23.09.2019 17332 0
What do pediatricians around the world agree on?
Excerpts from the “National Program for Optimizing Feeding of Children in the First Year of Life”
Breast-feeding
Mixed feeding
Artificial feeding
Regime and norms of nutrition for newborns
Formation of metabolism
The future health, physical and mental development of a newborn child depends on the nutritional status of a newborn child. While still pregnant, the mother, choosing a nutritious and varied diet for herself, had a beneficial effect on the development of the fetus and, of course, after its birth, she is ready to take care of the optimal diet and nutrition regimen for her baby. Medical scientists have conducted a number of studies to identify the relationship between nutrition in infancy and health status in adulthood in different population groups. As a result, the “Concept of Metabolic Programming” was formed and accepted by the medical community. Otherwise called the “Food Programming Concept”.
The beginning of a child's life and breastfeeding
Immediately after birth, the baby is put to the breast. This is very important for breastfeeding the baby and the psychological birth connection with the mother. In this case, usually the mother immediately begins to secrete milk to feed the baby.
Breast milk contains all the essential nutrients, enzymes, proteins and vitamins required for the growth and development of the baby. Breastfeeding is a sterile type of feeding, since mother's milk does not need to be sterilized, disinfected, or boiled. A woman simply needs to observe strict personal hygiene and safety rules when feeding. And the task of relatives and friends is to provide the nursing mother with nutritious, healthy food.
If a nursing mother drinks a sufficient amount of liquid per day in the form of water, milk, fermented milk drinks, natural juices, vegetable broths and berry fruit drinks, then there will be no problems with the availability of breast milk. But you need to be careful when choosing drinks and not drink drinks that can cause allergies in your baby.
The usual fluid intake is about 2 - 2.5 liters per day, and more is possible in the hot season. It is important to monitor the reactions of the baby's stool, the condition of his (her) skin and the presence of gases in the intestines to identify possible allergic reactions and intolerance by the body.
The baby is breastfed every 3-4 hours. This will be influenced by how much milk the nursing mother has and the baby’s health condition. Thus, you get 6 - 7 feedings per day.
Should you feed your baby at night?
You should approach this issue individually. Children's doctors and nutritionists recommend taking a 5-6 hour break at night. But not every child can withstand such a lack of food. And often children just want to be closer to their mother’s body, because they were in her womb for 9 months and they need to psychologically get used to such “loneliness.”
Should I give water to my baby?
Until 2 months, the baby is not given water, as it is contained in a sufficient amount of mother's breast milk.
Then the baby can be given water in small quantities, especially if this age coincides with the hot season, approximately 1 - 3 sips of the child. Water should not be sweetened with sugar.
What should you not eat while breastfeeding?
- Mom should not drink carbonated drinks, onions, garlic, strong tea and coffee. If you love coffee a lot, replace it with weak cocoa and milk in a small amount.
- You should be careful with chocolate and citrus fruits - they can cause allergic reactions.
- You should not eat smoked or spicy foods.
- You should stop smoking, drinking alcohol and taking medications. Consult your doctor when using medications. Alcohol can be replaced with children's vegetable and fruit juices. Experiment with them as cocktails. You will definitely love it!
Artificial nutrition
The stores have a large assortment of dry and liquid specialized formulas for ages from 0 to one year.
You should carefully read the information on the product. This is the composition, expiration date, method of use, recommended age of the child.
Formula for a child under 6 months should be as close in composition to breast milk as possible. The number 1 will be indicated on the packaging of such a mixture.
Be sure to check the integrity of the packaging.
How to calculate the serving dose for one feeding?
- First week - multiply the baby's age by 10.
- Subsequent weeks - the baby's weight is divided by 5 and also by the number of feedings.
- A month old baby approximately needs about 90 g of the finished mixture.
- Be sure to consult your pediatrician.
If the mixture causes a reaction in the form of gastrointestinal disorders, such as diarrhea, constipation or allergies - rash, spots on the body, you should change the mixture to another, more suitable one.
Sometimes a child eats very poorly and, for no apparent reason, refuses one type of formula in favor of another. Take these features into account. In cases where the child is not gaining weight well, you should also consult a doctor and change the type of infant formula.
The frequency of feedings remains the same as with natural feeding.
A bottle-fed baby should be given boiled water to drink. If the tap water is of poor quality and is in doubt, it is better to buy bottled water or order it from special companies.
Remember the rules of hygiene, cleanliness of dishes and the shelf life of uneaten formula. It should be stored in the refrigerator for no more than 6 hours, and it is better to throw it away immediately.
If the baby is not full, then you can supplement it, but if this happens often, then you need to consult a doctor. You may need to undergo appropriate tests to identify the cause.
Each children's clinic in big cities has its own children's kitchen, and you can use it by contacting your pediatrician.
What should not be done when bottle feeding a baby?
- Feed your baby cow's or goat's milk.
- Forcefully “stuff” the prescribed single portion into it or feed it after 15 – 30 minutes. Don't get used to disordered eating.
- Leave her alone with the bottle and go about her business. The baby may choke on food from the bottle.
- Allow air to get in instead of the mixture when feeding. Make sure the nipple is always filled with formula.
- Feed formula that is too hot or cold. The baby may get burned or get sick.
- If a child vigorously turns his head with his mouth open when you pick him up and cries at the same time, it means he (she) is hungry and nothing bad will happen if you sometimes break the strict feeding hours.
If your child spits up frequently and a lot, you can feed him/her an anti-reflux formula. If the digestion of the mixture is impaired, it is better to use fermented milk mixtures and mixtures containing beneficial bacteria. Consult your doctor!
Features of the nutrition of a bottle-fed child
Artificial feeding (IF), unlike breastfeeding, requires more accurate calculations, because formula is more difficult to digest than breast milk, so too much can lead to problems with the child’s gastrointestinal tract. But even such a task is feasible for a young mother.
We recommend: How to choose sweet corporate gifts for children?
Diet and feeding time
This is the most important component of proper care for an artificial baby.

For the proper development of an artificial child, you need to follow a diet
A child under 2 months should eat 8-9 times with a break of 2.5-3 hours, at 2-3 months - 7-8 times, at 4 months - 6-7 times, at 5-6 months - 5-6 times , and from 7 months to a year - from 4 to 6 times a day. In this case, one feeding will last no more than 15 minutes, because drinking from a nipple is much easier than sucking the breast.
Nutritional standards for IV
As a rule, manufacturers of mixtures indicate doses and norms on the packaging. But it still doesn’t hurt to know the average, approximate data.
Table of nutritional norms for children from 10 days to one year
| Age | Amount of mixture eaten per day |
| 10 days - 1.5 months | 1/5 of the child’s weight, 700–750 ml |
| 1.5 months - 4 months | 1/6 weight, 750–800 ml |
| 4 months – 6 months | 1/7 weight, 800–900 ml |
| 6 months – 8 months | 1/8 weight, 1000–1100 ml |
| 8 months – 12 months | 1/9 weight, 1000–1100 ml |
How many grams are in a daily and single dose and how to calculate them?
The amount of mixture can be calculated using the formula: weight/amount of daily dose depending on weight = daily dose of mixture in ml, daily dose divided by the number of feedings = single dose.

Cans of formula must indicate the norms for children of different ages.
This is interesting. The most popular calculation formula for a daily and single dose of formula for children on IV is called the Geibener and Cherny method.
For example, a baby weighs 4,850 grams. He is 2 months old, which means he should consume 1/6 of his body weight per day. Accordingly, 4850/6, we get a daily dose of 808 ml. We divide this amount by the number of feedings, we get a single dose - 135 ml. Another example: a newborn weighs 4,000 grams, eat 1/5 of its weight, it turns out that the daily dose is 800 ml, and a single dose is 100 ml.
Methods for calculating the amount of formula for children from 10 days to a month
In the first month, the baby is just beginning to adapt to the new diet. Therefore, the calculation of the amount of mixture is slightly different from that described above. There are two ways.
- Use Zaitseva's formula. We multiply 2% of body weight at birth by days of age, which gives the daily dose. We divide the result obtained by the number of feedings, which is equal to the volume of a single dose.
- Use the Finkelstein formula. If the baby weighed less than 3,200 grams at birth, then multiply the age in days by 70, the resulting value will be the daily dose. If the birth weight was more than 3,200 grams, then to obtain the daily norm, the age in days must be multiplied by 80.
In both cases, to determine a single dose, the daily dose must be divided by the number of feedings.
We recommend: Kefir for infants and children under one year of age
How many feedings does a 400 gram jar of formula last?
Again, these calculations will be approximate, since it all depends on how much your baby weighs and how many times a day you feed him. In addition, the older the child, the more he eats. On average, up to 2 months, 1 jar is required for 5–6 days; 5 jars are used per month. At 3-4 months, 1 can will last for 3-4 days, which means 7.5 cans will be needed per month.
Mixed feeding
Sometimes a baby receives mother's milk, but due to insufficient quantity from the mother, it has to be supplemented with artificial nutrition.
How to determine whether a baby has enough breast milk?
- If the child constantly cries and does not gain weight. You can check this by weighing yourself before and after breastfeeding for several feedings.
- You can also monitor the number of urinations. There should be at least 11 times a day. Use diapers or diapers to check the quantity.
With mixed feeding, the baby is first offered one breast. And then the second one. If the baby constantly shows anxiety and begins to ask for the breast almost immediately after feeding or an hour later, then he needs to be supplemented with formula. It is better to supplement feeding from a baby spoon or syringe, rather than from a bottle, to avoid the baby getting used to feeding with a nipple.
Take your time to do this every time. You need to know that lactation in a nursing mother can vary depending on her health status, food intake and overload.
You can go back to only natural breastfeeding if you monitor the number of urinations (you can count wet diapers 2 times a week), weigh the baby and just monitor his well-being.
In 1 month, the child gains about 400 - 1200 g of weight and grows by about 3 - 3.5 centimeters.
The second month is not much different from the first. The baby can be put to the breast more often during one feeding. The child’s weight increases by approximately 400 g - 2 kg per month, and height by 6 - 8 cm from the moment of birth.
Nutritional features of a breastfed baby
Breastfeeding (BF) is a natural continuation of the mother-child bond, which allows the baby to more easily cope with the stress of birth. But in the new world, the baby needs to learn everything, including numbers and eat (for this you need to develop a sucking reflex). So it’s not surprising that a new mother worries whether her baby is full.
First feeding
Colostrum, or the first portions of mother's milk, is a real treasure trove of nutrients for the baby. Good health and well-coordinated functioning of the baby’s immune system largely depends on the huge amount of vitamins, well-digestible proteins and antioxidants contained in colostrum.

The first feedings are important for the rest of the little person’s life.
This is interesting. The volume of a newborn's stomach is about 12 ml.
You can't overeat colostrum. At the first meal, the baby eats about 8 ml. Considering that the number of feedings per day is usually about 12 times, in total the newborn will eat approximately 100 ml of liquid. Every day the daily norm will increase by 10 grams.
Table of nutritional norms for a child 2–4 days of life
| Age (in days) | Amount of milk consumed at a time, ml | Amount of milk per day, ml |
| 2 | 20 | 210–220 |
| 3 | 30 | 300 |
| 4 | 40 | 400–440 |
There is another option for calculating the amount eaten. It requires a mathematical solution to the equation X x 10 = ml per single meal, where X is the age, that is, the days of the child’s life. For example, a newborn on the 7th day after birth should eat about 70 ml of breast milk at a time.
We recommend: How to choose organic products?
Table of nutritional norms for a child from 2 weeks of life to one year
| Age | Amount of milk consumed at a time, ml | Amount of milk consumed per day |
| 2 weeks | 60–90 | 20% of the baby’s body weight |
| 1 month | 100–110 | 600 ml |
| 2 months | 120–150 | 800 ml |
| 3 months | 150–180 | 1/6 baby's body weight |
| 4 months | 180–210 | 1/6 baby's body weight |
| 5–6 months | 210–240 | 1/7 of the baby’s body weight (800–1000 ml) |
| 7–12 months | 210–240 | 1/8–1/9 mass baby theme |
Feeding standards are given taking into account WHO recommendations, according to which complementary foods (vegetable, fruit purees, dairy-free porridge, etc.) are introduced into the child’s diet from 6 months.

Feeding standards are developed taking into account the introduction of complementary foods from six months of age
Please note that these figures are approximate, so a difference of plus or minus 5-10 grams is not significant. But what is really important is the interval between feedings. At first it should be no more than 2 hours. Then the intervals will increase, as the little one will suck more intensely, that is, receive more fluid. Improving the sucking reflex will lead to the fact that feeding time will decrease.
How to determine the amount of milk that needs to be consumed (depending on the child’s weight)?
So, numbers are a good thing, but many mothers will definitely have an absolutely logical question: how can you find out how much your child has eaten?
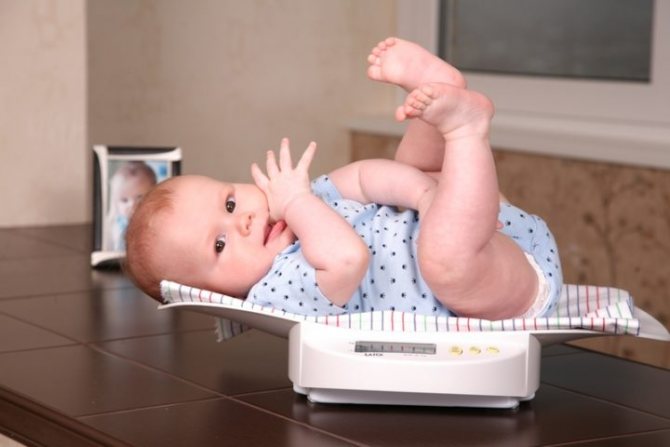

The easiest way to find out how much your baby has eaten is to weigh your toddler before and after meals.
To do this, you can weigh the baby before and after feeding. The difference will be the desired value. To calculate the daily intake, you need to add up all the feeding results obtained over 24 hours. This method is suitable for both natural and artificial scientists.
How long to keep a baby at the breast?
On average, the baby stays at the breast every 2-3 hours. How long should food intake last? Breastfeeding experts say about 30–40 minutes, unless the baby releases the breast earlier. By the way, feeding for 15–20 minutes is not a deviation from the norm if the child is gaining weight well and is not capricious. But staying “on the chest” for more than 40 minutes indicates that the baby is using the nipple as a pacifier, that is, playing. In the future, this can create a lot of inconvenience for both mother and baby, so it is better not to indulge in such entertainment.
Video. Dr. Komarovsky: the best feeding regimen for a newborn
Third month
This is a critical month in the sense that many parents begin to panic that the baby is hungry and only breast milk will not be enough for him. If the baby is breastfed, do not start feeding the baby if the baby is developing well and gaining the required weight!
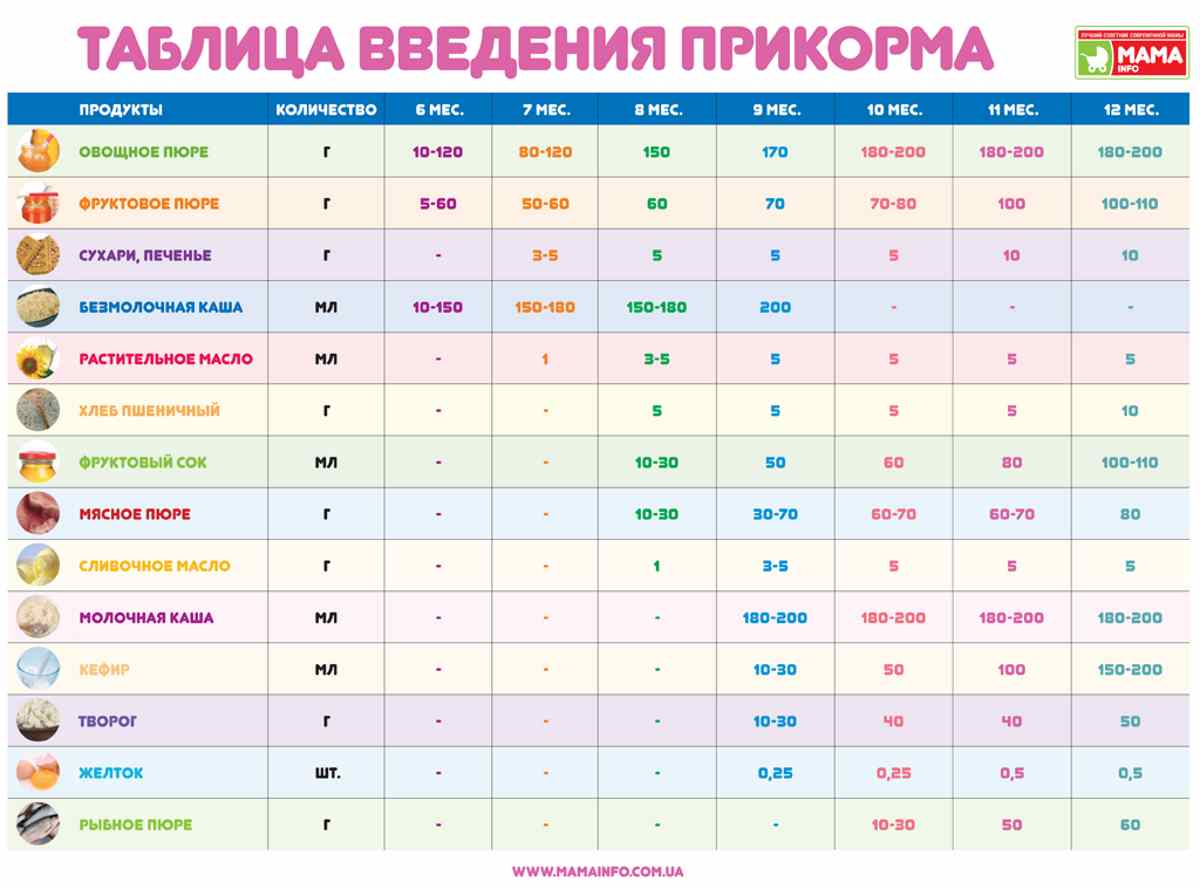
During this period, the baby’s body is still vulnerable, since its gastrointestinal tract is not sufficiently protected. Your worries are in vain and groundless about the lack of vitamins and nutrients found only in breast milk!
Weight increases by approximately 2200 - 2400 g, height by 8.5 - 9 cm from the moment of birth or 500 - 1300 g and by 3 - 3.5 cm per month.
Fourth month
You can give your child a few drops of fruit or berry juice diluted with water or breast milk. If your pediatrician is against innovations in your baby’s diet, you should listen to his recommendations. Below you can see the amount of complementary foods introduced to your baby. Those infants who are fed breast milk do not need to be given formula milk! Remember also that sugar should not be added to food or water until the baby is one year old. Salt can only be added from the age of 1.5 years.
Norms of consumed dishes:
Product | Quantity |
Formula milk | 700 ml |
Fruit juice | 40–50 ml |
Fruit puree | 40–50 g |
Vegetable puree | 150 g |
At 4 - 4.5 months you can start giving vegetable puree. Purees should have a uniform consistency, without hard lumps. What is recommended to make puree from: broccoli, cauliflower, zucchini. Gradually increase the portion.
| First day | 5 g |
| Second day | 10 g |
| The third day | 15 g |
| Fourth day | 20 g |
| Fifth day | 50 g |
| Sixth day | 100 g |
| Seventh day | 150 g |
Weight increases by approximately 2900 - 3000 g, height by 10 - 11 cm from the moment of birth or 500 - 1300 g and by 2 - 3 cm per month.
How to determine when it's time to introduce complementary foods
The development of each baby up to one year is an individual process, so it is impossible to determine a single age for introducing complementary foods. What to focus on? The presence of at least half of the signs listed below indicates that it is time to try to diversify your diet:
- He opens his mouth when a spoon with food is brought to his mouth;
- Holds head;
- During feeding, she can sit in a special high chair on her own;
- Closes the mouth when a spoon with food is in the mouth;
- Swallows food himself;
- Shows that he is not hungry (turns away).
Fifth month
Add apple, banana, pear puree. You need to refrain from berry purees. We introduce each new fruit or vegetable at intervals of 7–10 days and carefully monitor the reaction of the stool and the color of the skin. It is too early to give porridge to breastfed infants.
Table of norms for babies receiving formula instead of breast milk:
| Eating | Products and dishes |
| First | Adapted mixture |
| Second | Porridge up to 150 g |
| Third | Vegetable puree up to 120 g and 1 g vegetable oil |
| Fourth | Fruit puree up to 30 g and adapted mixture |
| Fifth | Adapted mixture |
For babies receiving mixed food with breast milk, the portion is as follows:
| Eating | Products and dishes |
| First | Mom's milk |
| Second | Porridge up to 150 g |
| Third | Vegetable puree up to 120 g and 1 g vegetable oil |
| Fourth | Fruit puree up to 30 g and mother's milk |
| Fifth | Mom's milk |
Do not be tempted to switch to a mixed diet from natural if you have breast milk and the baby is developing normally. He may develop gastrointestinal disorders, and there is a risk of becoming overweight.
Meanwhile, the weight increased by about 2 times, and the height by 13 - 15 cm from the moment of birth or by 300 - 1200 g and 2 - 3 cm per month
Nutrition at 9-12 months
By this point, the child should be familiar with all the products recommended in the table (porridge, fruits, vegetables, fermented milk, meat, baked goods). The nutrition of children under one year old still has its own characteristics:
- Cooking is done only by boiling or steaming. Fried and baked foods are not recommended for children under one year of age; it is best to give them only from 3 years of age;
- The use of spices, starch or other additives is prohibited;
- Shredded food should still take place;
- You may need to wait before introducing some foods to your baby. These include citrus fruits, nuts, exotic fruits, and so on, since there is a high probability of developing allergies. Sweets are also contraindicated until one year of age;
- During the first year of life, meals must be five times a day.
Feeding a child up to one year is something that must be approached with great responsibility. You should always remember that every child develops differently, so it is impossible to develop universal standards that must be strictly followed. Here is a table that contains only recommendations, but not an exact calculation. After introducing any new product, you should carefully monitor the body’s reaction, because something may not be at all suitable for an individual child.
Sixth month
Hooray! My favorite porridge for breakfast! Porridge can be cooked from oatmeal, rice, buckwheat. You need to start cooking porridge in water, gradually adding milk to the water after 7 - 10 days, increasing the amount. Monitor your baby's stool reaction and skin condition!
Avoid ready-made, store-bought cereals. It will be better if you buy full-fledged cereals, and then grind the cereal in a coffee grinder and cook the porridge. You can also grind the finished porridge to the desired consistency. This will be much healthier for your baby, since such porridge contains more fiber and nutrients needed by the intestines.
From 6 months we add to the diet a quarter of the yolk, a hard-boiled egg, diluted with vegetable broth or breast milk.
Add boiled potatoes, carrots, and pumpkin to the vegetable puree. Combine vegetables according to your baby's taste. Food will be much healthier if the vegetables are freshly prepared yourself, but if you have problems with cooking, you should buy ready-made products in the store. This is better than if the baby is left without any vegetable puree at all.
For breastfed children, the diet is presented below.
| Eating | Products and dishes |
| First | Mom's milk |
| Second | Porridge up to 150 g |
| Third | Vegetable puree up to 100 g |
| Fourth | Fruit puree up to 30 g and mother's milk |
| Fifth | Mom's milk |
For mixed-fed babies, food consumption standards are as follows:
| Eating | Products and dishes |
| First | Mom's milk |
| Second | Porridge up to 180 g and butter up to 1 g |
| Third | Vegetable puree up to 120 g and vegetable oil up to 3 g |
| Fourth | Fruit puree up to 60 g and mother's milk |
| Fifth | Mom's milk |
Artificial feeding:
| Eating | Products and dishes |
| First | Adapted mixture |
| Second | Porridge up to 180 g and butter up to 1 g |
| Third | Vegetable puree up to 120 g and vegetable oil up to 3 g |
| Fourth | Fruit puree up to 60 g and adapted mixture |
| Fifth | Adapted mixture |
Weight increases by 300 - 1000 g per month, height by 16 - 17 cm from the moment of birth.
Seventh month
The child actively moves and explores the world around him. He needs more calories and healthy nutrients. Many children love semolina porridge. Don't deny them this pleasure! If the child tolerates cow's milk well, porridge can be cooked entirely in milk.
The baby's first teeth appear and he begins to actively try everything “by the tooth”, and take into his mouth everything that catches his eye. You can give your child some crackers to try. Children enjoy gnawing on homemade crackers, the main thing is not to get carried away with this delicacy!
It's time to introduce butter and vegetable oil in small quantities into baby food. Monitor your baby's stool reactions and skin condition.
The new product, cottage cheese, will be very useful for the child and is vital for teeth growth.
For children who are breast-fed and mixed-fed, the diet will be as follows:
| Eating | Products and dishes |
| First | Mom's milk |
| Second | Porridge up to 200 g with mixture or cow's milk, butter up to 5 g |
| Third | Vegetable puree up to 150 g, vegetable oil up to 3 g, a quarter of chicken yolk, fruit juice up to 30 ml |
| Fourth | Fruit puree up to 60 g, cottage cheese up to 30 g, baby cookies or crackers, mother's milk |
| Fifth | Mom's milk |
Diet of dishes during artificial feeding:
| Eating | Products and dishes |
| First | Adapted mixture |
| Second | Porridge up to 200 g with mixture or cow's milk, butter up to 5 g |
| Third | Vegetable puree up to 150 g, vegetable oil up to 3 g, a quarter of chicken yolk, fruit juice up to 30 ml |
| Fourth | Fruit puree up to 60 g, cottage cheese up to 30 g, baby cookies or crackers, adapted mixture |
| Fifth | Adapted mixture |
Many doctors recommend introducing kefir into the child’s diet at this age. You can start by trying to dilute cottage cheese with kefir and look at the reactions of the baby's stool. And only then give kefir as a separate type of food. But if a child is prone to gastrointestinal disorders, this should not be done. You need to take an individual approach to introducing this product into the diet, after consulting with your baby’s pediatrician.
Over the 7th month, the child gains weight by 200 - 1000 g and grows by approximately 1.5 - 2.5 cm.
Eighth month
Give me some bread! I want meat!
You can add green peas to vegetable puree in small doses, carefully monitoring your stool and the presence of gases in the intestines. If in doubt, it is better to consult a doctor before introducing a new product into your diet.
The baby spends a lot of time actively awake by 8 months, and some children begin to take their first steps while holding onto support.
Proteins are simply necessary for a growing body at this age.
Meat is a new product for a baby of this age. Use lean meats - chicken, veal, young lamb, rabbit meat.
You can make boiled berry fruit drinks and compotes from berries such as lingonberries, currants, blueberries, blueberries, cherries, and plums.
Introduce one type of selected berries into the diet, carefully observing the child’s stool and intestinal reaction.
The optimal diet for breastfeeding (natural) feeding from birth:
| Eating | Products and dishes |
| First | Mom's milk |
| Second | Porridge up to 180 g, butter up to 1 g |
| Third | Vegetable puree up to 150 g, vegetable oil up to 3 g, meat puree up to 30 g, a slice of wheat bread, fruit juice up to 30 ml |
| Fourth | Fruit puree up to 60 g, cookies or crackers, mother's milk |
| Fifth | Mom's milk |
The diet of a baby with mixed feeding (complementary feeding began at 4–5 months) is as follows:
| Eating | Products and dishes |
| First | Mom's milk |
| Second | Porridge up to 200 g with cow's milk, butter up to 5 g, half a chicken yolk |
| Third | Vegetable puree up to 170 g, vegetable oil up to 5 g, meat puree up to 30 g, a slice of wheat bread, fruit juice up to 50 ml |
| Fourth | Fruit puree up to 70 g, cottage cheese up to 30 g, children's cookies or crackers, fermented milk drink up to 150 ml |
| Fifth | Mom's milk |
Portion norms for artificial feeding from the beginning of birth:
| Eating | Products and dishes |
| First | Adapted mixture |
| Second | Porridge up to 200 g with cow's milk, butter up to 5 g, half a chicken yolk |
| Third | Vegetable puree up to 170 g, vegetable oil up to 5 g, meat puree up to 30 g, a slice of wheat bread, fruit juice up to 50 ml |
| Fourth | Fruit puree up to 70 g, cottage cheese up to 30 g, children's cookies or crackers, fermented milk drink up to 150 ml |
| Fifth | Adapted mixture |
Weight can increase by 200-800 g in a month, and height can change by 1.% - 2 cm.
Ninth month
You can add beets to vegetable puree - they are very useful for the baby’s growing body. Also, you can mix cottage cheese with vegetable or fruit puree. Under no circumstances should a child be given fried foods intended for adults!
You can leave only 2 breastfeedings, but if there is enough milk and the baby asks for breastfeeding, you should not always replace the fourth feeding with a fermented milk product or yogurt.
And it is best to leave three breastfeedings at this age for the health and development of the baby. Therefore, you can exchange fruit juice for breast milk and give it for the fourth feeding.
Optimal food intake for breastfeeding from birth and for babies receiving complementary foods from 4 to 5 months:
| Eating | Products and dishes |
| First | Mom's milk |
| Second | Porridge with milk up to 200 g, butter up to 5 g, half a chicken yolk, fruit puree 40 g |
| Third | Vegetable puree up to 180 g, vegetable oil up to 5 g, meat puree up to 50 g, a slice of wheat bread, fruit juice up to 70 ml |
| Fourth | Fruit puree up to 40 g, cottage cheese up to 40 g, children's cookies or crackers, fermented milk drink up to 200 ml |
| Fifth | Mom's milk |
Table of norms for artificial feeding:
| Eating | Products and dishes |
| First | Adapted mixture |
| Second | Porridge with milk up to 200 g, butter up to 5 g, half a chicken yolk, fruit puree 40 g |
| Third | Vegetable puree up to 180 g, vegetable oil up to 5 g, meat puree up to 50 g, a slice of wheat bread, fruit juice up to 70 ml |
| Fourth | Fruit puree up to 40 g, cottage cheese up to 40 g, children's cookies or crackers, fermented milk drink up to 200 ml |
| Fifth | Adapted mixture |
By the end of the ninth month, the baby’s weight increases by 100–800 g, and growth by 1.5–2 cm per month.
Lure
At about six months of age, the baby's energy and nutritional needs begin to exceed the level at which they can be met by breast milk, and the introduction of complementary feeding becomes necessary. At this age, the child is ready to eat other foods and is developmentally ready. Not introducing complementary foods after the baby reaches six months of age or inappropriately introducing complementary foods can affect the baby's growth. The guidelines for proper complementary feeding are as follows:
- continue frequent, on-demand breastfeeding until the child is two years of age or older;
- Be sensitive when feeding your baby (for example, directly feed infants and assist older children. Feed slowly and patiently, encourage but not force, talk to your baby and maintain eye contact);
- practice good hygiene and proper food handling;
- Start at six months with small amounts of foods and gradually increase as the baby gets older;
- gradually increase the consistency of food and make it more varied;
- Increase the number of times your baby feeds - 2-3 times a day for children aged 6-8 months and 3-4 times a day for children aged 9-23 months, with 1-2 additional snacks as desired;
- Use fortified foods or vitamin and mineral supplements for complementary feeding as needed; And
- increase fluid intake, including through breastfeeding, and offer soft, favorite foods.
Tenth month
Low-fat varieties of fish are introduced into the crumbs' diet. Pollock, hake, trout, pike perch, carp, flounder. Fish puree should be given starting with half a teaspoon, observing the reaction of the stool and skin.
It is better to use ready-made fish baby food purchased in the store. Or cook it yourself by dipping the fish fillet in boiling water and boiling it well enough and checking in advance for the absence of fish bones, being sure that the product is fresh and 100% environmentally friendly.
Remember that the child already consumes significantly more drinking water, since he moves a lot and his food at this age is quite varied.
You can offer your child a berry such as a raspberry. Fruit juice and compote in combination with other berries will be a tasty treat for him. Do not give whole raw berries - at this age the health risk is not justified.
Product standards for a 10 month old baby:
| Product | Quantity |
| Vegetable puree | 200 g |
| Dairy-free or milk porridge | 200 g |
| Fruit puree | 110 g |
| Vegetable oil | 6 g |
| Butter | 5 g |
| Fruit juice | 110 ml |
| Rusk, cookies | 10 g |
| Wheat bread | 10 g |
| Meat | 80 g |
| Cottage cheese | 50 g |
| Yolk | 1/2 |
| Dairy products | 200 ml |
| Fish | 50 g |
Portions for breastfeeding (or complementary feeding from 4 to 5 months) are presented below:
| Eating | Products and dishes |
| First | Mom's milk |
| Second | Porridge without milk or with milk up to 200 g, butter up to 5 g, fruit puree 50 g, half an yolk, fruit juice 50 ml |
| Third | Vegetable puree or soup up to 200 g, vegetable oil up to 6 g, meat puree up to 80 g (fish puree up to 50 g twice a week), a piece of wheat bread 10 g, fruit juice 60 ml |
| Fourth | Fruit puree 60 g, cottage cheese up to 50 g, 2 cookies or crackers, kefir or yogurt up to 200 ml |
| Fifth | Mom's milk |
Artificial feeding method:
| Eating | Products and dishes |
| First | Adapted mixture |
| Second | Porridge without milk or with milk up to 200 g, butter up to 5 g, fruit puree 50 g, half an yolk, fruit juice 50 ml |
| Third | Vegetable puree or soup up to 200 g, vegetable oil up to 6 g, meat puree up to 80 g (fish puree up to 50 g twice a week), a piece of wheat bread 10 g, fruit juice 60 ml |
| Fourth | Fruit puree 60 g, cottage cheese up to 50 g, 2 cookies or crackers, kefir or yogurt up to 200 ml |
| Fifth | Adapted or fermented milk mixture |
In the tenth month, weight will increase by approximately 100–800 g, and height by 1 cm.
Nutrition for children under one year old by month: recommendations, tables, recipes.

One of the most exciting moments in a mother's life is carrying a baby and subsequently caring for him. To prevent problems associated with dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract and the development of allergic reactions, it is necessary to establish proper nutrition for children under one year of age by month.
Table of contents
|
From day one to 16 weeks
During spontaneous childbirth, the newborn baby is immediately applied to the mother's breast.
The baby receives the first drops of breast milk, called colostrum.
After four days, the mother begins to produce mature milk.
During childbirth complicated by medical intervention, the baby is applied for 30 minutes. to the mother's breast to stimulate milk production, then the baby is taken to the box.
The baby is returned to his mother, rested and recovered from anesthesia, after some time.
Breastfeeding children
With good lactation of the mother, the baby can eat only breast milk until the moment when it is no longer saturated with it, usually up to 6 full months.
Feeding occurs on demand, even at night, which does not overload the baby’s gastrointestinal tract.
If the baby is weakened and does not suck well, the woman needs to pump and bottle feed him.
During the period of producing breast milk and feeding the baby with it, a woman must adhere to the following rules:
• receive a balanced diet along with a complex of vitamins and minerals;
• maintain water regime;
• exclude harmful substances and products that cause flatulence.
According to established traditions, many mothers give their baby boiled water and herbal teas between feedings.
According to pediatricians, including Komarovsky, it is not recommended to additionally feed a child with other liquids, except in cases of unnatural fluid loss.
Mixed and artificial feeding
In case of weak lactation, when the secreted breast milk does not cover the baby’s needs, he is additionally fed with formulas (supplementary feeding), using the so-called mixed nutrition.
Useful tips for mothers: NUTRITION BY MONTH
In the complete absence of lactation, adapted milk formulas are used; such nutrition is called artificial.
Such children need to establish a feeding schedule and give formula at certain hours.
Organization of nutrition for children when feeding formulas
| Age | Number of feedings | Mixture volume, ml. |
| First week | 7-10 | 700 |
| Up to 8 weeks | 7-8 | 750 |
| Up to 16 weeks | 6-7 | 800 |
It is imperative to follow the rule of the temperature regime of the prepared mixture, which cannot be higher than the baby’s body temperature.
Nutrition from 17 weeks
Additionally, other food introduced, in mashed form, with the gradual replacement of one dose of breast milk or formula is called complementary feeding.
Pediatricians do not have a consensus on at what age an infant should change their diet.
The gradual inclusion of semi-solid foods is advisable from 17 weeks if the baby expresses a desire to try it or shows signs of hunger.
It should be remembered that in fact, the child’s digestive system will only be fully formed by the age of 2, and an early transition to semi-solid nutrition can cause deviations in the gastrointestinal tract.
Useful tips for mothers: Recipes for children under one year old
Characteristics of the beginning of complementary feeding according to Komarovsky:
• ambiguity of opinion regarding the introduction of semi-solid foods into the diet;
• the optimal period is 6 months of age;
• the feasibility of changing the diet at 4 months. not proven;
• interference with the diet of a four-month-old child up to 17 weeks is strictly excluded;
• doubling of the baby's weight from birth;
• ability to sit independently;
• the child may show interest in the food offered or refuse it.
According to WHO recommendations, the introduction of semi-solid food to infants aged 17 weeks and older is more of a psychological nature, since the child’s body does not fully assimilate pureed and digested food.
Psychological aspect of introducing complementary foods:
• introducing the baby to new food;
• activation of enzymes;
• formation of persistent reflexes of swallowing and chewing;
• interest in a new type of food;
• establishing adequate behavior in relation to food.
Recommendations of the Union of Pediatricians of the Russian Federation on the timing of introduction and names of complementary feeding dishes by month
| Product characteristics | Name | Administration period, months. |
| Cellulose | Fruit and vegetable juices | 4 |
| Cellulose | Fruit puree | 4-6 |
| Slow carbohydrates | Porridge | 6 |
| Cellulose | One-component vegetable purees | 5.5 |
| Cellulose | Multicomponent vegetable purees | 7 |
| Animal protein | Lean meat puree | 7.2 |
| Animal protein and calcium | Whole cow's milk | Not recommended at 1 year of age |
| Fermented milk product | Kefir | 6.9 |
| Protein | Cottage cheese | 6.5 |
| Lecithin, trace elements | Boiled egg yolk | 6.5 |
| Animal protein and fats | Fish | 7.5 |
| To improve metabolism and stimulate appetite | Meat broths | 7 |
Feeding a child by month to one year is a joint task of the mother and pediatricians, because it is impossible to calculate the size and start of introducing semi-solid food due to the individuality of each baby.
Nutrition from 17 to 24 weeks
Based on the recommendations of the Union of Pediatricians of the Russian Federation and established traditions in some families, changes in diet begin from the 17th week of the child’s body for the following reasons:
• underweight or overweight of the child;
• disorders of digestive functions;
• established diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia;
• meeting the needs for energy and vitamin-mineral complexes;
• the child's possible readiness to accept complementary foods.
The main meal is the consumption of breast milk, formula or mixed nutrition.
It is better not to give complementary foods to children with hereditary allergic reactions at this age.
First semi-solid foods:
• vegetable (carrot) puree is recommended to be included in the diet of children suffering from constipation and excess weight;
• fruit puree;
• fruit and vegetable juices.
Rules for first feeding:
• the first complementary feeding is ¼ teaspoon, in two weeks it is brought up to the norm of 30 grams;
• all complementary foods are introduced gradually with a slight regular increase;
• food should be at room temperature;
• it is unacceptable to introduce two different products at once;
• it is necessary to skip complementary feeding when the child is vaccinated, sick or moves;
• complementary feeding is best done between 10 and 12 noon;
• observe changes in color and surface of the skin, if there is redness, swelling, or a rash on the skin, stop introducing complementary foods and inform the pediatrician;
• monitor changes in stool, if there is a strong odor, pieces of mucus, changes in color, or the child is restless, stop complementary feeding and notify the pediatrician;
• overweight children are offered vegetable purees;
• For underweight children, complementary foods are given on a grain or milk-grain basis.
On the recommendation of the pediatrician, give the child multivitamin complexes.
Feeding babies from 6 months of age
If the child has taken food in the form of purees well since 17 weeks, then by six months the baby already has a full volume of one feeding in his diet, replacing breastfeeding or taking formula.
The volume of one serving is 100-150 g. If complementary feeding is being done for the first time, then it is necessary to use the recommendations from the paragraph on the nutrition of a child aged 17 to 24 weeks.
For children on artificial nutrition, the formula is replaced with one suitable for an older baby.
It is better not to change the manufacturer of the mixture.
Nutrition for babies over 29 weeks
When the baby turns 7 months old, a serving of porridge and fruit, ground into puree, making up a full meal is 150 grams.
The introduction of meat dishes prepared from lean meat and multi-component vegetable purees begins.
Food mashed with a fork is gradually introduced into the diet.
Nutrition for babies over 33 weeks
From the age of eight months, purees mashed on a coarse grater are introduced, and the reflex of pushing out food with the tongue fades.
During this period, the child is allowed to consume fish-based complementary foods containing essential amino acids and iodine.
Try to avoid food that can enter the child's respiratory tract - these are pieces of solid food from fresh apples, root vegetables, cookies, nuts, etc.
Feeding babies over 37 weeks
When the baby turns 9 months old, a serving of porridge and fruit puree for 2 full meals is 150-180 grams.
Dishes made from finely chopped raw fruits and cooked foods are introduced.
The size of the pieces is at least 1 cm, but not more than 2 cm.
The pieces are colorfully laid out on a plate in front of the child to arouse his interest and desire to grab the food.
Fermented milk products are introduced: kefir, yogurt, cottage cheese, etc.
Feeding babies from 41 weeks of age
At 10 months, the child should concentrate on food; try not to feed him, distracting his attention with the help of cartoons.
During this period, it is better to create a varied nutrition menu and stick to it. To maintain interest in food, it is worth arranging food on the plate in an unusual way.
The baby's menu consists of porridge, pounded meat or fish, cottage cheese, yogurt and fruit purees.
Nutrition for babies aged 45 to 52 weeks
By the age of one year, the child can already eat regular food along with all family members, with some exceptions:
• limited amount of salt in prepared dishes;
• exclusion of spices from the composition of dishes;
• do not give foods made only from fatty foods.
• all cooked products must be chopped or crushed;
• boiled meat is ground in a blender or minced in a meat grinder;
• careful inclusion of cubes of fruit, boiled potatoes and vegetables.
Physiological restrictions:
• the first and last feeding should not strain the gastrointestinal tract (breast milk, formula, kefir);
• stomach capacity is approximately 200 ml;
• in between meals, give the baby liquids: breast if desired, boiled water, weak tea, weak compotes.
It must be remembered that tea polyphenols interfere with the absorption of iron.
Every time you include a new dish in your baby’s diet, you must persistently invite him to try it, and only then give it as a full meal.
Menu for a child taking into account the daily needs of 12 months
| Characteristics of complementary feeding products | Mode |
| Light food | Early morning breakfast |
| — Slow carbohydrates — Fiber — Lecithin, microelements | Breakfast |
| To improve metabolic processes and abundant secretion of gastric juice: - Fiber, fast carbohydrates - Animal protein - Fiber | Dinner |
| — Protein — Fiber, fast carbohydrates | Afternoon snack |
| — Fiber — Light food | Dinner |
| Light food | Late dinner |
Proper nutrition of children from month to year allows you to shape the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract system without deviations and not strain the internal organs.
The psychological aspect is also important - establishing a diet and developing an interest in healthy food.
- about the author
- Recent publications
Svetlana Ovechkina
author of the publication (site editor)
TEACHER Higher pedagogical education. Director of the kindergarten.
Svetlana Ovechkina recently published (see all)
- Turkey as a first complementary food - 01/14/2021
- 7 month old baby’s daily routine – 03/28/2019
- Chocolate during breastfeeding - 03/25/2019
Eleventh month
The portions are quite varied, age allows you to combine products:
- You can cook jelly from berries and compote from dried fruits.
- Make a casserole from cottage cheese and vegetable puree.
- Mix cottage cheese or yogurt with vegetable or fruit puree.
Breastfeeding is done 2 times a day: in the morning and before bedtime. Do not deprive yourself and your baby of emotional communication and immune support.
A table for breastfeeding from birth or mixed nutrition (+ receiving complementary foods from 4 to 5 months) is presented below.
| Eating | Products and dishes |
| First | Mom's milk |
| Second | Porridge (dairy or dairy-free) up to 200 g, butter up to 5 g, fruit puree 50 g, half an yolk, fruit juice 50 ml |
| Third | Vegetable soup or vegetable puree up to 200 g, vegetable oil up to 6 g, meat puree up to 80 g (fish puree up to 60 g twice a week), wheat bread 10 g, fruit juice 60 ml |
| Fourth | Fruit puree 60 g, cottage cheese up to 50 g, 2-3 crackers or baby cookies, fermented milk drink up to 200 ml |
| Fifth | Mom's milk |
Artificial feeding:
| Eating | Products and dishes |
| First | Adapted mixture |
| Second | Porridge (dairy or dairy-free) up to 200 g, butter up to 5 g, fruit puree 50 g, half an yolk, fruit juice 50 ml |
| Third | Vegetable soup or vegetable puree up to 200 g, vegetable oil up to 6 g, meat puree up to 80 g (fish puree up to 60 g twice a week), wheat bread 10 g, fruit juice 60 ml |
| Fourth | Fruit puree 60 g, cottage cheese up to 50 g, 2-3 crackers or baby cookies, fermented milk drink up to 200 ml |
| Fifth | Adapted or fermented milk mixture |
By the end of the 11th month, weight will increase by approximately 100 - 500 g, while growth will increase by 1 cm per month.