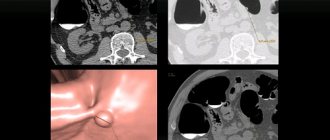
Positron emission tomography (PET) in combination with computed tomography is a modern diagnostic method that allows doctors to obtain information about metabolic changes in body tissues and the precise localization of these processes. Recently, PET CT examination has been increasingly used in oncology, cardiology and neurology. In these areas, it provides higher diagnostic accuracy compared to commonly used types of imaging diagnostics such as MRI, ultrasound, X-ray and CT.
Combined diagnostics using two methods of positron emission tomography and computed tomography allows you to detect a problem when it cannot be determined or is difficult to interpret using any of these methods separately. The uniqueness of this combined approach lies in the use of special software in which both types of images are analyzed and the results are compared. The result of the analysis is comprehensive information about the location, size and shape of abnormal foci, their structure and features of metabolic processes.
When is it prescribed and what does this study show?
The main area of application of PET CT is the diagnosis of malignant neoplasms. The study may be prescribed if the oncologist needs:
- identify a tumor node at stage zero, that is, when it cannot be detected in any other way;
- clarify the nature of the pathology detected during CT scanning, ultrasound, x-ray, etc.;
- determine the presence and localization of metastases, including distant ones;
- evaluate the results of chemotherapy at the very beginning of the course of treatment;
- differentiate tumor relapse or progression from necrosis that developed as a result of radiation;
- solve other specific problems.
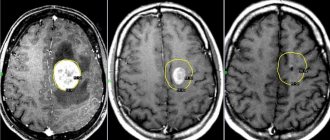
The most important advantage of this method in oncological diagnostics is the ability to determine absolutely all tumor foci, including the smallest metastases up to 1 mm in size, during one examination.
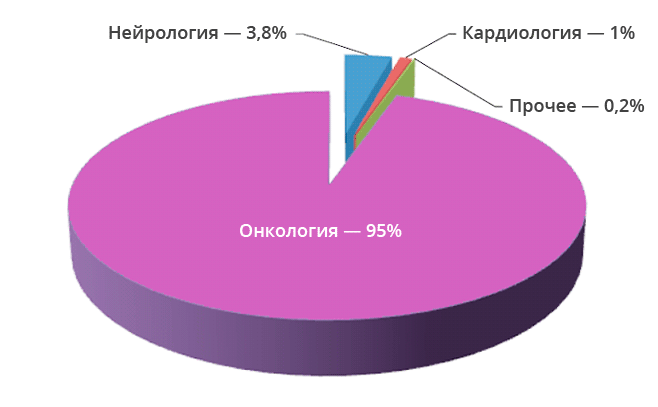
The second direction is the diagnosis of neurological diseases. Based on the examination results, neurologists can:
- assess the condition of the arteries supplying the brain and their role in cerebrovascular accidents;
- differentiate between malignant and benign brain tumors;
- establish the cause of dementia, including diagnosing Alzheimer's disease in the early stages;
- accurately identify foci of epilepsy, which is especially important when planning surgical intervention;
- obtain valuable diagnostic information for Parkinson's disease, Huttington's disease, degenerative diseases of the central nervous system (multiple sclerosis, etc.)
Cardiologists rarely resort to PET CT. In this case, the procedure allows:
- diagnose a temporary adaptive decrease in the volume of work of the heart muscle and differentiate it from heart failure;
- accurately determine areas of myocardial ischemia before surgery to restore impaired blood circulation (angioplasty, shunt installation);
- identify areas of post-infarction cardiosclerosis.
Types and modes of research
Depending on the diagnostic purposes, the following may be prescribed:
- full body scan;
- local brain scan;
- examination of the chest area.
Based on the type of radiopharmaceuticals (RP) used, PET is divided into:
- With 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose. Allows you to identify areas with different intensity of glucose accumulation. The cells of most cancers and other malignant tumors take up glucose most quickly. The more the drug accumulates in the tumor tissues, the brighter they glow in the images and the higher the degree of malignancy of the cancer cells.
- With choline, gallium-PSMA, PSMA-7. It is used in the diagnosis of prostate cancer, the tumors of which actively accumulate this substance. Choline is also sometimes used in liver and brain examinations.
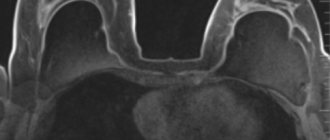
- With methionine or tyrosine. Provides high quality images when visualizing gliomas (a type of brain tumor);
- With 13N-ammonium. Used to diagnose changes in the heart muscle.
- With FP-CIT and F-DOPA. Used for Parkinson's disease.
- With F18-FBB. Prescribed for Alzheimer's disease.
If it is necessary to obtain clearer CT images, the patient may need the injection of a contrast agent, and therefore PET/CT is also distinguished without contrast and with contrast.
Limitations, contraindications, complications
In addition to the contraindications common to any diagnostic methods associated with radiation exposure, positron emission tomography is not performed:
- in the first month after completion of chemotherapy;
- in the postoperative period;
- in the presence of severe inflammatory processes or during the height of an infectious disease.
In all of the above cases, the reliability of the results will be insufficient.
In addition, examination by this method is not indicated for patients during radiotherapy treatment and immediately after its completion. The recommended pause after a course of RT is 3 months.
If the prescription rules are followed, the examination does not cause any side effects, and the radiation dose is so small that, if indicated, it can be prescribed to children and nursing mothers. The only possible complication is individual intolerance to radiopharmaceuticals (extremely rare) or contrast agent (higher probability).
Preparation for PET diagnostics
Preparation for the study varies depending on the type of study and the patient’s health characteristics.
General recommendations boil down to limiting physical activity, stopping drinking alcohol and smoking 24 hours before, and stopping carbonated water and food 6 hours before the test.
These recommendations must be followed because intense physical activity, excess glucose, the presence of nicotine and alcohol in the blood lead to changes in the intensity of radiopharmaceutical accumulation, and gases and food make scanning of the abdominal organs difficult.
To increase the accuracy of diagnosis and reduce the risk of side effects from the administration of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose, patients with diabetes mellitus take drugs that normalize the metabolism of sugars (trimetazidine, etc.) for 8–12 days before the examination. The day before the tomography, coffee is excluded from their diet and taking caffeine-containing medications is prohibited.
Before the choline PET/CT scan, a special diet is also prescribed, excluding protein-rich foods, B vitamins and some vegetables.
How the research is carried out
The patient is administered a radiopharmaceutical, most often intravenously, as well as a diuretic to accelerate the distribution of isotopes throughout the body. The radiopharmaceutical dose depends on the scope of the study and the patient’s weight.
After a certain period of time, during which the maximum accumulation of isotopes occurs in the parts of the body being studied, a scan is performed. In this case, the couch with the subject moves slowly inside or along the module with scanners. The whole process takes from half an hour to an hour or a little more.
After the procedure, it is recommended to consume large amounts of fluid to remove isotope decay products from the body, the lifespan of which is very short - from 2 to 22 hours. Thanks to this, no later than 24 hours later you can communicate with others, including pregnant women and children, without any restrictions.
Decoding the results
Data interpretation is carried out by radiologists with appropriate specialization. As a rule, it takes no more than an hour to evaluate the results and draw up a conclusion.
How to behave after the procedure
After passing the diagnosis, the patient can return home and do any household or personal business, but it is better not to visit work or other public places, since after the procedure the person is a source of radiation. At home, you should keep a distance of 1-1.5 meters from family members for 1 day. There are no other restrictions. Doctors give recommendations on how to quickly remove radiation after PET CT irradiation.
The main rule is to drink a lot of clean still water. Fluid helps the body recover faster.
Within 20-24 hours, radiopharmaceuticals disintegrate and are excreted in the urine. That is, within 1 day the body is completely restored, and the patient returns to his previous lifestyle. Patients doubt whether they can drink alcohol after a PET CT scan. The answer is definitely no. Drinking alcohol leads to a lack of fluid in the body, and during the recovery period water is necessary. Therefore, it is better to refrain from drinking alcoholic beverages for 1 day. Doctors' recommendations on how to behave after a PET CT procedure do not say anything about diet. You can eat whatever you want. There are no restrictions on nutrition after PET CT. On the contrary, you need to eat heavily and restore strength. Some patients ask what to do with clothing after a PET CT scan. Things pose absolutely no danger, so there is no need to burn or throw them away. You can continue to wear clothes.
Where can I get a positron emission tomography scan?
Not so long ago in our country the method was little known not only to patients, but also to doctors. Today in Russia, every self-respecting doctor knows what a PET/CT examination is, and modern PET centers operate or are actively being built in most large cities.
How to get tested for free under compulsory medical insurance
According to compulsory medical insurance, PET/CT can be done upon referral from the attending physician. This diagnosis is included in the list of services provided as part of compulsory health insurance. In most regions, examination under compulsory medical insurance requires a referral from the attending physician, and the service is provided on a first-come, first-served basis. The waiting time, depending on the region, ranges from 5 working days to two weeks.
Why?
Today, up to 90% of PET/CT studies in the world are performed on people suffering from cancer. The study is important from a number of perspectives:
- The study is important from the point of view of determining the degree of development and spread of the tumor process, detection of metastases, both regional and distant.
- In medical practice, there are situations when doctors are unclear about the nature of the process occurring in a particular organ. The study allows you to differentiate the process, distinguish between benign and malignant.
- The study helps to understand whether the treatment is effective.
- The study can be used to diagnose relapse of the disease.
When it comes to diagnosis, many cancers have the ability to actively accumulate fluorodeoxyglucose. This substance is used during the study. However, some types of cancers have low metabolism.
These types include:
- Highly differentiated cancerous neoplasms of the thyroid gland; Benign tumors of any location;
- Some kidney tumors;
- Some bone tumors;
- Liver tumors;
- Prostate tumors;
- Some types of sarcomas, lymphomas.
Having a low metabolic rate, they are poorly visualized by PET/CT. This means that other diagnostic methods are required.
PET CT examination: what is it from a scientific point of view
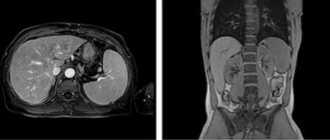
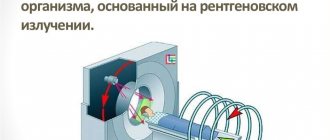
Positron emission tomography is based on the principle of capturing gamma radiation from isotopes with special sensors. These signals are interpreted using a special program that converts them into multi-colored luminous zones. The color of the luminous foci changes depending on the amount of isotopes captured by the tissues and, accordingly, on the intensity of the radiation.
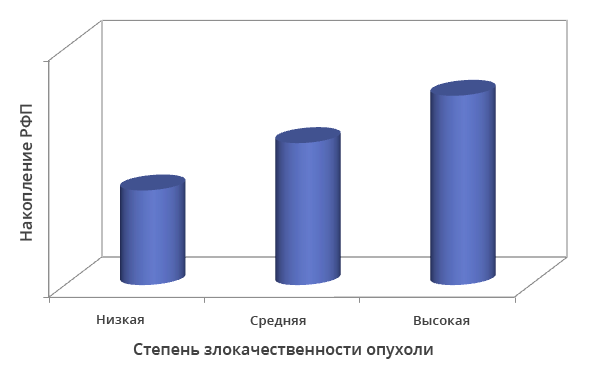
Dependence of radiopharmaceutical accumulation on the degree of malignancy of tumor cells
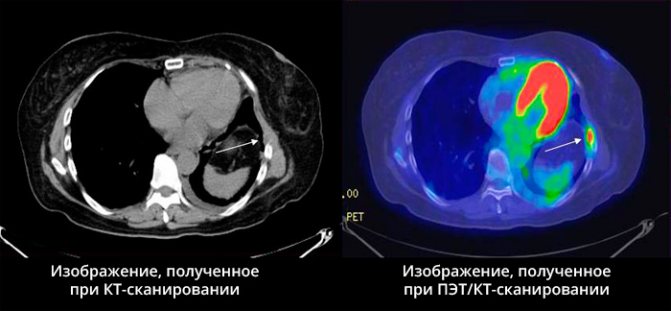
The more radiopharmaceuticals accumulate in the lesion, the “hotter” it is, that is, the brighter it glows. However, such luminous zones do not have clearly defined boundaries. Superimposing images obtained using computed tomography onto positron emission tomogram images eliminates this drawback.
What is the difference from other visual diagnostic methods?
No other imaging method except positron emission tomography allows one to see changes in metabolic processes at the cellular level, and in combination with a clear image of the lesion on a computed tomogram, this makes it possible to most accurately plan laparoscopy or targeted radiosurgery, determine metastases in the bones and solve other complex diagnostic problems. tasks.
Contraindications
Positron emission computed tomography is not performed in the following cases:
- for acute infectious diseases and exacerbations of chronic inflammatory processes;
- in general severe conditions of the patient;
- for psychoneurological disorders, claustrophobia and other ailments that make it impossible to calmly wait for the scanning procedure to be completed;
- with diabetes mellitus (with high glycemic levels);
- during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Technology development
Initially, PET examination was used in diagnostics as a separate technique. Due to the above-described features of the resulting images, its results were not informative enough. Therefore, all modern diagnostic systems are equipped with two types of scanners: positron emission tomography and computed tomography.
Each next generation of devices surpasses the previous one in accuracy of results and safety due to:
- equipped with innovative sensors and electronic units;
- increasing noise immunity;
- other engineering, technical and software solutions.
Recently introduced PET MRI complexes allow unhindered visualization of soft tissue tumors, including in organs blocked from the scanner by skeletal bones. In addition, this technique makes it possible to significantly reduce radiation exposure, since, unlike CT, MR imaging does not use ionizing radiation.