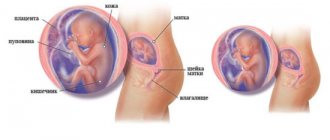
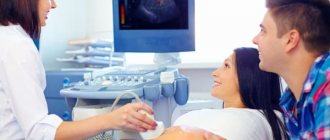
A pregnant woman can gain confidence in the health of her baby by undergoing a large number of examinations. They begin from the moment the pregnant woman is registered at the antenatal clinic and continue until childbirth. Doppler during pregnancy is prescribed when manifestations are detected that indicate the possible presence of abnormalities in the development of the fetus.
How the fetal heart is formed - the first contraction
Recent studies by German scientists have made it possible to understand how the heart of an embryo is formed and develops and why in the early stages the baby’s heartbeat can already be heard and even visually observed when examined using innovative technology. It is known that a hollow tube forms around the embryo in the fourth week of pregnancy, the purpose of which is to become the primary blood circulation.
Over the next week, a bend forms in the tube where the first contraction occurs, which will then be heard as the baby's heartbeat in the womb. Special cells are responsible for the formation of bends, which, joining the cells of the primary tube, “drag” them to the desired zone. The researchers found that this process depends on a chain of chemical reactions, and the tension of the tube tissue also plays an important role in the process of heart formation. Curls may not form if it is not large enough.
What happens next
Over time, the heart of an unborn child becomes more and more similar to the heart of an adult. By the sixth week, the interventricular septum forms and begins to grow, immediately followed by the interatrial septum. The fetal heart acquires an almost adult appearance by the eighth week of pregnancy.
It cannot be said that it is completely identical to an adult because oxygenated blood comes to the baby not from the lungs, but from the mother - at this time he is not yet breathing on his own, although the baby’s heartbeat is already clearly visible. At this stage, all the ventricles and atria function as a single hollow organ, and blood flows from one atrium to the other through the foramen ovale. This is what a special hole in the interatrial septum looks like. When the born baby takes his first independent breath, it will close immediately after birth.

What is Doppler ultrasound (USD) of the fetus?
The procedure is necessary to assess the condition of the fetus
and determine whether he is receiving enough oxygen. Based on the results of such a study, it will become clear whether there are any deviations and whether complications are possible during pregnancy.
Dopplerography in general is based on the fact that sound waves are reflected from moving objects in a completely different way than from stationary ones. Blood is a heterogeneous mixture of plasma and cells that are in constant motion, due to which the Doppler effect is applicable to them. Ultrasound scanning during pregnancy allows you to determine at what speed the blood moves through the vessels, what is the direction of its movement, as well as how intense the blood flow is. These indicators allow us to judge the size of the blood vessel and its diameter.
When to start measuring your heart rate
A baby's heartbeat during pregnancy at 6 weeks occurs at a frequency of 60 beats per minute. At this point, it consists of four hollow chambers with separate entrances and exits for the passage of blood. After two weeks, the baby’s heart rate increases sharply and can reach 150 beats in 60 seconds. This figure is considered normal, despite the fact that it is twice as high as that of the mother herself. The baby's heart rate is very high during pregnancy at 9–10 weeks - the little man's heart beats at a frequency of 170 beats per minute.
From the 35th day of pregnancy, the baby’s heart manifests itself through contraction. Its heartbeats are also detected earlier in a woman’s pregnancy. Answering the question at what time a child’s heartbeat can be measured, experts note that this is possible at the first appointment. Using an ultrasound with a conventional sensor - at 5 weeks, vaginal - at 3-4.

Why take heart rate measurements?
In the early stages of pregnancy, the baby’s heartbeat is practically the only indicator that gestation is proceeding according to the established algorithm without deviations or anomalies. Therefore, the sooner a woman registers for pregnancy, the sooner the gynecologist will be able to correlate the existing norms regarding the child’s heartbeat by week with the real situation in a particular woman. This will make it possible to diagnose serious congenital defects in the early stages, adjust the lifestyle and habits of the pregnant woman, and, if necessary, prescribe the necessary treatment. It was found that at the beginning of the 5th week the heart rate was 80-85 beats per minute. Subsequently, the correspondence looks like this:
| Gestation period (weeks) | Heart rate (beats/minutes) |
| 5 | 80–103 |
| 6 | 103–126 |
| 7 | 126–149 |
| 8 | 149–172 |
| 9 | 155–195 |
| 10 | 161–179; |
| 11 | 153–177 |
| 12 | 150–174 |
| 13 | 147–171 |
| 14 | 146–168 |
| Second-third trimester, before birth | 140–160 |
What deviations exist
Knowing the normative indicators of the child’s heart rate in accordance with the stage of pregnancy, it is easier for the doctor to begin treating diseases indicated by deviations from the norm. They can be associated with both a sharp decrease and an increase in the frequency of contractions. Depending on this, the fetus is determined:
- bradycardia - a deviation from the norm in the direction of decreasing the child’s heart rate below 100 and especially below 80 beats per minute, provided that the pulse is non-monotonic, rhythmic, can be corrected with medication and does not threaten the life of the fetus;
- tachycardia - a stable heartbeat of 170-200 beats per 60 seconds, does not threaten the life of the fetus, but if the situation worsens, it may require early delivery;
- monotonous heartbeat - inconstancy of the pulse depending on the phases of activity and rest, may indicate fetal hypoxia and requires the appointment of ultrasound with Dopplerometry.

Step-by-step online program for pregnant women
Prepare for childbirth online - on your own or with 24/7 support from specialists
- Yoga for every trimester
- Breathing during childbirth
- Meditation and relaxation techniques
- Video lectures on preparing for childbirth
- Nutrition program
- Consultations with experts
- Useful articles and books
- Psychological support
Get started now! First 7 days free
Causes of heart rhythm disturbances
In each case, when a child’s heart rate is abnormal, there are a number of reasons that cause them. So in case of bradycardia they can include:
- Rhesus conflict;
- multiple pregnancy.
- bad habits, deficiency of vitamins, fresh air;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- stress;
- umbilical cord entanglement;
- chronic heart and lung diseases of the mother;
- infectious diseases;
- high and low water levels;
- taking certain medications;
- dehydration due to prolonged toxicosis;
- premature placental abruption.
The reasons that cause tachycardia in a child’s heartbeat include:
avitaminosis;
- dehydration caused by prolonged toxicosis;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- maternal blood loss;
- taking certain medications;
- maternal heart and vascular disease;
- intrauterine infection.
There are also congenital heart pathologies in a child, which are diagnosed with concomitant developmental delays.
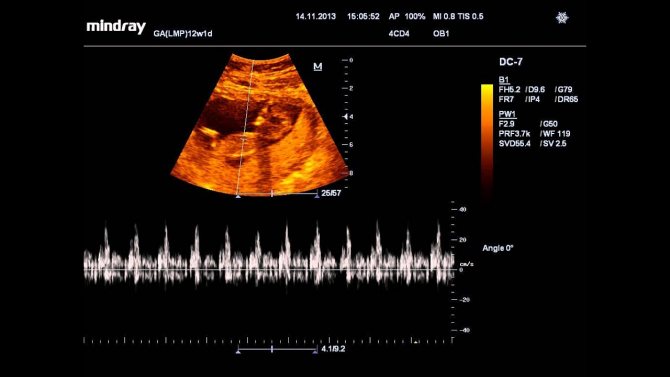
Congenital heart pathologies
If, in the event of disturbances in the child’s heartbeat, the doctor notes a lag from standard development indicators, this may be evidence of the development of a heart defect in the unborn baby. In this case, echocardiography or ultrasound of the little person’s heart is suggested - this study is usually done at 18-28 weeks of pregnancy. Worth going through
Echo-CG, including pregnant women from the “risk group”, who, for various reasons, have an increased likelihood of developing heart disease in the fetus:
- if a defect is suspected during an ultrasound scan of the fetus;
- over 40 years old;
- suffering from diabetes mellitus;
- those who have had infectious diseases during pregnancy;
- with congenital heart defects;
- who have already given birth to children with congenital heart defects.
Timely identification of possible pathologies will allow you to choose the appropriate method of delivery, as well as provide the child with appropriate assistance immediately after his birth.
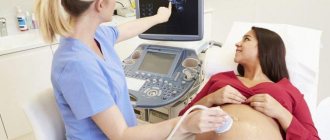
When are pregnant women prescribed Doppler ultrasound of the fetus?
Carrying out ultrasound examination during pregnancy has certain norms and deadlines. Diagnosis is possible from 16 to 20 weeks of pregnancy - at this time the placenta is already formed. The examination is included in the screening program in the third trimester of pregnancy - 30-34 weeks. Sometimes the procedure can be scheduled a little earlier, at 20-24 weeks.
Arterial hypertension
During pregnancy, Doppler may be prescribed if high blood pressure is detected. This phenomenon in itself is extremely undesirable, since it can threaten the health of both the expectant mother and the baby. Delayed diagnosis can cause the development of failure of the cardiac and renal systems, strokes, heart attacks, and vision disorders.
Threat of miscarriage or premature birth
Premature birth and termination of pregnancy are the most dangerous conditions, since a woman can lose her child. This can be prevented by ultrasound examination during pregnancy (what it is was said above) and assessment of the state of the blood supply to the placenta and blood vessels as a whole, as well as the doctor’s decision-making based on the receipt of the necessary information.
High degree anemia
Anemia is caused by low iron levels in the blood, as a result of which red blood cells cannot cope with providing oxygen to tissues. In this case, an ultrasound scan is necessary to examine the fetus.
and identifying the baby’s health status. The child will first suffer from an acute lack of oxygen. If we are talking about grade 2 anemia, its treatment should be immediate and carried out exclusively in a hospital setting.
Large uterine fibroids
During pregnancy, an ultrasound scan may be prescribed due to the fact that uterine fibroids have been identified. The neoplasm itself is benign and does not pose a threat to the life and health of the woman and fetus. The danger is that fibroids can begin to collapse at any time, and pregnancy provokes an increase in the nodes. However, in many patients, pregnancy in the presence of small fibroids proceeds normally.
Infection of the genital area
Ultrasound scanning of the fetus is extremely necessary when detecting infectious diseases. Such infections can provoke various developmental abnormalities, so careful monitoring of the health of both the woman and the fetus is necessary.
Methods for measuring heart rate - ultrasound
There are many proven methods for listening to the heartbeat of a child in a pregnant woman. They are performed at different stages of pregnancy and can be performed not only to determine the frequency and rhythm of the baby’s heartbeat, but also for other purposes determined by the doctor. These include, first of all, the most popular and frequently used – ultrasound.
Ultrasound examination is performed from the first to the fifth month of pregnancy. In the early stages, the examination is carried out transvaginally - through the vagina, in a later period through the abdominal wall - transabdominally. During pregnancy, 3 ultrasounds are required. At the very first ultrasound study, heart contractions are determined, at the second, the heart chambers are examined to exclude defects or other pathologies, and at the third, you can find out the sex of the child.
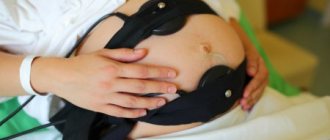
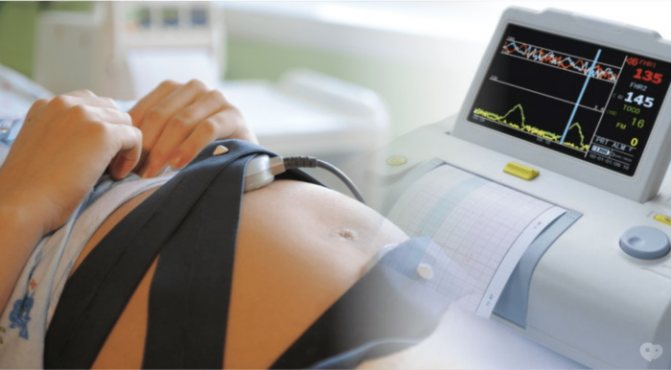
CTG (cardiotocography) and auscultation
To determine the child’s heartbeat, cardiotocography is also used - registration and analysis of heart function in various conditions - during movement, in its absence, under the influence of various stimuli and uterine contractions. The method makes it possible to determine oxygen deficiency, when it exists, which is dangerous by reducing the adaptive capabilities of the body, slowing development and growth, and other pathologies.
Auscultation is used to listen to heart sounds with a stethoscope through the abdominal wall of a pregnant woman. The procedure is carried out during visits to the gynecologist, as well as during childbirth with an interval of 20 minutes to monitor the baby’s condition and determine the position of the fetus. Head presentation is diagnosed when the baby's heartbeat is below the mother's navel, transverse - when the heartbeat is level with the navel, above the navel - evidence of breech presentation.
Preparing for the study
It is necessary not only to find out the norms of Doppler ultrasound during pregnancy
, but also decide how to prepare for the procedure. It is worth knowing that there is no need to carry out any special preparatory procedures - just sign up for a diagnosis and come to the doctor. The only thing worth taking care of is having a napkin with which you can remove the remaining gel after the diagnosis is completed. Doppler ultrasound examination is not much different from a regular ultrasound examination; the doctor will simply conduct the scan in two modes.
Ways to hear the fetal heartbeat yourself
You don’t have to wait until your next doctor’s visit to hear the beating of a little heart. There are ways to listen to your baby's heartbeat yourself using, for example, a stethoscope. The device is inexpensive, but you will need an assistant to listen. It will also be difficult to hear the sound of the heartbeat before the 25th week. It is important not to confuse the heartbeat with the baby’s movements and the mother’s peristalsis. They also use a fetal doppler - a fairly expensive portable device with headphones that allows you to listen to the baby’s heartbeat as early as 8-12 weeks; it is not advisable to use it frequently and do sessions lasting longer than 10 minutes. It is possible to listen to the heartbeat by placing your ear up. Starting from the 30th week, the baby’s heartbeats become pronounced. They can be recognized simply by listening to the belly of the expectant mother.