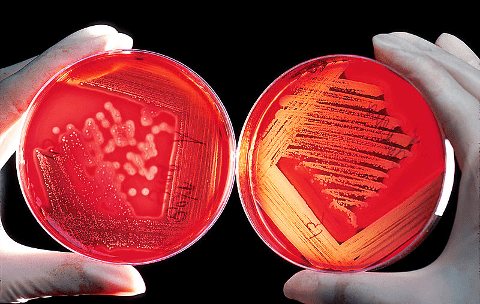
Bacterial seeding is performed in several ways, including the disk diffusion method, E-test, and dilution method. In each case, a specific type of test is performed.
Disk method
A common and simple way to determine the type of bacterial microflora. The material to be tested is placed in a Petri dish over the entire surface, and small cardboard disks soaked in a certain type of antibiotic are placed. Afterwards, the cup is tightly closed and placed in a thermostat at human body temperature for 12 hours.
Urine culture is prescribed for suspected infections of the genitourinary tract and urogenital tract
Under the influence of the diffuse processes of the antibacterial drug, a zone of suppression of pathogenic microflora is formed. At the end of the analysis, the diameter of the identified suppression zone is measured.
E-test
The bacterial sowing method is similar to the disc-diffusion method, however, instead of cardboard discs, a special scale-strip with varying intensity of antibiotic impregnation is placed in the bowl.
The inoculation is incubated for about 12 hours, after which the effectiveness of each impregnated zone of the strip is assessed. The choice of antibiotic based on the test result depends on the severity of the inhibition zone in a certain area of the strip.
The E-test is a simple and accessible testing method, but it is expensive.
Breeding methods
The analysis is based on serial double dilution of the antibiotic from maximum to minimum concentration. 1 ml of biomaterial is diluted 10 times in 10 test tubes with nutrient medium. In the test tube where the growth of pathogenic microflora stops, the maximum limit for the number of pathogens in the sample is designated. The same method is used to detect sensitivity to antibiotics.
Minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC)
Minimum bactericidal concentration is the lowest concentration of an antibacterial substance that destroys pathogenic bacteria by 100%.
The MBC indicator is also taken into account in the treatment of those patients who have no effectiveness from previously prescribed etiotropic therapy.
Analysis of flora and MBC is especially used against the background of osteomyelitis, generalized sepsis or inflammation, bacterial myocarditis, endocarditis.
Modern laboratories are equipped with the necessary equipment to determine the type and sensitivity of bacteria. Obtaining results takes 1-2 days, which depends on the transport of the received material and the type of research.
Decoding the results
To determine the sensitivity of the antibiotic, zones of suppression of the growth of colonies of pathogenic strains are assessed. Resistance categories are not constant and are therefore regularly revised due to changes in sensitivity to antibacterial drugs.

Flora analysis is constantly used in various medical fields
Mutation of pathogens is also caused by indiscriminate use of antibiotics without additional research. Clinicians distinguish several types of interpretations:
- clinical;
- microbiological.
The evaluation of a clinical method is based on the effectiveness of a particular drug. Microbiological interpretation is based on the distribution of antibiotic concentrations and the degree of suppression of pathogenic activity at each concentration. Thanks to microbiological interpretation, the dose of the drug is selected to achieve high therapeutic results.
Decoding by pathogen type
An antibiotic sensitivity test is also necessary when the nature of the inflammatory process is unclear. Considering that after taking antibacterial drugs, pathogenic strains can mutate and change their condition, microorganisms are classified into resistant, sensitive, and conditionally sensitive.
Sustainable
Resistant or resistant bacteria are characterized by further growth and pathogenic activity even when taking maximum doses of the drug. In this case, long-term treatment and the prescription of combined antibiotics with different concentrations are required.
Conditionally sensitive
Conditionally sensitive or intermediate-resistant bacteria provoke different therapeutic outcomes. The therapeutic effect is achieved by increasing the daily dose of the drug and constantly adjusting the concentration of the antibiotic.
How the research is carried out
In the laboratory, the collected material is placed in a thermostat with a nutrient medium, where the conditions necessary for bacterial growth are created - temperature and humidity at a certain level.
After 4-10 days - this depends on the biological material and microorganisms to be identified, control and additional studies are carried out.
Diagnostics are carried out in three stages, each of them has its own purpose:
- Qualitative research. The presence of microorganisms in the crop is checked. If they are identified, the shape of the pathogen, its color, density of fractions and “aggressiveness” - the ability to destroy certain inorganic and organic compounds - are determined.
- Quantitative diagnostics. Sets the pathogen concentration. This is important for predicting the course of the disease and selecting the combination and dosage of prescribed drugs.
- Antibioticogram. The sensitivity of the inoculated microflora to antibacterial or antimycotic drugs is determined. This is necessary to prescribe effective therapy.
Table of interpretation of the results of the main microbiological indicators | University Clinic
Femoflor - decoding of microbiological indicators
| Concentration of microorganisms | Index | Decoding | Further actions | |
| Control of material intake | Less than 10^4 | Poor quality of material for analysis | The number of microorganisms is insufficient for analysis. The test must be retaken | |
| More than 10^4 | Good quality of analysis material | There are enough microorganisms in the smear to conduct research | ||
| TBM – total bacterial mass | Less than 10^6 (vagina) Less than 10^5 (urethra and cervical canal) | Poor quality of material for analysis | The number of microorganisms is insufficient for analysis. You need to retake the test a little later | |
| More than 10^6 (vagina) More than 10^5 (urethra and cervical canal) | Good quality of analysis material | There are enough microorganisms in the smear to conduct research | ||
| Microorganism | Absolute indicator | Relative indicator | Decoding | Further actions |
| Lactobacillus | 10^5- 10^6 and more | From -0.3 to 0 (70-100%) | Sufficient amount of healthy microflora | a woman’s genital tract corresponds to the norm |
| 10^5 or less | -1 to -0.3 (10-70%) | Moderate decrease in the amount of healthy microflora | This picture is observed with vaginal dysbiosis, inflammatory processes and genital infections. Treatment is carried out aimed at normalizing the amount of healthy microflora | |
| Less – 1 (10%) | Significant reduction in the amount of healthy microflora | |||
| Microorganism | Index | Decoding | Further actions | |
| Less than 10^4 | Pathogenic microorganisms of ureaplasma and mycoplasma are found in the genital tract or urethra in very small quantities. This number of pathogenic microorganisms is often ignored, so the form may indicate that they were not detected | Norm. No treatment required | |
| More than 10^4 | The number of ureaplasmas and mycoplasmas exceeded the norm, leading to infection | Antimicrobial treatment is carried out | ||
| Candida | Less than 10^3 | Norm. This number of pathogenic microorganisms is ignored, so the form may indicate that they were not detected | Norm. No treatment required | |
| More than 10^3 | Exceeding the norm | Candidiasis (thrush). Antifungal drugs are prescribed |
| Microorganisms | Absolute indicator | Relative indicator | Decoding | Further actions |
Enterobacteriaceae
| Less than 10^4-10^5 | Less than -3 (0.1%) | Norm. This number of pathogenic microorganisms is ignored, so the form may indicate that they were not detected | The amount of opportunistic flora is insignificant, so it cannot cause any diseases |
| More than 10^5 | -3 to -2 (0.1-1%) | Slight excess of level | The number of opportunistic microorganisms, harmless in small quantities and dangerous when the concentration increases, exceeds the norm. Measures must be taken to eliminate this situation. Otherwise, this can lead to the development of purulent lesions of the genital tract, dysbiosis, gardnerellosis and other infections | |
| -2 to -1 (1-10%) | Moderate excess level | |||
| Over -1 (10%) | Significant excess of normal level | The number of opportunistic microorganisms is much higher than normal. This condition is a sign of dysbiosis of purulent lesions of the genital tract and other infections of the urogenital tract. Drugs are prescribed that reduce the number of pathogenic microorganisms and restore healthy bacterial flora |
| Pathogen | Norm | Diagnosis | Actions |
| Mycoplasma genitalium | Not detected | Mycoplasmosis | The analysis reveals two types of mycoplasmas hominis and genitalium. The first type refers to conditionally pathogenic microorganisms, and the second to pathogenic flora. If Mycoplasma genitalium is detected, antibacterial drugs are prescribed |
| Chlamydia trachomatis | Not detected | Chlamydia | Antibacterial drugs are prescribed to treat chlamydia |
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae | Not detected | Gonorrhea | Antibacterial drugs are prescribed to treat gonorrhea |
| Trichomonas vaginalis | Not detected | Trichomoniasis | Antitrichomonas drugs are prescribed |
| HSV-1,2 | Not detected | Infection with the herpes virus | Antiviral drugs are prescribed |
| CMV | Not detected | Cytomegalovirus infection |
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
The undoubted advantages of the bacteriological culture method include high diagnostic accuracy.
This allows you to find the target of the disease and hit it “right” by prescribing highly targeted drugs in the most effective dosages and combinations. Thus, the patient’s recovery period is significantly reduced and therapy is ultimately more gentle. This happens due to the fact that drugs that provoke side effects are not prescribed, while working “idle”.
The disadvantages of the method are the long execution time, specific requirements for the conditions for collecting material, the arrangement of the laboratory and the qualifications of laboratory doctors.

The timing of the analysis can vary from 4 to 10 days, depending on the type of study.
Stool analysis takes 4 to 7 days to prepare. Sowing from the nose and throat – 5-7 days. It takes the longest to prepare a blood test for sterility – 10 days.
Preliminary results can be expected within 3 days. However, in acute conditions there is no time to wait. In this case, broad-spectrum antibiotics or several drugs are prescribed, which creates a large burden on the patient’s body and is fraught with side effects of the drugs. This is another argument in favor of the fact that you should not neglect the disease and self-medicate.
Contact the clinic on time for timely diagnosis and prescription of adequate therapy.
Rules for collecting biological material and preparing for analysis
When taking biological material, the sterility of instruments and containers is of primary importance. If these rules are not followed, the material becomes contaminated with bacteria from the environment, which makes bacterial seeding ineffective.
Blood and urine are taken into dry sterile test tubes, and other materials into a container with a transport nutrient medium.
It is important to quickly deliver the material for bacterial culture to the laboratory and adherence to transportation rules, since microorganisms can die.
Bacteriological culture is not performed while taking antibiotics! If you are taking antibacterial drugs or stopped taking them 10 days or less before the test, tell your doctor.
How to collect material for bacterial sowing:
- Urine . Collected after mandatory morning hygiene procedures. Take an average portion of about 10-15 mg in a sterile container. Deliver in no more than 2 hours.
- Nasopharyngeal swab . Before the procedure, you should not drink, eat, brush your teeth, rinse your mouth or rinse your nose.
- Cal . It is collected in the morning without the use of enemas or laxatives using a sterile spatula into a sterile container. Care must be taken to ensure that no urine gets into the material. Deliver to the laboratory no more than 5 hours later.
- Sputum . Collection is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach. Before doing this, thoroughly brush your teeth and rinse your mouth with boiled water. Sputum must be delivered to the laboratory within 1 hour.
- Samples from the genital organs . Taken no earlier than a month after stopping antibiotics. A smear can be taken from women 14 days after their period. Women should not urinate for 2 hours before the procedure, men – 5-6 hours.
- Breast milk . Before collecting milk, it is necessary to disinfect the area around the nipple with an alcohol solution. The first 15 ml is not used. For analysis, take 5 ml into a sterile container. The material must be delivered within 2 hours.
It is best to take biomaterial in a medical facility or directly in the laboratory - this guarantees compliance with all rules and timely delivery, which means maximum diagnostic reliability.
Main indications
Bacterial culture is prescribed for:
- diagnosis of hormonal imbalances;
- treatment of infectious, urological, gynecological, and oncological diseases;
- inflammatory diseases of organs and systems;
- acid-base balance disorders;
- suspected sepsis;
- ENT diseases;
- the need to change the drug that causes the allergy;
- ineffectiveness of the drug or the body becoming accustomed to it.
Based on the degree of susceptibility to antibiotics, there are 3 groups of harmful microorganisms.
Sensitive. They can be neutralized with a minimal dose of antibiotic.
Moderately resistant. Suppressed by the maximum dose of the antibacterial drug.
Sustainable. Not susceptible to antibiotics even at higher dosages.