What is the research?
Cytology smear is a modern, painless and highly accurate diagnostic method that allows you to identify malignant processes and pathogenic microorganisms that cause inflammation.
The method is based on the study under a microscope of the morphological features of cells in biological material. The widespread use of smear cytology in gynecology has led to a significant reduction in cancer mortality.
The undoubted advantage of the test over other methods is its high accuracy in diagnosing the initial stages of cancer. A detailed study of the morphological features of neoplasms allows you to choose the optimal treatment method.
Why is a smear for oncocytology performed?
A smear for oncocytology is a way to detect cancer and any altered cells in the cervical area. It helps to detect precancerous conditions in time and prescribe treatment in a timely manner.
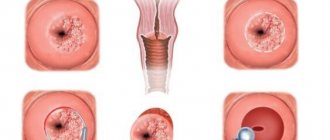
When carried out correctly, it detects dysplasia, cancer and any atypical cells. Indicates inflammatory processes occurring in the pelvic area and detects disturbances in the structure of the epithelium.
Why is it so important to screen for cervical cancer?
The cervix is the element of the female reproductive system that is most sensitive to malignant processes. Cervical cancer (cervical cancer) is a malignant formation that can be treated only in the early stages.
The insidiousness of the disease lies in the fact that it is often asymptomatic. Pathological signs may appear in the later stages, when treatment becomes ineffective.
The only way to prevent this condition is timely diagnosis. In this regard, every woman is obliged to regularly visit a gynecologist and undergo the necessary examination.
Oncocytology for the elderly
There is a strong opinion among ordinary people that oncocytology is necessary only for young women of childbearing age. Because of this, many patients who have reached menopause refuse this type of diagnosis.

When they accidentally get an appointment with a gynecologist, the disease is already in its final stages. In order not to endanger life, a smear is taken every year, regardless of age. The epithelium often changes during menopause, when hormones are less produced.
Who is the study for?
An initial cytology smear is recommended for all women 3 years after the start of intimate life. The test is performed annually for the next three years. In the future, if the results are negative, screening is carried out once every 2-3 years.
In older women (after 65 years), the frequency of diagnostic measures is determined individually. Provided that all previous test results were negative, screening can be stopped.
In addition, there are indications for which a cytology smear is performed unscheduled:
- presence of HPV (human papillomavirus). The infection is predominantly sexually transmitted and is the main provoking factor in malignant processes. Moreover, even a condom does not serve as complete protection against the virus, since infection is possible through microcracks in the skin and mucous membranes;
- genital herpes. The chronic course of the disease can cause malignant processes;
- other sexually transmitted diseases - chlamydia, gonorrhea, etc.;
- pathological vaginal discharge;
- complicated childbirth, abortion, surgery;
- cervical erosion;
- cancer in remission;
- the period of preparation of a woman for conception;
- changes in cervical tissues detected in speculums or during colposcopy.
Online consultation with a gynecologist
Online consultation
During the consultation, you will be able to voice your problem, the doctor will clarify the situation, interpret the tests, answer your questions and give the necessary recommendations.
How to properly prepare for the test?
Proper preparation for the test directly affects the accuracy of the results. For two days before the procedure, you should avoid:
- sexual intercourse;
- douching;
- use of vaginal creams, suppositories, tampons, medications.
The test is not performed during menstrual bleeding, as well as 5 days before and 5 days after it. In addition, acute inflammatory processes are a contraindication.
During pregnancy, especially after 22 weeks, the test is performed only for emergency indications. It should be remembered that this procedure increases the likelihood of miscarriage and premature birth.
Oncocytology and pregnancy
Pregnancy is a huge burden on a woman’s body, so you should prepare for this process in advance. Be sure to undergo a full gynecological examination to exclude the presence of any inflammation and abnormalities.
Diseases can worsen due to stress, so it is important to treat them before conception. If you neglect the tests, there is a threat to the fetus, especially during the formation of internal organs and systems. The risk of spontaneous abortion also increases.
If all processes are stable, it is advisable to check for oncocytology three times. When there is a high probability of miscarriage, the procedure is canceled. The decision is made by the attending physician, taking into account the patient’s condition, the presence of concomitant diseases and other conditions.
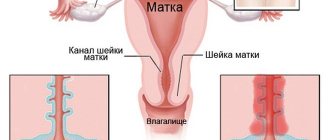
How should biological material be collected?
Often the cause of incorrect test results is a violation of the technique for collecting and processing biomaterial. Proper collection of biological material ensures that during microscopic examination of samples they will contain sufficient quantities of the following elements:
- flat epithelium;
- transformation zones (junctions between squamous and glandular epithelium);
- glandular epithelium.
The transformation zone is of greatest clinical importance, since it is in it that more than 80% of cancer cases are formed. Insufficient coverage of this area significantly reduces the quality of diagnosis.
If the patient has diseases of the cervical canal (erosions, tumors), the biomaterial is taken specifically.
Taking a smear for cytology in women is performed using cytobrushes, which allow you to collect material from hard-to-reach areas. The instruments have other significant advantages - safety and painlessness of the procedures.
Reasons for positive and negative responses
Distortion of the results occurs due to improper preparation for the procedure, as well as for the following reasons:
- due to hormonal changes in young girls under 18 years of age and in women during menopause;
- when menstrual blood gets into the sample;
- due to manipulations in the vaginal area when talc comes into contact with medical gloves or lubricant from ultrasound;
- contamination of the material with sperm, residues of vaginal suppositories and other substances;
- in case of violation of the rules for taking a smear;
- due to neglect of the peculiarities of preparation and coloring of the finished material.

Diseases of the genitourinary system, hormonal fluctuations and the low level of qualifications of the gynecologist can affect the conclusion. Because of this, it is recommended to visit reliable specialists, and if discomfort occurs in the vaginal area, be sure to undergo all tests.
Types of tests
Screening can be carried out using the traditional or liquid method. In a traditional test, biological material is applied to laboratory glass and dried at room temperature. Disadvantages of such diagnostics:
- some biological material remains on the specialist’s instruments and gloves;
- the method does not include a filtering step;
- the cells on the glass are distributed unevenly, forming several layers.
Such features of the study may affect the reliability of the result.
Liquid technology avoids many problems related to the quality of smears. With this technique, the sample is examined in full. The samples taken are placed in a test tube with a stabilizing medium. Thus, the shelf life of the material is extended to several months. Using a centrifuge, the material is filtered, which increases the information content of the result.
During the study, various methods of staining preparations are used:
- Papanicolaou test (Pap test);
- according to Romanovsky;
- according to Gram.
All methods are based on staining of certain cellular structures, which makes it possible to identify different types of epithelium and distinguish healthy cells from malignant ones.
How to behave after the procedure?
After the procedure, it is recommended to abstain from intimate life, the use of vaginal tampons and douching for 1-2 weeks.
Minor bleeding may occur for 1-2 days after the test.
How long does the analysis take?
The speed of analysis depends on the workload of the laboratory and its distance from the place where the material was collected. In regular clinics, glasses are collected to the required quantity and then sent for testing. When the laboratory is located at the clinic, results can be obtained in 1-3 days.
In some cases, a conclusion is issued within 24 hours during an urgent diagnosis.
When liquid oncocytology is used, and the laboratory is located in another city, patients have to wait up to two weeks. The compensation for the wait is high information content and a low risk of false conclusions.
What does the study show?
The test result may be positive or negative. If atypical elements are found, they are described in detail in the conclusion.
The results form may also contain data on the degree of vaginal cleanliness and the number of leukocytes in the smear.
When assessing the results of the study, various methods are used: Bethesda, Papanicolaou and others.
Interpretation of results according to the Bethesda scale
The Bethesda scale is used by specialists in all developed European countries. Thanks to this, having received the result of the study in one country, you can easily continue treatment in another.
The cancer risk grading used is:
- NILM - no oncology.
- LSIL. - low likelihood of developing cancer.
- HSIL - high risk of developing cancer.
- CIS is invasive cancer.
Interpretation of Pap test results
| Class | What does it mean |
| 1 | No oncology |
| 2 | Morphological changes in cells associated with inflammatory processes |
| 3 | The smear contains single cells with indirect signs of cancer (suspicion of cancer) |
| 4 | Single cells with obvious signs of malignancy were found in the biomaterial |
| 5 | A large number of atypical cells were detected in the samples |
Terminology used
- Dyskaryosis is an abnormal cell condition that is a precursor to oncology. Cell nuclei become larger than their cytoplasm. In the absence of pathologies, everything should be the other way around.
- Dyskeratosis (leukoplakia) is a pathology that is accompanied by keratinization of epithelial tissues. When chronic, the disease can degenerate into a malignant process.
- ASC-US is an English abbreviation that means that atypical cells of unknown origin were found in the biomaterial.
- Koilocytosis is an increase in cell nuclei, which is a sign of HPV.
- Glandular hyperplasia is an intensive growth of glandular epithelium, which can lead to a precancerous condition.
- Leukocyte infiltration - shows an excessive number of leukocytes in the smear.
- Proliferation is accelerated cell division, which is observed during inflammatory processes.
- Atrophic type of smear - indicates hormonal changes in the body. For menopausal women, this result is normal.
Making a diagnosis after the study
The transcript of the study results contains information for a specialist and is not a final diagnosis. It is difficult for a patient without special education to understand highly specialized terms. This information cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-medication, therefore, with any test results, you should consult a gynecologist.
If the test results are positive, the patient may be prescribed a repeat test and additional diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- extended colposcopy;
- cervical biopsy.
- bacterial sowing;
- PCR diagnostics.