Determination methods and standards
Duration is measured through special tests. Most popular by:
- Sukharev;
- Duque;
- Lee White;
- Morawice.
In a hospital setting, it is possible to conduct any study in a short period of time. The clotting rate is different for each test.
Method according to Sukharev
Conducting a study related to the duration of bleeding according to Sukharev, you will need to take capillary blood. The required material is placed on the glass.
Special glass is used
Blood is taken from the glass for analysis until it thickens. The time is measured until the device can no longer draw blood. The normal value is 30 – 120 seconds.
Lee White method
For this study of the rate of bleeding control, venous blood is required. Enough material is taken to fill 3 test tubes. Preheated to body temperature (approximately 37 degrees). Place at an angle and evaluate the clotting time of all tubes. This method is used as an express method for assessing coagulability. Clotting of 1 ml of blood normally occurs in 5-7 minutes.
Morawitz method
The simplest method of determination is the Morawitz method. You will need laboratory glass, blood from your finger. The technique is simple: the blood is placed on a glass and the time is noted before it becomes coagulated. To determine the state of the coagulation system, the norm of bleeding duration is used. Each age has its own norm. It is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of a person when conducting an examination.
It is important to know! Blood type plays a role in the study. The coagulation of capillary and venous blood is different.
Duque method
The method involves piercing the earlobe. Bleeding is then assessed using filter paper. The time according to the Duque method ranges from 1 to 4 minutes - the normal value. If blood is present for more than 4 minutes, there are clotting problems.
No special tubes needed
When conducting research, a special puncture needle is required. Artificial bleeding must be spontaneous. Bleeding is considered to have stopped when no traces of blood are visible on the paper. Paper is applied every minute. The Duques bleeding assessment is a good way to get an accurate result.
Other methods
There are several ways to determine the duration of bleeding. We can distinguish: thrombin generation test, thrombodynamics, thromboelastography. Several methods can be used in research. This allows you to get a more accurate result.
When taking a coagulogram, you must adhere to all doctor’s instructions in order to get an accurate result.
General analysis
It is one of the basic tests required when visiting many specialists.
General analysis among specialists may also be referred to as “clinical”, or bear the abbreviation KLA. It is a whole set of tests aimed at determining both the quantity and parameters (size, etc.) of various blood cells.
The test allows blood sampling from both a vein and a finger (capillary).
Indications for use, preparation for the study
This is one of the most common laboratory tests performed to assess the general health of a patient. Prescribed for routine medical examinations, preparation for surgery, and included in the medical commission.
Symptoms for which a doctor may prescribe OAC: complaints of fatigue, weakness, apathy, signs of an infectious disease or inflammation, and elevated body temperature. A timely test allows you to diagnose and promptly treat a whole range of serious diseases.
The results of your analysis will be as reliable as possible if, before taking it, you:
- the day before your visit to the clinic, exclude alcohol and medications from your diet (in consultation with your doctor);
- You will not take it for 8 hours before the test (you can drink still water);
- Half an hour before donating blood, it is advisable not to overexert yourself physically and emotionally. Try not to smoke either.
General blood test indicators
The blood test includes a number of parameters. First of all, this is the calculation of the number of red blood cells (oxygen transport), leukocytes (ensure the fight against bacteria and viruses), platelets (blood clotting) per microliter or liter of blood. This also includes other indicators that describe the shape, volume and other characteristics of the cells being studied.
The basic table with blood sampling results includes:
- hemoglobin level
- hematocrit
- average red blood cell volume
- average hemoglobin content in an erythrocyte
- average hemoglobin concentration in erythrocytes
- platelets
- white blood cell count
- red blood cell count
In addition to basic indicators, the doctor may prescribe a leukocyte formula (the ratio of different forms of leukocytes as a percentage) and a calculation of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). Professionals call such a comprehensive study a “clinical blood test.”
Blood clotting indicators
In a detailed blood test, there are a number of indicators that play an important role and directly affect the duration of bleeding. Capillary and venous blood is suitable for laboratory research. The result must be interpreted by a doctor.
Clotting time
According to Sukharev, coagulation began in 30 seconds, and ended in 3-5 minutes. The norm for children is approximately the same as for adults. If the White method is used, venous blood should clot within 7 minutes. Exceeding the indicators is a deviation. If an abnormality is detected, diagnostics are required to determine the cause.
Duration
Length
The duration of bleeding according to Duque is no more than 4 minutes. The indicator should not exceed this value, regardless of the location of the puncture (ear, fingertip). The duration of bleeding is influenced by several factors. In healthy people, bleeding often stops within the first 2 minutes.
Prothrombin time
This indicator is detected by performing a coagulogram. Blood plasma is used. Prothrombin time should be approximately 11-16 seconds. It is important that the laboratory technician performs all steps correctly.
Partial active thromboplastin time
APTT is an indicator of the effectiveness of internal coagulation. The normal value is 25-39 seconds. This indicator is the norm for women and men.
Thrombin time
TV values determine the presence of deviations in the final stage of coagulation. Thrombin time refers to the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin under the influence of thrombin. The norm is considered to be 12-20 seconds.
Other indicators
Important indicators of the coagulogram are the number of platelets and fibrinogen. In adults, the platelet level is 150-400 g/l, in children - 150-350 g/l. The normal level of fibrinogen is 2-4 g/l.
Bleeding time
Bleeding time
- a test that characterizes, on the one hand, the elasticity of blood vessels and their ability to contract during injury, and on the other hand, the state of the platelet hemostasis system. It characterizes the functional activity of platelets and the interaction of platelets with the vascular wall. Bleeding time is assessed by the duration of bleeding after damage to the skin of a certain depth. Bleeding time can be measured in three ways: the template method, the Ivey method, or the Duque method. Bleeding time depends on the elasticity of the vascular wall, as well as on the number and functional activity of platelets.
Indications
Analysis of blood parameters is most important, since in a healthy person these indicators are relatively constant, any change in them is an indicator of changes in the human body.
Bleeding time is usually assessed if the patient shows clinical signs of impaired hemostasis. This study, in combination with platelet counts and other indicators of the blood coagulation system, is advisable to carry out as part of the preoperative examination.
Preparation
No special preparation required. It is recommended to take blood samples no earlier than 6–8 hours after your last meal. On the eve of the study, alcohol consumption, smoking, physical and emotional stress should be avoided.
If the patient is taking medications, you should consult with your doctor about the advisability of conducting a study while taking medications or the possibility of discontinuing it before the study; the duration of withdrawal is determined by the period of removal of the drug from the blood.
Interpretation of results
Units: min.sec
Normal bleeding time is:
- 3–6 min (SI: 3–6 min) using the template method;
- 3–6 min when assessed according to Ivey (SI: 3–6 min);
- 1–3 min (SI: 1–3 min) when assessed according to Duque.
Bleeding time according to Duque Indicators Norm (min):
- male indicators: 0–90 years: 2.0–4.0;
- female indicators: 0–90 years: 2.0–4.0;
- pregnancy 1–40 weeks: 2.0–4.0.
An increase in bleeding time is observed with:
- severe lack of platelets in the blood (thrombocytopenia of any origin);
- impaired platelet function, congenital or acquired;
- long-term use of certain medications (aspirin and other antiplatelet agents, some antibacterial agents, etc.);
- autoimmune diseases;
- vasculitis;
- DIC syndrome.
A decrease in bleeding time is observed with increased spasticity of the capillaries.
The essence of the main analyzes
Each method used reflects a different moment of coagulation. The essence of the indicators:
- platelet level - reflects the number of cells involved in starting the coagulation mechanism;
- TV - indicates how the last stage of coagulation proceeds;
- APTT - shows the ability of plasma coagulation factors to create a clot;
- coagulability according to White - reflects the ability of blood to form a clot.

Deciphering indicators on your own is problematic; you need to consult a specialist.
Deviations from the norm
Time may exceed normal values. Blood may clot too quickly. In this case, it is necessary to carry out diagnostics to determine the root cause. Deviations may be in favor of fast or slow clotting. Accelerated clotting may indicate intoxication, dehydration, autoimmune damage, or disruption of the endocrine system. Slow blood clotting occurs due to:
- cirrhosis;
- leukemia;
- lack of certain vitamins;
- hemophilia.
Normally, the bleeding time is approximately the same for all people, so the deviation is extremely easy to identify.
Duration of bleeding according to duka is normal
Bleeding time is the interval between the time tissue damage occurs and the blood flow stops. This indicator is quite important for absolutely all people, as it indicates the level of blood clotting.
Basic criteria for blood clotting
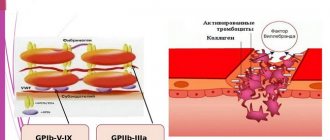
The duration of the bleeding process is directly affected by blood clotting. Thanks to this process, blood loss during wounds is prevented. Blood clotting is part of the work of hemostasis. Coagulation consists of primary hemostasis, hemocoagulation, coagulation, plasma hemostasis, secondary hemostasis.
Thanks to this process, the formation of strands of blood protein called fibrin is observed in the blood. It forms blood clots, which eliminates the possibility of blood flow and stops bleeding.
Bleeding disorders are affected by a variety of causes. In order to avoid undesirable consequences, you need to know the normal blood clotting time and compare it with your indicators.
In order to find out as accurately as possible the duration of bleeding in your body, you need to take a blood test called a coagulogram and hemostasiogram.
Thanks to the results of this comprehensive analysis, the presence of certain diseases in the patient is determined. Initially, a normal bleeding time is required, which ranges from 1 to 3 minutes. It takes 10 minutes for the bleeding process to complete.
You can find out the duration of bleeding as accurately as possible using a special analysis. For this purpose, you must contact a medical center.
Indicators
Interpretation of a blood test for coagulation
Bleeding and the speed at which it stops directly depends on certain indicators.
The rate of blood clotting directly depends on:
- Thrombosed time
- Bleeding time
- Clotting time
- Antithrombin 3
- Fibrinogen
The main indicator of the characteristics of the blood clotting process is thrombin time. Normally it should last from 14 to 21 seconds. This indicator directly depends on what methods of determining it are used. Antithrombin 3 is an indicator that affects the formation of the smallest number of blood clots. This is a regulator of the coagulation circulatory system.
The fibrinogen level should be from 2 to 4 g/l.
Thanks to this criterion, it is possible to characterize the functions of the blood coagulation system and determine the possibility of inflammatory processes in the body. It may be influenced by several medical factors.
Bleeding in an adult should last between 2 and 4 minutes. The level of blood clotting directly depends on its characteristics. A blood clot should form within 2-5 minutes. The faster it is formed, the sooner the bleeding will stop.