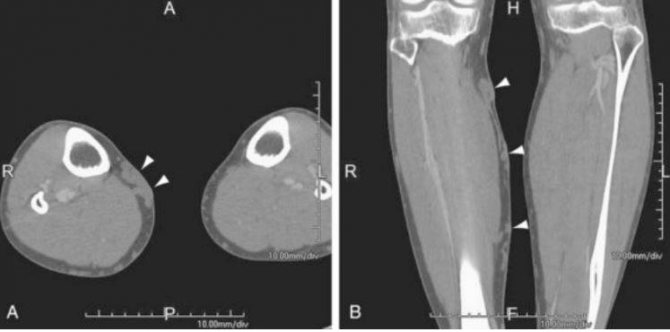
Computed tomography or CT scan of the leg is a method of radiological diagnosis of a wide range of diseases affecting the bones and soft tissues of the lower extremities from the knee to the foot. Compared to conventional radiography, computed tomography allows you to diagnose pathologies of the ligaments, cartilage, muscles and tendons of the leg. CT is significantly superior to other diagnostic procedures in terms of information content and specificity when examining bones, and therefore is usually the method of choice for diagnosing diseases of the lower leg.
The method is based on the use of a moving set of X-ray sources and detectors rotating around the patient’s body. The result is detailed images in the form of layer-by-layer sections through the area of interest. To reconstruct the image, sophisticated computer technologies are used to create two-dimensional images of the area under study and three-dimensional models.
Indications for computed tomography of the leg bones
Computed tomography of the leg is used to diagnose the following pathologies:
- Injuries – fractures, cracks of the tibia or fibula, intra-articular complex fractures (fractures of the plateau, tibial condyles);
- Damage to the ligamentous apparatus (ruptures, sprains of ligaments and tendons);
- Osteoarthritis (knee, ankle joints);
- Osteomyelitis of the lower leg bones, other infectious and inflammatory processes;
- Bone cysts;
- Assessing the results of treatment of fractures, repositioning bone fragments, planning surgical interventions;
- Benign and malignant neoplasms of soft tissues and bones of the leg (including metastatic lesions of the bones of the leg).
A CT scan of the leg is also performed if the patient has the following complaints:
- Pain, swelling of soft tissues arising after traumatic exposure;
- Spontaneous pain in the bones of the lower leg, without any apparent cause;
- Swelling of soft tissues, redness of the skin, space-occupying formations, determined visually or during physical examination.
CT scan of the foot - indications
There are the following indications for CT scan of the foot:
- consequences of injuries, accompanied by prolonged pain and ineffectiveness of conservative therapy;
- swelling in the arch of the foot or toes of unknown origin;
- crunching sound when moving the foot;
- deformations in the area of the phalanges of the fingers, leading to impaired movement;
- ulcerative and other defects due to diabetes mellitus or venous pathology;
- rheumatic lesions of small joints of the foot and hand;
- clinical signs of tumor lesions.
A CT scan is often recommended before surgery. A three-dimensional model of the foot, obtained using a special computer program, helps plan the course of the operation and make it minimally invasive.
Contraindications for CT scanning of the lower leg bones
CT scanning of the leg bones is contraindicated in the following cases:
- Pregnancy at any stage is a contraindication for CT scanning;
- Children under 5 years of age (for older children, CT is performed only with a referral from the attending physician).
Contraindications for CT scan of the leg bones with contrast:
- Kidney diseases accompanied by chronic renal failure (before the examination, kidney function is assessed using a blood test for creatinine). The use of contrast in such cases can lead to further deterioration of renal function, up to acute renal failure;
- Allergic reactions and individual intolerance to radiocontrast drugs;
- Treatment of diabetes mellitus with metformin - discontinuation of the drug is required due to incompatibility with contrast. Otherwise, complications during diabetes mellitus in the form of ketoacidosis are possible;
- Allergy to iodine.
Contraindications
The examination uses contrast agents containing iodine. Therefore, one of the main contraindications is intolerance to iodine and iodine-containing drugs. There are other conditions and diseases for which the procedure is not prescribed:
- renal and liver failure;
- multiple myeloma;
- severe pain syndrome;
- general serious condition;
- claustrophobia;
- mental illnesses that make it impossible to lie still;
- hyperkinesis;
- excess weight exceeding the norm that the equipment can support;
- pregnancy.
Lactation is a relative contraindication. After the examination, it is not recommended to breastfeed for 2-3 days.
Why do you need contrast when performing a CT scan of the leg bones?
Computed tomography may be performed with contrast agents. To do this, contrast containing iodine is injected into the patient's venous vessel. Since the latter has the ability to absorb X-rays, the use of contrast enhancement allows areas showing abnormal accumulation of the drug to be visualized in the images. This facilitates the diagnosis of neoplasms and provides a more accurate determination of the nature of the pathology.
However, since the tissue of the lower leg bones absorbs X-rays well, the use of a contrast agent is rarely required.
Why contrast is needed
Why use a contrast agent if a CT scan is planned to examine the vessels of the lower extremities - this question is relevant for many patients. It is this technique that allows us to examine the condition of the blood vessels in detail. The image will clearly show whether there are pathologies of the arteries, the diagnostician will determine whether surgery is necessary, or whether conservative therapy can be used. If a CT scan of the vessels of the patient’s lower body is to be performed, then the use of contrast is a prerequisite. The specialist will be able to examine in the image all the features associated with the blood supply to the extremities: the structure of the capillaries and even their very small branches.
Thanks to the connection to a computer, you can see the state of the tissues in a three-dimensional image, and this factor significantly expands the possibilities of the study. It is possible to perform a CT scan of the lower part without contrast, but often this technique is not very informative, so examination is rarely prescribed.
Preparing for a CT scan of the leg
Computed tomography of the lower leg bones does not require special preparation. The examination can be done at any time, after which the patient can immediately return to their daily routine. There is no need to follow any diet or refuse food or water. Despite this, there are several rules aimed at ensuring safety and preventing complications that must be followed during any medical procedures.
- Be sure to report any health problems, including allergic reactions, chronic diseases, injuries, surgeries;
- List any medications you are taking;
- Women need to exclude the possibility of pregnancy;
- Before having a CT scan with contrast, avoid drinking alcohol to reduce the risk of side effects. Drink more fluids to prevent dehydration, which increases stress on the kidneys.
How is a CT scan of the leg bones performed?
A tomograph - a device for performing CT scans - has a ring shape with a hole in the center with a diameter of about 80 cm. The device is equipped with a movable table to accommodate the patient. The table passes through the center of the device and moves forward during the examination, ensuring scanning of the entire examination area.
Positioning the patient and setting up the equipment takes 5-10 minutes, and the scanning procedure itself lasts less than one minute. The use of contrast agents increases the duration of the examination by 10-15 minutes.
Deciphering the received images can take from several minutes to several hours, depending on the workload of the clinic and the complexity of the case. The results of the examination are usually provided on a CD with a record of the procedure and in written form.
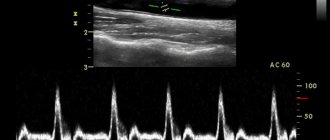
Photo of CT angiography of the lower extremities
The radiologist interprets the results and issues a conclusion. At the Magnit diagnostic center in St. Petersburg, our doctors will answer any questions, and CT angiography of the arteries of the lower extremities often plays a leading role in establishing the final diagnosis. We have selected several photo tomograms with characteristic pathologies:
Sagittal (A) and axial (B) images of CT angiography show occlusion of the left superficial femoral artery (indicated by arrows)
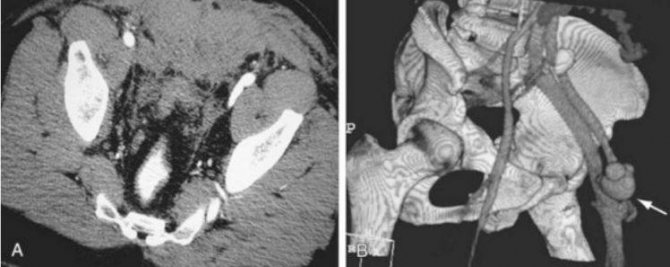
Arteriovenous fistula between the femoral artery and femoral vein on CT angiography of the arteries of the lower extremities (indicated by an arrow)
Dilation of the saphenous veins on CT angiography (varicose nodes are indicated by arrows)
What does a CT scan of the leg show?
After completing the examination, the radiologist examines a series of images of the bones and soft tissues of the lower leg. During the study, the condition of bone tissue is assessed, its density and mineralization are determined. Pathological changes in the form of cracks, violations of the integrity of the bones of the lower leg are determined, neoplasms, areas of sclerosis, and destruction of bone tissue are identified. The extent of the pathology, the connection with the periosteum and surrounding soft tissues are assessed. The identified pathological signs characteristic of a particular disease are classified.
What does a CT scan of the lower extremities show?
Computed tomography is a non-invasive study that uses X-rays to obtain cross-sectional images and create a three-dimensional model of the circulatory system or organs. Typically, a CT scan of the lower extremities is performed using contrast to assess the condition of the vessels of the legs; this examination is also called CT angiography.
This method allows doctors to examine in detail all changes in large arteries and small vessels. At the same time, the risk of adverse effects due to radiation exposure is minimal.
Indications
A doctor may recommend a CT scan of the lower extremities in the following situations:
- swelling of the legs;
- numbness and pain;
- varicose veins;
- hematomas;
- loss of sensation;
- vascular damage due to injury;
- suspicion of arterial disease, characterized by blockage of the vessel;
- problems with blood circulation in the feet, for example, with diabetes;
- pathology of arteries and veins.
CT angiography is also used in preparation for surgical interventions and to assess the effect of the therapy received.
What does a CT scan show?
Thanks to cross-sectional images, specialists can use images to identify and enlarge pathological areas for more detailed study. As part of the examination, doctors will be able to determine:
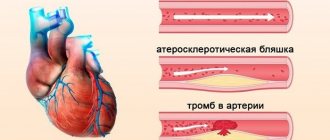
- thrombosis;
- chronic venous insufficiency;
- atherosclerosis;
- aneurysms of various origins;
- vascular development abnormalities;
- phlebeurysm;
- angiopathy;
- acute form of arterial thrombosis;
- tumors;
- Tayakasu disease;
- rheumatic vascular lesions;
- phlebothrombosis.
How is the procedure performed?
CT scan of the lower extremities is performed with contrast. To do this, an iodine-containing drug is injected into a vein during the study, which accumulates in the circulatory system, which allows for improved visualization.
The procedure takes only 15-25 minutes. During this period, it is important to remain still so that the pictures are clear.
The examination takes place in a special room, and the doctor monitors the progress of the diagnosis through a special window. First, the specialist will help the patient lie down on a mobile table and fix the limb. When scanning begins, the frame will begin to rotate around the desired area, taking pictures.
During the tomography or before it begins, an intravenous injection is given, which may be accompanied by a feeling of heat, nausea and a metallic taste in the mouth; these side effects quickly disappear.
The images obtained during the CT scan are interpreted by a radiologist or attending physician.
Tomography is carried out in two directions - CT of veins and CT of arteries, so pay attention to what kind of research you need so that unforeseen situations do not arise later.
MRI or CT scan of the leg - which is better?
Magnetic resonance imaging is a modern and sensitive method. Unlike CT, MRI allows more accurate diagnosis of pathologies of soft tissues, such as ligaments, tendons, muscles, and cartilages. However, the sensitivity of magnetic resonance imaging for complex fractures of the articular surfaces of the tibia may be insufficient. For this reason, a differential approach is applied to the diagnosis of pathologies of the lower leg - if bone tissue pathology or fractures are suspected, it is preferable to use computed tomography, and for pathologies of the joints and soft tissues, MRI is indispensable.
There are differences in cost - usually a computed tomography scan of the lower leg is cheaper than a magnetic resonance imaging scan. However, the higher cost of MRI is offset by the safety due to the lack of radiation exposure present in CT scanning.
The diagnostic appointment center VSEMRT.RU specializes in providing advice to patients in need of CT or MRI in St. Petersburg. Call by phone to choose the optimal diagnostic method for your case, find the clinic closest to you, find out the price of the examination and make an appointment.