LH hormone, determination, analysis in Saratov
Patients and patients of Sarclinic periodically ask the doctor questions related to hormonal testing of women and
men, girls and boys, girls and boys. luteinizing hormone LH are extremely common . What is LH hormone, how to determine LH hormone ? How are the hormones LH and FSH related? What is the norm for lg ? What to do if LH in women is increased , LH is decreased ? What should be the ratio, the normal ratio of LH and FSH ? Why determine the LH level? Why are LH and prolactin high, low, reduced, elevated, above normal, below normal? How to donate blood for blood tests in men, children, boys, girls, guys, girls, women? How are LH FSH estradiol, progesterone, TSH interrelated, if they are increased or decreased?
Various issues related to hormonal levels are interesting. What is the normal ratio of LH and FSH? How does lg behave during pregnancy, is there less or more of it? When to take hormones , on what day in the first phase, in the second phase, during pregnancy, after ovulation, without ovulation, if the follicular phase, luteinizing phase, or ovulation?
And also current issues. What to do if the gynecologist ordered a test for the LH hormone, and it was found to be decreased or increased? How does lg release occur (graph)? How to find out normal LH readings, do you need an explanation? Do I need a blood test for LH hormones ? Where to treat high LH levels? Where to go if the female hormone FSH and LH are elevated? What are the reasons for the increase? How to calculate the LH FSH index? How does pregnancy proceed with elevated LH? What is the price, the cost of analysis in Saratov, in Russia? Why is LH elevated , but FSH is normal, and where to go?
In a smaller percentage of cases, questions about pregnancy are asked. How to lower LH levels during pregnancy, increase LH levels in a girl, and does alcohol affect its levels? Why do you need immunochrome lg express? How to cure a deficiency or excess of the hormone LH? Is treatment necessary and where to go if luteinizing hormone in women, men is normal, increased, decreased, low, high? What to do if there is a luteinized cyst, or luteinized follicle syndrome, polycystic ovary syndrome? gynecology in Saratov , andrology, endocrinology, and reproductology
help
High LH: causes and treatment
The pituitary gland is one of the most important endocrine glands in men and women. It synthesizes most of the most popular biologically active substances, which are responsible for the normal functioning of the entire body. Luteinizing hormone (LH, luteotropin) is one of them.
It is one of the activators of internal organs, since it is responsible for the increased release of progesterone in women and testosterone in men. An increase in the amount of LH or a decrease in it can significantly affect a person’s sex life.
In most cases, if there is an excess or deficiency of this biologically active substance, adequate treatment of the disease may be necessary.
Functions
Luteinizing hormone, together with follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and prolactin, is one of the sex hormones. Its main task in women is to stimulate the synthesis of progesterone, a biologically active substance that is necessary for conception and normal development of the child. In men, it is responsible for the production of testosterone and maintaining the normal state of the reproductive system.
If the LH level is elevated in the blood of the fair sex, it means that ovulation has most likely occurred. There is a special interaction of this substance with FSH, which regulates the correct menstrual cycle.
Symptoms
The main danger of elevated levels of this hormone in women is disruption of the normal menstrual cycle. As a result:
- irregular bleeding
- development of iron deficiency anemia,
- inability to get pregnant,
- increased risk of miscarriage,
- pathology of other internal organs and systems.
Such a picture should definitely alert the patient. Here, appropriate treatment and care for the girl’s body is necessary. However, she should be the first to consult a doctor if the above symptoms occur. Otherwise, therapy may have significantly less effect.
In men, high levels of this substance can cause the development of sexual dysfunction. Lack of testosterone leads to:
- significant decrease in libido,
- poor blood flow to the penis during sexual intercourse,
- reducing the amount of ejaculate,
- complete loss of orgasm,
- obesity,
- weakening of muscles.
In any case, it is necessary to carry out appropriate healing of the body and reduce high levels of the hormone.
What is luteinizing hormone LH in women, men, children?
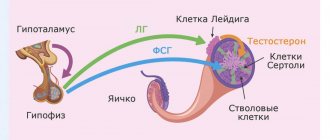
Luteinizing hormone LH , lutropin , luteotropin belongs to the group of pituitary hormones. Luteinizing hormone , LH is synthesized in the anterior pituitary gland. LH is similar in chemical structure to the hormone FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone). LH is a glycoprotein with a molecular weight of more than 30 kDa, which consists of 2 subunits (alpha subunit and beta subunit). The subunits are connected by high-affinity non-covalent bonds. For LH, the alpha subunit is common. Stimulation of the synthesis of gonadotropins occurs through the combined action of gonado-releasing hormone and sex steroid hormones. To maintain normal LH levels, an optimal frequency of pulsed GnrH stimulation is required. With various deviations, the level of circulating gonadotropins decreases. Sex steroid hormones have a direct effect on the sensitivity of the pituitary gland to the stimulating effects of GnrH.
The role of LH in menopause
During menopause, the LH hormone, like other components of a woman’s hormonal background, undergoes significant changes, which means its level is highly dependent on the age and condition of the human body.
Due to aging, the concentration of luteinizing hormone increases significantly, thereby suppressing the production of other hormones, in particular estradiol. It is the “off-scale” LH level in older women that indicates the onset of menopause, also known as menopause.
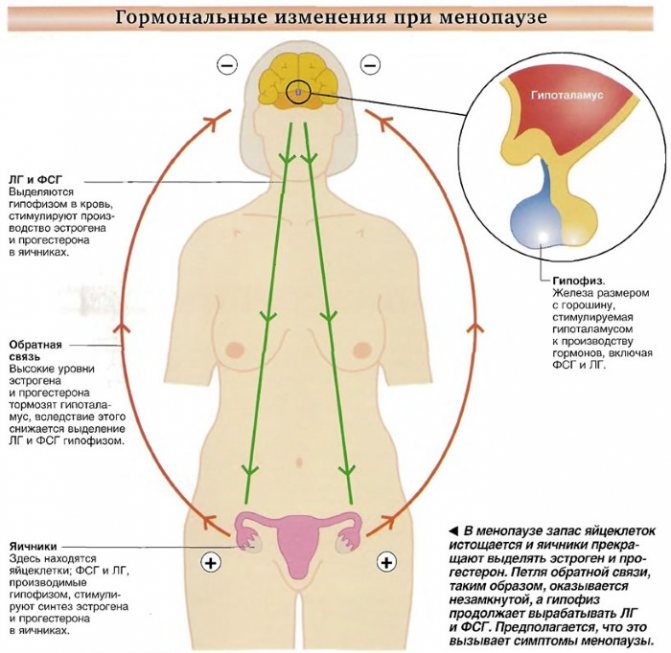
A significant increase in the level of the hormone in question is due to the inability of the aging body to use it for its intended purpose, as a result of which LH accumulates, manifested in an increase in hormonal concentration in vital systems, revealed by a special blood test.
What is LG responsible for?
Luteinizing hormone stimulates the production of estrogen by the female ovaries. LH regulates the functions of glandulocytes. LH has complex interactions with FSH. Both hormones jointly regulate the germinal function of the testes. By negative feedback mechanisms, peptide inhibins inhibit the follicle-stimulating function of the pituitary gland. This leads to a decrease in the strength of the effect of FSH on the testes, but does not weaken the effects of LH. Inhibin regulates the interaction of LH and FSH, which manifests itself in the regulation of testicular functions. LH, together with FSH, affects the growth of egg follicles in women. The level of luteinizing hormone varies depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle. In the early follicular phase, LH levels are reduced, followed by a gradual increase in LH until ovulation occurs. The LH surge stimulates ovulation in women. Then the level of luteinizing hormone in the blood drops sharply. A subsequent increase in LH occurs at the beginning of the menstrual cycle. In men, LH stimulates Leydig cells. Testicular interstitial Leydig cells produce testosterone.
Decreased LH
A reduced level of luteinizing hormone is determined in patients with the hypothalamic form of amenorrhea, luteal phase defect, hyperprolactinemia, Sheehan syndrome, Simmonds syndrome, galactorrhea-amenorrhea syndrome. Also, a decrease in the concentration of the hormone is possible in patients with excess body weight, as well as under stress and as a result of taking certain medications.
In men, low LH levels are possible due to stress, obesity, and taking certain medications.
Luteinizing hormone in women and men is reduced, decreased, low, below normal, reduced level
LH is decreased, low, decreased, below normal (reduced level) is observed in diseases, pathological conditions, processes such as dysfunction of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, hypopituitarism, delayed onset of synthesis and action of lutropin and follitropin in puberty (constitutional growth retardation and puberty syndrome). development), galactorrhea-amenorrhea syndrome, isolated deficiency of gonadotropic hormones with anosmia or hyposmia (Callamann syndrome, Kallmann syndrome), neurotic anorexia, isolated deficiency of lutropin (fertile eunuch), hyperprolactinemia, taking digoxin, megestrol, oral hormonal contraceptives, phenothiazines, progesterone ( reduces the peak of lutropin), estrogens (in large doses), Prader-Willi syndrome, sports amenorrhea, hypothalamic tumors.
FSH and LH: role in the body
There are several levels of hormonal regulation of the functioning of the reproductive system: the hypothalamus, pituitary gland and the ovaries and testicles themselves. FSH and LH are pituitary hormones produced by the central endocrine gland, the secretion of which depends on the liberins and statins of the hypothalamus.
Follicle-stimulating - responsible for the formation of reproductive gametes, taking an active part in oogenesis and spermatogenesis. FSH promotes the appearance of a dominant follicle, ensures the growth of its membrane and the synthesis of estrogens, testosterone, and also increases the susceptibility of genital cells to LH. Luteinizing - affects the development of the genital organs, as well as the synthesis of testosterone and estrogens. Increased levels of LH and high FSH in women in the ovulatory phase promote the release of the egg from the follicle; LH is also responsible for the formation of the corpus luteum and the production of progesterone.
How to lower or increase luteinizing hormone LH?
Sarklinik knows how to lower LH in men and women, how to increase LH in women and men in Saratov, Russia. Treatment aimed at restoring the level of luteinizing hormone (increasing or decreasing LH levels) can improve sexual function, restore reproductive function, and a woman’s menstrual cycle. Sarklinik knows how to lower LH, how to increase LH, how to increase LH levels, how to lower LH levels. If your luteinizing hormone is not produced, you do not know whether your LH is normal, or whether your LH may be increased, decreased, high, low, above normal, below normal, be sure to contact a specialist. You can go to the official website sarclinic.ru Dr. Remember that peak levels of luteinizing hormone trigger ovulation. This peak level can be determined using an ovulation test.
Luteinizing hormone is normal
Once a woman's monthly cycle has established itself, LH levels will depend on its phase. On the days of ovulation it will be highest. Cycle phases:
- follicular (from the 1st day of menstruation to the 12-14th day of the cycle) – 2-14 mU/l;
- ovulation (from the 12th to the 16th day of the cycle) – 24-150 mU/l;
- luteal (from the 15-16th day until the start of the next menstruation) – 2–17 mU/l
- after the onset of menopause, the amount of the hormone in the blood increases and ranges from 14.2 to 52.3 mU/l.
Using quantitative indicators of LH, you can establish:
- ovulation, which will allow you to determine the days in which the probability of conception is very high. The onset of ovulation is characterized by an increase in LH levels, special ovulation tests work on the same principle. A few days before the onset of possible ovulation, a test is used to determine the level of LH in the urine daily. If the test result is positive, ovulation will occur within 24 to 48 hours);
- causes of infertility and miscarriage;
- a number of women's diseases.
If symptoms such as an irregular monthly cycle, uterine bleeding, signs of hirsutism, miscarriages, infertility, or decreased libido appear, it is recommended that you first take a test for LH levels in the blood. If sexual development is too rapid or vice versa - its delay, growth cessation, infertility treatment using IVF, it is necessary first of all to establish the quantitative value of LH.
To obtain more accurate research results, several rules should be followed: blood sampling from women is done on days 3–8 or 19–21 of menstruation, on an empty stomach. If the results are higher or lower than normal, this indicates disturbances in the functioning of the body and will require appropriate treatment.
The ratio of LH and FSH is normal, LH/FSH
What is the normal ratio of LH and FSH , what is the normal ratio of LH/FSH , luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone in girls, young women, women? In girls, before the onset of menstruation, the normal LH/FSH ratio is 1. A year after the onset of menstruation, the normal LH/FSH ratio in girls is from 1 to 1.5. If a girl or woman has a menstrual cycle for more than 2 years, that is, from approximately the age of 14 years until menopause, the normal LH/FSH ratio is from 1.5 to 2.
Diagnosis of female sex hormones - what tests and when to do?
Analysis of the concentration of female sex hormones is important at many stages of a woman’s life, including:
- when abnormalities are detected in the body that may indicate an excess or deficiency of one of the hormones,
- during many unsuccessful attempts to get pregnant,
- for menstrual irregularities,
- during pregnancy,
- in the perimenopausal period, to check hormone levels and the possible decision to introduce hormone replacement therapy,
- in cancer prevention.
A doctor who specializes in hormones is an endocrinologist. The specialist may order specific blood tests and indicate, among other things:
- at what point in the cycle should you go to the laboratory,
- how to prepare for the test,
- When is the best time to get your blood tested?
This all depends on the need to check the level of a specific hormone and the exact purpose of the analysis.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
When should you donate blood for an LH test?
Sarclinic testing for LH and luteinizing hormone if

a girl or woman has endocrine diseases, decreased libido, lack of ovulation, female infertility, miscarriage, excess hair growth on the body, face, under the arms, problems with menstruation, oligomenorrhea, amenorrhea, no menstruation, hirsutism, no menstruation, scanty menstruation, irregular menstruation, dysfunctional uterine bleeding, polycystic ovary syndrome, menstrual irregularities, irregular periods, endometriosis, decreased libido, growth retardation during puberty (puberty), underdevelopment of the genital organs (clitoris, labia minora, labia majora, vagina ), underdevelopment of the mammary glands (small breasts, 0, 1, zero, first breast size, only nipples), premature puberty, male infertility, poor spermogram, decreased potency in men, impotence, weakened erection, when evaluating hormonal therapy, when taking hormonal contraceptives (GOCs, hormonal oral contraceptives).
Text: ® SARCLINIC | Sarclinic.com \ Sarlinic.ru Photo: (©) Mtoome | Dreamstime.com \ Dreamstock.ru The woman depicted in the photo is a model, does not suffer from the diseases described and/or all similarities are excluded.
Related posts:
Male infertility: analysis, test for infertility in men, how to determine
Where can I get a spermogram? Spermogram Saratov analysis interpretation
How to conceive a girl, conceive a daughter correctly by ovulation, table, in what position
FSH hormone, norm in men, women, high, low, level
Contraception: methods, means, methods, types of contraception, how not to get pregnant
Comments ()
Symptoms and signs of decreased LH levels
- violation of the MC;
- hair loss, brittle nails;
- swelling;
- sudden weight gain or loss;
- depression;
- feeling of chronic fatigue;
- spontaneous miscarriages;
- violation of the cyclicity of ovulation or absence of ovulation;
- infertility.
- reduction in the size of the scrotum and testicle;
- disturbance of spermatogenesis;
- weight gain;
- decreased libido and potency.
In hereditary diseases (Marfan's disease), visual impairment, spinal deformity, and congenital contractures of the fingers and elbows are observed.
Sheehan syndrome occurs as a result of complicated childbirth, in which hypoxia of the pituitary gland occurs. There is a violation of lactation, unexplained weight gain, increased sensitivity to cold, drowsiness, memory impairment, oligomenorrhea.