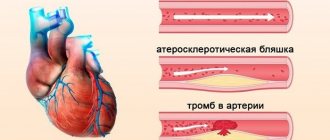
Changed blood vessels in the legs and alarming symptoms are a reason to do CT angiography of the lower extremities
CT angiography of the lower extremities (CTA) is a non-invasive test that allows you to evaluate the vessels of the legs. This type of diagnosis is recommended by a phlebologist or vascular surgeon. Previously used catheter angiography is now practically not performed, as it is associated with high risks (pseudoaneurysm, arteriovenous fistulas). Modern CTA has advantages - the absence of serious complications, quick results, lower cost, and the ability to examine patients with pacemakers and implants. For better visualization of vascular structures and nearby soft tissues, an iodinated contrast agent is injected.
What does CT angiography of the lower extremities show?
Reconstruction of CT angiography of leg vessels
CT angiography can evaluate the entire arterial tree, from the aortic arch to the vessels of the toes, if indicated. CT angiography of the lower extremities demonstrates the arterial wall and its lumen, which makes the procedure indispensable in assessing atherosclerotic plaque or aneurysm morphology. Tomograms show changes in nearby tissues, and bone structures are well visualized. The results of CT angiography provide the vascular surgeon with complete information about the location of the obstruction, the severity of vascular diseases, and allow one to determine the appropriate strategy for surgical intervention. CT angiography of the lower extremities shows:
- systemic or regional arterial insufficiency due to atherosclerosis;
- Buerger's disease (thromboangiitis obliterans), vasospastic processes;
- trauma and its consequences (hematomas, blood clots, vascular intimal ruptures, their compression, occlusion, dissection, as well as aneurysm, pseudoaneurysm, arteriovenous fistula);
- inflammatory changes (vasculitis);
- condition after removal of the fibular graft (vascular assessment);
- non-traumatic thrombosis of a vessel or an installed stent;
- arterial embolism;
- tumor masses in the lumen of the vessel;
- congenital vascular anomalies and arteriovenous malformations;
- disorganized vessels, including feeding neoplasms;
- vein diseases
CT angiography of the arteries of the lower extremities is used to monitor the dynamics after open or percutaneous revascularization. The study is performed before plastic surgery if they plan to remove material for autotransplantation. Duplex scanning and MRI are preferred for assessing changes in postthrombophlebetic syndrome and vascular mass, but CT angiography also finds lesions in patients being evaluated for peripheral ischemia. Multidetector computed angiography has a larger coverage volume and ultra-high spatial resolution, and the speed of the diagnostic procedure allows for a reduction in the amount of injected contrast agent. CT is preferable to MRI for the evaluation of microangiopathies.
How is the procedure performed?
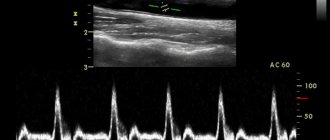
Duplex Angloscanning of the upper/lower extremities is a simple procedure. The patient needs to take off his clothes so that the doctor has access to the areas of the body being examined, and lie down on the couch. The surface of the hands or feet is lubricated with a special gel, thanks to which the sensor moves easily over the skin - this facilitates better registration of ultrasonic waves.
The examination lasts no more than 20-30 minutes. The doctor moves the sensor along the vessel, and an image created based on the reflected ultrasound signal is displayed on the monitor. A two-dimensional image on the screen makes it possible to assess the condition of the vessels, understand whether they are narrowed, whether their walls are thickened, and also determine the location of atherosclerotic plaques and blood clots.
How to do CT angiography of the arteries of the lower extremities
To avoid blurring on tomograms, complete immobility is required during the diagnostic procedure.
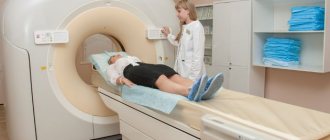
The technician places the patient on the CT scanner table in a supine position, using pillows and straps to ensure immobility.
To obtain images of blood vessels, a catheter is inserted into a vein, through which a radiopharmaceutical is automatically delivered at certain intervals during the examination (diagnostics with bolus contrast). In some cases, especially in patients with fragile and small veins, the contrast agent is injected using a syringe. The diagnostic procedure is controlled remotely. In a CT scan, X-ray emitters and detectors rotate around a given area, recording the amount of radiation absorbed. Normal anatomical structures and pathologically altered tissues reflect different volumes, which is the basic principle of diagnosis. The obtained data is processed using a computer, and special programs restore a three-dimensional image of the area under study on the monitor.
MSCT (multispiral computed tomography) is a more advanced type of CT that allows you to adjust installation parameters for each patient individually. Images can be stored, printed or copied to any electronic storage medium.
Preparation for angiography of the extremities

Eat a light snack 40 minutes before contrast injection to help avoid nausea and dizziness.
Preparation for CT angiography of the vessels of the lower extremities does not require any special measures; it is enough to choose comfortable clothes without metal parts, and remove all jewelry, hairpins, and glasses before the procedure. This measure will prevent the appearance of artifacts (blurs) on the film that affect the quality of tomograms.
It is better to sign up for diagnostics by phone or through the form on the website, taking with you all the results of previous examinations, a referral from a doctor and the result of a blood test for creatinine. At the Magnit diagnostic center in St. Petersburg, this testing can be completed for an additional fee immediately before performing CT angiography of the arteries of the lower extremities; in this case, you must arrive at the clinic 15 minutes earlier. The study is carried out using the express method.
48 hours before performing contrast, in agreement with the endocrinologist, it is necessary to stop taking Metformin (a hypoglycemic drug) and its analogues. During lactation, it is recommended to store milk for 2 subsequent feedings.
To reduce the manifestation of autonomic reactions to the administration of the radiopharmaceutical, you should have a light snack 40 minutes before the procedure.
Advantages and diagnostic capabilities of CT
The accuracy of the data obtained is one of the main advantages of CT examination. Even minor violations are visible in layer-by-layer images. Tomography shows:
- inflammatory processes;
- blood clot formation;
- phlebeurysm;
- developmental abnormalities and vascular obstruction;
- tumor formations of various origins.
The procedure takes little time (10–30 minutes), is absolutely painless and does not require invasive intervention. A CT scan is carried out using x-rays, but this is not something to be afraid of. The radiation dose is calculated taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient and does not affect health.
Which is better: CT angiography of the lower extremities with or without contrast?
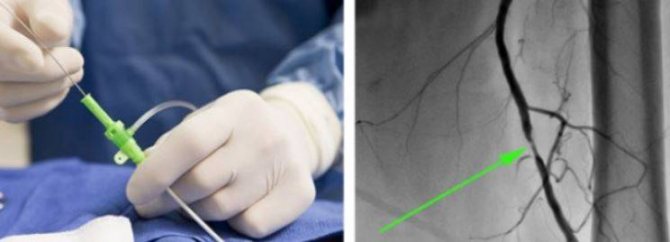
Contrast in CT angiography provides better visualization: on the left is the process of vessel catheterization, on the right is an angiogram with an arrow indicating the pathological zone
To obtain the most detailed images, contrast is necessary. There is no need to be afraid of administering contrast in the absence of contraindications; complications in the form of anaphylactic reactions are extremely rare. Doctors have a range of drugs in their arsenal to provide emergency medical care in urgent situations. The price of CT angiography of the lower extremities varies in different clinics; at the Magnit diagnostic center, the cost of diagnostics is affordable for most patients, as there is a flexible system of discounts.
Indications and contraindications

CT angiography has its indications and contraindications
CT angiography of the lower extremities is justified if the results of other diagnostic methods cannot be interpreted unambiguously. The study can be performed if there are the following complaints:
- pain in the lower extremities;
- fatigue in the legs after minor physical activity;
- swelling in the ankle area;
- paresthesia in the feet and legs;
- cramps in the calf muscles (especially at night);
- changes in the skin (pattern wear, atrophy of hair follicles, dryness and flaking, the appearance of hyperpigmentation and areas of ulceration);
- visible deformation of blood vessels, compaction, etc.
With claudication, there is a possibility of occlusive diseases of the peripheral arteries, which are associated with the abdominal aorta (its bed is additionally assessed and an aneurysm is excluded).
During pregnancy and childhood, other examination methods are preferable, since X-ray radiation and contrast are contraindicated for this category of people. In this case, MRI and ultrasound of the lower extremities with Doppler (duplex scanning) are performed. For health reasons, it is possible to perform MSCT without enhancement. The administration of contrast is unacceptable to patients with a burdened allergic history (hypersensitivity reactions to iodine), chronic renal failure and hyperfunction of the thyroid gland.
Who is indicated for CT scan of blood vessels?
Leg pain and mobility problems can occur at any age. There are many possible causes of discomfort: from ordinary fatigue to serious illnesses. Dangerous symptoms include:
- numbness and frequent swelling of the fingers and feet;
- feeling of coldness in the legs;
- stiffness of movement, muscle pain;
- change in skin color;
- the appearance of spider veins, etc.
CT scans are prescribed not only for the purpose of diagnosing disorders. This study is also carried out after operations to monitor the recovery process and before surgery to prevent complications. In case of injuries, computed tomography is effective for clarifying the location of the injury, detecting hematomas and the source of hemorrhages.
Photo of CT angiography of the lower extremities
The radiologist interprets the results and issues a conclusion. At the Magnit diagnostic center in St. Petersburg, our doctors will answer any questions, and CT angiography of the arteries of the lower extremities often plays a leading role in establishing the final diagnosis. We have selected several photo tomograms with characteristic pathologies:
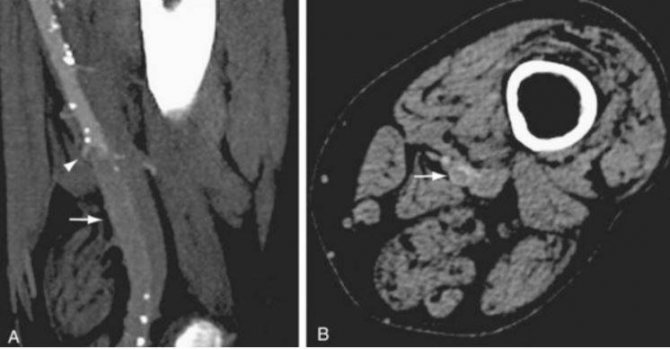
Sagittal (A) and axial (B) images of CT angiography show occlusion of the left superficial femoral artery (indicated by arrows)
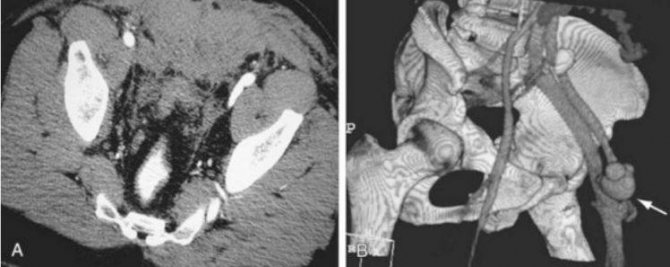
Arteriovenous fistula between the femoral artery and femoral vein on CT angiography of the arteries of the lower extremities (indicated by an arrow)
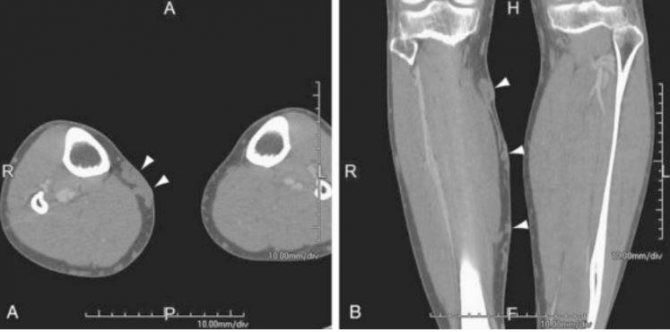
Dilation of the saphenous veins on CT angiography (varicose nodes are indicated by arrows)