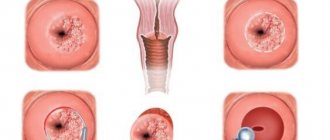
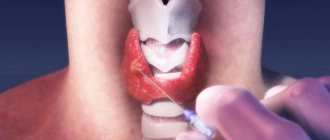
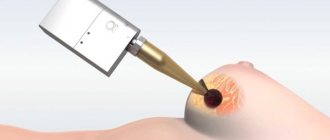
Endometrial aspiration biopsy, or Pipelle biopsy, is an easy-to-use, informative method of gynecological diagnostics that allows you to establish an accurate diagnosis and refrain from conducting more serious and painful studies. The procedure is considered minimally invasive and quick. The examination itself lasts no more than 5 minutes, the entire appointment takes up to 20 minutes. To collect the endometrium, the gynecologist uses a pipel - an instrument in the form of a plastic tube with a diameter of 3-4 mm with side holes and a piston. By pulling the piston, cells necessary for histological examination enter the tube.
Indications and contraindications
Endometrial aspiration biopsy is performed only as prescribed by a doctor. Such diagnostics can identify many different diseases. Most often it is prescribed for:
- Endometriosis.
- Infertility.
- Detection of polyps in the uterus.
- Endometrial hyperplasia (thickening of the mucous membrane) of the uterus.
- Unstable menstruation.
- Continuous bleeding after childbirth or abortion.
- Chronic endometritis.
- Miscarriage.
- Pathologies during menopause.
Pipelle biopsy will be indicated in preparation for in vitro fertilization (IVF). The results of the analysis will allow you to find out the condition of the endometrium before starting the use of hormones.
Contraindications to aspiration biopsy are: pregnancy at any stage, acute infectious and inflammatory diseases of the uterus and appendages, poor blood clotting (for example, hemophilia), severe cervical stenosis.
Why is an endometrial biopsy performed?
A biopsy is the removal of a tissue sample for subsequent examination in the laboratory.
Reference! The endometrium is the mucous membrane lining the uterine cavity. In case of fertilization, it takes part in the formation of the placenta. The thickness of the endometrium varies depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle. In the middle of the cycle, that is, the most favorable time for conception, it has the greatest thickness and increased blood supply. During menstruation, the old layer is shed, and then a new one grows.
The health of the endometrium affects the well-being of a woman’s sexual sphere – her normal sex life and ability to conceive.
Laboratory analysis of endometrial tissue allows us to diagnose:
- its pathological growth (hyperplasia);
- insufficient thickness (atrophy);
- endometritis (inflammatory process);
- endometriosis;
- precancerous conditions;
- endometrial cancer.
Typically, studies are histological or immunohistochemical in nature.
Reference! Histological analysis is the examination of a piece of tissue (biopsy) under a microscope to study its structure. The thinnest sections are made from the sample taken and stained with special substances. Using histology, it is possible to establish the type of tissue (for example, glandular, epithelial, muscle, stromal), the degree of change in its structure, as well as the type of tumor.
Immunohistochemistry is a more modern and differentiated technology. When using it, a tissue section is also performed, which is exposed to reagents. The method allows you to study the receptors of tissue cells, their sensitivity to hormones, as well as the activity of certain genes in them. Thanks to immunohistochemical analysis, it is possible to establish not only the tissue, but also the organ origin of cells. Also predict the rate of tumor growth, the body’s response to chemotherapy, and select hormonal drugs for treatment.
The doctor decides what type of research should be used, as both methods have their own characteristics and limitations.
Sometimes a bacteriological analysis is performed, thanks to which bacterial pathogens that provoke inflammation of the endometrium can be identified.
Diagnoses of “endometrial cancer” and “chronic endometritis”, “endometrial hyperplasia” can be established solely based on the results of histology or immunohistochemistry.
A sample of the endometrium is collected for laboratory testing using curettage or aspiration methods.
Reference! Aspiration is a procedure for removing suction from a cavity or pathological focus.
Aspiration biopsy is performed using a tube with a suction device (syringe or electric suction). Pipelle biopsy is an improved type of aspiration biopsy.
Benefits of the procedure
Experts highlight the following undeniable advantages of endometrial aspiration biopsy:
- Simplicity and painlessness.
- High information content.
- There is no need for general anesthesia.
- Atraumatic (uterine tissue is not damaged, the risk of inflammation is minimal).
- The ability to obtain material from hard-to-reach areas of the organ.
- It is performed without dilation of the cervix.
After endometrial aspiration biopsy, the patient can leave the clinic almost immediately.
How and when to perform aspiration biopsy
In most cases, aspiration biopsy is performed on an outpatient basis without the use of anesthesia.
The Peipel catheter, which is used to collect biomaterial, is a thin (2-4 mm in diameter) plastic tube with a piston, which is then removed, causing fragments of endometrial tissue to be drawn inward.
After receiving the biomaterial, it is immediately sent for histological examination.
It usually takes about 1 minute to aspirate a piece of endometrial tissue.
Preparation
Aspiration biopsy does not require lengthy or complex preparation. Before the examination, it is recommended to take a smear for vaginal microflora, standard blood tests, and undergo an ultrasound of the female genital organs. At the preliminary consultation, the gynecologist will definitely ask about all the medications the patient is taking. It is especially important to know if among them there are anticoagulants - medications that thin the blood. On the eve of the study, the specialist may cancel them. It is important to perform a pregnancy test before aspiration biopsy and make sure it is negative.
You should also keep a menstruation calendar and know the phase of the cycle, because the study can be scheduled for different periods. If chronic endometritis is suspected, the diagnostic procedure is carried out in phase 1 of the menstrual cycle (from the first day of menstruation until ovulation, while the egg matures). In all other cases, endometrial aspiration biopsy is performed any day.
It is recommended to abstain from sexual intercourse, use tampons, and limit physical activity for three days. It’s a good idea to stick to proper nutrition and maintain hydration.
Nuances of preparation
Before a pipel biopsy of endometrial tissue, the gynecologist must make sure that there is no acute inflammatory process in the patient’s genitals. This requires taking gynecological smears for infections. You should also consult your doctor about taking blood thinning medications before the procedure. The full list of preparatory measures includes:
- consultation and examination by an obstetrician-gynecologist;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- blood test for human immunodeficiency virus and syphilis;
- blood test for hepatitis B and C;
- clinical blood test;
- smear for genital infections;
- smear for cytology.
Sexual rest is required two to three days before the operation.
Features of the event
Aspiration biopsy is performed on an outpatient basis, in a specially equipped room. After the patient is placed on the gynecological chair, the doctor examines the vagina, then carefully inserts a special speculum, opening the cervix. Often, for a more comfortable examination, the cervix is treated with a local anesthetic solution. At this stage, proceed directly to the biopsy. Through the cervical canal, the tip of an instrument, a pipel, is inserted into the uterine cavity. In order to collect the endometrium, the piston is pulled back. It creates negative pressure, creates a vacuum, and tissue cells are released into the plastic tube. Carefully turning the pipel, the doctor removes it from the cervical canal. After this, the material is sent to the laboratory for histological examination. The duration of endometrial aspiration biopsy is about 20 minutes. Processing information and preparing a conclusion takes 1-2 weeks.
Research methodology
The gynecologist selects the date for pipell endometrial biopsy based on the presumptive diagnosis or problems that need to be solved. So, for example, to identify the causes of infertility, the study is carried out in the first half of the menstrual cycle, and in order to monitor the results of treatment - in the second. For patients who have already reached menopause, the test can be scheduled on any day.
Features of preparation
In order to identify contraindications to pipel biopsy and determine the woman’s general health, an examination by a gynecologist is required two weeks before the examination. Additionally, you may need to take a smear for microflora. If the analysis results reveal an infection, the vagina is sanitized and the smear is repeated. In addition, an ultrasound of the pelvic organs is often prescribed before the biopsy.
It is also important for the attending physician to know what medications the patient takes on a regular basis. If anticoagulants are used, the specialist may temporarily stop taking them a few days before the scheduled procedure. The use of hormonal medications is also excluded, as they can affect the condition of the endometrium.
The patient should begin to independently prepare for the biopsy 2-3 days before it is performed. During this time it is necessary:
- Maintain sexual rest.
- Do not use vaginal ointments, creams, or douche.
In the morning before the endometrial biopsy, careful hygiene of the external genitalia should be performed. The study is carried out with a full bladder, so you should refrain from going to the toilet immediately before the procedure.
Material collection
Pipelle endometrial biopsy can be performed in a gynecological office. It usually does not require pain relief. Most women report only discomfort or mild pain during material collection. In case of increased sensitivity, local anesthesia may be used.
After the patient has positioned herself on the gynecological chair, the doctor inserts gynecological speculum into the vagina and fixes the cervix. Next, a Peipel probe is placed into the cervical canal and carefully moved forward. When it reaches the required level, the doctor removes the piston, thereby creating negative pressure in the cylinder cavity. As a result, the endometrial tissue is drawn into the side opening of the probe. Biological material is collected from different places in order to obtain the most accurate result.
After aspiration of the mucous membrane tissue has been performed, the doctor carefully removes the device. The resulting material is applied to a sterile glass slide and sent for histological examination. The total duration of a pipel biopsy usually does not exceed 20 minutes.
Period after the procedure
After a pipel biopsy, women often feel satisfactory and there is no need for hospital observation. You may experience discomfort, similar to menstruation, for 24-48 hours after the procedure. In the first days, there may be various types of bleeding from the vagina. During this period, it is necessary to abstain from sexual intercourse. After 3-4 days, intimate relationships can be resumed, making sure to use contraception.
After aspiration biopsy of the endometrium, menstruation occurs on time or with a delay of up to 7-10 days. If the delay is longer, you should consult your gynecologist. It is also important to tell your doctor if you feel unwell in general, fever, dizziness or fainting.
Research results
If no pathology is detected, then the results of the study will indicate that the mucous layer corresponds to the phase of the female cycle and age, and no signs of atypia were found.
If we talk about pathological conditions, then diagnostics allows us to identify:
- Endometritis.
- Underdevelopment of the endometrium or its atrophy.
- Discrepancy between the thickness of the mucous layer of the uterus and the day of the cycle.
- Atypical endometrial hyperplasia.
- Hyperplasia (glandular-cystic or simple diffuse).
- Adenomatosis (precancerous condition).
- Degeneration of the endometrium into a malignant tumor.
Additional examinations are possible if any disease from the list above is detected. The doctor will talk about this in detail during the consultation. If the biopsy provides enough data to establish an accurate diagnosis, then treatment will be prescribed.
What is pipell endometrial biopsy?
Aspiration pipel biopsy of the endometrium is performed using a pipel-type probe. It is a hollow flexible silicone tube with a diameter of about 3 mm, at the end of which there is a hole. A piston is inserted on the opposite side.
To collect tissue, the doctor carefully inserts the probe into the uterine cavity and pulls back the piston. This creates negative pressure. The endometrium is stretched and enters the cavity of the tube, the contents of which are then sent to the laboratory.
A flexible, soft and thin tube provides the most delicate effect on the tissues of the genital organs, so aspiration performed using the “Pipel” is a painless and minimally invasive manipulation.
The procedure is prescribed:
- For bloody discharge during the intermenstrual period (acyclic bleeding).
- For bleeding in menopausal women.
- For pain during sexual intercourse.
- If ultrasound reveals endometrial pathology.
- For the diagnosis of infertility and miscarriage.
- To monitor the condition of the endometrium during hormonal therapy.
Pipel endometrial biopsy before IVF or when planning pregnancy is also included in the list of mandatory studies.
Advantages of the method
Pipelle endometrial biopsy is a minimally invasive and virtually painless procedure, in contrast to diagnostic cleaning, which is essentially a surgical intervention. Curettage is performed exclusively in a hospital using general anesthesia. After it, the woman needs to stay in the clinic for several hours, and if complications arise, for a day.
Pipelle aspiration biopsy of the endometrium is performed on an outpatient basis. The insertion of the probe does not require dilation of the cervical canal, is less traumatic and involves the use of local anesthesia. Due to the minimal invasiveness of the intervention, the risk of complications is minimized. The procedure, as a rule, does not affect the woman’s well-being, which allows the patient to leave the clinic immediately after the procedure.
In terms of its diagnostic value, the Pipelle biopsy technique is not inferior to curettage.
Pipel endometrial biopsy: interpretation of results
Histological examination of the endometrium is completed on average within a week.
Results of pipell biopsy of the endometrium during histological examination:
- The analysis may not reveal deviations from the age norm and cycle phase. This is a negative result, which means the woman is healthy.
- The study can diagnose pathological growth (hyperplasia) of the endometrium and determine its type.
Hyperplasia is a benign pathology caused by an excess of female sex hormones. Most cases (about 75%) occur during the premenomaus period.
Histology allows us to identify 4 types of hyperplasia:
- Simple diffuse or glandular.
- Complex (adenomatosis).
- Local, which means the presence of single polyps.
- Atypical, which is characterized by the presence of atypical cells.
Reference! Cells with a disrupted structure that do not correspond to their normal (typical) characteristics are called atypical. Atypia may be characterized by loss of polarity of arrangement and disruption of the structure of the nuclei.
Detection of cellular atypia is important for the prevention of endometrial cancer, since some of their types are capable of malignancy and are considered a precancerous condition.
- Endometrial cancer is diagnosed when malignant cells are detected.
- Histological examination may reveal insufficient thickness of the mucous membrane - atrophy or hypoplasia.
- Based on the results of the analysis, a diagnosis of endometritis can be made - an inflammatory process of the tissue lining the uterine cavity.
- The discrepancy between the thickness of the endometrium and the phase of the cycle during which the material was collected indicates hormonal disorders in the patient.
Possible complications
During aspiration biopsy, only sterile, disposable instruments are used. The procedure follows a standardized protocol in compliance with all aseptic rules. During the study, no surgical manipulations (incisions, sutures, etc.) occur. That is why the risk of complications is minimal. It is important to understand that the diagnosis does not affect the ovaries and their work, and does not affect future pregnancy.
Despite this, aspiration biopsy, like other medical procedures, has several unpleasant consequences. Typically, patients report moderate pain in the lower abdomen, slight discharge, sometimes mixed with blood, headache, and increased body temperature. Inflammatory processes rarely develop in the uterus and appendages.
Pipel biopsy is a proven and safe diagnostic method. The accuracy of determining pathology and various types of disorders is up to 90%. The resulting tests make it possible to assess the condition of the mucous membrane, identify malignant cells and the causes of disorders of the reproductive organs.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Indications for biopsy
Diagnostics may be recommended for the following diseases and conditions:
- too much menstrual flow;
- spotting outside of menstruation;
- cycle disorders;
- any endometrial neoplasms;
- infertility;
- miscarriage;
- adverse effects of hormonal therapy;
- bleeding during menopause;
- unsatisfactory condition after artificial termination of pregnancy (bleeding, pain, etc.);
- chronic endometritis;
- atrophic changes in the endometrium.