Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
The taste of blood in the mouth is quite common. However, this symptom should never be ignored. Of course, the reasons for its appearance can be quite harmless, for example, a slight injury to the gums or eating food from clay dishes. However, an unpleasant taste can also indicate very dangerous pathologies. Let's figure out why a metallic taste may appear in the mouth and what to do to eliminate it as soon as possible, and most importantly, remove the reasons for its appearance.
Conventionally, all the causes of a pronounced metallic taste can be divided into three groups:
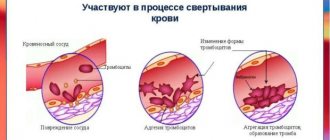
- Dental problems are usually associated with increased bleeding of the gums.
- Oral injuries.
- Internal pathologies.
Taking various medications often leads to a taste of blood in the mouth.
Oral injuries
If the mucous membrane is damaged, a little blood may enter the taste buds and, accordingly, a metallic taste appears in the mouth.
The causes of mucosal injury may be:
- tartar in the mouth;
- improper dental care, for example, using a brush that is too hard;
- incorrectly installed dentures;
- incorrectly installed braces.
Often the cause of the taste of blood in the mouth is a more significant injury, such as to the esophagus or throat. For example, a strong cough often leads to mucosal injuries. After an injury, a small amount of blood enters the mouth and causes an unpleasant taste.
Metallic taste
36558 August 24
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Metallic taste in the mouth: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
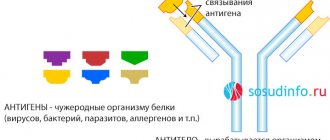
A metallic taste in the mouth can appear for various reasons: due to certain diseases, taking medications, the presence of metal structures in the oral cavity (dentures, crowns), and heavy metal poisoning.
It is necessary to pay attention to this symptom if it persists after eating food and occurs repeatedly during the day.
Types of taste
Depending on the frequency and duration of the metallic taste in the mouth, it can be characterized as a quickly passing or long-lasting condition.
What diseases cause a metallic taste?
A passing metallic taste in the mouth usually appears after drinking iron-fortified mineral water.
.
This water is sometimes prescribed to patients suffering from iron deficiency anemia. In addition, a metallic taste can be caused by taking certain medications
: metmorphine (for diabetes), ferrous salts, antibiotics (ketolides, nifuratel), antihistamines, bismuth preparations.
In the presence of metal dental crowns, bridges, and braces,
an aftertaste may occur if the structures contain dissimilar metals that create a galvanic couple.
A metallic taste may occur in patients with cancer who are undergoing radiation or chemotherapy
. In foreign medicine, this phenomenon is called chemo mouth (“chemical mouth”) or metal mouth (“metal mouth”). This uncomfortable condition prevents you from eating properly (food and water taste like iron), which leads to exhaustion.
Metallic taste may be a sign of dysbiosis
. Intestinal microflora breaks down complex protein compounds into low molecular weight organic and inorganic substances (including metals). In particular, bifidobacteria promote the absorption of iron and calcium ions from the intestines into the blood. A deficiency of these microorganisms in the gastrointestinal tract causes the accumulation of iron compounds, which affect taste. Symptoms of dysbacteriosis are complemented by decreased appetite, nausea and vomiting, bloating, flatulence, and belching. Skin manifestations of dysbacteriosis (itching, redness, rashes) are possible.
Poisoning with heavy metal salts
most often occur in enterprises: during industrial accidents and releases of toxic waste into the external environment, when lead vapor enters the body at gas stations, paint and varnish factories, etc.
Intoxication with heavy metals is also possible when using pesticides or when staying near large highways for a long time.
Signs of poisoning include a metallic taste in the mouth, nausea, and vomiting. Possible pain when swallowing, abdominal pain, and stool disturbances. There is a disturbance in the functioning of the nervous system: an excited state may be replaced by dulling of consciousness, tremors, convulsions, and visual hallucinations occur. Characterized by sleep disturbance.
Diseases of the gums and oral mucosa
, accompanied by ulceration of the mucous membrane, lead to the appearance of blood in the mouth, which gives a metallic taste. These diseases cause pain when eating food, swelling and bleeding of the gingival papillae, and the appearance of plaque on the tongue.
Gingivitis or stomatitis occurs due to poor oral hygiene and various diseases (vitamin B12 deficiency, diabetes mellitus, cancer, viral and autoimmune pathologies).
In addition, gingivitis can be a consequence of hormonal imbalance, such as during pregnancy.
Taste disorder (dysgeusia) is possible due to a violation of nervous regulation
,
damage to brain structures
. In these cases, patients may complain of a bitter or metallic taste in the mouth even when eating regular food.
Disorders of the gustatory sensory system, which can occur as a result of tumors and injuries, are accompanied by distortion of taste and the appearance of unpleasant tastes.
Which doctors should I contact
? If you have a persistent metallic taste in your mouth, you should contact them to make a preliminary diagnosis. In the future, you may need to consult a dentist, or.
Diagnostics and examination
To make a preliminary diagnosis, it is necessary to clarify with the patient details about working conditions and a list of medications taken. The doctor may test the taste sensitivity of different areas of the tongue. The patient is asked to taste citric acid, salt, sugar, and sometimes other substances. Depending on the test results, the severity of the violations is determined. If poisoning with heavy metal salts is suspected, the doctor prescribes a number of laboratory tests: a clinical blood test, a test for free hemoglobin in the blood using photoelectrocolorimetry; quantitative determination of mercury or other substances in blood and urine.
Internal pathologies
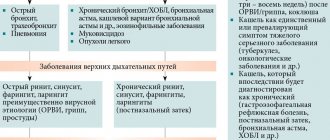
The most common diseases of internal organs that lead to the taste of blood in the mouth include:
- bronchitis;
- pneumonia (pneumonia);
- lung abscess;
- lungs' cancer;
- cystic fibrosis;
- tuberculosis;
- dysfunction of the heart;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT);
- diseases of the ENT organs.
Neurological diseases can also cause the taste of blood in the mouth. A signal travels through the nerve fibers of the brain to the taste buds; if its transmission is disrupted, an unusual taste may appear in the mouth.
However, neurological problems accompanied by a blood taste usually have other unpleasant manifestations. For example, they may be accompanied by headaches, hearing problems, hand tremors, trembling eyelids, and lumbago in certain areas of the face.
In very rare cases, the taste of blood in the mouth is caused by heavy metal poisoning. A similar problem often awaits workers in chemical laboratories and metal processing plants. Intoxication of the body is accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms - attacks of dry cough, nausea, aching limbs, swelling of the gums, and lack of appetite.
Taking medications

A side effect of medications may include a taste of blood in the mouth. If this happened precisely because of the medications, you should stop taking them and consult your doctor. Medicines belonging to the group can lead to such a reaction:
- ganglion blockers used for hypertension - Pyrilene, Pentamin, Hexonium;
- antihistamines – Diazolin, Claritin, Cetrin;
- antibiotics - Ampicillin, Levomycetin, Vilprafen.
The taste of blood in the mouth may appear after taking Centrum, Vitrum and other vitamin complexes intended for pregnant women. This reaction can be caused by medications that contain iron and nutritional supplements, for example, Ferlatum, Hemohelper.
Dental diseases
The most common cause of the taste of blood in the mouth remains dental diseases and lip lesions. Diseases are easily recognized by reddish-colored saliva, inflamed oral mucosa, and the presence of ulcers and erosions.
The main dental problems that cause the taste of blood in the mouth are:
- gingivitis - inflammation of the gums;
- stomatitis - damage to the mucous membranes;
- cheilitis - lip injuries;
- periodontitis is inflammation of the periodontal tissues.
Injuries and physical stress

Sometimes injury to the mucous membrane leads to this problem. You may bite your lips or cheeks while sleeping, talking, or chewing. The taste of blood in the mouth is caused by:
- very rough brushing of teeth;
- poorly supplied dentures and braces;
- injury caused by a broken tooth or the sharp edge of a filling.
In all cases, the root cause must be eliminated. As a result of stress on the body, some manifestations become aggravated. Sometimes this happens during intense power loads. This means that the gums are very weak. During exercise, more blood flows in and they begin to bleed. Those men who are actively involved in sports or work hard jobs often develop a similar taste in their mouths.
What to do if you taste blood in your mouth?
First, you should contact your dentist. The doctor will confirm or deny dental diseases, prescribe effective gum treatment or refer you to another specialist.
If the taste of blood in the mouth appears for a short time, you can eliminate it using traditional methods of treatment. For example, rinse your mouth with water and lemon juice or a water-salt solution. You can also get rid of the unpleasant taste using a chamomile solution. To prepare it, you need to pour 5 g of dried flowers into 500 ml of water and cook for 7-10 minutes in an enamel bowl. The product must be infused for an hour.
A decoction of oak bark will also help get rid of the taste of blood in your mouth. To prepare it, 10 grams of raw material should be steamed with boiling water and left for about an hour.
An effective means of treating gum inflammation and eliminating such unpleasant symptoms as the taste of blood in the mouth is ASEPTA Active mouth rinse. This combined action remedy is used for infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, and also quickly relieves bleeding and inflammation of the gums. The rinse has an antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect, does not contain alcohol, fluorine and dyes, so it is perfect for treating even those with the most sensitive tissues.
Ways to get rid of pathology

If the taste of blood in the mouth appears for a short time, then it can be eliminated using traditional methods. To do this, rinse your mouth with water and lemon juice. Instead of acidified water, you can use a soda-salt solution.
At home, you can get rid of the symptom by:
- Chamomile solution : 5 g of dry raw material is poured into 500 ml of water and boiled in an enamel bowl for 7-10 minutes. The product is infused for 1 hour.
- Oak bark decoction : 10 g of raw material is steamed with boiling water and left for about an hour.
Clinical researches
The effectiveness of various ASEPTA mouth rinses has been repeatedly proven clinically.
For example, it has been clinically proven that the two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component rinses - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Sources:
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- The effectiveness of the use of Asept “adhesive balm” and Asept “gel with propolis” in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis and gingivitis in the acute stage (Municipal Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk, Kaminskaya T. M. Head of the therapeutic department Kaminskaya Tatyana Mikhailovna MUZ City Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk
- The effectiveness of complex therapy in the treatment of periodontal diseases. (Department of Periodontology of the SF State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education MGMSUIM.A.I. Evdokimova. Moscow.) Nemeryuk D.A. - Associate Professor, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Dikinova B.S. - Postgraduate Student of the Department of Periodontology of the SF Tsargasova M.O. - Postgraduate Student of the Department periodontology SF Yashkova V.V. - postgraduate student of the Department of Periodontology of the SF Department of Periodontology of the SF State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education MGMSUIM.A.I.Evdokimova. Moscow
Reviews
Tatiana. Samara:
It took me a long time to get rid of the taste of blood in my mouth. After a full examination prescribed by the doctor, it turned out that this was due to cholecystitis. Appropriate treatment was carried out. After that everything got better.
Yuri. Khabarovsk:
I have not seen a doctor, although my gums bleed often. However, this happens because I sometimes brush my teeth with a brush with too hard bristles, which damages my gums. I didn’t know that this problem could lead to big troubles, now I will be more careful when choosing a toothbrush.
If a metallic taste appears in your mouth, you should listen to your body. With minor damage to the mucous membrane, such a symptom disappears over time without any intervention, without causing noticeable harm. However, most pathologies, especially those associated with internal organs or severe injuries, require immediate and complete treatment.