Ultrasound diagnosis of the fetus is an integral part of a comprehensive examination during pregnancy. Being a safe method, ultrasound allows you to evaluate the dynamics of the development of the embryo, as well as identify the pathology of its internal organs. Normally, three screenings are carried out, during which fetometric data, including the cephalic index, are necessarily examined and calculated.
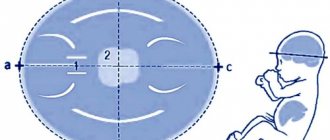
The cephalic index (CI) is understood as the ratio between the biparietal size of the fetal head and a line drawn from the protruding point of the forehead to the back of the head, which is then multiplied by 100%. This allows doctors to find out not only the shape of the unborn child’s head, but also to suspect various defects and anomalies in the development of the structures of the central nervous system.
- Skull structure options
- Dolichocephalic head shape
- Brachycephalic head shape
- Mesocephalic head shape
Skull structure options
As a result of ultrasonography, the resulting cephalic index may indicate different forms of the fetal head:
- mesocephalic;
- dolichocephalic shape of the fetal head;
- brachycephalic.
As a rule, they are considered normal and extremely rarely may indicate pathology.
Dolichocephalic head shape
A dolichocephalic skull shape is assigned if the CI does not exceed 71%. This indicator does not indicate a delay in brain development or severe neurological pathology.
Dolichocephaly is characterized by the fact that the head of the unborn child is somewhat elongated towards the back of the head (from the chin) and has an oblong appearance in the oblique plane.
It is important to understand that the structure of the skull is significantly influenced by the position of the fetus in the uterus. Thus, the dolichocephalic form most often occurs with breech presentation, which is often the reason for cesarean section.
Being a variant of the norm, this shape of the skull in some cases serves as a nonspecific sign of chromosomal diseases such as Down syndrome. It is worth noting that this disease is diagnosed by a combination of clinical and phenotypic data, as well as by the results of a genetic examination, and not just by the index. If a newborn child has neurological symptoms, then dolichocephaly can be considered as one of the types of craniostenosis - premature fusion and closure of the sagittal suture.
Over time (after birth), the size and structure of the skull may change towards average values. Especially if you perform the correct corrective massage.
Brachycephalic head shape
It is worth talking about the brachycephalic shape of the head if the cephalic index gives a value exceeding 85%. In this case, the head is extended towards the back of the head from the forehead, giving the skull a “flattened” appearance.
In the vast majority of cases, this form is considered the norm. However, much less often the cause of brachycephaly can be:
- craniostenosis (this time the coronal suture is overgrown);
- birth injury;
- intrauterine infection, in particular toxoplasmosis.
Often, brachycephalics are in the womb in a breech position, which is an indication for a cesarean section.
Mesocephalic head shape
Despite the fact that each person is individual, approximately 75-82% of the population has a mesocephalic variant of the skull structure, which is considered normal.
The cephalic index for this form corresponds to 71-85% and is an average value. The above variability is acceptable both at the 20th week of pregnancy and immediately before birth.
This shape of the fetal head is considered the absolute norm and does not indicate any pathology.
To summarize, it should be noted that the examination of the head is based not only on calculating the index, but includes a number of indicators that can give a holistic picture so that the ultrasound doctor can adequately assess its size, shape, structure and possible deviations.
Appearance Analysis. Cephalic and facial index.
In order to begin describing appearance, we need to decide what we mean by appearance. I want to emphasize that this is not a superficial similarity of facial features, but a set of physiological parameters.
The similarity of faces does not mean that it is formed by the same horoscope indicators. Compare: two similar flowers can belong to completely different plants of different species and subspecies. Even genetically related twins, born at approximately the same time with the same positions of the planets, obey the laws of nature, and the further the moment of birth of one twin is from the other, the less similar they are to each other in terms of appearance. This fact also completely crushes the theory of appearance analysis based on the Moon. With the same nakshatra and pada of the Moon, the parameters of the twins’ appearance react to something more subtle - and this, of course, is the lagna of the horoscope. I plan to write about the method of analyzing the appearance of twins later. First, it is important to analyze those parameters that we will consider essential for the analysis of appearance.
Assessment and description of appearance belongs to the section Medical Astrology. In order to begin the analysis, you need to highlight the measurable parameters of human appearance, turning to the basics of physiology. The main measurable indicators are
- width, length and structure of the skull
- morphological parameters of the face
- geometry of the figure
It is these parameters that are set by the lagna. They are genetically determined and set the framework of a person who develops in environmental conditions. The environment, of course, also makes its own adjustments, but they are already superimposed on genetic conditioning.
The parameters must be amenable to numerical description, that is, we must arm ourselves with a centimeter and measure distances point by point. They must also be universal - that is, they can be applied to a person of any nationality and race.
The science of anthropology studies the structure of the body, and its section of craniometry gives us clear instructions on how to measure the skull and what points to pay attention to. For demonstration, I will take two parameters cephalic index and facial index.
Cephalic Index = Skull Width / Skull Length * 100.
There are three types:
- Dolichocephalic long-narrow-headed (value less than 77)
- Mesocephalic length slightly greater than width, but not dominant (between 77 and 80)
- Brachycephalic short-broad-headed (more than 80)
Shown here are two contrasting skulls - a long-narrow one and a short-wide one.
We can immediately associate the shape with astrological indicators: if the fire and air elements are expressed in the lagna, then the skull tends to be narrowed, if the earth and water elements are short and wide. We will find the most striking examples in gandants.
This option can be very useful when you have access to a person, rather than analyzing appearance only from a photo. It is rare to find photographs of a person where one can reliably judge the length and width of his skull. Let's move on to a more accessible option.
Facial Index
First you need to measure the full facial height - the distance from the top point of the root of the nose to the bottom point of the chin. Then measure the maximum width of the face - the distance between the cheekbones. And calculate using the formula:
Full Face Height/Face Width*100
If you get less than 84, then this is a Euryprosopic - low (short)-broad-faced
If you get from 84 to 88, this is the Mesoprosopic - average face
If you get more than 88, this is a Leptoprosopic - high (long)-narrow face
In fact, with pronounced indicators, we see this even without measurements. Some people have a narrow and elongated lower face, others have a wide and short one. Appearance also gives an idea of the character of the native. Anthropologists study how facial characteristics affect behavior and image in society.
Here we can also connect the facial index with the lagna indicators. Fire gandants give pronounced leptoprosopics. The first nakshatra padas give a high facial index. We can build on this, highlighting the most contrasting types. This parameter will help you make an informed choice in favor of the lagna, especially when it comes to rectification in the gandanta.
Let's demonstrate this with examples.
- Nicolas Cage is a leptoprosopic. Lagna Mula 1st pada. Sagittarius-Aries
- Barack Obama is leptoprosopic, facial index 93* Lagna Dhanishtha 1st pada. Capricorn-Leo
- Tony Blair is leptoprosopic, facial index 91.9 Lagna Rohini 1st pada. Taurus-Aries.
- Bill Clinton is leptoprosopic, facial index 90. Lagna Hasta 1 pada. Virgo-Aries.
Researchers of facial morphology claim that the higher the facial index, the more leadership qualities a person has. For example, Abraham Lincoln has one of the highest facial indexes.
This is consistent with astrological interpretations - if the native has a fiery navamsha lagna, then he behaves like a leader when building relationships with people. For example, in successful politicians, athletes, world leaders, innovative scientists, as a rule, you will see the dominance of fire navamshas in combination with a strong Mars. This can be expressed through the following indicators:
- Navamsa lagna of Aries, Leo, Sagittarius
- Navamsa lagna Scorpio, lord Mars is strong
- strong Mars in the rasi chakra and its placement in the navamsha lagna
My observations: the stronger Mars is in the chart, the greater the facial index, provided that Mars is associated with the navamsha lagna. If the navamsha lagna is influenced by strong benefics, juroprosopik (low facial index) appears.
Example: Adlai Stevenson . Lagna Rohini 1st pada. Taurus-Aries. Mars is exalted. Facial index 101.
Contrasting example:
Winston Churchill. Lagna Uttaraphalguni 4 padas. Virgo-Pisces. Venus is exalted in Navamsha Lagna. Facial index 75.

An interesting study uses candidate facial morphology to predict the outcome of political elections*. It has been established that the higher the facial index, the higher the chances of success - with equal indicators (approximately the same political program), the public gives preference to the candidate with a higher facial index. This happens when the election race is most often based on the candidate’s charisma, ability to persuade and promote his ideas, rather than on a great contrast of political ideas.
Let us demonstrate this using the example of the political confrontation between Tony Blair and William Hague.
The figure shows how different these faces are in geometric parameters. Tony Blair has a facial index of 91.9 - leptoprosopic. William Hague has a facial index of 81.5 - a juroprosopic.
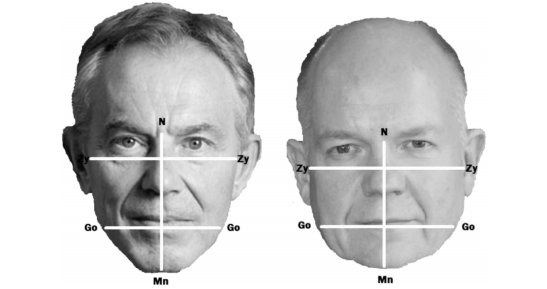
Astrological indicators:
Tony Blair - Taurus, Rohini, Aries navamsha (fire). Strong Mars in Lagna in both Rasi and Navamsa
William Haig - Aquarius. Dhanishtha, Scorpio navamsha (water). Mars in rasi in Gemini, in navamsa in Pisces (much weaker). Aspect of strong Venus on navamsha lagna.
We can say that the reaction to these two types of faces is completely different. The reaction that the native evokes in others is already inherent in his navamsha lagna, because through it he builds relationships in the process of interacting with people. Navamsha lagna is the “best me”, the self that can be maximally manifested in the future, the self that strives for perfection**. A person’s path is already written through the Navamsha Lagna, and this will be reflected in his appearance. Here we see that Tony Blair has the path of an open leader, while William Hague has the path of a hidden politician, business executive, and hidden reformer.
From this presentation we can draw conclusions that will help researchers of astrological parameters of appearance:
- for research you need to take measurable and universal indicators
- appearance directly correlates with navamsha lagna
- geometric shapes imprinted in the structure of the skull are the basis on which all other influences can be superimposed
Anna Bricheva © Mitra Varuna Project
* Analysis of facial morphology of UK and US general election candidates: Does the 'power face' exist? Shofiq Islam, Christopher J. Taylor, Jonathan P. Hayter
** For a deeper understanding of Navamsa Lagna, you can refer to the course NAVAMSA VARGA. PARTNER. TEACHER.FAITH.
If you would like to contribute to the research and provide your physical and astrological data, I would be glad to receive feedback.
Causes
Abnormal development of the skull can be caused by the following circumstances:
- genetic factor (hereditary pathology or failures during osteogenesis);
- breech presentation of the fetus during pregnancy;
- marginal placenta previa along the posterior wall;
- large fruit size;
- oligohydramnios;
- premature birth;
- birth injury;
- vitamin D deficiency (bone plates bend under pressure due to low strength);
- the child spent several weeks in the intensive care unit or intensive care unit;
- monotonous position during sleep;
- hypertonicity of the neck muscles.
The risk of dolichocephaly increases if the newborn spends most of the time lying on his back. The bones of the skull in a small child can move forward (inward) and upward. Pressure on the back of the head and parietal bones is a threat to deformation of the facial skeleton: displacement of the ear, involvement of the forehead, eye sockets, cheekbones, upper and lower jaw. An upward displacement increases the height of the cranial vault and can provoke protrusion of the frontal bone and cheeks.
Dolichocephaly, as an independent phenomenon, is not an anomaly, provided that it does not progress.
Sometimes a narrow head and protruding nape are noticeable from birth in a child with one of these congenital syndromes:
- Marfan syndrome (connective tissue in children with this disease develops incorrectly, they are characterized by gigantism, inconsistency of body parts, including the head, with generally accepted proportions and symmetry);
- Sotos syndrome (developmental disorders of the bone skeleton and central nervous system, large head, disproportionate skeleton and moderate mental retardation);
- Crouzon syndrome (progressive deformation of the cerebral and facial parts of the skull, craniostenosis);
- ectodermal dysplasia (damage to the ectoderm of the embryo, resulting in poor hair, skin, teeth, enlarged frontal bone and other anomalies);
- Proteus syndrome (extremely rapid bone growth, sometimes accompanied by tumors);
- Bloom's syndrome (short stature, increased reaction to ultraviolet light, long and narrow face with prominent ears and nose, high risk of cancer);
- deletion (partial loss) of chromosome 10.
Interpretation of the first ultrasound at 10-14 weeks
Ultrasound at 10-14 weeks allows you to identify some gross fetal defects (for example, anencephaly - complete or partial absence of the cerebral hemispheres, calvarial bones and soft tissues), as well as form a risk group for chromosomal pathology of the fetus based on measuring the thickness of the nuchal translucency , which can be correctly assessed precisely at this stage of pregnancy.
Information When a pregnant woman is classified as a risk group, she is then asked to undergo a more detailed study, for example, such as prenatal karyotyping , that is, a study of the chromosome set of the fetus.
A typical protocol for ultrasound examination at 10-14 weeks of pregnancy is presented in Table 1.

From the first day of the last menstruation, the gestational age at each specific point in time is calculated, and its compliance with the period set on the basis of ultrasound data is determined. This indicator is used due to the fact that we do not know the exact moment of fertilization of the egg by the sperm and the beginning of embryo development.
Based on the gestational age established based on the totality of the above data, the expected date of birth is necessarily set, corresponding to 40 weeks of pregnancy. If there are two or more fetuses, each is examined separately.
When performing an ultrasound, 2 methods are used: transabdominal (examination through the anterior abdominal wall) and transvaginal (examination through the vagina), which is also necessarily noted in the protocol.
To determine the duration of pregnancy and the correspondence of the period to the indicated first day of the last menstruation, an indicator such as the coccygeal-parietal size of the fetus (CTR) - the maximum distance from the head to the tailbone. The measurement is carried out during a sagittal scan of the embryo (the sagittal axis from the Latin “sagitta” - arrow, that is, directed from front to back, and the plane passing through the sagittal axis divides the human body into two symmetrical halves). When the fetus moves, CTE is measured at the moment of maximum extension. Standard indicators of the coccygeal-parietal size of the embryo/fetus depending on the gestational age are shown in Table 2.
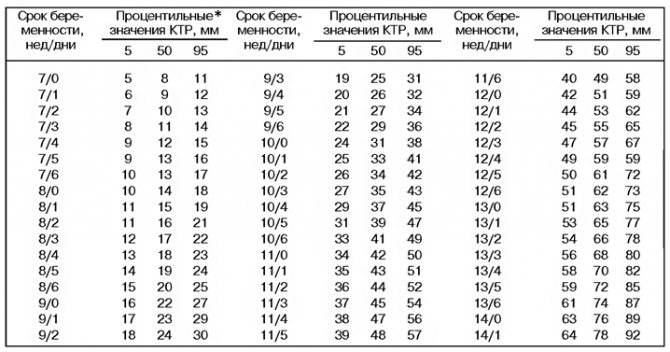
* Percentile is a medical statistics concept. To determine it, a large sample is taken from the population, which is examined for a certain characteristic. Next, from all the values, the average is selected, which is the 50th percentile, and everything that lies in the range from the 5th to the 95th is taken as the norm. Accordingly, values below the 5th and above the 95th percentile require further examination.
Another indicator examined during ultrasound is fetal heart rate (HR) . A change in heart rate may indirectly indicate a chromosomal pathology, but in the early stages it usually does not have much diagnostic value. This indicator is more important in late pregnancy, when intrauterine fetal suffering can be determined based on changes in heart rate. Standard indicators of fetal heart rate depending on the stage of pregnancy are shown in Table 3.

One of the most important points that must be determined during an ultrasound at 10-14 weeks is the thickness of the nuchal translucency space (TN) - the amount of fluid on the back surface of the baby’s neck. To determine it, there are strictly defined criteria:
- The pregnancy period is from 10 weeks to 13 weeks 6 days, since it is technically difficult to determine this indicator at an earlier stage. After 14 weeks, the child’s lymphatic system copes with excess fluid, so the determination of TVP ceases to be informative.
- The CTE of the fetus should lie in the range from 45 to 84 mm.
- The study is carried out using a sagittal scan of the fetus.
An increase in this indicator indirectly indicates the possibility of a child having Down syndrome (trisomy 21 chromosomes - that is, instead of 46 chromosomes normally, the child has 47 chromosomes), which requires a more serious examination (prenatal karyotyping) to confirm or exclude the diagnosis. Standard indicators for the thickness of the nuchal translucency of the embryo/fetus depending on the gestational age are presented in Table 4.
During an ultrasound at 10-14 weeks, the following anatomical structures of the embryo/fetus are examined: bones of the calvarium, “butterfly” (ultrasound picture of the structure of the brain), spine, stomach, anterior abdominal wall (for the presence of intrauterine hernias), bladder, bones of the extremities. But at this time it is not always possible to exclude developmental defects, therefore, if deviations are detected, they are entered in the special notes column, and then, together with the obstetrician-gynecologist and, if necessary, geneticists, a decision is made on the need for a more in-depth examination.
During an ultrasound examination, extra-embryonic organs such as the yolk sac and chorion are also examined. The yolk sac is a provisional (temporarily existing) organ that exists until 12 weeks of pregnancy, is necessary for the early development of the embryo, after 12 weeks it ceases to exist, decreases in size and remains at the base of the umbilical cord. Its size (internal diameter) is important when diagnosing a non-developing pregnancy.
The chorion is the outer embryonic membrane covered with villi, which, together with the wall of the uterus, subsequently forms the placenta, thanks to which the fetus is nourished during pregnancy. Its localization gives an idea of the further localization of the placenta (which is necessary to know to determine pregnancy management tactics), and a change in thickness may indicate the presence of intrauterine infection of the embryo/fetus, Rh conflict, as well as malnutrition of the fetus, although this indicator is also more informative in late stages of pregnancy.
In addition, during the first screening ultrasound, structural features of the uterus (for example, bicornuate uterus, double uterus, saddle uterus) and its appendages (primarily the presence of ovarian cysts) are noted. These indicators are also important for determining further pregnancy management tactics.
If necessary, the ultrasound diagnostician notes in the protocol the date of repeated ultrasound control.
Symptoms
Pay attention to the shape of the skull. If it is narrow and long, the front and back protrude, and the sides are less wide than expected, this is dolichocephaly. Just a feature of development. It becomes a pathology if it physically interferes with the child or bothers the parents. The dolichocephalic head shape is a temporary phenomenon at an early age. Observe the child’s growth process; once every 3-6 months you can photograph the head from the front, top, side to objectively assess the changes. Lack of improvement is a sign of necessary correction of dolichocephaly.
The dolichocephalic head shape is characterized by deformation of the parietal and temporal bones with a convexity oriented in the opposite direction (inward), which can cause pressure on the cerebral cortex. Complications - horizontal strabismus, refractive errors of the eye (impaired image focusing: myopia or farsightedness, hearing loss).
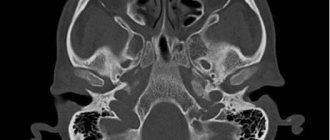
Early diagnosis is carried out by a pediatric neurologist, guided by visual criteria. Ultrasound and CT are used to clarify.
Can dolichocephaly be asymmetrical?
Characteristics of symmetrical (isolated) dolichocephaly: the cephalic index (calculated from the results of ultrasound, CT) deviates from the norm, but there is no asymmetry of the cranial vault, the shape of the head is elongated, there is a noticeable narrowing in the area of the parietal bones, the ears are not displaced.
Asymmetrical dolichocephaly is a combination of an elongated head shape with plagiocephaly, CI is not normal, there is asymmetry of the cranial vault when viewed from above (sloping in the area of the frontal and occipito-parietal bones), displacement of the ears.
Is it possible and how to independently assess the shape of a child’s skull?
Parents can focus on visual criteria and subjective assessment of neurological symptoms (with mild and moderate dolichocephaly it does not appear). Examine the child's head and take into account the diagnostic criteria. If you are not sure whether your baby has dolichocephaly, but notice a sloping area on the head, read this article to determine the type of deformity. There you will also find universal correction methods.
Hair often hides problematic head shape. If necessary, dampen and smooth them. Ask your child's permission before palpating or photographing the head to avoid any unpleasant feelings associated with the diagnostic process. Prepare something in advance for distraction: toys, pacifier, bottle, phone or tablet.
The difference in appearance between dolichocephalic, brachycephalic and mesocephalic (examples with photos)
The concepts of dolichocephaly (narrow and long head), brachycephaly (wide head) and mesocephaly (normal skull shape) are based on visual criteria and indicators of the cephalic index (ultrasound diagnostic achievement).
Cephalic or cranial index (CI) is the ratio of the width of the cerebral part (vault) of the skull to its length. You can calculate it yourself using data from the fetal ultrasound protocol or CT results. It is necessary to divide the biparietal size (BPR) by the fronto-occipital size (FOR) and multiply by 100. Compare the result with the values in the table below.
| Head shape | The value of the cephalic index |
| Ultralichocephaly | below 65 |
| Hyperdolichocephaly | 65+ |
| Dolichocephaly | 70+ |
| Mesocephaly | 75+ |
| Brachycephaly | 80+ |
| Hyperbrachycephaly | 85+ |
| Ultrabrachycephaly | 90+ |
Terms such as dolichocephaly and brachycephaly have multiple meanings. In medicine, they are used to classify anomalies associated with the development and structure of the skull; with their help, they can determine non-pathological features of the shape of the head, for example, in orthopedics and orthodontics. Dolichocephaly in racology is one of the signs for inclusion in a certain anthropological group.
If you see the term dolichocephalic head shape in the ultrasound report, it means the child has a long skull. The decision about the severity of this feature, the presence of pathologies in the fusion of cranial sutures and the need for correction is made after birth. Predictions can be made in advance only by the presence of pronounced developmental pathologies, by analyzing craniometric parameters (for example, cephalic index) or by the results of a genetic test.
Photos of children who were diagnosed with dolichocephaly in infancy.
Ultrasound interpretation by weeks of pregnancy
Details Category: Ultrasound in obstetrics and gynecology To determine the anatomical and functional state of the fetus during pregnancy, there are a number of methods, the most common of which is ultrasound .
In order to identify malformations and diseases, an ultrasound screening test (a universal rapid examination covering more than 85% of pregnant women). It allows you to make decisions about further tactics for managing each pregnancy, as well as to identify pregnant women at risk for developing various complications for the fetus and mother.
an ultrasound examination during the following screening periods of pregnancy:
- 10-14 weeks
- 20-24 weeks
- 32-34 weeks
How to correct the shape of your head?
The list of available treatment measures depends on the diagnosis, clinical picture and age of the child. The best results will be achieved when parents work together with the attending physician (neurologist, pediatrician, physiotherapist or orthopedist), but sometimes only the help of relatives is enough (if the deformity is not severe).
Correct positioning of the newborn
Ideally, a positioning program should be followed from the moment the baby is born. Main stages:
- loose clothing for newborns, which protects but allows free movement (to prevent dolichocephaly, it is necessary to ensure mobility of the head, neck, and arms);
- do not swaddle or cover the baby with a blanket (it is better to purchase a heated mat for the playpen);
- organize a place for games on a hard surface (hard mattress, educational play mat or regular carpet);
- encourage changing positions while lying and sitting, do not allow the child to lean on his back for a long time, unless there are medical indications;
- You can increase the comfort and safety of your child with the help of an orthopedic pillow and mattress (check with your doctor before purchasing);
- do not hang toys above your head, disperse them in several places to attract attention and provoke head movements (avoid stationary positions);
- Limit the time you use your highchair (only during meals) and car seat (only when traveling);
- if the child falls asleep in a position where there is pressure on the back of the head (a dense back or a hard surface), transfer him to the crib);
- alternate feeding positions, change the supporting hand during rocking.