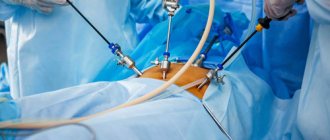
Features of laparoscopy
Different types of laparoscopic procedures have their own characteristics.
Main stages of laparoscopy:
- The operation is performed under general anesthesia. Before laparoscopy, the patient will be consulted by an anesthesiologist to make sure there are no allergies or contraindications to anesthesia;
- the doctor makes 3–4 small incisions (5 to 10 mm) in the abdominal wall;
- the abdominal cavity is filled with carbon dioxide. This increases the viewing sector, makes manipulations accurate and safe;
- A laparoscope is inserted through the incisions, and, if necessary, special instruments are used to perform therapeutic manipulation;
- the surgeon visually controls the surgical field and all his actions on the monitor screen, increasing their accuracy and efficiency.
How long does the operation take?
The duration of a laparoscopic operation or examination is from 1.5 to 2.5 hours, depending on the volume and type of intervention.
Sign up for a consultation
Diagnostic laparoscopy
Traditional methods of examining the abdominal cavity (ultrasound, CT, MRI) do not always provide enough information to make a diagnosis and draw up a treatment plan. In some cases, the doctor needs to examine this or that organ “with his own eyes,” or perform various manipulations. In such situations, diagnostic laparoscopy is prescribed. In addition to the “live” assessment of the condition of the abdominal organs, this operation allows:
- Identify developmental anomalies.
- Determine the presence of adhesions in the abdominal cavity.
- Determine the exact location of the pathological focus.
- Take a sample of biological material for further research.
In some cases, therapeutic measures, for example, removal of adhesions, can be carried out directly during diagnostic laparoscopy.
Laparoscopy in gynecology and abdominal surgery at the Yauza Clinical Hospital
We perform a wide range of laparoscopic examinations and surgeries. Let's name the main ones:
- laparoscopic appendectomy;
- laparoscopic cholecystectomy;
- laparoscopic hernioplasty;
- laparoscopic bowel resection;
- laparoscopy of the ovaries and fallopian tubes;
- laparoscopic removal of myomatous nodes;
- laparoscopic hysterectomy;
- laparoscopy for endometriosis;
- laparoscopy for infertility;
- laparoscopic removal of ovarian cyst;
- laparoscopic sacrovaginopexy for prolapse and prolapse of the genital organs - vagina, uterus.
Laparoscopic appendectomy
Appendectomy is one of the most common operations in surgical practice to remove an inflamed appendix.
Indications for laparoscopic appendectomy are:
- detection of appendicitis during diagnostic laparoscopy;
- acute appendicitis;
- the presence of diabetes mellitus in patients with appendicitis (this reduces the risk of postoperative infectious complications);
- significant obesity (laparoscopic access ensures minimal tissue trauma).
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
This is the most effective way to remove the gallbladder in case of gallbladder disease.
The main indications for surgical intervention are as follows:
- cholelithiasis and its complications (acute blockage of the bile duct, etc.);
- polyps in the gallbladder;
- inability of the gallbladder to receive or secrete bile.
Laparoscopic hernioplasty
Laparoscopic hernioplasty is removal of an inguinal hernia using the laparoscopic method. Our specialists remove all types of abdominal hernias - inguinal, femoral, umbilical - regardless of their origin. We use modern intraoperative tracking systems, mesh alloprostheses that strengthen the abdominal wall and eliminate recurrence of hernia.
Laparoscopic bowel surgery
We perform laparoscopic removal of intestinal tumors, resection of individual sections of the intestine for nonspecific ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease.
Gynecological laparoscopic surgeries
Make an appointment for a consultation
Among the indications for diagnostic or therapeutic laparoscopy in gynecology are the following:
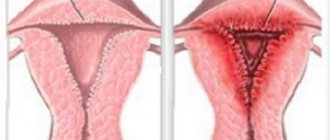
- endometriosis;
- uterine fibroids;
- ovarian cysts and tumors;
- emergency gynecological pathology;
- tubal and ovarian infertility;
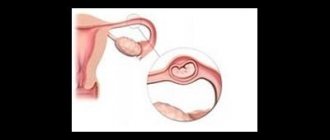
- suspected ectopic pregnancy;
- preparation for IVF;
- prolapse (loss) of the walls of the vagina, uterus.
LAPAROSCOPIC OPERATIONS
Laparoscopic surgery in modern gynecology and, especially, in reproductive medicine, plays an irreplaceable role in the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases of the reproductive system. It is when performing laparoscopy that it is possible to solve women's problems that prevent the natural conception of a baby or create conditions for the successful implementation of an IVF program.
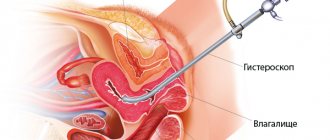
Diagnostic laparoscopy is a minimally invasive and, therefore, low-traumatic surgical research technique in which the doctor visually examines the abdominal organs and pelvic organs (uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries) through small incisions on the abdominal wall. Typically, diagnostic laparoscopy is performed through one or two of these incisions. To improve the size of the field of view, a small amount of harmless inert gas is injected into the abdominal cavity.
Through one incision, a laparoscope is inserted, which is a thin telescopic tube with a lens at one end and an eyepiece at the other, which is attached to a digital video camera (to transfer the image to the monitor and record it on a medium for later viewing with the patient and discussing the results of the study) .
Through another, even smaller incision, a manipulative instrument is inserted, with the help of which the doctor displaces the internal genital and abdominal organs, studying them in detail.
Diagnostic laparoscopy is often performed under general anesthesia, but can also be performed under local anesthesia in combination with light sedation.
If during such an examination a pathology is revealed that can be eliminated, the doctor will immediately do so. In most cases, diagnostic laparoscopy takes no longer than 15 minutes.
Preparation for diagnostic laparoscopy
Before performing diagnostic laparoscopy, as well as before other surgical interventions, the patient must undergo an appropriate examination.
First of all, a set of standard studies is carried out: urine and blood tests (general, biochemical, coagulogram), electrocardiogram, chest x-ray, ultrasound of the pelvic organs, analysis of discharge from the genital tract. The patient should not take food or liquid 8 to 10 hours before surgery. In addition, it is recommended to limit smoking and alcohol intake. Before the operation, the patient needs to undergo a cleansing enema.
Operative (therapeutic) laparoscopy.
For surgical laparoscopy, it is enough for the doctor to make two or three incisions on the anterior abdominal wall with a length of 5 - 7 mm. After the operation there are no scars left. In other words, there are no cosmetic problems.
If monoportal laparoscopy, also practiced at the FERTY-LINE clinic, is performed, then it is necessary and sufficient to make only one incision 10 mm long in the navel area.
What problems can be solved with surgical laparoscopy?
With the help of laparoscopic intervention, you can perform almost all operations that are performed in the open (laparotomy) way.
First of all, surgical laparoscopy is advisable for removing various cysts and ovarian cysts, separating adhesions and restoring the patency of the fallopian tubes, removing myomatous nodes (with preservation of the uterus), surgery on the fallopian tubes during ectopic pregnancy, as well as for complete removal of the uterine body and uterine appendages.
There are pathological situations, the solution of which is generally impossible without the use of laparoscopy: elimination of foci of genital endometriosis and, therefore, elimination of a powerful factor for the existence of infertility in women. This technology has opened a new era in the diagnosis and treatment of infertility, allowing for significant improvement in results.
Timely detection, by ultrasound or during diagnostic laparoscopy, and removal of ovarian tumors by laparoscopic methods have significantly reduced the incidence of ovarian cancer.
Laparoscopy can be either an independent operation or combined with hysteroscopy or operations with vaginal access (for example, for prolapse of the walls of the vagina and uterus, urinary incontinence).
The advantages of laparoscopic technique are undeniable. the next day after endoscopic surgery ; recovery and recovery after surgery occurs much earlier than in cases with conventional laparotomy techniques.
Patients report less severe postoperative pain or no pain at all compared to patients after laparotomy. The incidence of adhesions in the abdominal cavity and pelvis is minimal, long-term results are much better, since laparoscopy in combination with intraoperative ultrasound allows the removal of formations invisible to the naked eye (fibroids, endometriomas or ovarian cysts), which leads to a decrease in the number of relapses.
Mini laparoscopy
Mini-laparoscopy is a type of laparoscopy that has the following advantages:
1) even smaller incisions are needed on the anterior abdominal wall and, as a result, the patient’s negative sensations in the postoperative period are practically eliminated.
2).The cosmetic effect is even more pronounced than with conventional laparoscopy
3) such an operation can be called fully outpatient, with a minimum (one-day) stay of the patient in the clinic.
Minilaparoscopy at the FERTI-LINE clinic is performed with instruments no more than 5 mm thick. The technique is acceptable for solving most gynecological problems, except for cases of removal of fibroids and cysts of impressive size. Traditional laparoscopy is suitable for solving such problems.
Fertiloscopy or transvaginal hydrolaparoscopy
A type of laparoscopy used to examine the pelvic organs and check the patency of the fallopian tubes.
The essence of this method is that a special thin needle is used to make a puncture in the posterior vaginal fornix, through which a sterile solution is injected into the abdominal cavity in order to straighten the tissue and improve visibility in the pelvis. Then, in the same way, a thin endoscopic instrument, a fertiloscope with a video camera, is inserted through the vagina. With their help, the doctor can examine and evaluate the condition of the uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes. With fertiloscopy, you can evaluate the patency of the fallopian tubes by injecting a contrast agent into the uterine cavity and directly observing how it distributes through the tubes and exits into the abdominal cavity.
This method is distinguished by almost 100% diagnostic accuracy of the condition of the woman’s reproductive system and, in fact, is not inferior in this regard to traditional laparoscopy. In addition, this procedure is carried out under short-term anesthesia, which allows the woman to leave the clinic after a couple of hours.
Unfortunately, if any pathology is detected in the pelvis: adhesions, endometriosis, ovarian cysts, the method does not allow it to be corrected, which means that you will have to go back to the operating table to eliminate these diseases using traditional laparoscopy. This is perhaps the only drawback of transvaginal hydrolaparoscopy.
It is appropriate to emphasize that the degree of mastery and implementation of endoscopic techniques is the key to the proper quality of medical services provided. Patients need to take this into account when choosing a gynecological clinic.
Contraindications to laparoscopy
Contraindications to laparoscopy include the following:
- decompensated hypertension, accompanied by hypertensive crises;
- decreased blood clotting, hemophilia.
- decompensated respiratory failure;
- significant bloating,
- ventral hernias with a tendency to strangulate;
- abdominal abscesses;
- the presence of a large number of fistulas and scars of the anterior abdominal wall.
If you are wondering where to have laparoscopic surgery in Moscow, contact the Clinical Hospital on Yauza. Our specialists will conduct a thorough diagnosis and, if necessary, perform surgical intervention.
Indications for implementation
Indications for laparoscopy are:
- diagnostic examination of the pelvic organs;
- uterine fibroids;
- genital endometriosis;
- idiopathic infertility;
- chronic pelvic pain;
- ovarian pathologies (cysts, space-occupying formations, sclerocystosis);
- pathologies of the fallopian tubes (obstruction, hydrosalpinx, sactosalpinx, tubal pregnancy, etc.), as well as tubal ligation for the purpose of sterilization;
- pelvic organ prolapse;
- isthmic-cervical insufficiency;
- adhesive disease of the pelvis.
Advantages of laparoscopy at the Yauza Clinical Hospital
- Doctors. Experienced, highly qualified surgeons with extensive experience in diagnostic and therapeutic laparoscopy.
- Modern equipment. The Clinical Hospital on Yauza is equipped with equipment from the world's leading manufacturers - Karl Storz, Covidien, Erbe, etc.
- Safety. Minimal risks of bleeding and complications.
- Innovative design of operating rooms. Infection-resistant seamless monolithic blocks, 5 levels of sterility, thanks to a complex ventilation system.
- Low morbidity. Absence of significant postoperative scars and pain.
- Fast recovery. The length of stay in the hospital is no more than a day. The recovery period is 2 times shorter compared to abdominal surgery.
- Only positive patient reviews about laparoscopy. Patients who underwent laparoscopy in our hospital are satisfied with the results.
- Good cosmetic result. After the laparoscopy procedure, there are no scars left on the skin.
We work seven days a week, service in two languages: Russian, English. Leave your phone number and we will call you back.
- About the center
- Doctors
- Branches and services
- Programs
- Stock
- Prices
- Contacts
st.
Volochaevskaya 15, building 1 Rimskaya, Pl. Ilyich, from 8:00 to 21:00 Site map About actions in case of fire © 2021. LLC "Clinical Hospital on the Yauza". LICENSE No. LO-77-01-016723 Processing of personal data Policy for the processing and protection of personal data Regulations on anti-corruption policy Rules for the provision of medical services
- Reviews Ask a question Make an appointment
- +7 Write to us
© 2021. LLC Clinical Hospital on Yauza. LICENSE No. LO-77-01-016723 Processing of personal data
Progress of the operation
As before any other surgical intervention, the patient undergoes certain preparation the day before. First of all, you need to pass standard tests, do an ultrasound, take an ECG, and consult with doctors of other specialties. Laparoscopy is performed under general anesthesia, so you should avoid eating and drinking on the day of surgery.
The operation begins with the first puncture in the navel area. Through it, a special port for instruments (trocar) is inserted into the abdominal cavity. A video camera is inserted through the same port. In order to straighten the abdominal cavity, gas is injected into it. After this, the surgeon will be able to conduct a full examination of the organs and install additional trocars, usually no more than three. Instruments are then inserted into the abdominal cavity through ports and the necessary actions are performed.
The rehabilitation period after surgery is reduced on average by half (compared to classical operations) and is better tolerated by patients. The time for discharge from hospital is also reduced. Usually the patient can return home within a week after the operation, but it is necessary to strictly follow all the recommendations given by the doctor.
Contraindications
Absolute contraindications include:
- cancer of the ovary or fallopian tube;
- chronic diseases of the cardiovascular or respiratory systems in the stage of decompensation, as well as acute renal and liver failure;
- bleeding disorders that cannot be corrected;
- obesity degrees III and IV;
- any violations that prevent the patient from being in the so-called Trendelburg position during the operation, in which the pelvis is elevated in relation to the head (sliding hernia of the diaphragm, cerebral vascular pathologies);
- hemorrhagic shock.
In addition, there are relative contraindications, which include severe adhesions in the pelvis, acute infectious diseases and some other disorders.
Rehabilitation period
Wound healing after laparoscopic intervention occurs much faster than after classical surgery. Basic care is treatment with an antiseptic solution. If you follow the doctor's recommendations, there are practically no complications. In the first days, pain is possible, but it goes away on its own. Sometimes it is necessary to wear a post-operative bandage. After a week you can return to your normal rhythm of life.
The only limitation is avoidance of heavy physical activity for 1–2 months. It depends on the individual characteristics of the organism.
Indications for diagnostic laparoscopy in gynecology
Indications for diagnostic gynecological laparoscopy are:
- Diagnosis of acute diseases of the pelvic organs with an unclear clinical picture;
- differential diagnosis of acute genital diseases and acute surgical and urological pathology.
- Finding out the causes of infertility.
- Pain syndrome of unknown etiology.
- Monitoring the dynamics of the inflammatory process of the pelvic organs.
- Staging of the malignant process.
- Monitoring the preservation of myometrial integrity during hysteroresectoscopic intrauterine interventions.