Most people become interested in leptin when they are diagnosed with chronic inflammation or an autoimmune disease. What is leptin and how does it affect health? The article has a lot of useful information about leptin.
The article is based on the findings of 75 scientific studies
The article quotes authors such as:
- Center National de la Recherche Scientifique, Lille, France
- Department of Neurosurgery and Physiology, University of California, Los Angeles School of Medicine, USA
- Department of Internal Medicine and Molecular and Integrative Physiology, University of Michigan, USA
Please note that the letters in brackets (1, 2, 3, etc.) are clickable links to peer-reviewed scientific studies. You can follow these links and read the original source of information for the article.
What is leptin?
Leptin is produced primarily by the body's fat cells . Scientists call it a “satiety hormone,” which can influence body weight reduction. It is also often called the “obesity hormone.” And finally, it is called the “hunger hormone.”
Initial studies hyped leptin's purported weight loss effects, but further research showed that leptin is not the diet pill everyone was looking for. There are no clinical studies that support the anti-fat effects of leptin. ()
Research shows that leptin levels increase with increased energy reserves, food intake, and glucose uptake, while they decrease with increasing age and exercise.
In fact, leptin levels increase exponentially , rather than linearly, with increasing body fat mass . This means that increasing body weight can cause leptin levels to rise dramatically. Fat cells secrete more than 50 different hormones and signaling molecules. ()
Functions of leptin
Leptin was initially known to be secreted by adipose tissue and to circulate at levels directly proportional to total body fat. ()
However, it is now considered a multifunctional hormone that is produced by various tissues and organs, including the placenta (), kidneys (), salivary glands () and stomach. ()
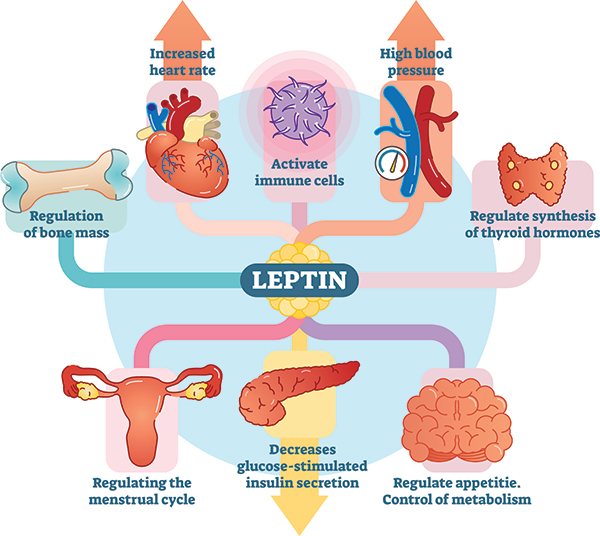
Some people think that leptin is one of the 4 important hormones that determine weight. However, no research supports such a simplistic approach, since many hormones and factors are involved in the management of body weight.
Leptin is synthesized in adipose tissue, and its receptors are found in highest concentrations in the hypothalamus and hippocampus of the brain. ()
Recent theories suggest that the more fat we have in our bodies, the more leptin we produce. Some scientists argue that leptin is released into the blood and travels to the brain, where it sends a satiety signal to the hypothalamus. There, it tells the brain that we have enough fat stored, that we don't need to eat, and that we can burn calories at a normal rate. However, this is still considered a hypothesis and has not been clinically confirmed. (, )
In some studies, long-term elevated leptin levels have been associated with obesity, overeating, and inflammatory diseases, including hypertension, metabolic syndrome, and heart disease. () However, a cause-and-effect relationship has not been established.
Other theories suggest that leptin resistance may contribute to hardening of the arteries and the development of atherosclerosis. These theories are still controversial. ()
The Link Between Leptin and Weight Gain
Normally, leptin reduces the feeling of hunger, promotes weight loss, fat breakdown, and glycogen accumulation. It is one of the important regulators of eating behavior. Its amount in the body directly depends on the volume of adipose tissue.
With obesity, there is more of the hormone in the blood than required, but resistance to it occurs. As a result, there is no inhibitory effect on appetite, which leads to accelerated weight gain and an even greater increase in fat cells. In patients with leptin resistance, external administration of the hormone does not change fat metabolism. The exception is obesity, which is associated with a mutation in the gene responsible for its synthesis.
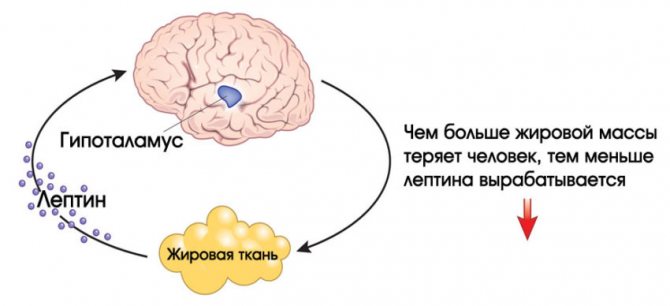
An interesting feature is that in the absence of an effect on weight loss, leptin can provoke excessive activity of the sympathetic nervous system. This is one of the reasons for the development of hypertension and tachycardia in obesity. This phenomenon is explained by the fact that with leptin resistance, the hormone cannot cross the blood-brain barrier of the brain, but its peripheral effects persist.
Normal leptin levels
Leptin levels can be measured using a blood test. Results are usually reported as a unit of measurement - ng/ml (nanograms per milliliter).
Normal Leptin Levels
are in the range of
4.7 – 23.7 ng/ml,
although they may vary slightly between laboratories. These values may also depend on the person's age, gender and time of day when the test was taken.
- Time of day : Leptin levels may be higher at night than during the day. ()
- Gender : Women have higher leptin levels than men. ()
Research shows that the level of leptin circulating in the blood is directly proportional to the amount of fat in the body, and that it can change depending on food intake. (,, )
A leptin test is usually ordered for overweight/obese people, especially if they have a family history of obesity. It may also be useful for an obese person who has symptoms of frequent, constant hunger.
Sometimes leptin levels are tested along with other tests, such as overall thyroid health, glucose levels, cholesterol and insulin. This list of tests can help determine the health status of an overweight/obese person and identify causes that may contribute to or impair the health of such people.
How does leptin work?
In this section, we'll dive deeper into the science of leptin. Research on the hormone leptin is still in its early stages, and none of the results listed below are due to the use of leptin medications. The scientific findings below focus on the potential of naturally occurring leptin in the human body.
If you are concerned about your leptin levels or increased weight, consult your doctor.
Food and energy consumption
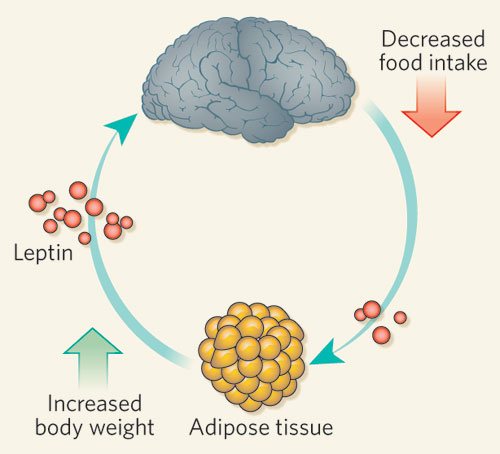
When people lose weight (lose weight), leptin levels typically fall , the digestive system is activated, and food intake typically increases. ()
According to one hypothesis, this may be due to the fact that losing weight imitates a state of moderate hunger , and the body tries to fight it by stimulating food cravings. The same thing happens during long-term or intermittent fasting. ()
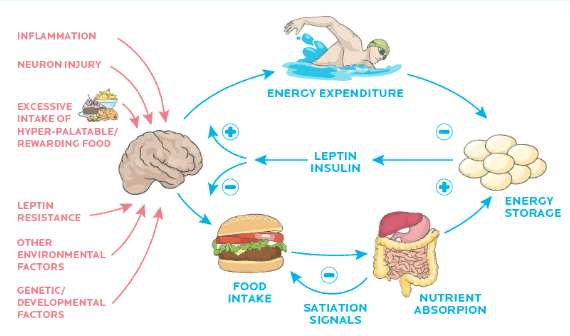
Reasons and ways to increase (red arrows) and decrease (blue arrows) leptin levels.
On the other hand, the more fat cells a person has and the more weight they gain, the more likely they are to have elevated leptin levels. Only 5-10% of obese people are diagnosed with leptin deficiency. ()
Scientists say that the body usually interprets an increase in the number of fat cells as a state of abundance, but at this time leptin resistance develops and its signals no longer affect the brain. The body continues to require energy from food beyond measure.()
To back up this theory, some scientists believe that obesity can also increase the fight-or-flight response (producing the hormone cortisol) as the body tries to get out of the dangerously long “overeat and rest” phase. Scientists say high leptin levels are intended to facilitate weight loss in such cases. However, these theories remain clinically unproven.
Body weight management
Let us remember that leptin is one of the 4 hormones that determine weight. It is produced in adipose tissue, while its receptors are located in greater numbers in two important areas of the brain (hypothalamus and hippocampus). ()
Leptin acts as a signal to the brain to suppress the desire to consume food and ensure that excess calories are stored (in fat cells).
At the same time, it protects lean tissue from being overloaded with fat. Elevated leptin levels are associated with increased body fat mass, increased size of individual fat cells, overeating, and extreme hunger. In rodents, it increases energy expenditure by using brown fat for energy. ()
The more fat, the more leptin is produced. This feedback loop, when functioning normally, keeps body weight in homeostasis: eating more food increases body fat, which leads to increased leptin production, which reduces appetite and increases energy expenditure. ()
The primary action of leptin is believed to occur in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus. Scientists have studied how it suppresses the desire to eat food and increases energy expenditure in animals, at least in part by activating POMC and CART neurons and suppressing the neuropeptides NPY and AgRP. ()
In animals, leptin increases BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor or brain-derived neurotrophic factor) in the hypothalamus. Some researchers believe that BDNF may mediate the effects of leptin on food intake and energy homeostasis. The potential synergy of leptin with GLP-1 (glucan-like peptide-1), CCK (the neuropeptide cholecystokinin), and amylin (a peptide hormone that is produced by β-cells of the pancreatic islets of Langerhans) in reducing food intake is an area of research. (, )
Other findings from cell studies that examined the effects of leptin on the human body:
- Increase in thyrotropin-releasing hormone
(TSH, TRH) – through STAT3 and MSH/MC4R (), MSH () and CRH. () - Release of growth hormone ()
- Inhibition of AMPK , an energy sensor that is activated by a decrease in ATP.
- Changes in mTOR in the hypothalamus, which can affect appetite. ()
- Dopamine in the ventral tegmentum (latin tegmentum, an area of the brain potentially involved in the formation of cognition, motivation, orgasm, addiction, strong emotions associated with love), which can influence how healthy a person considers food. ()
- Arterial pressure ()
- MSH (melanocyte-stimulating hormones, through binding to MC3R/MC4R), which are able to activate the nervous system in the kidneys (MC4R) and influence blood pressure (MC3R). ()
- Inhibition of neuropeptides NPY and AgRP. ()
None of these mechanisms have been studied in humans.
Leptin and the immune system
Scientists are studying leptin in cell studies to see if it increases with infectious and inflammatory stimuli, such as liposaccharides from bacteria, turpentine and cytokines. They also want to know how it affects oxidative stress in macrophages and monocytes, and whether leptin can attract immune cells to areas of inflammation. (, , , )
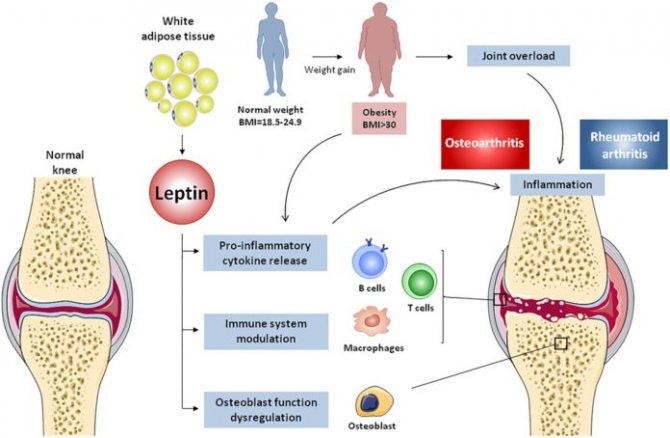
Increased body weight increases the amount of circulating leptin and promotes increased immune inflammation, such as in osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis.
The leptin receptor is found on B and T lymphocytes, neutrophils and monocytes, suggesting that it plays a role in immune activation and inflammation . () In this context, leptin may be one of the mediators responsible for the low-grade general inflammation that may be present in chronic pathologies associated with metabolic syndrome or atherosclerosis, which are associated with obesity , especially central obesity. Therefore, leptin may be considered as a therapeutic target in some diseases, such as autoimmune diseases, to control the excess immune response.
How leptin interacts with other hormones
Current and future research is looking to determine whether leptin has the following effects :
- Increased release of growth hormone ()
- Increases corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) in the PVN but decreases stress-induced ACTH and cortisol in mice. ()
- Stimulating the release of thyroid hormones - TSH, T4. (, ) Leptin can prevent the decrease in T3 levels during fasting. ()
- Increases IGF-1, preventing IGF-1 levels from decreasing during fasting. ()
- Increased estrogen
- Decreased ghrelin (, )
- Increased levels of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) (,, )
- Inhibition of progesterone in placental cells. ()
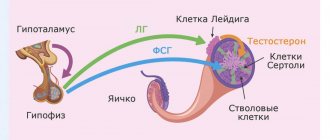
Limited research has shown that higher leptin levels are associated with lower testosterone levels in men , even with normal body weight or BMI. On the other hand, it has been shown in studies that leptin supplementation prevented the decrease in testosterone from fasting in men (by increasing LH). Therefore, the interaction between leptin and testosterone is still unclear. (, )
Causes of obesity
In addition to high levels of leptin or its genetic deficiency, obesity can develop due to:
- endocrine pathologies (hypothyroidism, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, etc.);
- genetic disorders accompanied by a predominance of aerobic metabolism in cells and an economy of carbohydrate and lipid compounds;
- prolonged stress (nervous stress is accompanied by an increase in the level of glucocorticoid hormones that stimulate the formation of fatty deposits);
- lack of physical activity;
- chronic sleep deficiency and fatigue;
- unbalanced nutrition, overeating, frequent snacks on the go, abuse of fatty foods, fast foods, foods containing easily digestible carbohydrates, excessive consumption of sweets and starchy foods, etc.
- treatment with steroid drugs;
- brain tumors, skull injuries, empty sella syndrome.
Leptin levels are elevated
High leptin levels can be caused by the following factors:
- Binge eating (, )
- Emotional stress ()
- Inflammation (, )
- Obesity ()
- Pregnancy ()
- Preeclampsia ()
- Gestational diabetes ()
- Sleep apnea ()
If you think you have a disordered leptin system, talk to your doctor about any health problems you may have that may be related to leptin.
Negative effects of elevated leptin
Inflammation
Leptin is a marker of inflammation as it responds to inflammatory cytokines from adipose tissue. Autoimmune diseases are associated with increased secretion of leptin. () Both in structure and function, leptin resembles the cytokine IL-6.
Leptin increases the release of the proinflammatory cytokines TNF-alpha, IL-2, IL-6 and IL-12. ()
It also increases the amount of C-reactive protein (CRP) in the blood. ()
Leptin triggers the release of proinflammatory cytokines from many cell types, including microglia in the brain. (), and is a mediator of cytokine-induced diseases, for example, thyroid diseases. ()
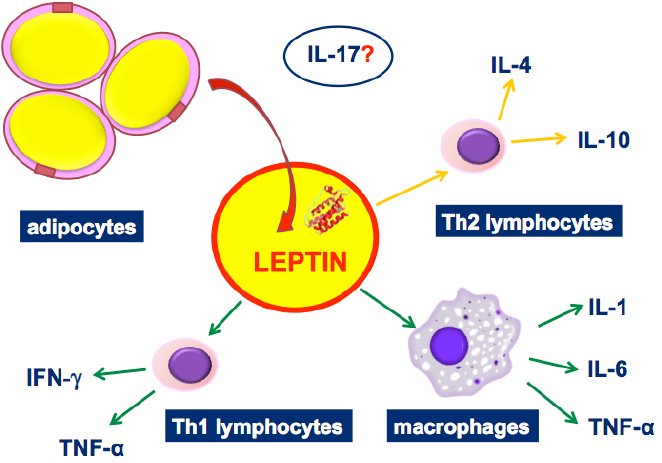
Pro- and anti-inflammatory effects of leptin. Leptin is produced primarily by adipocytes from yellow adipose tissue. This protein causes activation of macrophages/monocytes and increased release of pro-inflammatory cytokines (eg TNF-, IL-1 and IL-6), and through stimulation of Th1 lymphocytes, production of TNF- and IFN (green arrows). The proinflammatory activity of leptin occurs through inhibition of Th2 action and release of IL-4 and IL-10 (orange arrows). (source)
Numerous studies have shown elevated leptin levels in chronic inflammatory conditions. () It also stimulates the growth of both red and white blood cells. ()
High leptin levels are associated with higher white blood cell counts in both men and women. ()
Fatigue
Leptin is thought to cause inflammatory fatigue. () Its values are higher in women even with weight loss, and women are more often diagnosed with chronic fatigue syndrome. ()
This is thought to be partly due to testosterone suppressing leptin in men . ()
Increased leptin levels were associated with greater fatigue in people with chronic fatigue. Some scientists believe that it plays a causal role in such fatigue; however, chronic fatigue is a controversial and poorly understood condition, and this conclusion is by no means unanimous. ()
Blood leptin levels are also associated with the severity of fatigue in patients with chronic hepatitis C and irritable bowel syndrome. ()
In people diagnosed with chronic fatigue, leptin increases to a greater extent in response to an increase in the hormone cortisol. ()
Th-1 immune response
Leptin activates the JAK2-STAT3 pathway and stimulates the Th1 immune response . () By activating STAT3, it also stimulates the inflammatory Th17 response. () Leptin also altered human dendritic cells toward Th1 dominance. ()
Leptin has also been found to be essential for Th1-dependent inflammatory processes, acting as a critical regulator of CD4 T cells. ()
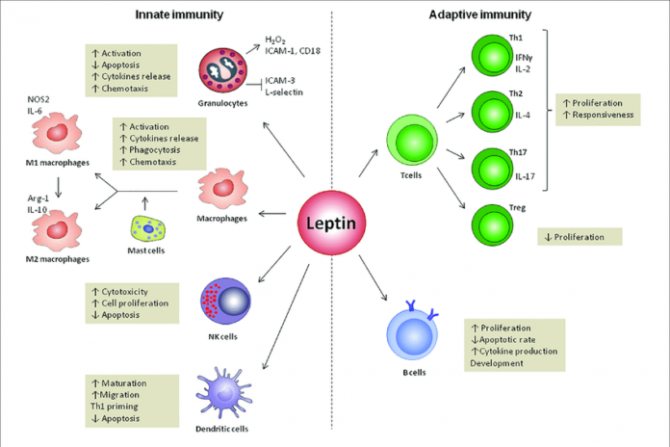
The effect of leptin on various types of immune cells. Leptin promotes a switch toward a pro-inflammatory Th1 (which secretes IFNy) rather than an anti-inflammatory Th2 (which secretes IL-4) phenotype and facilitates the Th17 response. (source)
The effect of leptin, which polarizes immune T cells toward a Th1 response, appears to be mediated by stimulating the release of IL-2, IL-12, and IFN-gamma (all Th1 cytokines) and inhibiting the production of the anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10 and IL-4 . (, )
A dominant Th1 immune response was associated with leptin excess in this study in dialysis patients. (). Just because you have a dominant Th2 immune response doesn't mean leptin isn't causing problems. This simply means that it causes various problems .
Mast cells
Mast cells in human skin, lungs, intestines, and the genitourinary tract contain leptin and leptin receptors, suggesting that leptin binds to mast cells . ()
It appears that leptin causes mast cells to be more inflammatory. ()
In patients with metabolic syndrome, a positive correlation was observed between leptin levels and the number of mast cells in adipose tissue , suggesting that leptin may stimulate mast cells. (])
Leptin is associated with (probably enhances) mast cell activation in children with asthma who exercised. ()
It suppresses appetite, in part, by increasing histamine release and activating histamine H1 receptors in the hypothalamus. (, )
Regulatory immune T cells
Leptin interferes with the production of regulatory immune Treg cells . Treg cells are an important part of the immune system, creating tolerance to substances that would otherwise trigger an inflammatory immune response. ()
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA)
Leptin increases the body's stress response and sympathetic nervous system activity (fight or flight). () This activates the HPA axis and reduces heart rate variability (the change in the interval between the onset of two adjacent cardiac cycles). ()
Cancer
Leptin promotes the growth and spread of cancer . This is one reason why obesity is considered a risk factor for cancer. () It enhances angiogenesis by increasing the level of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).
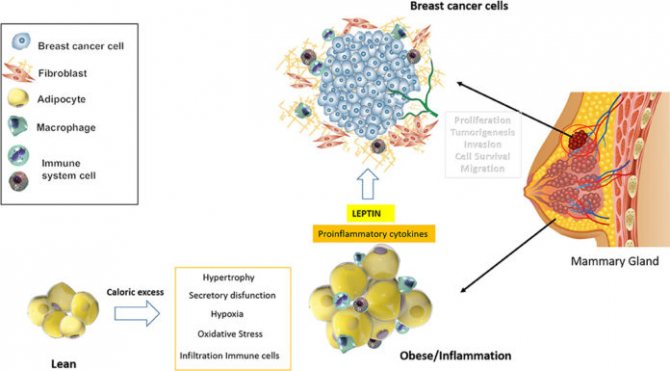
The figure summarizes the mechanisms linking obesity or excess adipose tissue to the development of breast cancer. (source)
Heart diseases
Leptin receptors are found in heart cells. (). Scientists have linked high leptin levels to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease . ()
In obese people, leptin levels are the most significant indicator of higher levels of fibrinogen, a blood clotting factor that is considered one of the most important risk factors for cardiovascular disease. ()
Additionally, elevated leptin is also associated with high blood pressure (), although this may be due to leptin resistance, since giving rats extra leptin lowers blood pressure. ()
Leptin increases the production of endothelin-1 (ET-1), which is a powerful vasoconstrictor . () By constricting blood vessels through endothelin-1, leptin may increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease. ()
Sensitivity to pain
Higher levels of leptin in the body can lead to increased pain sensitivity in the body. This is due to its ability to cause inflammation, which plays a role in pain. ()
In a study of 3 fibromyalgia patients, they reported higher levels of pain on days when their leptin levels were elevated. A cohort study of 5,600 postmenopausal women found similar results. ()
Leptin can increase pain by activating inflammatory cytokines - IL-1b, IL-6, IL-18, or blocking signaling pathways that affect pain sensitivity. ()
Nutrient Absorption
Leptin is secreted by stomach cells and enters the small intestine. It enhances the absorption of butyrate (), accelerates the intestinal transport of fructose () and oligopeptides. ()
On the other hand, leptin reduces the absorption of glucose () and galactose. () It also inhibits the absorption of proline, beta-alanine and glutamine. () By blocking the absorption of glucose and amino acids, it thereby helps in weight loss.
However, blocking glucose uptake increases the risk of malnutrition.
Leptin resistance
Many researchers argue that long-term high leptin levels can lead to the development of leptin resistance, just as long-term high insulin levels can lead to insulin resistance.
A recent study found that leptin resistance in the muscle of obese people leads to increased fat absorption (within muscle) and decreased fatty acid oxidation, compared with lean, leptin-sensitive people. ()
Leptin resistance in muscles.
Since muscle tissue is the primary site of fatty acid oxidation in the body, and leptin (along with adrenaline) is one of the main triggers of fatty acid oxidation in skeletal muscle, it is safe to say that leptin resistance creates a major blockage in the fat burning process.
Symptoms of leptin resistance may include:
- Weight gain and difficulty losing weight
- The desire to have a snack soon after eating, especially in the evening ()
How to increase the satiety hormone leptin and sensitivity to it
Overcoming leptin resistance is important not only for weight loss, but also for the treatment of diseases such as arterial hypertension, coronary insufficiency, type 2 diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, and metabolic disorders in polycystic ovary syndrome.
It is recommended to influence the most studied mechanisms of leptin resistance:
- reducing animal fats in the diet by half - replacing meat with fish at least 6 days a week;
- refusal of sugar, flour products;
- the menu should consist of 80% vegetables (except potatoes), half of them should be served raw;
- the source of carbohydrates can only be whole grains, vegetables, berries and fruits;
- sleep at least 7 hours (lack of sleep even for 2 hours leads to a decrease in leptin levels and an increase in ghrelin in the blood, which means attacks of uncontrolled appetite);
- treatment of sleep apnea syndrome and foci of chronic inflammation;
- When using a diet to reduce body weight, it must be correctly balanced in terms of the number of calories and the ratio of food components. Overeating and starvation lead to hormonal imbalance;
- A number of antidiabetic drugs to overcome insulin resistance have the ability to restore the response to leptin. In frequency, this has been proven for Metformin, and Byeta can imitate all the main effects of the hormone.
We recommend reading the article about the hormone somatostatin. From it you will learn about the main functions of somatostatin, what an excess of pancreatic hormone leads to, the properties of a synthetic analogue, as well as the indications for use and side effects of the hormone.
And here is more information about the hormone melatonin.
Leptin is produced by adipose tissue cells. Normally, it inhibits the deposition of fats and activates their combustion, reducing appetite. With obesity, more of it is produced than necessary, but the tissues lose sensitivity to it. Leptin resistance is considered a risk factor for type 2 diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, recurrent thrombosis, and osteoporosis.
To study the level of the hormone in the blood, preparation is necessary. If deviations from the norm are detected, correction of nutrition and lifestyle is recommended.
Factors affecting leptin levels
Leptin increases after eating , more due to carbohydrates than due to fat, in both obese and healthy people. (, )
During psychological stress, the body secretes leptin intensely, and high leptin levels are associated with increased food consumption. () A syndrome of “seizing” of psychological stress is formed.
Diet
Overeating during meals increases leptin production. In contrast, eating smaller meals and a higher proportion of protein, or foods with a low glycemic index, can lead to lower leptin levels. (, )
A low-carbohydrate, low-fat diet may reduce the release of leptin by fat cells. ()
Anti-inflammatory foods such as fatty fish, olive oil, nuts, fruits and vegetables can also reduce leptin production. ()
Some nutritional rules to reduce leptin:
- For breakfast, it is advisable to eat 20-30 grams of protein
- It is better to limit your meal time to 18.00. You need to stop eating at least 3 hours before bedtime.
- Reduce the number of meals by 2-3 times with no snacks between them.
- Reduce the amount of carbohydrates in your diet. Switch only to foods with a low glycemic index.
- Reduce portions when eating. Don't eat your fill.
Starvation
Short-term fasting (24-72 hours) reduces leptin levels. ()
Intermittent fasting is considered the safest and most accessible form of fasting. Talk to your doctor before making significant changes to your diet. You may have contraindications to fasting. ()
Psychological stress
Emotional stress, the stress hormone cortisol, and anti-inflammatory steroid medications (corticosteroids) increase leptin levels. Reducing stress helps lower leptin levels. (, )
Physical activity
Any physical exercise reduces leptin production. (, )
Toxins and inflammation
Endotoxins (bacterial toxins, disturbances in the breakdown and digestion of food, impaired detoxification in the liver) in both rodents and humans lead to an increase in leptin. (, )
Why is it harder for women to lose weight?
The concentration of leptin in the blood of women is approximately 3 times higher due to the stimulating effect of estrogens (female sex hormones) on its formation. With a sharp restriction of caloric intake or fasting, the body reacts to this by decreasing the level of leptin, increasing the synthesis of ghrelin (the hunger hormone), and increasing cortisol and insulin in the blood.
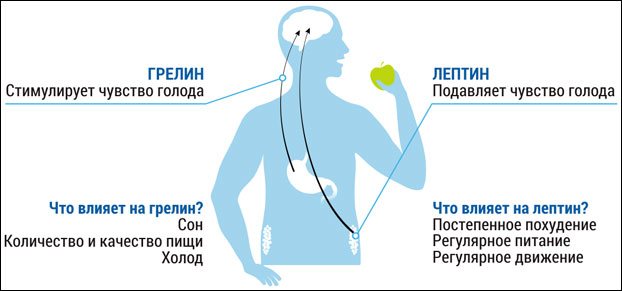
As a result of a strict diet, a chronic stress reaction develops, which provokes not the consumption of fat, but its accumulation. Therefore, the process of weight loss stops, and the woman’s hormonal levels also change.
Since it is impossible to fight a constant feeling of hunger for a long period of time, eating breakdowns occur. During such periods, everything in the body is ready for the accelerated deposition of fat reserves, which is the reason for the increase in weight above the initial one at the end of the diet.
It has been proven that for women with obesity and high blood leptin, the maximum benefit comes from physical activity accompanied by a moderate reduction in calories, and for men, dietary restrictions are more important.